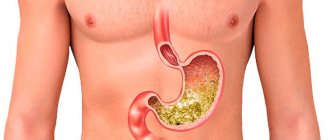
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is one of the most common chronic diseases of the digestive system that occurs due to reflux. Reflux is the reflux of stomach or duodenal contents into the esophagus, causing damage (including erosion) to the mucous membrane of the esophagus, as well as often irritation of the larynx, pharynx, trachea and bronchi.
1
Consultation with a gastroenterologist in MedicCity
2 Examination in MedicCity
Causes of reflux:
- decreased tone of the lower esophageal sphincter (occurs due to the consumption of alcohol, nicotine, caffeinated drinks, certain medications, and can also occur during pregnancy);
- increased intra-abdominal pressure (can occur as a result of obesity, flatulence, pregnancy);
- diaphragmatic hernia;
- fast and plentiful consumption of food (in this case, food intake is accompanied by swallowing air and, accordingly, an increase in intragastric pressure);
- excessive consumption of foods high in animal fats, fried, hot, spicy foods, etc., which take a long time to digest, which provokes an increase in pressure inside the stomach;
- duodenal ulcer.
Causes of esophageal erosion
The development of pathology can be caused by:
- increased intra-abdominal pressure
- weakening of esophageal muscle tone
- reduction in the length of the esophagus due to the presence of a tumor or inflammation
- liver diseases
- change in the diameter of the esophageal opening
- osteochondrosis (kyphosis) of the spine
- old age
The diseases listed above can cause hiatal hernia. And they, in turn, can cause the development of mucosal erosion.
Symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease
The release of stomach contents causes irritation of the esophageal mucosa and provokes inflammation, which is accompanied by the following characteristic symptoms:
- heartburn, burning sensation behind the sternum;
- belching;
- sour taste in the mouth (acid reflux);
- nausea and vomiting;
- blood in vomit or stool;
- extraesophageal symptoms (difficulty or pain when swallowing, chest pain, irritation in the throat, hoarseness, cough, shortness of breath, arrhythmias).
These signs usually appear and intensify after eating, physical activity, or in a horizontal position. Adopting an upright posture and drinking alkaline mineral water can reduce symptoms.
If heartburn recurs several times a week for 4-8 weeks, you need to consult a gastroenterologist. Do not ignore such symptoms! erosions and ulcers of the esophagus , precancerous (Barrett's esophagus) and oncological (esophageal cancer - adenocarcinoma) diseases can occur Extraesophageal complications are also possible - the development of bronchial asthma , chronic bronchitis, pneumonia.
Features of esophageal esophagitis
Depending on the course of the disease, there are 3 types:
- Spicy;
- Subacute;
- Chronic.
Acute esophagitis is divided into 3 degrees:
- Damage to the surface of the esophagus without ulcerative and erosive defects;
- Damage to the organ mucosa with necrosis and ulcerative defects;
- The lesion covers the submucosal layers, causing deep defects and bleeding. Scar structures may form after treatment.
According to the classification of Savary and Miller, chronic esophagitis is divided into 4 degrees:
- First. Hyperemia without erosive changes in the distal sections;
- Second. Small erosions merge, but do not affect the entire mucosa.
- Third. Characterized by the formation of ulcerative lesions in the lower third of the esophagus.
- Fourth. Chronic ulcers and stenosis occur.
In the chronic form of the disease, the mucous membrane of the esophagus becomes loose, swollen and covered with mucus. During a histological examination, the doctor reveals cellular infiltration, atrophy of the esophageal glands with the formation of microabscesses and cysts. Prolonged lack of treatment leads to dysplasia and atrophy of the mucosa with the formation of heterotopic areas of the gastric type. They secrete hydrochloric acid, which leads to the development of Barrett's syndrome.
Based on the nature of the inflammatory process and clinical picture, doctors distinguish the following types of esophagitis:
- Hemorrhagic;
- Catarrhal;
- Necrotic;
- Hydropic;
- Pseudomembranous;
- Phlegmonous;
- Exfoliative;
- Erosive.
Necrotizing esophagitis appears in severe infectious pathologies and agranulocytosis, and is characterized by the formation of deep ulcers.
The appearance of hemorrhagic esophagitis is influenced by some viral and infectious diseases. They cause hemorrhages in the wall of the esophagus.
The most common are catarrhal and edematous forms. They are characterized by hyperemia and swelling of the mucous membrane.
The cause of phlegmonous esophagitis can be a foreign body entering the wall of the esophagus.
Pseudomembranous and exfoliative types of the disease develop with diphtheria and scarlet fever.
Erosive esophagitis occurs due to acute infectious pathologies and the action of irritating substances on the wall of the esophagus.
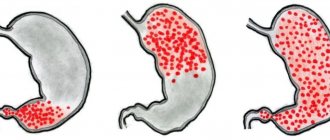
According to the prevalence of inflammation and its localization, gastroesophageal reflux disease is of 3 types:
- Distal;
- Proximal;
- Total.
Depending on the factor that provoked esophagitis, it comes in 4 forms:
- Nutritional. Occurs when consuming spicy and hot foods and strong alcoholic drinks.
- Allergic. Develops against the background of food allergies.
- Stagnant. Appears when food debris is retained in diverticula
- Infectious. Develops as a result of viral and bacterial infections.
- Professional. Occurs when exposed to harmful production factors.
Diagnosis and treatment
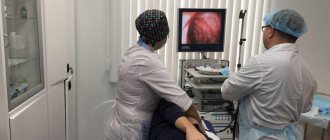
At MedicCity, we conduct a comprehensive gastroenterological examination, which allows us to identify any diseases of the digestive system in the early stages. If you have any symptoms of gastrointestinal diseases, our experienced gastroenterologists will help you. Diagnosis is carried out using modern endoscopic equipment in a gentle manner using sedation (medicated sleep for the duration of the study).
The basis of treatment for GERD is the rapid relief of symptoms of the disease, as well as the prevention of complications. Antisecretory drugs are used (for example, proton pump inhibitors); for bile reflux (bile reflux), ursodeoxycholic acid and prokinetics are prescribed. The treatment regimen is prescribed by the doctor, taking into account the individual characteristics of the course of the disease and concomitant diseases in the patient.
1 Endoscopy with sedation in MedicCity
2 Evis Exera II Olympus CV-180 is a high-end digital endoscope used for gastro- and colonoscopic examinations in MedicCity
Short-term relief of symptoms can be achieved with the help of antacids. Also effective against belching and heartburn is a folk remedy - a decoction of flaxseed. However, remember that getting rid of the symptoms of a disease does not mean curing it.
Treatment of GERD dictates changes in the patient's lifestyle. It is important to get rid of the habit of smoking, change eating behavior (especially if you are overweight, obese), follow a diet, reduce the consumption of coffee, chocolate, carbonated drinks, sour, fatty foods that increase gas formation, etc.
You should avoid a horizontal position when sleeping - sleeping with the head of the bed elevated helps reduce the number of reflux.
It is necessary to stop taking medications that can lead to a decrease in the tone of the esophageal sphincter or cause damage (for example, with erosions) to the mucous membrane of the esophagus and stomach (oral contraceptives, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, etc.).
Patients with GERD should avoid heavy lifting and exercise that involves bending over.
In order to prevent complications and relapses of the disease, dynamic monitoring by a gastroenterologist is recommended. Contact your doctor at least once every 6 months, for example, in the fall and spring, when chronic diseases may worsen!
The material was prepared with the participation of a specialist:
Therapy for esophageal erosion
When a diagnosis is made, pills are prescribed to treat the disease. The action of the drugs is aimed at relieving inflammation, reducing the likelihood of contact of the esophagus with hydrochloric acid during reflux, and improving the ability of the intestines to cleanse.
To achieve a positive effect, you should take medications strictly according to the regimen prescribed by your doctor. To completely cure esophageal erosion, several courses may be required. Next, you need to prescribe a preventative regimen.
Sign up for FCS
Don't delay treatment
Why choose American Medical Clinic?
- Team of professionals. Candidates and doctors of medical sciences, professors and associate professors of departments of leading universities, doctors of the first and highest qualification categories work in the clinic 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. We work without holidays or weekends to ensure that you are healthy and happy.
- Regular professional development. Each doctor regularly takes advanced training courses, attends seminars, goes on internships, participates in conferences, and undergoes training abroad. This helps maintain the qualifications of doctors at the highest level. Today, the training of AMK doctors allows them to train young doctors, acting as experts at European-level seminars.
- Hi-tech. We regularly invest not only in training and professional development of personnel, but also in purchasing the most modern equipment from leading European manufacturers.
- The value of time. The American Medical Clinic has created all the conditions for a comfortable, comprehensive examination and diagnosis of a patient on the day of treatment.
- Trust from clients. Over 25 years of impeccable work, more than 500,000 patients have entrusted their health to us. More than 80% of patients recommend us to their family and friends.
- Guarantees. We are 100% responsible for the quality of the services provided, the high level of which is confirmed by many years of experience. The attention and sensitive attitude of doctors with more than ten years of experience in medical practice give a sustainable positive result.
Nutrition for acute esophagitis:
In case of exacerbation of esophagitis, diet 1A should be followed for no more than 10 days. This diet is strict and if you stick to it, the symptoms of the disease will stop fairly quickly. As soon as the discomfort and symptoms of exacerbation subside, you can move to table 1B. This table is more complete in nutrients.
Notice!
Acute esophagitis is a contraindication for spa treatment: it is better to go to a hospital.
If you have a chronic
form, then you should regularly
carry out preventive treatment
.
conclusions
Dexlansoprazole at a dose of 60 mg has shown its effectiveness and safety in the treatment of the erosive form of GERD. The results of a comparative effectiveness study showed that by the 56th day of course treatment, epithelialization of SOP defects occurs in 100% of patients and the disappearance of the main symptom that reduces the quality of life - heartburn. For maintenance therapy, a dosage of 30 mg is sufficient and does not lead to a recurrence of erosive and ulcerative lesions of the oral cavity and symptoms. Taking the drug once a day, regardless of meals, was noted by patients as convenient, which leads to high adherence to treatment.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Recipes for dietary dishes for esophagitis:
Sample menu for one day:
Breakfast:
Oatmeal cooked in water with milk, red apple compote.
Lunch:
Steam omelette. Rose hip decoction
Dinner:
Chicken soup with noodles and vegetables. Pike perch fillet with boiled potatoes. Herb tea.
Afternoon snack:
Low-fat yogurt. Cookie. Weak tea.
Dinner:
Dumplings with cottage cheese. Tea with milk.
Before bedtime
You can drink a glass of warm milk.
How to support digestive health
Restoration of the gastrointestinal tract affected by alcohol differs from the treatment of a non-drinker in that it is more radical and categorical. To get a positive result, you need to be 100% ready for the strictest diets.
Gastroenterologists prescribe for alcohol addicts:
- Make sure that the volume of plant and dairy products prevails over carbohydrates.
- Regularly eat fish, eggs, meat.
- Plan 6 meals a day, including snacks.
- Replace black tea with herbal infusions of mint and chamomile.
- Completely exclude industrial sausages, sausages, thick broths and fried foods from the diet.
- Eat nuts, fruits, fresh or stewed vegetables every day - maximum fiber for the complete removal of toxins.
- Drink rosehip decoction, fruit drinks, non-carbonated clean water and dried fruit compote.
Restoring damaged organs is possible only if you completely abstain from alcohol. And this is the most difficult moment of the entire treatment process. If you see that your loved one or relative cannot cope on their own, call. We return alcoholics of any experience to a sober life.
Nutritionist comments:
Therapeutic nutrition for esophagitis allows you to get rid of unpleasant symptoms in the shortest possible time and normalize the functioning of the entire gastrointestinal tract. Neglect of diet or systematic violations of it can lead to the development of dangerous complications.
“The right choice of a sanatorium is a significant step towards maintaining and increasing health. “Gorny” is a resort complex that combines the experience and knowledge of Russian and Soviet balneology. The presence of modern medical equipment and innovative installations, the professionalism of the staff and love for their work will serve as the key to extending longevity,” - head doctor of the sanatorium Alexander Olegovich Karaulov.
List of permitted products:
| Porridges and cereals | Buckwheat, rice, semolina, oatmeal |
| Dairy | Milk, sour cream, low-fat fermented milk products, butter, unsalted cheese |
| Vegetables | Potatoes, zucchini, cauliflower, carrots, pumpkin, beets |
| Meat | Beef, veal, chicken, rabbit, turkey |
| By-products | Boiled tongue and liver |
| Fish | Low-fat varieties of river fish |
| Fruits | Bananas, apricots, pears, sweet apples, melons |
| Soft drinks | Weak tea, rosehip decoction, compotes and jelly from sweet fruits and berries |