You will not come across the term erythematous gastroduodenopathy in the office of a gastroenterologist, since this condition is not actually a diagnosis.
Rather, a frightening phrase will appear in the conclusion of the endoscopy result, to which this very doctor referred you. We invite you to figure out together what pathology is hidden under a complex and incomprehensible name.
What does diagnosis mean?
To clearly understand the meaning of the term, let us turn to the literal translation. So:
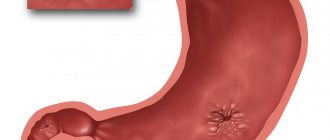
- Erythema (erythema, Greek) - means redness, redness. Most often, the term is used to refer to redness of the skin and mucous membranes. If in the conclusion of your EGD the description begins with the word “erythematous,” it means that the internal mucous membranes of the organ have a bright red color, which corresponds to inflammation.
- Gastro (gaster, Greek) – stomach. The names of all diseases associated with this organ begin as follows - gastritis, gastroduodenitis, etc.
- The prefix duodeno - (duodena, Greek) denotes a connection with the 12 duodenum. If it is present in the name, it means that the pathology affects the area of the duodenum 12.
- Pathia – (páthos, Greek) – means illness, suffering.
Thus, erythematous gastroduodenopathy means redness (inflammation) of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum.
Causes
Redness of the mucous membrane occurs due to the negative impact of environmental factors or pathological changes in the body itself.
- Poor nutrition. If your diet is dominated by fatty, fried, spicy foods, this leads to stomach irritation.
- Alcohol abuse and smoking have a negative impact on health.
- Long intervals between meals. The stomach produces hydrochloric acid, which is necessary for digesting food. It is also a factor of aggression: if the stomach cavity is empty, the acid damages its own walls, causing hyperemia.
- Erythematous gastropathy occurs after taking certain medications (aspirin, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs).
- Pathogenic microorganisms and fungi cause inflammation. The main role is played by Helicobacter pylori, treatment in this case is aimed at eliminating the etiological factor.
- Constant reflux of the contents of the duodenum into the stomach (reflux) leads to atrophy and redness.
To worry or not?
Pathology is not considered an official diagnosis; rather, it denotes endoscopic syndrome, that is, it describes the condition of the superficial tissues of the stomach and duodenum, which does not extend to deeper layers.
The condition can be acute or chronic. Acute inflammation may be associated with temporary irritation of the mucous membranes, which occurs after overeating, drinking alcohol, spicy and spicy foods, and marinades. Persistent irritation is also observed in patients who smoke. Fans of too hot food also periodically suffer from gastropathy, but these symptoms quickly pass.
A chronic form of inflammation is observed in patients with other diseases of the digestive system. Also, endoscopists detect the syndrome of erythematous gastroduodenopathy during or at the recovery stage after acute or chronic gastritis or peptic ulcer.
You should not ignore the pathology, because in the presence of provoking factors, it will not slow down to spread into the deeper layers and transform into a new, acquired disease.
Degrees and types
Endoscopist doctors distinguish 2 forms of pathology:
- Focal erythematous gastroduodenopathy - the term refers to the presence of redness in a limited (local) area of the mucous membrane. In this case, the EFGDS conclusion will contain an exact indication of the department where there is inflammation. This may be the antrum, cardia, fundus of the stomach, duodenal bulb or part of the intestine.
- The diffuse form is diagnosed if the redness is widespread and visible in many areas of the gastric and duodenal mucosa.
The syndrome is also divided into degrees:
- Grade 1 pathology is common and is associated with temporary, shallow irritations of the mucous membranes. Stage 1 responds well to therapy, sometimes to eliminate it it is enough just to correct the diet; you do not need to take medications;
- Grade 2 means that the process has a chronic course, that is, redness and inflammation of the mucous membranes is always present. Grade 2 occurs in patients with chronic gastritis and other diseases of the digestive tract.
Complications and prognosis
Frequent complications of duodenopathy include gastritis, reflux disease, and ulcerative-erosive lesions of the mucous membranes. Sometimes the preconditions for a cancerous tumor are formed. Advanced disease is complicated by bleeding and iron deficiency anemia.
The prognosis with timely diagnosis and adequate treatment is favorable . Full recovery is doubtful when exposed to negative factors (smoking, alcoholism), as well as in advanced pathology and the oncological process.
About the reasons in detail
The cause of erythematous gastroduodenopathy is not always a diet disorder or an existing disease of the digestive system. The condition may have a different origin. The following factors provoke hyperemia of the mucous membrane:
- Microbial or fungal infections of the mucous membrane.
- Taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications. Hormones, anticoagulants for a long time.
- Chronic metabolic disorders.
- Vitamin deficiencies.
- Constant stress and overwork, high physical activity.
- Hereditary factor.
- Increased acidity of the stomach contents.
- Starvation diets.
- Bad habits.
At grade 1, gastroduodenopathy does not manifest itself sharply - clinical symptoms appear periodically and disappear as soon as the diet is normalized. Grade 2 erythematous gastroduodenopathy is characterized by a more pronounced clinical picture, which is similar to the manifestations of chronic gastritis.
Important! The condition is not a reason for hospitalization of the patient, and does not exempt him from military service.
Symptoms
Clinical manifestations of duodenopathy are not always noticeable . Unfortunately, the question of diagnosis often arises when a patient consults a doctor in the late stages of degenerative-atrophic processes.
Typical symptoms of duodenopathy:
- nausea, vomiting after eating;
- pain in the intestines, epigastrium, stomach;
- decreased appetite;
- heartburn, flatulence, foul gas;
- stool disorder.
Note! A direct sign of duodenopathy or gastroduodenopathy is spastic sharp pain in the gastrointestinal parts of the digestive system, the appearance of nausea or vomiting 15-20 minutes after eating.
Symptoms of erythematous gastroduodenopathy
The most common symptom of erythematous gastroduodenopathy is heaviness in the stomach that occurs after eating. Moreover, for the symptom to appear, the patient does not have to overeat; heaviness occurs even after a snack. Sometimes this condition is accompanied by severe nausea, which is difficult to cope with. This is due to the fact that when the mucous membrane becomes inflamed, the production of enzymes is disrupted, food digestion proceeds slowly, causing discomfort.
If the foci of redness are located in the antrum and spread to the area of the duodenal bulb, peristalsis suffers: the food bolus has difficulty moving through the digestive tract, stagnates in the lower parts of the stomach, causing the patient bloating, unpleasant belching of air, heaviness in the epigastrium and disorders intestinal activity. Pathology in this case provokes constipation or diarrhea.
If erythematous gastroduodenopathy with an erosive component is detected, pain syndrome is added to the above symptoms. This condition is dangerous due to its rapid degeneration into erosive gastritis or peptic ulcer. Therefore, the doctor must explain to the patient the need to follow a gentle diet. When hyperemia is combined with atrophy, the prevailing symptom is heaviness in the epigastrium and flatulence. In this case, the doctor prescribes enzyme preparations (Omez, Festal, Mezim) to stimulate the activity of the stomach.
The common symptoms of erythematous gastroduodenopathy include the following:
- weakness, fatigue, increased irritability;
- lack of appetite, stomach discomfort;
- anemia associated with impaired absorption of nutrients;
- weight loss;
- periodic vomiting not associated with poisoning;
- plaque on the mucous membranes of the mouth, especially on the tongue.
Painful symptoms disappear if the patient’s regimen and diet are normalized. If you ignore periodic ailments, the pathology will quickly develop complications and first transform into gastritis, and later into peptic ulcers. The signs of erythematous gastroduodenopathy in the acute stage or during initial detection are similar to the symptoms of exacerbation of chronic gastritis. Therefore, treatment and nutrition for acute conditions are similar to treatment recommendations and diet for chronic gastritis.
What is duodenopathy
Duodenopathy (duodenitis) is a common symptom complex, inflammation of the lining membranes of the duodenum of a chronic, recurrent nature . With combined inflammation with the lining of the stomach, they speak of gastroduodenopathy.
The inflammatory process is constantly progressing, despite the periodic occurrence of symptoms. The clinical picture of gastroduodenopathy resembles a stomach and duodenal ulcer, and with duodenopathy of the lower digestive tract - cholecystitis, acute pancreatitis. Patients complain of weakness, pain during meals or at long intervals between meals, sour belching, and flatulence.
Note! Gastroduodenopathy accounts for 34% of all diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and is a trigger for peptic ulcers, gastritis, and erosion. Inflammation of the duodenum is chronic in almost 90% of clinical cases.
The disease code according to ICD-10 is K29 - gastritis and duodenitis.
Classification
There are several classifications of the disease : according to the form, prevalence and type of duodenopathy.
are classified according to form , and limited and generalized inflammation according to prevalence.
, which is determined through endoscopic diagnosis, is also of great clinical importance
- Erythematous duodenopathy . The main feature is redness and slight swelling of the membranes of the duodenum. The erythematous form is often combined with other diseases and changes in the structure of the intestinal mucosa along its entire length.
- Hyperemic . Hyperemia is diagnosed if the membranes of the duodenum are swollen, the mucous membrane is loose, red, and there are bruises.
- Erosive . The formation of erosive foci on the lining membranes due to trauma, burns, stress, and severe metabolic disorders. Gastropathy with the formation of ulcerative-erosive foci is often combined with organ failure and becomes a consequence of the pathogenic activity of Helicobacter pylori infection and gastroesophageal reflux.
- Stagnant . The disease is accompanied by impaired motor function of the small intestine, and decreased peristalsis is observed. The bolus of food stagnates, and the gastric juice contained in it leads to inflammation. With chronic stagnation, duodenogastric reflux is formed - the reflux of chyme from the lumen of the duodenum back into the stomach. Congestion poses a danger to the function and integrity of the membranes of all parts of the digestive organs.
- Catarrhal . Inflammation is often caused by congestive duodenopathy. In the esophagus there is an alkaline environment, in the stomach there is an acidic environment, reflux and congestion contribute to an imbalance of microflora; in different parts of the intestine, enzymes characteristic of one organ negatively affect the membranes of other parts of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms are often vague, and it is quite difficult to identify the disease at an early stage.
- Focal . One of the violations of the integrity of the membranes of the duodenum is focal (limited) erythematous duodenopathy. When multiple lesions appear, they speak of the development of a diffuse form of the disease. According to the results of endoscopy, the membranes are hyperemic and inflamed. The danger lies in the appearance of crater-shaped wounds, which, if left untreated, can transform into a peptic ulcer.
- Superficial . One of the common forms of the disease, the initial stage of pathological changes. Lack of treatment leads to chronic duodenopathy. The membranes thicken, and swelling of other parts of the gastrointestinal tract is observed.
- Atrophic . The disease becomes a consequence of tissue atrophy and impaired secretion of important digestive enzymes. This form is accompanied by the development of gastritis and gastric or duodenal ulcers.
We recommend: How to choose a medicine for rotavirus for children and adults?
According to morphology, duodenopathy is classified into follicular (lymphoid duodenopathy) and moderate type of changes in epithelial structures. This also includes erythematous proximal duodenopathy.
The key difference between all forms of gastroduodenopathy is the degree of damage to the membranes of the gastrointestinal tract; one type can transform into another and be complicated by an infectious process.
Why is it dangerous?
The main danger is associated with irreversible changes in the functions of the intestines and stomach , the spread of pathological changes throughout all parts of the digestive tract.
Damage to the mucosa during gastroduodenitis (photo)
Lack of therapy and non-compliance with clinical recommendations often lead to ulceration of inflammatory foci , disruption of the integrity of the lining membranes and deeper submucosal layers. Atrophic processes can become a trigger for cell atypia and the occurrence of a cancerous tumor.
Treatment and diet
Drug treatment for erythematous gastroduodenopathy is rarely prescribed. The main therapeutic method in this case is diet. Don't be alarmed and think that your diet should be reduced to diet soup and cereals, this is not so. On the contrary, the daily food set should be varied in order to provide the body with the necessary substances.
The restrictions apply only to frankly unhealthy foods - smoked meats, marinades, too hot and too cold dishes. You should not drink alcoholic and carbonated drinks, overeat heavily, or “sit” on coffee alone throughout the day. A sick stomach should not be empty, so carefully consider your daily diet.
To help, we suggest you familiarize yourself with the material, where we examined in detail the principles of nutrition for superficial gastritis. Dietary recommendations for this disease and erythematous gastroduodenopathy are identical.
Folk remedies
For erythematous gastroduodenopathy, it is allowed to be treated with traditional methods. Herbal infusions gently relieve inflammation of the mucous membrane and help restore damaged mucous membranes. We offer you several simple herbal medicine options for the stomach.
A simple collection to relieve inflammation
The main component of this collection is yarrow. 50 grams of dried crushed yarrow flowers and herbs are poured into 400 ml of water and boiled over low heat for 40 minutes. After the broth has cooled, it is filtered and taken warm, a third of a glass, before main meals.
Composition for stimulating digestion
To prepare this decoction, prepare a mixture of the following components:
- centaury;
- yellow gentian;
- chicory flowers;
- fumaria officinalis;
- yarrow;
- St. John's wort.
Do not be alarmed by such variety - the raw materials for preparing the decoction are sold in any pharmacy. Mix the ingredients in equal quantities, take 3 tablespoons of the prepared mixture and pour 400 ml of boiling water. Seal tightly and leave for 4 hours. Strain the broth and take it warm before your main meals - breakfast, lunch and dinner.
These recipes are given in the “Newest Therapist's Handbook”, written by the famous Russian doctor, E. A. Nikolaev.
Treatment methods
Treatment of duodenopathy is predominantly conservative, prescribed after studying the causes , severity of the pathology, complications, clinical and life history. The success of therapy depends on eliminating the root cause of inflammation of the duodenum.
The treatment regimen includes the following drugs:
- antibiotics when harmful bacterial microflora is attached;
- agents that reduce the acidity of gastric juice, the negative effects of bile acids in reflux disease;
- drugs to stimulate the motility of the gastrointestinal tract, especially with nausea, mild intoxication with stagnant food bolus;
- proton pump inhibitors to normalize secretion;
- histamine H2 receptor blockers, M1-cholinergic receptor antagonists;
- means for stimulating the synthesis of hydrochloric acid at reduced pH;
- gastroprotectors to restore the integrity of the membranes of the gastrointestinal tract;
- antacids and bismuth preparations to relieve the effects of damaging factors and heartburn.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic, and enzyme drugs are prescribed as symptomatic therapy . To increase the body's resistance to infections, vitamin complexes and immunomodulators are indicated.
Surgery
Surgical intervention is used in several cases:
- if the root cause of the disease is anomalies in the shape and development of internal organs;
- when severe complications occur (massive bleeding, perforation, necrosis of the membranes);
- during the formation of benign and malignant tumors.
Folk remedies
Alternative medicine is not used as monotherapy during exacerbation , however, it significantly improves the patient’s condition during remission in the chronic form of duodenopathy and gastroduodenitis.
There are several popular recipes for regular use:
- 2 tbsp. tablespoons of flaxseed are ground in a mortar, pour 0.5 liters of boiling water and leave for an hour. The infusion is drunk in the morning on an empty stomach and throughout the day 30 minutes before meals. The course of treatment is 30 days, after which a week break is taken.
- Composition for stimulating digestion . A handful of a mixture of chamomile, celandine, St. John's wort is poured into 1 liter of boiling water, left for several hours, filtered and drunk instead of regular tea. There is another version of the mixture: chamomile, St. John's wort, plantain, yarrow.
- A simple collection to relieve inflammation . Nettle, chamomile, oak bark are poured into 1 liter of boiling water, brought to low heat for 10 minutes, then left at room temperature until completely cooled. Drink 100 ml 4-5 times a day before meals.
We recommend: Symptoms and treatment of proctalgia in women and men
When using folk remedies, it is important to take into account the likelihood of allergies and individual intolerance to certain components.
Homeopathy
You can start homeopathic treatment only after acute attacks of the disease have stopped in order to reduce the risk of relapse in the near future and increase remission.
Popular drugs of this pharmaceutical group:
- Cephaelis ipecacuanha, Arnica montana;
- Nux vomica, Spascupreel, Gastricumeel;
- Argentum nitricum;
- Iris versicolor, Kalium bichromicum, Acidum sulfuricum;
- Sulphur.
Homeopathic medicines have Latin names, the concentration of active substances in them is hundreds of times lower , so it is impossible to get instant results. However, with long-term use, a persistent therapeutic effect is observed.
Important! Additionally, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed to accelerate the recovery of the digestive system and maintain stable remission. Popular procedures are calcium electrophoresis, diadynamic and galvanic currents, electrosleep, wave therapy, inductothermy.
Diet
Proper therapeutic nutrition is of great importance . During the period of exacerbation, exclude all aggressive products that can worsen the condition of the mucous membranes. In the acute period, fasting with a transition to frequent meals in small portions is indicated. Food must be pureed to reduce the digestive load.
It is also important to adhere to the drinking regime : clean water, unsweetened compotes, fruit drinks, decoctions of rose hips and rowan berries. Fruit juices are pre-diluted with water and drunk only during the period of remission.