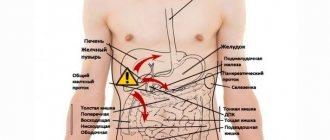
Abdominal pain is one of the most unpleasant, as it deprives a person of the ability to move normally and eat food. The reasons can be simple, not requiring urgent medical attention, or serious, in which case surgical treatment will have to be resorted to. Abdominal pain is usually projected based on the location of the organ in which pathological processes begin. It plays a role where exactly it hurts - on the right or left.
Causes of pain
Doctors state that usually the pain that patients complain about is in the lower abdomen. The most common cause is inflammatory processes in the small intestine. The normal functioning of the latter is disrupted, the process of malabsorption begins, leading to poor health.
Anyone who experiences constant or intermittent pain in the area below the navel should immediately consult a doctor. There are many reasons that can cause illness, and some of them pose a threat to health. These include:
- strangulated umbilical hernia;
- circulatory disorders;
- the presence of irritation of the mucous membranes in the intestines;
- development of inflammatory processes in the jejunum, or jejunitis;
- fermentation disturbance;
- obstruction.
Each of the pathologies described above has its own symptomatic picture, which is characteristic specifically for it.
Problems with the small intestine
Intestinal obstruction is one of the most dangerous diseases. It begins episodically, but then develops into a constant dull, squeezing pain, as oxygen access to the damaged area is stopped and ischemia develops. Treatment is only surgical. A delay in delivering the patient to a medical institution leads to tissue necrosis, disruption of the integrity of the intestine and the release of feces into the peritoneum.
Jeunitis is a disease that occurs independently or against the background of problems with the higher organs of the gastrointestinal tract - the duodenum, gall bladder, pancreas. The villous apparatus is damaged, absorption is impaired, and an inflammatory focus occurs in the small intestine. Infectious cases predominate, but chronic forms of the disease occur.
The main symptoms are severe gas formation, rumbling, pain in the umbilical area or above. Treatment: antibiotics, diet. Impaired mesenteric circulation is typical for people who have a history of atherosclerosis or other vascular lesions. The pain is in the nature of contractions, especially severe after eating. The cause may be thrombosis or vascular strangulation by neoplasms. Symptoms are vomiting, diarrhea, high body temperature, sticky cold sweat. Treatment is surgical.
Exacerbation of chronic jeunitis
Chronic jejunitis is a long-term inflammation of the jejunum. The pathology is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- development of spastic pains affecting the middle of the abdomen (caused by spasms of the intestinal wall);
- flatulence;
- inflammatory process in the lymph nodes of the mesentery - pain in this case is determined below/to the right of the navel and in the area of the left hypochondrium.
The disease is characterized by severe diarrhea that occurs after eating. If the condition worsens, the risk of developing gangliolitis is high. With such an outcome, the nature of the pain changes: it transforms from spastic to burning.
Irritable bowel
Pathologies associated with functional disorders include irritable bowel syndrome. Its signs are:
- regular constipation and diarrhea, as a result of disturbances in intestinal motility;
- severe flatulence;
- cramping pain under the navel.
The peak manifestation of these symptoms occurs in the first part of the day. Difficulties with bowel movements become especially frequent after breakfast and are preceded by a cutting pain. After visiting the toilet, temporary relief may occur. During the day, the patient experiences belching and heartburn, while the pain in the abdomen dulls but does not disappear. As night approaches, a person feels heaviness.
Causes of abdominal pain below the navel in men
Any cramping pain that develops in the lower abdomen in men almost always indicates a disturbance in the gastrointestinal tract. The most common causes are: Crohn's disease, the presence of adhesions, ulcerative colitis, tumors of malignant origin. It is worth noting that all of the listed gastrointestinal pathologies can be diagnosed in women.
Crohn's disease
The disease occurs in a chronic format. Any part of the gastrointestinal tract can be involved in the pathological process, but most often the large intestine and the final section of the small intestine are affected. The exact reasons why Crohn's disease develops. It is generally accepted that viruses and bacteria become provoking factors. Transmission of the disease gene by inheritance cannot be ruled out.
Crohn's disease can be diagnosed in patients of all ages: teenage girls, girls and boys, and adults. But the pathology is especially common in men aged 40 years. Symptoms of Crohn's disease include: sharp pain in the abdomen below the navel, weight loss due to diarrhea, and fever.
Treatment of pathology comes down to the elimination and alleviation of pathological symptoms. The patient is prescribed corticosteroids, anti-inflammatory and painkillers. Without treatment, a man may experience:
- internal bleeding;
- gastrointestinal obstruction;
- perforation of the intestinal wall.
In this case, the patient is prescribed urgent surgery.
Adhesive disease
Abdominal pain below the navel in men can develop due to adhesions formed in the abdominal cavity. The functioning of the intestines is disrupted, which can result in unpleasant sensations, even painful ones. It is customary to distinguish two types of adhesive pathology: with severe pain in the lower abdomen, with the periodic development of intestinal obstruction.
The following symptoms may indicate the presence of adhesions:
- soreness below the navel;
- problems with passing gases;
- bloating;
- nausea, periodically ending with vomiting.
Nonspecific ulcerative colitis
If a man has pain in the lower abdomen, the cause may be ulcerative colitis. The disease is diagnosed in men 2 times more often than in women.
The disease occurs much more often in men than in women
Typical signs of the development of ulcerative colitis are:
- frequent diarrhea;
- anal bleeding;
- dull pain felt below the umbilical area;
- discharge of pus from the anus during bowel movements.
The disease is treated with corticosteroids. In severe cases, the patient is hospitalized.
Violation of the blood vessels of the mesentery
The cause of the condition is blockage of the mesenteric vessels by blood clots. Most often it forms in people with diagnosed heart and vascular diseases. The pathology is characterized by severe cramping pain localized in the navel area. Some reduction in pain occurs when a person takes a knee-elbow position. The pain is practically uncontrollable even with the administration of morphine derivatives.
During an attack, the patient experiences cold, sticky sweat, increased blood pressure and severe tachycardia. Later, vomiting and diarrhea join the symptoms. After six to twelve hours, the pain subsides, which is explained by the death of the nerve receptors of the intestine. Blood appears in vomit and feces. If left untreated, the patient develops peritonitis, and in the worst case, death.
Symptoms of jejunal obstruction
Symptoms of jejunal obstruction include pain in the navel area. Moreover, the pain may increase or decrease depending on the clinical picture of the disease. If the disease worsens, the person vomits of various types and contents. To the point that a person’s vomit may contain intestinal mucus. The patient has problems with stool, it is completely or partially absent. Gases begin to gradually accumulate in the intestines and all this provokes painful and unpleasant sensations in the peritoneal area.
If the pain near the navel goes away, then other symptoms come after it. This is a violation of blood pressure, a feeling of weakness in the body, dysfunction of the cardiovascular system. All these symptoms indicate that the patient’s condition is deteriorating sharply and he needs emergency hospitalization. If appropriate medical care is not provided in time at this stage, the outcome can be fatal.
Insufficient enzyme production
If the body stops producing certain enzymes in the required quantities, enzyme deficiency occurs, which is also called enzyme-deficiency enteropathy. In some cases we are talking about a congenital pathology, in others – about an acquired one. In both cases, the process of parietal digestion is disrupted. Food, without being completely digested, goes into fermentation, irritation of the mucous membranes that line the small intestine occurs.
Attacks of pain often occur when eating sweets or lentils, beans and other similar foods.
The symptomatic picture appears only when a person eats foods to which he has developed intolerance. Typically, the body stops digesting gluten. Then, when this substance enters the esophagus, pain, flatulence, light-colored diarrhea appear, it contains particles of food that have not had time to digest.
There is only one treatment: completely remove food that is not digestible. Additionally, the doctor prescribes enzyme preparations that replace those enzymes that the body does not produce.
Umbilical hernia
When an umbilical hernia is strangulated, sharp, cramping pain also occurs. The doctor, examining the patient, discovers the presence of an oblong lump under the skin of the abdomen. Learn more about gastric hernia.
Diverticulosis
The disease develops in the sigmoid colon. It is characterized by some “protrusion” of the navel. The formation of diverticula is possible in all parts of the gastrointestinal tract. A person is admitted to a medical facility with complaints of pain in the left lower abdomen. The disease is accompanied by increased signs of infection with fever and weakness.
Appendicitis
Everyone knows that doctors first check patients with acute abdominal pain for inflammation of the appendix, or appendicitis. This is reasonable, because the disease progresses at lightning speed and leads to the death of the patient if surgery is not performed on time. The fact that the pain indicates appendicitis is indicated by its displacement to the right side of the abdomen. The longer the attack lasts, the stronger the pain. If you press on the point under which the appendix is located, the patient will feel a pain. Possible fever.
Colic
If a person consumes a lot of foods that contain fiber, and also if there is a lot of chocolate and coffee in the diet, then he is at risk for this disease. Colic is often accompanied by chills and general weakness.
Parasites
If there are worms, a person may also feel pain below the navel. In addition, there is an increase in temperature, deterioration of well-being, and frequent vomiting and diarrhea. Treatment begins with determining the type of parasite, after which drugs can be prescribed to combat it.
Crohn's disease
Or granulomatous enteritis can affect any part of the intestine, most often manifesting itself in the ileum (ileitis). This is an inflammatory disease that develops in genetically predisposed individuals with impaired autoimmune response with concomitant intestinal infections. The clinical picture includes intoxication (lethargy, fatigue), fever, diarrhea, weight loss, abdominal pain, often simulating attacks of appendicitis, bloating, vomiting, loss of appetite. The disease can be complicated by perforation of the intestine, intestinal obstruction, toxic megalkolone, fistulas in the bladder. Endoscopy and intestinal biopsy help establish the diagnosis.
Spikes
Sometimes adhesions develop in the abdominal cavity, which put pressure on the intestines and cause pain. In this case, the normal functioning of the intestines is disrupted, up to the occurrence of obstruction.
The fact that the adhesive process has begun is indicated by:
- pain under the navel;
- severe bloating;
- flatulence;
- attacks of nausea leading to vomiting.
Adhesions can be removed. Today, laparoscopy is used for this.
Colitis
In men, less often in women, the cause of pain may be the presence of ulcerative colitis. The disease is caused by non-healing ulcers in the large intestine.
It is characterized by symptoms such as:
- debilitating diarrhea;
- bleeding from the anus;
- dull aching pain;
- pus released from the anus during bowel movements.
Therapy takes place in a hospital setting.
Intestinal infections
They usually occur in children and are more easily tolerated by adults. There are two types.
Table. Intestinal infections
| View | Description |
| Toxic infections | Caused by food poisoning. A toxic infection begins, in which pain first manifests itself exclusively in the navel, and then extends to the entire abdominal cavity. Additional symptoms include fever, diarrhea, vomiting and severe nausea. |
| Intestinal infections | They occur after eating unwashed foods or drinking unfiltered water. Some are transmitted by airborne droplets. The symptoms are similar to food poisoning, but very soon the body temperature rises to a critical level, attacks of pain turn one into another without stopping. A person can remain in this state without treatment for up to two weeks. |
Infections, especially in children, are most often treated in the infectious diseases department of the hospital.
Abdominal pain below the navel in women
Pain in the lower abdomen in women, localized below the umbilical zone, indicates the presence of certain problems. It is not always possible to establish the exact cause, since due to the vagueness of the symptoms, the woman is unable to identify the location of the pain with maximum accuracy.
Among the main causes of pain in the lower abdomen in women, it is worth highlighting the following:
- Strangulation of the umbilical hernia. The pathology is accompanied by sharp cramping pain. Upon external examination, an oblong seal is detected.
- Intestinal obstruction. In this case, cutting pain occurs in the abdomen, provoked by muscle spasms.
- Diverticulosis of the sigmoid colon. The disease is diagnosed by the characteristic protrusion of the navel. Diverticula can form in any part of the gastrointestinal tract. The formations are always accompanied by pain, which is often felt on the left. In addition to these signs, the patient's body temperature may increase significantly.
- Appendicitis. If sudden pain appears below the navel - when it is the lower abdomen that hurts - shifting to the right side, the development of appendicitis can be suspected. Typically, as the condition worsens, the pain intensifies. When you press on the area where the appendix is located, severe pain is felt. An increase in body temperature may occur.
- Cancerous tumors of the gastrointestinal tract. The pathology is accompanied by a characteristic pain syndrome: the pain occurs in short-term contractions.
Other gastrointestinal pathologies can also cause pain in the abdomen below the navel. These are: gastritis, increased acidity of gastric juice, Crohn's disease, volvulus, dysbacteriosis, colitis.
Pain in the umbilical region may indicate a strangulated hernia
Abdominal pain in the navel area may be a sign of the development of enzyme deficiency. Incompletely digested food causes fermentation processes, which leads to severe irritation of the small intestinal mucosa. An additional sign of pathology may be the development of flatulence after eating a large amount of sweets or legumes.
A sharp pain in the center of the abdomen in the navel area is most often intestinal colic. Its development can be caused by eating foods high in fiber, as well as strong coffee and chocolate. In some cases, it is accompanied by general weakness and chills.
Soreness near the umbilical space on the left is a sign of helminthic infestation. Sometimes the condition is accompanied by:
- increased body temperature;
- nausea and vomiting;
- deterioration in general health.
Features of pain in women
If a woman’s stomach hurts below the navel and menstruation is due soon, then most likely we are talking about premenstrual syndrome. Characteristic symptoms of this condition:
- psycho-emotional stress: irritability, fatigue, nervousness, weakness;
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- the discharge stops completely.
Some women experience pain in the lower belly button every month. This course of premenstrual syndrome is quite normal, especially for nulliparous women. But if the pain is too severe, you should contact your treating gynecologist and get examined.
The reasons why the stomach hurts below the navel are quite numerous. Soreness under the belly button is a fairly common symptom that indicates existing health problems. The cause of abdominal pain below the navel in most cases is inflammation of the small intestine. Poor functioning of the jejunum is accompanied by a state of malabsorption and this has a very negative impact on overall well-being. That is why prolonged pain below the umbilical area and around is a symptom that requires urgent medical advice.
Possible causes of pain in a child
Abdominal pain near the navel or below is not uncommon for a child. There are quite a few causes of the pathological condition, ranging from ordinary constipation to severe gastrointestinal lesions.
Possible causes of abdominal pain below the umbilical zone in a child may be:
- Foodborne toxic infections or poisoning. The disease begins with the development of soreness around the umbilical region. Then the pain spreads over the entire surface of the abdomen. Additional symptoms also develop - nausea, ending with vomiting, diarrhea, increase in general body temperature (sometimes to significant levels).
- Intestinal infection. The development of pathology is caused by dirty hands, insufficiently washed vegetables and fruits, consumption of unboiled and untreated water, as well as by airborne droplets. At the very beginning, the intestinal infection resembles food poisoning in its course - the child complains of soreness in the umbilical area. But unlike poisoning, his body temperature rises very high, he experiences uncontrollable vomiting and severe diarrhea. Abdominal pain occurs constantly, which practically does not subside. Pathological symptoms can persist for up to 10 days.
- Appendicitis. Inflammation of the cecum in childhood begins with vomiting and difficulty defecating. A little later, the child begins to complain of abdominal pain appearing below the navel.
- Worm infestation. If pain develops in the navel area, the presence of a helminthic infection cannot be ruled out. The child may be infected with roundworms, lamblia, etc.
- Gastritis. The cause of pain may be exacerbation of gastritis. Inflammation of the gastric mucosa has an acute onset, but is not accompanied by severe pain. Accompanying signs of gastritis include pain in the stomach, nausea, belching and heartburn.
- Cholecystitis. Acute inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis) can also cause abdominal pain. Symptoms of the disease include increased gas production, bloating, increased body temperature and a darker color of urine.
- Incarcerated umbilical hernia and intestinal colic. In both cases, the child experiences severe pain.
Abdominal pain in a child requires the closest attention
What can you do if you develop abdominal pain below the navel? As a rule, doctors recommend calling the duty team. Taking any pain-relieving medications is prohibited, as this may blur the current symptoms and complicate the diagnosis.
Pain in the umbilical area
Pain in this area usually occurs in case of impaired mesenteric circulation. This pathology occurs when plaques form and block blood vessels. This clinical picture occurs during myocardial infarction. In this case, cholesterol plaques accumulate in the blood vessels, which block blood access to the heart muscle. As a result, the heart does not receive the required amount of oxygen and nutrients. Symptoms of pain in the umbilical region are expressed in the form of painful, acute, excruciating contractions that only stop if the person assumes the fetal position. Pain in the umbilical region does not go away even after taking the drug morphine. Symptoms of pain in the peri-umbilical area manifest themselves in the form of increased sweating, with this disease the sweat is mostly sticky and cold.
Among other things, a person experiences a panicky state of horror and fears for his health. Pain may appear or disappear as a result of the fact that the nerve receptors of the intestine gradually die. At this stage, the patient begins to bleed. Blood appears not only in the vomit, but also in the feces. The next stage of the disease is peritonitis. If you have pain in the umbilical area, then there is no need to take risks and self-medicate. In this case, qualified specialists will be able to provide assistance.