The spasm that occurs in the epigastric region cannot always be attributed to physiological changes associated with the pressure of the growing uterus. At such an important time for every woman, chronic processes affecting the gastrointestinal tract often worsen. The body experiencing hormonal upheavals malfunctions, as evidenced by obsessive nagging or acute pain.
Uncomfortable sensations during the period of bearing a child can occur in the expectant mother both in the early and late stages. The localization of spasms depends on the cause of the disorder. The “painful” list includes various organs and systems, including the digestive tract. To understand where a spasm occurs, you need to pay attention to a set of signs.
How to determine if your stomach hurts
Unpleasant cramping sensations during pregnancy appear in the intestines, upper abdomen and epigastric region. Damage to the gastric zone is indicated by discomfort on the left under the ribs or directly above the navel.
The condition becomes alarming if the pain is severe, cutting and persists for a long time. Other causes for concern are vomiting, diarrhea, abnormal consistency and color of stool (dark or streaked with blood), malaise, and increased body temperature.
Causes of stomach pain
Factors that provoke discomfort along with a growing uterus are the following:
- Stress and troubles.
- Regular overeating due to increased appetite.
- Non-compliance with diet. If the breaks are too long, hunger pains occur.
- Lack of acid in the stomach to digest incoming foods. This condition is called hypoacid syndrome.
- Tension of the abdominal muscles accompanying toxicosis or poisoning.
- Intestinal dysfunction.
Another important and dangerous reason for stomach pain in an expectant mother is the development of a fungal or microbial infection.
It can enter the body regardless of the trimester, negatively affecting the growing fetus and woman. It is the pathogenic flora that often triggers the mechanism of diseases that occur with a violation of the integrity of the mucous structures. If such changes were present in the anamnesis before conception, the risk of relapses increases during pregnancy.
Exacerbation of gastritis
In most situations, the onset of an attack is indicated by cramps in the epigastric region. Intense pain is explained by the formation of sensitive areas on the walls - erosions, the irritation of which leads to severe spasm. Often, pancreatitis and colitis develop simultaneously with gastritis, involving the pancreas and intestines, respectively.
Along with stings, dull aching pains that persist over a long period of time can be diagnosed. In the chronic course of the disease, spasm and bloating occur immediately after eating, if there are fatty or sour dishes on the menu. It is unpleasant even to touch the stomach in the projection of the stomach.
Peptic ulcer
When superficial processes give way to deep ones, doctors note the formation of structures prone to bleeding that can scar. With this pathology, a woman begins to feel pain immediately after finishing a meal or a maximum of an hour and a half after it. There are complaints of regularly recurring paroxysmal spasms. In case of acute stabbing sensations, it is necessary to exclude a life-threatening perforation.
In addition to pathogenic flora, the provoking factor of the ulcerative process is physical or nervous overload.
If an abnormal structure has formed not only in the stomach, but also in the duodenum, discomfort occurs an hour and a half after breakfast, lunch or dinner. An increase in this interval is possible when eating food with a high acidity level. Doctors include boiled meat and dairy products as such.
Sometimes the pain syndrome makes itself felt even before eating. To improve this situation, many women need late-night snacks. The optimal dishes for this category of expectant mothers are carefully crushed purees and liquid porridge with milk.
Movement, weight and size of the fetus
At this time, global processes occur in the child’s body:
- The adrenal glands increase in size. They become larger than the kidneys. This is necessary for the production of the hormone. It will reduce the effects of stress that the baby will experience during birth.
- The liver accumulates iron, which is necessary for the normal supply of blood cells to the baby in the first year of life.
- The mucous membranes lining the child's stomach and intestines are completely covered with villous epithelium, thanks to which the child will be able to accept and digest food. The intestines begin to contract more actively.
- The child’s neurons are covered with a protective sheath, which is necessary for normal coordination of movements in the future. This is not a quick process, which will last until birth and throughout the entire first year of the baby’s life.
- The cartilage in the nose and ears becomes harder. At the same time, the bones of the child’s skull remain soft. This is necessary for easier passage of the baby through the birth canal. Two fontanelles are not covered by bone tissue at all.
- At this time, the baby’s facial features have already clearly formed; they are clearly distinguishable. Individual patterns on fingers (fingerprints) also appeared.
- The skin becomes lighter, lanugo disappears. But the eyes and hair have not yet acquired a permanent color.
- The child's lungs are developing rapidly. This process is facilitated by the hormone cortisone, which is produced in increased quantities by the mother’s body. While the lungs are “turned off,” blood will begin to flow to them immediately after the baby is born. There is enough surfactant so that the child can breathe normally.
- The immune and endocrine systems and sensory organs continue to form.
The baby's weight at 37 weeks is 2.8-2.9 kg and it continues to increase every day. The growth of the fetus at this time can reach up to 49 cm, and the circumference of the head and abdomen are equal. Every day there is less and less space left in the uterus, so the woman clearly feels even the slightest movements of the child. This is not surprising, because every week the child gains 1 cm in height alone.
At 37 weeks of intrauterine life, the baby should take its permanent position. In 95% of cases, the baby lies head down, although other options are not excluded.
Sometimes the baby’s movements can give a woman uncomfortable and even painful sensations, because he has grown noticeably and can push with greater force. The expectant mother needs to listen to the baby's movements. He should move at least 10 times every 12 hours, that is, almost every hour. If the child moves much more often or, on the contrary, there are no movements for several hours, then you should definitely consult a doctor.
Stomach pain during early pregnancy
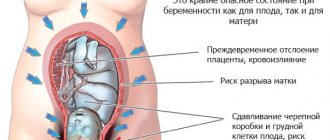
Characteristic epigastric cramps in the first trimester are signs of an ectopic pregnancy or possible miscarriage
. In such conditions, negative sensations are localized below the navel.
There are several reasons that explain stomach pain in the early stages:
- The nervous system's response to stress.
The first 12 weeks of pregnancy are characterized by maximum mood swings, a sharp transition from joy to irritability and sadness. The mucous membrane lining the digestive tract reacts sharply to such jumps. A serious hormonal imbalance complements and aggravates the picture. - Toxicosis due to the restructuring of the female body.
Due to constant nausea, vomiting, and a negative reaction to smells, expectant mothers avoid eating food. The result is a deterioration in the condition of the gastrointestinal tract due to vitamin and mineral deficiency.
It is in the first trimester that chronic processes can worsen. Therefore, women with a history of gastrointestinal pathologies should carefully monitor their diet, regimen, and plan a visit to a gastroenterologist.
We take tests, undergo examinations
If there are no abnormalities during pregnancy, then the woman will need to submit urine for a general analysis. The doctor will also measure her blood pressure, measure the height of the fundus of the uterus and the volume of the abdomen.
The height of the uterine fundus is 37 cm. If this figure is exceeded, the doctor may suspect polyhydramnios. This often becomes a reason for sending a woman to a maternity hospital. This will allow doctors to constantly monitor the situation. If the height of the uterine fundus has decreased, it means that the baby will soon be born, as this indicates its prolapse.
As for protein in the urine, normally it should be absent there. If protein appears in the urine shortly before childbirth, this is an alarming signal. It is possible that a woman is developing preeclampsia. This is one of the severe forms of toxicosis that develops in late pregnancy. Other signs of preeclampsia are: surges in blood pressure, swelling, and weight gain. At this time, the child will suffer from lack of nutrition and oxygen starvation. At the same time, the load on all organ systems of a woman increases.
Stomach pain during late pregnancy
The main cause of discomfort in the last trimester is compression of the gastrointestinal tract by the growing uterus. It is the digestive organ and lungs that suffer from the changes that occur to the maximum extent. In addition, at this time the sphincter, which is responsible for moving food, weakens. If the mechanism is disrupted, the contents begin to flow back with belching and heartburn.
In order not to aggravate the condition, a pregnant woman’s stomach should not be overloaded.
Overeating is fraught with indigestion and spasms throughout the entire tract. The upper abdomen can also become sore due to a serious infection. If additional symptoms include weakness and upset bowel movements, then this is food poisoning, which should be treated only under the supervision of a doctor.
It is worth paying close attention to stomach pain, diagnosed at 39–40 weeks. If the spasm is accompanied by discomfort in the lower back, an examination by a gynecologist is required for timely detection of labor. Uterine pressure at the end of pregnancy is not the main provoking factor, since the baby is already descending into the pelvic area.
Doing an ultrasound
A woman at 37 weeks should visit a gynecologist every 7 days. At this time, the doctor monitors the body’s preparation for childbirth, may examine the cervix, and always listens to the baby’s heartbeat.
As a rule, the woman has already undergone a planned ultrasound, which is the third one. However, sometimes another ultrasound examination is required, for example, when there is a need to clarify the position of the baby in the uterus. Sometimes he does not fall head down, but turns his back or side. In this case, the question of performing a caesarean section may arise.
During an ultrasound, the doctor assesses the size of the fetus, the condition and amount of amniotic fluid and compares them with the norm. At the same time, it is necessary to clarify the maturity of the placenta, the condition of the umbilical cord, uterus and cervix.
At this time, a woman can study as much information as possible on breastfeeding; it is impossible to find any artificial nutrition that could replace mother’s milk. It contains antibodies and other unique components that are essential for a growing body. It is also worth mastering the subtleties of caring for a baby, because he will be born very soon.
Accurate diagnosis
Drawing conclusions about the condition of a pregnant woman can only be done after a comprehensive examination, which includes:
- External examination and palpation of the abdomen.
- Listening to the heart rhythm and lungs to exclude serious internal pathologies.
- Donation of blood, urine, feces for laboratory tests.
- Study of gastric juice.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
If there are doubts about the diagnosis and intense pain persists, the doctor may prescribe a CT scan, MRI, or gastroscopy to make a decision. Another diagnostic procedure is laparoscopy, which allows, with minimal intervention, to visually assess the condition of the hollow structures of the gastrointestinal tract.
Treatment of stomach pain in pregnant women
It is unacceptable for an expectant mother to independently choose medications at home to eliminate spasms in the epigastric area. Most pills for restoring the health of the digestive tract are dangerous for both the pregnant woman and the growing baby. Therefore, priority is given to gentle methods, folk recipes, and herbal remedies.
The following treatment regimens may be considered:
- For severe pain, the use of homeopathy is indicated. Iberogast can be prescribed in small doses. A two-time dose of no more than 20 drops is allowed.
- To improve the condition, herbal decoctions with a sedative effect are prepared. These are valerian, lemon balm, motherwort.
- For normal and high acidity, use a mixture of chamomile, yarrow, and St. John's wort. A tablespoon of the mixture is poured into a glass of boiling water. After two hours of infusion, the medicine is ready for use. You need to drink it in three doses before breakfast, lunch and dinner.
- If low acidity is detected, cumin, wormwood, fennel, thyme, and oregano are indicated. The herbs are combined in equal proportions and brewed according to the instructions on the package.
- During pregnancy, in the absence of allergies, you can treat stomach pain with honey. Both the pure product and its mixture with aloe juice are useful.
Another effective remedy is mineral water. By agreement with the doctor, it is allowed to add Essentuki and Borjomi to the daily diet. The main thing is not to overdo it with the medicine, since excessive consumption of liquids in general and salty drinks in particular can lead to undesirable edema for a pregnant woman.
A complement to the main therapy is bed rest, maximum rest, following a strict diet with a ban on fatty, spicy foods. It is advisable that food enters the stomach with short breaks every 6-7 hours. Portions should be small.
How many months is this?
As a rule, most pregnant women believe that they will carry a child for 9 months. However, this is not an entirely correct belief. Doctors count a little differently. If we consider a standard pregnancy, without any deviations, then it will last 280 days.
There is such a thing as an obstetric month. So it is equal to 28 days, that is, it has exactly 4 weeks of 7 days. Therefore, the 37th week is the first week in the ninth obstetric month and the onset of labor at this time is quite normal.
How to prevent pain syndrome
It is unlikely that it will be possible to completely eliminate discomfort and spasms in the epigastric region during pregnancy. But negative feelings can be minimal if the following conditions are met:
- Late evening and night snacks and overeating are excluded.
- Smoked foods, pickles, marinades, seasoned and fatty foods become taboo while pregnant.
- An undesirable addition to the diet is foods containing coarse fiber, due to its difficult digestion.
- Long breaks in nutrition are unacceptable.
- If you are concerned about morning sickness, immediately after waking up you need to fill your stomach with neutral food. It could be a banana or biscuits, crackers.
- You should not go to bed immediately after eating. It is advisable to maintain an interval of at least 20 minutes.
General recommendations for all pregnant women regarding timely examination by a doctor, minimizing stress, anxiety, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are also appropriate. A constant regimen and dosed physical activity are important.
37th week of pregnancy for baby
At the 37th week of pregnancy, the baby’s height is approximately 48 cm, and his weight is 2,600 g. Externally, the fetus is almost no different from a newborn; all facial features are developed, and cartilaginous tissue is clearly visible. The accumulation of subcutaneous fat at this stage of pregnancy makes the body contours softer and rounder. The baby’s skin gradually smoothes out, it is no longer as pink as in the previous weeks of intrauterine development, and the integument gradually becomes lighter. The baby's body is still abundantly covered with lubricant, but the amount of vellus hair decreases noticeably, vellus hair remains only on the shoulders and back, and in some babies it disappears almost completely.
This week the accumulation of fatty tissue continues. It reaches a maximum of 15% of the child’s total body weight. It is difficult to overestimate the importance of adipose tissue for newborns; it is this tissue that protects the child from overheating or hypothermia, since the baby’s thermoregulation system after birth is not yet sufficiently formed and continues to develop in the first months of the little person’s life.
At this stage, not only the volume of subcutaneous fat increases, but also the muscles and skeleton intensively develop. The child constantly moves his arms and legs. These unique workouts help increase muscle mass. The baby also makes rhythmic breathing movements that strengthen the intercostal muscles and diaphragm, preparing the respiratory organs for childbirth.