According to statistics, approximately a fifth of the adult population of the planet suffers from various manifestations of intestinal dysfunction. This disease occurs due to certain intestinal problems and is often called intestinal disorder or “irritable bowel syndrome.”
It manifests itself in the form of abdominal pain and stool disorders, for which there are no specific reasons. This disease is functional and for this reason, it is rarely confirmed using various laboratory tests.
Reasons for intestinal disorder
Intestinal upset often occurs due to overwork or stress.
Functional bowel disorders occur in many adults. And symptoms arise for no apparent reason.
They are characterized by severe pain in the abdominal area and the appearance of diarrhea. The age category of patients is people of active age from 25 to 60 years. Causes of intestinal upset:
- The disease often occurs against a background of overwork and stress. The body reacts to constant nervous tension with a malfunction of the intestines.
- Another cause of the disorder is intestinal infections, untreated infectious diseases of the stomach and intestines, which worsen when the body’s defenses weaken.
- If a person suffered from a disorder of the microflora, then diseased intestinal walls can periodically make themselves felt.
- A negative reaction of an organ to the presence of a certain product is called individual intolerance. More often, the irritant is fatty heavy foods, stale foods, and an abundance of fiber-rich foods in the diet.
- Allergy to products that do not combine with each other or are allergens for humans.
We must understand that the cause of pain and loose stools is the formation of toxins that poison the entire body. With a long process, they can cause disturbances in the functioning of other organs. In women, intestinal function is often disrupted due to hormonal conditions in the period preceding menstruation.
Acute diarrhea
A very common condition, usually resulting from eating food or water contaminated with bacteria, their toxins, viruses and protozoa. Infectious diarrhea is usually short-lived, so an infectious cause is rarely identified in patients with diarrhea for more than 10 days. Alcohol intoxication, various drugs, including antibiotics, cytotoxic drugs, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, can cause acute diarrhea.
Traveler's diarrhea is also recognized
. It develops in the first days in people traveling to exotic regions of the planet other than their own and is associated with the consumption of food and water with a different qualitative and quantitative composition of non-pathogenic microbial flora.
We can talk about the acute nature of diarrhea if the duration is no more than 3 weeks; otherwise, diarrhea is considered chronic.
Signs of the disease
Bloating is a symptom of an intestinal disorder.
Painful and unpleasant symptoms occur simultaneously. This is bloating, cutting pain. They are not always accompanied by diarrhea. Sometimes constipation occurs.
If signs of concern appear, it is imperative to undergo a medical examination.
If the tests are normal, the ultrasonic examination does not reveal an alarming picture, then most likely a diagnosis can be made - an intestinal disorder or irritable organ syndrome.
Usually the pain begins in the morning. They can be aching, tolerable. But when increased gas formation occurs, they become sharp and bursting. Flatulence is accompanied by frequent loose stools, but no relief comes. The distension does not decrease. The abdomen makes gurgling sounds and the stool contains clear mucus.
Consequences of the disease
The very manifestation of the disease causes anxiety and anxiety in a person; it is accompanied by pain and unpleasant sensations. But poor functioning of the digestive tract can be complicated by serious consequences:
- With frequent loose stools, fluid and beneficial microelements leave the body. All organs lose nutrients that are not replenished. A decrease in calcium content threatens diseases of the cardiovascular system, changes in blood pressure, and the progression of vegetative-vascular dystonia. With a lack of this important element, limb cramps are observed, especially at night. Sand and kidney stones can also form.
- When magnesium is lost, disturbances occur in the functioning of the nervous system and psyche. A person gets tired quickly, often gets irritated and nervous without reason.
- Frequent intestinal dysfunction threatens to disrupt the entire digestive system.
Dysbacteriosis - symptoms and treatment
Symptoms of intestinal dysbiosis can hardly be distinguished from the symptoms of its complications. This is because dysbiosis is a syndrome that makes a significant contribution to the development of many diseases.
Complications can be divided into several groups:
- neuropsychiatric diseases : depression, Alzheimer's disease, multiple sclerosis, anxiety disorder, schizophrenia, autistic disorders, Parkinson's disease;
- diseases associated with insulin resistance : insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, obesity, type II diabetes mellitus, hypertension, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[7];
- autoimmune pathologies : type I diabetes mellitus, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, primary sclerosing cholagnitis[8];
- allergic diseases - bronchial asthma, atopic dermatitis, food allergy[9];
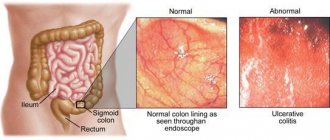
- systemic inflammation - Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, irritable bowel syndrome, celiac disease and colorectal cancer.
Neuropsychiatric diseases
Depression and anxiety disorders are correlated with the predominance of Firmicutes over Bacteroides[12].
Multiple sclerosis is associated with a significant reduction in Clostridia species XIVa and IV, an increase in Methanobrevibacter and Akkermansia, and a decrease in Butyricimonas[8].
In a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease, microbiota accumulate in amyloid plaques[13].
The connection between schizophrenia, autistic disorders and Parkinson's disease with dysbiosis has been proven. But there is still debate about whether this connection is primary or concomitant.
Autoimmune pathologies
Type I diabetes mellitus is associated with a positive correlation between autoantibodies and microflora - islet cells, Bacteriodes and Bilophila. A negative association was also found with Streptococcus and Ruminococcaceae. In addition, the spread of Faecalibacterium leads to a decrease in the level of glycated hemoglobin[8].
Rheumatoid arthritis is intensified due to molecular mimicry - the bacteria Prevotella copri, Parabacteroides sp. and Butyricimonas reproduce the structure of two autoantigens of the organism. As a result, there are much more antigens in the inflamed synovial tissue. And the more GNS antibodies, the more severe the symptoms of arthritis (8). Probiotics can be used to reduce pain, swelling and improve blood counts during various phases of arthritis[22].
Systemic lupus erythematosus is accompanied by a decrease in the species diversity of microflora. This increases the number of Ruminococcus gnavus bacteria fivefold. The amount of antibodies to these bacteria is directly related to disease activity[20].
Primary sclerosing cholagnitis is associated with a decrease in microflora diversity. Alpha diversity increases after fecal microbiota transplantation. Because of this, alkaline phosphatase decreases by more than half, which indicates the influence of microbiota on autoimmune processes in the liver ducts[21].
Allergic diseases
Bronchial asthma is associated with an increase in respiratory microflora - Haemophilus influenzae, streptococci, Moraxella bacteria - and a decrease in the intestinal microbiome - bifidobacteria, Akkermansia, Faecalibacterium, Morganella, Lactobacillus bacteria. Inhalation of “agricultural dust”, which is saturated with bacteria and their components, can weaken the allergic reaction.
Atopic dermatitis occurs when the skin is colonized by Staphylococcus aureus against a background of increased sensitivity of the immune system and disruption of the skin barrier. Superantigens of staphylococci increase the concentration of IgE - antibodies designed to protect the body from parasites. If antibodies are absent, antigens attack their own tissues and cause allergies - they activate Th2 / Th22 inflammatory lymphocytes and promote the appearance of dendritic cells[23].
The opposite effect is achieved with epidermal staphylococcus. It suppresses the production of CD4, white blood cells involved in the immune response. The membrane protein TLR-2, by binding to normal skin flora, stimulates the production of antimicrobial peptides and an increase in tight junctions, which strengthens the skin barrier.
Allergies to food appear when there is excessive diversity of microflora. Excessive gut microbial enrichment in 3-month-old infants increases the risk of developing food hypersensitivity by one year of age. When the intestines are enriched with microbes at 12 months, this no longer happens.
When the numbers of Ruminococcaceae and Lachnospiraceae bacteria increase, children develop milk allergies. If the flora is enriched with Firmicutes bacteria, including Clostridia, then the allergy may resolve by school age.
Peanut or tree nut allergies occur when microbial diversity is reduced and Bacteroidetes are increased. Allergy symptoms and diarrhea may be relieved by the presence or oral administration of 17 strains of Clostridia.
Systemic inflammation
Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis occur due to an overly aggressive immune response to beneficial intestinal flora in genetically susceptible individuals. The breakdown of proteins, peptides and amino acids by flora in the distal colon leads to the formation of various biologically active metabolites that can affect the viability of epithelial cells. A decrease in the number of bacterial species that produce butyrate leads to excessive activation of toll receptors, which can impair immunity due to changes in gene activity.
Irritable bowel syndrome is associated with a decrease in the number of lactobacilli, bifidobacteria and an increase in the number of aerobes compared to anaerobes. This disruption of the microflora modifies pain and motor responses[12].
The microbiota in this case becomes both the cause and the target of intestinal motility disorders, visceral hypersensitivity and neuroimmune signals. This occurs due to disruption of the mucous barrier, activation of receptors to which bacteria attach, as well as dysfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis (HPA axis).
How does HPA axis dysfunction occur? Cytokines and excess short-chain fatty acids increase levels of cortisol, the stress hormone. It goes to the pituitary gland, hypothalamus, amygdala, hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. The return signal from the brain leads to changes in intestinal motility and sensitivity, the epithelial barrier and the production of neurotransmitters are disrupted in the form of an increased response to environmental factors.
Why is intestinal motility impaired? Microbiota modulates intestinal motor function. Its composition can change through toll and node receptors. As a result, the permeability of the intestinal wall increases, and bacterial metabolites gain access to the submucosa. This alters the expression of genes that are involved in smooth muscle function and neurotransmission. Normal E. coli enhances contraction of the colon, and pathogenic strains of E. coli disrupt the contractility of muscle cells and inhibit motility. Exposure to Lactobacillus rhamnosus significantly impairs acetylcholine-stimulated contraction.
Celiac disease is a unique autoimmune disease. It is caused by genetic factors DQ2/DQ8 and an environmental trigger - gluten, but they are not enough to cause the disease to develop. The trigger for celiac disease is a disruption of the microbiota in predisposed children at the time of introduction of complementary foods - high proportions of Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, Corynebacterium, Gemella, Clostridium, Enterobacteriaceae and Raoultella and lower proportions of Actinobacteria, Bifidobacterium[32].
Since gluten intolerance becomes more common in adulthood after many years of eating grains, environmental exposure becomes an additional factor in the development of celiac disease.
Colorectal cancer - rectal cancer - is also associated with microflora disturbances. Advanced dysbiosis triggers chronic inflammation. Because of this, host-produced antibacterial peptides, secretory IgA, mucins, cytokines or neurotransmitters accumulate. Also, the remains of damaged cells and many reactive forms of oxygen and nitrogen accumulate in the body. When copying errors occur during intestinal cell division (dysplasia), these substances contribute to malignant degeneration.
Cancer development occurs according to the “driver-passenger” model:
- “drivers” - certain strains of bacteria - disrupt the microenvironment of the mucous membrane, damaging DNA;
- “passengers” - pathological flora - after damage to the membrane, they colonize it, which leads to chronic inflammation, direct tissue damage and tumor formation[15].
Other complications of dysbiosis
The risk of contracting sexually transmitted diseases , including HIV infection, increases. In girls, this is facilitated by a deficiency of Lactobacillus bacteria, which produce lactic acid and hydrogen peroxide to protect against pathogenic microorganisms[29]. In men, the risk of acquiring HIV infection increases with a high concentration of anaerobic bacteria in the microbiota under the foreskin.
Threat of premature birth . In women before 24 weeks' gestation, lower vaginal levels of Lactobacillus crispatus and higher levels of BVAB1, Sneathia amnii, TM7-H1, Prevotella and nine additional taxa may serve as a marker of this risk[7].
Risk of developing cardiovascular diseases . Periodontal bacterial DNA has been found in atherosclerotic plaques in patients suffering from coronary heart disease and atherosclerosis. Bacteria can initiate or aggravate atherosclerotic processes. This activates the innate immune system, directly involving mediators that are activated by plaque antigens[15].
Risk of developing esophageal cancer - adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. This risk is related to the composition of the oral microbiome. The periodontal pathogens Tannerella forsythia and Porphyromonas gingivalis are correlated with an increased risk of adenocarcinoma. A lower risk of this disease was observed due to depletion of the beneficial genus Neisseria and Streptococcus pneumoniae. There is also a relationship between bacterial biosynthesis of carotenoids and protection against the development of adenocarcinoma[27].
How to determine the disease
If you observe symptoms of intestinal disorder, you should consult a gastroenterologist.
If these symptoms appear, you should consult a gastroenterologist.
He begins the examination with a personal conversation, finds out how often disturbing symptoms occur, what and how the person eats, what kind of wakefulness and rest regime he follows.
Then, using palpation, the doctor examines the patient’s abdomen, determining the bloating and activity of individual zones. The pain can be concentrated in certain areas of the abdomen or spread to the entire intestine. The condition of the large intestine is especially carefully examined.
Additionally, the doctor may recommend examination by a proctologist. If during the interview the patient complains of purulent and bloody discharge, the lower intestine must be examined using sigmoidoscopy. Such a study is necessary for chronic constipation. Sometimes diagnosis requires an x-ray examination and a laboratory study of the composition of the discharge.
Main causes of intestinal diseases
- predisposition can be inherited;
- unbalanced diet;
- low-quality products;
- increased psycho-emotional stress;
- living in places with poor ecology;
- work in hazardous production;
- intestinal infections;
- taking strong medications;
- deficiency of vitamins, micro and macroelements;
- deviations from the physiological norm of body weight, both thinness and overweight;
- presence of bad habits;
- physical inactivity.
The main reasons, as you can see listed above, depend on lifestyle and can be corrected, with the exception of heredity.
9 out of 10 people on the planet have problems with the digestive tract, expressed in one form or another. For example, today every fifth patient examined is diagnosed with IBS, and the female half suffers 4 times more often, and the bulk of patients are people over 30 years of age.
Methods for eliminating intestinal disorders
The first condition for getting rid of intestinal disorder is to normalize your diet and establish a routine and a healthy lifestyle.
First of all, you need to eat foods that do not cause flatulence and irritation of the intestinal walls. These foods include some fruits, sweet and fatty foods, and strong coffee.
The diet is developed by the doctor taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient and the nature of the disease. It includes foods and supplements that are high in fiber. It is important for the patient himself to understand the seriousness of the disease and strictly follow the doctor’s instructions, to rearrange his life in such a way as to avoid stress and emotional tension whenever possible.
How to restore bowel function
If you have a bowel disorder, the first thing you need to do is choose the right diet. Fatty foods, spicy and irritating foods are excluded. For the first 2-3 days you should eat jelly, porridge with water, rice water, and low-fat soups. Bread should be eaten dry. They return to their usual diet gradually and only after stabilization of the gastrointestinal tract.
Medicines that can be used without a doctor’s prescription include:
- Antidiarrheal;
- Enterosorbents;
- Rehydrating agents.
You definitely need to drink as much as possible. After stool normalization, it is advisable to take probiotics; they will help prevent the development of dysbiosis.
For recurrent intestinal disorders, examination is necessary. Qualified therapists treat patients with gastrointestinal pathologies. You can make an appointment by phone, choosing a convenient appointment time on a weekday or weekend.
Causes of intestinal disorders in older people
A narrowing of the esophagus can cause intestinal upset.
Bowel problems often occur in older people. Metabolic processes slow down with age. This can cause stagnation in the intestines.
If left untreated, they can cause serious illness and complications. Moreover, negative processes develop quickly.
The cause of the disorders may be a narrowing of the esophagus or large intestine. After strokes, similar phenomena often occur against the background of brain disorders.
Older people often suffer from constipation. This happens as a result of a sedentary lifestyle, a lack of fiber in the diet of vegetables and fruits, and a violation of the water consumption regime. If the reasons are more serious, they can only be determined by a doctor during examination.
Constipation may accompany toxic goiter or hypothyroidism. The intestines are influenced by endocrine system disorders and psychological factors.
Treatment of bowel dysfunction
The doctor needs to determine the cause of intestinal dysfunction
Before treating intestinal dysfunction, the doctor must determine the cause of the disease. If the reason for its development was a long-term stressful condition, then the attending physician can recommend the patient various relaxing activities: yoga, running, jogging, walking in the fresh air.
They help relax the body and stabilize the nervous system. If the stressful state does not go away and accompanies the patient for a very long time, then various sedatives and antidepressants may be prescribed.
If the causes of intestinal dysfunction are something else, then depending on them, the following medications may be prescribed:
- antispasmodics - to combat pain
- laxatives – to combat constipation
- antidiarrheals – to combat diarrhea
To relieve pain due to intestinal dysfunction, Sparex, Niaspam, Duspatalin, etc. are often used. They have a relaxing effect on the intestines and promote normal contraction. However, in some cases their use is prohibited because they contain peppermint oil, which should not be taken by women during pregnancy.
Another name for bowel dysfunction is irritable bowel syndrome.
Laxatives soften stool and help normalize the bowel movement process. While taking these medications, the patient should drink plenty of fluids to protect the body from dehydration. Bowel dysfunction accompanied by diarrhea will require the use of various binding agents, such as imodium and loperamide.
They slow down intestinal motility and increase the length of time stool remains in it. As a result, liquid stool has more time to thicken and bowel movements are normalized.
For intestinal disorders, it is recommended to follow various diets, the therapeutic effects of which are similar to those of medications. Patients who suffer from constipation need to take more fluids, eat bran bread, various oils, fish, meat, and cereals. At the same time, it is extremely undesirable for them to consume coffee, jelly, chocolate and pastries made from butter dough.
In case of diarrhea, food that accelerates intestinal motility and the process of emptying should be excluded from the patient’s diet. The diet may include coffee, tea, and dry biscuits. It is recommended to consume kefir and cottage cheese, while eggs and meat are excluded for a while.