Norm and pathology
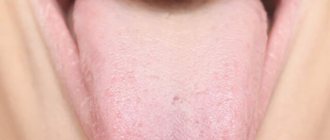
Language is a kind of mirror of the functioning of the body. When it is clean, pink, with visible taste buds, the person is healthy and most likely does not suffer from bad habits. But even a loose white coating, through which the surface of the tongue is visible, is considered as a variant of the norm. It can change shade depending on the time of year: in summer it can be more intense due to hot weather, in winter it becomes white-yellow, in autumn it becomes almost transparent. In addition, a yellow coating on the tongue in the morning appears in heavy smokers and those who drink too much coffee.
However, a change in the color of the tongue may be a consequence of malfunctions in the internal organs, mainly the liver, kidneys, stomach, pancreas and gall bladder. If the plaque has become dense, thick, bright yellow or brownish-yellow, and there is also bad breath, you should consult a doctor and identify the cause of the problem.
Attention!
Typically, “safe” soft deposits come off easily and, if brushed well, will not reappear. But if the plaque returns, we are dealing with pathology.
Natural color of the tongue in a healthy child
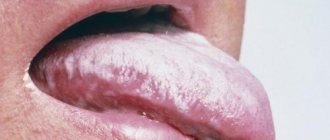
There are many cases when light-colored accumulations on the uvula do not require treatment. For example, during the examination in the morning, the mother may notice light deposits in a small amount. They are easy to clean off and are considered normal. At 1 year of age, such plaque is also diagnosed. These are often milk traces from mother's milk or its substitutes. Therefore, a thin light film is quite acceptable. But the natural shade of the surface of the tongue should be visible through it.
In healthy children, the color of the muscle organ is pale pink. At the same time, it must be mobile, all movements must be made unhindered and without difficulty. The condition of a child's tongue is significantly affected by humidity levels, as well as the temperature in the room where the baby is. For self-diagnosis, the mother needs to conduct visual examinations of her child’s oral cavity. Cleaning the baby's mouth is also necessary. First, this is done using special pharmaceutical wipes, and when the child grows up, a children's brush with a surface for treating the tongue is used.
Secondary symptoms
- layer thickness. If the natural color of the tongue is not visible through the plaque, we are dealing with severe processes or chronic diseases. A thin layer, on the contrary, indicates an initial stage or a slight deviation from the norm;
- coverage area (fully or partially);
- consistency. It can be thick, soft, dry or flaky;
- ease of removal. Dense thick plaque is usually difficult to remove. A softer, thinner layer is easier to clean, but can quickly reappear.
Which doctor should I contact?
The first specialist you need to contact after identifying a tongue coated with a white coating is a pediatrician. After carefully examining the child’s oral cavity, the doctor will assess the condition of the teeth and gums and check the lymph nodes. After this, he will make a diagnosis and prescribe effective medications to eliminate the underlying disease.
If it was not possible to determine the cause of the formation of layers during the examination, the pediatrician will give a referral to an infectious disease specialist, gastroenterologist, endocrinologist or other specialized specialists. In some cases, doctors prescribe a bacterial culture from the surface of the tongue and a general blood and urine test. Based on the results of laboratory tests and examination, the small patient will be prescribed suitable treatment.
What should parents do?
In cases where a white coating appears on a child’s tongue only in the morning or after eating dairy food, is easily removed and does not return during the day, this should not cause concern to parents. For infants and children under one year of age, plaque from the tongue can be removed with a finger wrapped in a piece of clean gauze or bandage. Finger movements must be careful. For older children, plaque is removed from the tongue using a soft toothbrush. It is safe for children of any age to treat the oral cavity with a soda solution.
For a child over 3 years old, the solution is used as a rinse; for younger children, the tongue is wiped with a gauze swab dipped in a soda solution. If the white coating is difficult to clean off from the surface of the tongue, does not disappear within several days, or is accompanied by a burning sensation and painful sensations, parents should show the child to the doctors. These may be specialists such as a dentist, pediatrician, gastroenterologist. Only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment for a child.
Treatment
To get rid of unsightly deposits, unpleasant odors and other symptoms, you need to determine their cause. To do this, you need to contact a therapist who will conduct an examination and prescribe additional tests and examinations (general analysis and blood biochemistry, throat culture, gastroscopy, ultrasound, coprogram, etc.). Based on the results, he will recommend therapy, diet and, if necessary, give a referral to a gastroenterologist, infectious disease specialist, dentist or other specialist.
After treating the root cause of plaque, its intensity should decrease. But to speed up the process, doctors recommend paying more attention to oral hygiene, brushing the surface of the tongue twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush (but not a scraper, so as not to cause injury), drinking more water and rinsing your mouth with herbal decoctions.
Prevention
It is not always possible to prevent the formation of plaque on the tongue, especially if it is a symptom of an infectious, viral or fungal infection. But you can reduce the likelihood. The recommendations will not be new: you need to adhere to a healthy lifestyle, do not smoke, do not abuse alcohol, drink coffee and tea in moderation, exclude too fatty, spicy and fried foods, include more vegetables, fruits, whole grains in your diet, give preference to lean varieties of meat and fish and do not take medications (especially antibiotics) without a doctor's prescription.
Fungal infection
The development of thrush in the child’s mouth occurs as a result of the growth of Candida fungi. Intensive reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms occurs as a result of the influence of various factors.
Often babies become infected with thrush during childbirth, crossing the birth canal
These include:
- Weakened immune system.
- Dysfunctions of the microflora of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Hormonal disorders.
- Conducting antibacterial therapy.
- Excessive dryness of the oral mucosa.
Infection with Candida fungi occurs under the following conditions:
- In utero. Infection can occur through the placenta, umbilical cord and amniotic fluid.
- During childbirth. Often babies become infected with thrush during childbirth, crossing the birth canal. Therefore, it is important for women to exclude the development of thrush, especially in the last stages of pregnancy.
- Finding a child in a hospital and maternity hospital. Inappropriate and non-sterile care of the child contributes to the child becoming infected from health care workers.
- Poor sanitary conditions at home. Babies are born with a weakened immune system. Therefore, keeping a child in an unsterile home environment promotes the penetration of various microorganisms and bacteria into his body.
Diagnosis of candidal glossitis involves a complete collection of anamnesis data and conducting various types of comprehensive research.
Important! In most cases, when diagnosing thrush in a child, an instrumental examination is not performed.
For these purposes the following is carried out:
- Microscopic examination of the oral mucosa by taking a scraping from plaque and then examining it under a microscope. This allows you to determine the presence of Candida mycelium threads and yeast-like cells.
- Bacteriological research. Allows you to identify the type of Candida fungus and the number of its colonies. Sowing mushrooms on a nutrient medium helps install the most effective antifungal drug. This is necessary, since many medications have different effects on grown fungal colonies.
- Serological study. It is carried out if necessary to study antibodies that are concentrated in the blood serum.
Thrush as a cause of white plaque
Thrush in the mouth of newborns appears in 15% of children under one year of age. The causative agent of the disease is the Candida fungus. It enters the child’s body from the outside or during childbirth/breastfeeding (provided that the fungus is in the body of a nursing woman), actively affecting the oral mucosa.
Causes of thrush in newborns
Candidiasis is more common in premature babies
Candidiasis will not occur without a fungus - that’s for sure. And the factors due to which the disease will receive an impetus for development are varied.
- Anatomical features of the structure of mucous membranes in newborns. The protective function of the oral mucosa in babies is just developing, so the ability to repel germs is imperfect. In the first months after birth, children have low salivation, and the amount of antifungal components in saliva is extremely small.
- Any damage to the inner shell greatly increases the risk of catching a fungal infection.
- Immunodeficiency in the body. A lack of immune cells and insufficient activity of all other defense mechanisms is observed in all babies at the beginning of life. But the period when the immune system is weakened is the optimal time for the development of diseases, including candidiasis.
- Imbalance of intestinal microflora. For the first time after birth, healthy microflora in the intestines is at the formation stage. An imbalance of microflora and further thrush can cause intestinal infections.
- Candidiasis can develop after taking antibacterial agents. The intestinal microbial community is not able to recover after therapy, which means Candida fungi can become more active.
- Prematurity. The risk of candidiasis is greatest in premature babies - due to the fact that they are less resistant to all of the above factors.
There are 3 forms of candidiasis in a child:
- Easy. White grains with the consistency of cottage cheese form in the mouth. Typical location: tongue, cheek area. The condition does not cause concern for the baby.
- Moderate weight. A coating of cheesy consistency partially affects the oral cavity. Redness of the mucous membrane is observed, attempts to remove plaque are accompanied by bruising.
- Heavy. High-density plaque covers almost the entire oral cavity and cannot be removed. The baby cries and may refuse to feed.
It is necessary to visit a doctor at the first manifestations of the disease to prevent its development. In the initial stages, thrush responds well to treatment.
How to treat thrush
Therapy for thrush includes the use of local (ointments, suppositories, creams) and general (tablets, injections) agents.
Medicines are chosen exclusively by a pediatrician - drugs that are effective for treating an adult can negatively affect a child due to the risk of adverse reactions.
Of the entire list of drugs against candidiasis, only 2 are used to treat young children:
- Fluconazole;
- Nystatin.
The dosage will be chosen by a specialist taking into account the baby’s weight and the severity of the disease. Timely treatment starts guarantees a quick recovery.
Blue coating on the tongue
A blue tongue is a sign of blood stagnation.
Very often, various diseases of the cardiovascular (congenital heart defects, arrhythmias, heart failure) and nervous system (hemorrhages, cysts, epilepsy) lead to the fact that blood flows through the tissues more slowly than it should - cyanosis or cyanosis appears on the limbs, lips and language. Therefore, if you notice such a symptom in your child, you should urgently contact your doctor for advice.
Read also: Now the beauty and health of your child is completely in your hands
Let's sum it up
Modern doctors, just like their ancient predecessors, rightly consider the condition of the tongue to be one of the criteria for human health. When examining the tongue, its mobility, density, color, moisture, presence or absence of plaque and other factors are assessed. A white coating found on a child’s tongue can be a “signal” of the onset of a disease, even in cases where other symptoms have not yet manifested themselves. In this case, the coating can cover both the entire surface of the tongue and its individual sections, be dense or loose, and be easily or difficultly removed from the surface of the tongue.
Green coating on the tongue
The appearance of a green coating on the mucous membrane of the tongue often frightens parents, especially if it is found in a newborn or infant.
The most common cause of this phenomenon is candidiasis - a fungal infection of the oral cavity that occurs due to imperfect immune defense in the body of a 1-year-old baby or while taking strong antibacterial drugs.
This plaque has varying color intensities and can spread to other parts of the oral cavity, found on the cheeks, palate and lips. After removing it, you can see the red surface of the tongue with small blisters or ulcers, which cause discomfort to the child.
You should start treating green plaque only after consulting a doctor. Therapeutic measures will consist of taking special drugs with antifungal action and local antiseptics to treat thrush and prevent bacterial complications.
Read also: How bite affects posture and spinal health
Brown coating on the tongue
A brown tongue in a child is not such a rare occurrence. There can be many reasons for this:
- Severe diseases of the digestive system , accompanied by inflammatory changes, stagnation of bile in the bile ducts, and disruption of the digestive processes.
- Constant dehydration of the child's body due to high ambient temperatures or insufficient fluid intake.
- Insufficient intake of B
- Taking certain medications : antibiotics, antiseptic solutions, concentrated herbal decoctions.
It is very difficult to establish the exact root cause of the appearance of such a dark plaque. This can only be done by an experienced doctor, who, after additional examinations, will be able to prescribe the optimal treatment.
Black coating on the tongue
The presence of a black coating on a child’s tongue looks quite scary, and there may be several reasons for this phenomenon:
Bacterial sore throat is often accompanied by the appearance of dark plaques on the mucous membranes, even black. In this case, the child will have signs of inflammation in the tonsils: red throat, high fever, pain when swallowing, weakness.
Hidden forms of diabetes mellitus, which lead to persistent disruption of the acid-base balance in the body. Excess acid or acidosis will cause darkening of the tongue.
Taking some antibiotics causes the growth of pathogenic microflora in the mouth, which causes the mucous membranes to become permanently stained black.
Treatment of such plaque will consist of eliminating the causes that caused its appearance. After a sore throat is treated, medications are stopped, or diabetes is identified and compensated for, this symptom will most likely go away on its own.