An ovarian cyst is a cavity filled with contents. This benign disease can be congenital or acquired. Cystic formations are detected in women of different age groups, and even girls who are not sexually active.
Often the disease is asymptomatic, without causing discomfort, and is detected during an ultrasound examination.
What is a cyst
The content of the article
More than a third of women of all ages develop neoplasms in the ovaries, namely cysts. An ovarian cyst is a neoplasm located on the wall of an organ and filled with fluid. In most cases, a woman does not even suspect that any disturbances have occurred in her body.
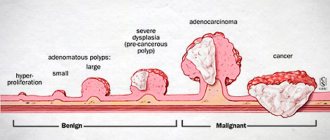
Cysts can be dangerous and harmless. Safe (functional - small, without inclusions of pathological cells) disappear over time and have virtually no effect on a woman’s life. Other types of tumors are dangerous to health and must be removed surgically. If you delay treatment for an ovarian cyst, remember about possible complications: the development of a malignant tumor, suppuration and rupture of the cyst, followed by peritonitis.
Symptoms
In most cases, the development of cystic formation in the stomach is asymptomatic. Therefore, patients with this disease very rarely complain of deterioration in health.
If the tumor grows to a significant size, or a concomitant pathology develops that affects the process, some symptoms characteristic of such a disease begin to appear. In such a situation, the patient complains of the presence of:
- painful manifestations in the digestive tract,
- loss of appetite,
- instant weight loss,
- bowel dysfunction (diarrhea appears),
- nausea and vomiting,
- heartburn, belching,
- flatulence (bloating).
Causes
The main reason for the formation of cysts is hormonal changes in the body associated with endocrine diseases, ovarian dysfunction and other changes, such as age-related ones.
It is noted that cysts often occur after abortions, stress and other traumatic factors. All the causes of cysts have not yet been precisely studied, but it is known that they are provoked by:
- inflammatory processes in the ovaries;
- sexual infections;
- Ovarian endometriosis is a disease in which cells from the uterus (endometrium) enter the ovarian tissue;
- congenital abnormalities of the reproductive system;
- termination of pregnancy, especially those carried out by surgical curettage;
- excess weight;
- metabolic diseases;
- imbalance of sex hormones.
Acquired ovarian cysts
- Follicular
- occurs if the follicle does not rupture and the egg does not come out. During ultrasound, they can be observed on both ovaries. Sometimes there are several such formations. - Endometrioid cysts
are manifestations of ovarian endometriosis. They are formed from endometrial uterine cells that enter the ovary. These cellular structures react to hormonal changes caused by the menstrual cycle - they increase in size before the onset of menstruation, and then begin to bleed. There is nowhere for the released blood to flow out, so it forms cysts, which are called “chocolate” due to the coagulated dark bloody contents. - Corpus luteum cysts
occur due to hormonal imbalances. After the follicle emerges, the corpus luteum produces progesterone for some time, which is necessary for pregnancy. But, if conception does not occur, this formation should resolve. Sometimes this does not happen and a cystic formation forms in the ovary. Sometimes the formation reaches a large size and begins to bleed. - Cysts in polycystic disease
can be multiple. Polycystic ovarian syndrome is associated with metabolism, so women experience infertility, miscarriages, cardiovascular disease, diabetes and even mental illness.
Congenital ovarian cysts
- Dermoid
, formed from embryonic glandular tissue. These formations may contain hair, fat, teeth, cartilage, and bone tissue. Dermoid cysts can reach a size of 25 cm. Although malignant degeneration of the cyst occurs only in 1-2 percent of cases, a large tumor puts pressure on neighboring organs, causing pain and dysfunction; - Paraovarian cysts
, arising from embryonic tissue, are located next to the ovaries. The reason for their appearance is a violation of the intrauterine formation of the girl’s internal genital organs. Paraovarian cysts grow very slowly, but can reach enormous sizes (up to 30 cm).
Diagnosis of cysts
In order for the gynecologist to determine whether the patient has a cyst, he first of all conducts an examination and sends her for an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs. If the ultrasound does not give accurate results, then the following procedures are performed:
- Ultrasound of the ovaries;
- blood tests for biochemistry and tumor markers;
- test to determine the presence of pregnancy, including ectopic.
Additional studies performed to diagnose complications associated with the formation of an ovarian cyst:
- a urine test is carried out to find out whether the patient is losing blood during the day (in addition to the days of menstruation);
- puncture of the posterior vaginal vault to determine whether there was hemorrhage in the abdominal area;
- laparoscopic examination.
Specifics of pain
In approximately 70% of all cases of the disease, an ovarian cyst, in the early stages, forms and grows without any symptomatic manifestations that would force a woman to immediately consult a doctor. Despite this, in certain cases the clinical picture can still be pronounced. Pain with an ovarian cyst can be localized and moderate, or intense, spreading throughout the abdomen.
Most often, pain with an ovarian cyst is localized in:
- Lower abdomen;
- Groin area;
- Lower back;
- Sacrum;
- Lower limbs;
- Rectum.
Which ovarian cyst causes lower back pain? Aching pain radiating to the lower back with an ovarian cyst is provoked by irritation of the nerve endings of the peritoneum, spasms of the bladder and other hollow pelvic organs. Cystadenomas and malignant cysts cause pain to appear much earlier. This is due to the fact that such cysts grow very quickly and can grow into the abdominal wall, bladder, and rectum.
Why is an ovarian cyst dangerous?
Ovarian cysts increase in size, interfering with the work of neighboring organs. By disrupting the functioning of the reproductive system, they often cause infertility. Sometimes cysts develop into cancer.
The most serious complication of these formations is rupture of the membrane, in which the cystic contents leak into the abdomen. The woman has to undergo emergency surgery to remove the tumor capsule, often including part of the ovary. Torsion of cysts that have a “leg” is no less dangerous. There is a disturbance in blood flow, accompanied by tissue necrosis. Without treatment, this complication is fatal.
In order not to endanger life and health, it is necessary to identify and treat ovarian cysts in a timely manner.
Possible complications
The presence of a cyst that is not a malignant formation is a dangerous factor in the development of ovarian cancer. More often than others, endometrioid and mucinous cysts are susceptible to the pathological process.
In addition to the risk of malignancy, ovarian cysts pose the following dangers:
- Twisting of the cyst leg can result in inflammation of the peritoneum due to impaired blood supply and necrosis.
- Ovarian cysts are one of the causes of infertility in women and difficult pregnancy.
- There is always a risk of cyst infection and subsequent suppuration.
- The list of possible consequences of an ovarian cyst includes rupture and internal bleeding.
Despite the predominant absence of symptoms, the cyst can manifest itself with sharp pain, fever, and tension in the abdominal muscles. In order not to bring the situation to such an outcome and to minimize the risk of complications, you should visit a doctor at the first alarming symptoms.
What do normal ovaries look like during ultrasound examination?
Normally, during an ultrasound examination, both ovaries are almost the same size:
- length – 30-41 mm;
- width – 20-31 mm;
- thickness – 14-22 mm;
- volume - about 12 cubic ml.
Due to the maturing follicles, the surface of the organ looks bumpy. Since the ovary is well supplied with blood, its tissues contain many blood vessels.
Typically, at least 12 cells mature in two ovaries. Among them stands out a dominant follicle measuring 10-22 mm, from which an egg will be released in the middle of the cycle. If ovulation has already passed, the corpus luteum is visible inside the ovary, secreting hormones necessary for implantation and development of the embryo. If conception does not occur, the corpus luteum dissolves.
What do the ovaries look like with cysts?
Ultrasound examination allows not only to identify cystic formations, but also to determine their type. Sometimes this requires several ultrasound examinations at different periods of the menstrual cycle:
- A dermoid cyst
has quite dense contents, so it looks lighter than others. Areas of heterogeneous structure are found inside. The walls of the formation are quite thick - 7-12 mm. Since the cyst grows very slowly, repeated ultrasound on any day of the menstrual cycle does not reveal changes in its size and structure. - A paraovarian cyst
is located outside an unchanged ovary. As a rule, it is single-chamber. Its size and appearance do not change depending on the day of the menstrual cycle. - The endometrioid cyst
has a smooth, clear shape. Wall thickness 2-9 mm. Inside there are structures that have a high density and resemble a honeycomb. Therefore, on the screen the cyst looks like a dark formation separated by light areas. The eggs in such an organ do not mature, but the other healthy ovary works normally. Before the critical days, the size of the cyst increases. In parallel, an enlargement of the uterus may be observed. - The follicular ovarian cyst
has thin walls and an even dark color. It is common - these neoplasms account for up to 20% of cases of ovarian tumors. In most cases, it gradually decreases in size, as can be seen on a repeat ultrasound. Sometimes follicular cysts do not resolve, being found even in women with long-extinct menstrual function. - A corpus luteum cyst
is similar in appearance to a follicular cyst. To differentiate them, Doppler ultrasound is performed. On examination, a bright circle is visible around the cystic formation, which doctors call the “ring of fire.” There is no blood flow inside the cystic formation itself.
Reviews
Julia
I would like to express my gratitude to your doctors. Deciding to have surgery is always scary. I, like hundreds of other people, tried to give it up. It’s good that the doctor clearly explained the consequences of refusal in my case. The operation was quick and easy, and I spent the postoperative period with you. I’m happy with everything, I got rid of the problem, and I can live a full life again.
Igor
The fact that the work of the clinic is organized at a high level is noticeable already at the entrance. The reception, diagnosis, consultation with the doctor also left the most pleasant impression. The treatment was chosen very competently. The cyst disappeared, and along with it the pain.
Catherine
The clinic is equipped with an excellent modern device for ultrasound diagnostics. The doctors identified the cyst and were able to select treatment until complications appeared. Almost immediately after the therapy, I was able to get pregnant, for which I am sincerely grateful to the doctors at the hospital.
Vlada
Thanks to Igor Anatolyevich for the wonderfully performed operation. I did not experience any pain or fear. But after the operation I began to feel much better. The attitude towards patients in the clinic is simply wonderful. They know how to calm and encourage.
What to do if you find a cyst in the ovary
Detection of an ovarian cyst during an ultrasound is not a reason to panic. Small tumors can often be cured by prescribing hormonal drugs and vitamins A, B, and C. Under the influence of medications, the size of the tumor decreases over several menstrual cycles.
It is better not to touch small congenital cysts that are not disturbing or growing. You just need to visit a doctor and do an ultrasound to monitor the tumor. To exclude malignant degeneration, it is necessary to periodically donate blood for tumor markers.
When planning a pregnancy, it is better to get rid of the cyst, because... it may begin to grow or burst during a period when surgery is unsafe. After a properly performed operation, cysts do not recur. But women prone to the appearance of such formations should be observed by a gynecologist.
Disease prevention2
Since the cyst does not always make itself felt by external manifestations, it is simply impossible to detect it on your own. Only regular monitoring of women by a gynecologist with an ultrasound will help identify the problem and begin to treat it in a timely manner, preventing complications from occurring.
Prevention of ovarian cysts is, first of all, attention to your body, giving up bad habits, and observation by a specialist. Do not allow the development of chronic diseases, do not give the problem a chance to grow like a snowball. As long as all body systems are in a healthy state and balance, there will be no reason for the appearance and development of an ovarian cyst.
Features of treatment of ovarian cysts
The following factors influence which treatment method the doctor chooses: the woman’s age, parameters of the ovarian cyst, the general health of the patient, and concomitant diseases. Treatment of the cyst may initially be hormonal, then laparoscopic.
Functional cysts are treated with hormonal therapy and, if the method does not bring results, the patient is sent for surgery, which can be performed either laparoscopically or laparotomically. If the presence of a cyst is dangerous to life and health, the woman is urgently operated on.
Growing dermoid, paraovarian and endometrioid cysts are removed laparoscopically through small incisions in the anterior abdominal wall. Modern methods make it possible to remove cysts while preserving the ovary, which is important for women planning to have children in the future.
After surgery, the gynecologist prescribes a course of treatment to restore the proper functioning of the woman’s reproductive system. In addition to medications, hirudotherapy (intravaginal) and homeopathic medications are often prescribed. If the patient is overweight, a nutritionist and endocrinologist are involved in the treatment process.
If the patient is planning to have children, surgery to remove the cyst cannot in any way affect the likelihood of conception. In extreme cases, operations are performed even during pregnancy. Sometimes this does not affect the development of the fetus, but, in rare cases, there is a need to terminate the pregnancy, since the threat to the life and health of the mother is extremely high.
Our advantages
- Our medical center employs doctors with extensive practical experience.
- We have a special innovative design of operating rooms: infection-resistant seamless monolithic blocks, 5 levels of sterility, thanks to a complex ventilation system.
- The gynecology department is equipped with the latest generation equipment - surgical equipment from recognized global manufacturers of medical equipment - “Karl Storz”, “Covidien”, “Erbe”, etc.
- All procedures are carried out in the most comfortable conditions for the patient.
You can see prices for services