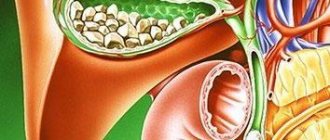
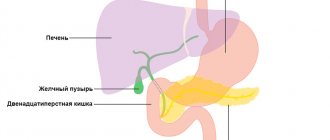
The gallbladder is classified as an auxiliary organ of digestion. Its main task is the accumulation of bile, which is produced by the liver. Our body needs bile to digest animal fats. Therefore, disturbances in the functioning of the bladder are accompanied by digestive disorders and pain in the right hypochondrium. In this case, the patient undergoes an ultrasound of all abdominal organs, during which the gallbladder is examined.
- What it is?
- Who is prescribed an ultrasound of the gallbladder?
- How should you prepare for an ultrasound?
- How is the procedure done?
- What are normal indicators for the gallbladder?
- What pathologies of the gallbladder can be detected on ultrasound?
What is an ultrasound examination of the gallbladder?
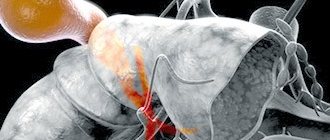
The gallbladder is located just below the liver, approximately at the level of the last rib, on the right side of the abdominal cavity. In normal condition, this organ cannot be palpated. Instrumental and laboratory methods (ultrasound, radiography, computed tomography) are used to diagnose it. The simplest and most accessible way to examine an organ is ultrasound.
Ultrasound, or echography, is a fast, informative and safe diagnostic method for the patient’s health. It is based on the ability of ultrasonic waves to penetrate the structures of our body and be reflected from them. The denser the tissue or organ is in the path of ultrasound, the more the characteristics of the reflected wave change. The ultrasound machine detects these changes, processes them and displays an image of the organ on the monitor.
Echography of the gallbladder allows you to determine the shape and location of the organ, its size, examine the ducts and identify stones and tumors. For ultrasound examination of the gallbladder, the transabdominal method is used, that is, scanning through the anterior wall of the abdomen. The procedure is carried out using ultrasound sensors with a frequency of 2.5-3.5 MHz. With this scanning mode, ultrasound waves can penetrate only to a depth of 23-25 cm. Therefore, for very obese people, ultrasound is a little informative method.
In addition to the standard procedure for ultrasound scanning of the gallbladder, echography is also prescribed to determine the function of the gallbladder (ultrasound with a choleretic breakfast). The essence of such an ultrasound is to monitor how much the organ contracts when eating food. During the study, the patient is asked to eat choleretic food (eggs or sour cream), then the release of bile is observed. Diagnosis of bladder function takes place in several stages. This ultrasound takes about an hour.
Diagnostics
Basic methods for examining the gallbladder and bile ducts:
- ultrasound examination (ultrasound);
- computed tomography (CT);
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- X-ray with contrast agent. Shows the conductivity and contractility of the channels, the presence of stones, structures, formations;
- endoscopic sounding;
- laboratory research methods.
The basic method of diagnosis is ultrasound. The method is informative and accessible, providing up to 95% reliable information. Using ultrasound, the structural features of the gallbladder, the presence or absence of stones from 0.3 cm are established.
Computed tomography is an additional diagnostic method that determines the need for surgery. X-ray with a contrast agent allows you to determine the conductivity and contractility of the channels, the presence of stones, structures and formations.
Who is prescribed an ultrasound of the gallbladder?
The gallbladder is examined in cases of liver dysfunction, as well as during ultrasound diagnostics of the abdominal organs. In addition, the reasons for prescribing an ultrasound are:
- pain on the right side of the body,
- discomfort or heaviness in the liver area,
- icteric syndrome,
- injuries and damages,
- monitoring of the treatment performed,
- suspicion of stones or tumors formed.
The only contraindication for ultrasound is an open wound in the scanning area. Using an ultrasound sensor in such a situation can lead to infection in the wound.
Types of diseases
There are a large variety of gallbladder diseases, but they can all be divided into main types:
- Inflammatory processes - caused by fungi, viruses, infections, can cause a disease such as non-calculous cholecystitis;
- Stagnation of bile. Due to the disturbance in the composition of bile, there is an increased risk of cholelithiasis;
- Neurological diseases. Due to a disruption in the flow of impulses into the gallbladder, the release of the required amount of gastric juice fails;
- Hereditary predisposition and genetic abnormalities. Most often, a congenital bend of this organ is observed;
- neoplasms in the gallbladder: polyps, malignant tumors.
How should you prepare for an ultrasound?
In order for the echography of the gallbladder to be accurate and informative, patients need to go on a diet. The main goal of the diet is to reduce the process of gas formation in the intestines. Gas bubbles interfere with the passage of ultrasound waves, which affects the quality of the ultrasound image.
A few days before the ultrasound scan you should avoid:
- carbonated and alcoholic drinks,
- dairy products,
- fatty and spicy foods,
- fresh vegetables,
- sweet fruits,
- legumes,
- black bread and yeast baked goods.
If patients are prone to flatulence, they are recommended to take adsorbents (activated carbon) and enzyme preparations (pancreatin). If you need to take any medications, you should tell your doctor about them. Taking medications may affect the accuracy of the results. The procedure is carried out on an empty stomach. The last meal is allowed 8-10 hours before the ultrasound. During this period of time, the gallbladder has time to fill with bile again, so it will be easier to examine it.
Dietary restrictions also apply to children. Remove sweets and fruits from your child's diet a few days before the ultrasound. Children, like adults, undergo the procedure on an empty stomach. Children under one year old should not be fed 3 hours before an ultrasound scan, children under 4 years old should not be fed 4 hours before, and children under 8 years old should not be fed 6 hours before. Preparation for an ultrasound examination for children over 8 years of age is the same as for adults.
If you have previously undergone an ultrasound examination of the gallbladder, then take with you copies of the protocols; by comparison, you can evaluate the dynamics of recovery or worsening of the organ’s condition. Bring a small amount of food to the clinic before your ultrasound function test. This could be boiled chicken egg yolks, cottage cheese or sour cream. You will be told exactly what to take and in what quantities when you schedule an ultrasound.
Treatment
In general, with such diseases, you need to follow a diet for the rest of your life, otherwise re-inflammation may occur, which will lead to complex consequences. Standard methods of treating diseases of the hepatobiliary system are based on compliance with nutritional rules. If you do not follow them, drug therapy will not help you fully recover. What to eat if you have gallbladder and bile duct disease ?
- The first thing you need to do is remove all spicy and fatty foods from the menu.
- You cannot drink soda or alcohol.
- You need to take food by the hour and in fractions, about 6 times a day, with the obligatory addition of warm food to the diet.
- It is important to eat oatmeal, buckwheat, barley, vegetable soups and purees, lean meats and fish, milk and fermented milk products with a minimum percentage of fat.
- Reduce intake of concentrated black tea, coffee, cocoa.
- You need to choose fruit drinks, nectars, and herbal teas.
- You need to add first cold-pressed vegetable oils to your food: olive, sesame, flaxseed.
Tablet-based treatment is based on the general clinical and personal characteristics of the body. The doctor may prescribe medications with enzymes, painkillers, antispasmodic medications, medications for the resorption of stones and with an antimicrobial effect. The choice of drug is made by the attending physician.
Now you know the symptoms and diseases of the gallbladder and biliary tract . Do not be ill!
How is the procedure done?
As a rule, ultrasound is performed in the first half of the day, always on an empty stomach. Under no circumstances should you drink or eat before the procedure. Even a small amount of water or food provokes the release of bile from the bladder. The organ decreases in size, which makes it difficult to diagnose. You should also refrain from chewing gum before visiting the clinic; it also provokes the secretion of gastric juice and bile. If you are scheduled for an ultrasound examination in the afternoon, then a light breakfast is allowed 6-8 hours before the ultrasound.
The duration of the procedure is 10-15 minutes. The patient is asked to remove his outer clothing and lie on his back on the couch. Before the ultrasound, the sonologist applies a small amount of gel to the patient's skin in the area being examined. The gel ensures continuous contact between the ultrasound transducer and the skin and improves the transmission of ultrasound waves.
During the scan, the doctor moves the sensor over the patient's skin at the location of the organ. To view the gallbladder from a different angle, the patient is asked to change position (sit down or roll over on his left side). The monitor displays the organ and surrounding tissues. The data obtained is included in the study protocol, which is given to the patient. Your attending physician will decipher it and make a preliminary diagnosis.
Carrying out an ultrasound with a choleretic breakfast differs from the standard procedure. During the study, the patient needs to eat several chicken eggs, a glass of full-fat sour cream or cream. Instead of food, a sorbitol solution can be used. First, the organ is scanned at rest. Then the patient must eat a choleretic breakfast, after which 4 ultrasounds are performed at intervals of 15 minutes. On each of them, the ultrasound specialist notes how much the gallbladder has shrunk. Ultrasound with determination of function allows you to determine which type of biliary dyskinesia the patient has (hypomotor or hypermotor disorder).
What are normal indicators for the gallbladder?
During an ultrasound, first of all, the shape, contours and size of the organ are determined. The gallbladder has the shape of a hollow pear, with smooth and clear edges. Its length ranges from 7-14 cm, and its width from 3 to 5 cm. The thickness of the bubble walls is 2-3 mm. The volume of the bile is 40-70 ml. These parameters are considered normal ultrasound for an adult. Normal sizes for the gallbladder of children depend on the height and weight of the child; they are determined using specially compiled tables.
In addition to determining the size of the organ, during the scanning process its ductal system (common bile and lobar bile ducts) is studied. Their diameter, permeability and the presence of concretions (stones) in them are determined. The diameter of the lobar ducts is 2-3 mm, and the common bile duct is 6-8 mm. The common bile duct unites with the Wirsung (pancreatic) duct and flows into the duodenum. Bile enters the gastrointestinal tract along this route.
In normal condition, the organ and its ducts do not have stones or other formations. If any deviations from normal values are detected, the patient is prescribed additional diagnostics.
The norm for ultrasound to determine function is considered to be a reduction of 70% from the initial level, which suggests the absence of dyskinesia.
Causes
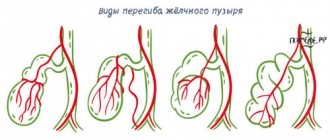
A bend in the gall bladder can occur in any part of the organ.
A bend can occur in various parts of the gallbladder for a variety of reasons. The most dangerous thing is the bending of the body of the gallbladder, in which bile is released in fairly large quantities. Let's look at the main causes of gallbladder bending:
- Great physical activity. With physical exertion and regular lifting of weights, prolapse of internal organs can occur, which leads to kinking of the gallbladder with all the consequences.
- Obesity. Obesity has a detrimental effect on many internal organs. They become covered with fat, become deformed, and shift. The gallbladder is no exception. A kink in the gallbladder is not the worst thing that can happen with severe obesity, but its consequences are noticeable.
- Congenital pathology. This is perhaps the most common cause of a bent gallbladder. During the formation of the internal organs of the embryo, a disturbance in the proportion of growth and size of the organs may occur. In this case, the liver and gall bladder are subject to deformation. Such changes can last a lifetime.
- Pregnancy. During pregnancy, the uterus grows and puts pressure on the internal organs. The liver and gallbladder may also suffer from this. Then a temporary bend of the gallbladder is formed, which is subject to restoration after childbirth. However, this is rare. Most often, the bend is congenital, but makes itself felt only during pregnancy.
- Poor nutrition. Alternating fasting with overeating leads to increased production of pancreatic juice and stagnation of bile.
- Age-related changes. With age, internal organs prolapse, which leads to kinking of the gallbladder, age-related constipation and other diseases.
- Atypical location of the gallbladder. In addition to congenital deformation of the gallbladder, it may also have an atypical location relative to the liver. In this case, the gallbladder becomes more mobile and prone to kinks and stagnation of bile.