Cancer is not an infectious disease, and cancer cannot be contracted through food, sex, or airborne transmission. At least it doesn't spread like that among people. Even if cancer cells are transplanted into a healthy person, they will not take root.
The only thing that can be transmitted from person to person in this sense is a predisposition to developing cancer. First, children from their parents may inherit genes that increase the risk of developing certain types of cancer. Secondly, there are viruses and bacteria that can also contribute to cancer.
- Cancer and human papillomavirus (HPV)
- Helicobacter pylori and cancer
- Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)
- Hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus
- Herpes virus type 8
- Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1
- Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
- Similar articles
Doctors know what to do when they see patients with a hereditary predisposition to developing cancer - there are good guidelines for this case. But with viruses and bacteria, things are more complicated: some of them have been studied in sufficient detail, but many are only at the stage of study. It is now known that only in rare cases do people infected with these viruses or bacteria develop cancer. Usually this is facilitated by some additional factor, such as smoking or a seriously weakened immune system, so often the main direction of the fight is precisely the elimination of such additional risks.
Cancer and human papillomavirus (HPV)
May provoke: cancer of the cervix , vagina, vulva, penis, anal canal, mouth, throat, head, neck.
How it is transmitted: most often through sexual contact (vaginal, anal and oral sex). There are 150–200 types of HPV, but only about 10 can lead to cancer.
How to prevent and treat: contrary to the opinion of many gynecologists, you cannot get rid of HPV with the help of immunostimulants, antiviral drugs and physiotherapy. None of these methods have proven effective and are not used anywhere in the world. In most cases, the body copes with the virus on its own within a year or two. Sometimes this does not happen - in this case, the likelihood of developing cancer is higher (the process takes 10–20 years).
In order to detect pathological changes in the cervix in time, women from 25 to 30 years old are recommended to do a Pap test every 3 years. From 30 to 65 years old, do a Pap test or HPV test every 5 years. If precancerous changes are detected, there are several options to prevent the development of cancer. This is, for example, cryocoagulation, tissue removal with a laser or radio knife.
Condoms and latex wipes (for oral sex) help prevent infection with HPV and chlamydia, which, in the presence of the oncogenic type of human papillomavirus, appears to contribute to the development of cancer. But condoms and latex wipes are not 100 percent effective. There are now vaccines that protect against two common oncogenic types of HPV (they, in particular, are responsible for 70 percent of cases of cervical cancer). However, only women and men under 26 years of age can be vaccinated, and preferably before the start of sexual activity. The minimum age at which the vaccine can be used is 9 years.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Syphilis - symptoms and treatment
How long after contact do the first signs appear?
The first symptoms of syphilis appear on average after 21 days, but the period can extend up to three months.
External signs of syphilis
Primary syphiloma (chancroid) is a symptom of the primary period of syphilis, a sign of which is erosion or ulceration that occurs at the site of penetration of pale treponema into the skin or mucous membranes. The formation of a chancre begins with the appearance of a small red spot, after a few days it turns into a nodule with a crust, when rejected, a painless erosion or ulcer of an oval or round shape with clear boundaries is exposed.
Dimensions of chancre:
- ordinary - 1-2 cm in diameter;
- dwarf - from 1 to 3 mm;
- giant - from 2 to 5 cm.
Most often, chancre is single, but with repeated sexual intercourse with an infected partner, multiple rashes may appear. Multiple chancres include “bipolar” chancre, in which ulcers occur simultaneously on different parts of the body, and “kissing” chancre on contacting surfaces.
In 90-95% of cases, the chancre is located in any area of the genital organs. The fact that it is often found at the base of the penis indicates that the condom is not fully effective in preventing syphilis. Very rarely, chancre can appear inside the urethra, in the vagina and on the cervix. An atypical form of chancre in the genital area is indurative edema in the form of extensive painless thickening of the foreskin or labia majora.
Outside the genital organs, chancres are most often found in the area of the mouth (lips [10], tongue [11], tonsils), less often in the area of the fingers (chancre-felon) [5], breast [3], pubis, and navel. Casuistic cases of the appearance of chancre in the chest area [12] and eyelids have been described.
Folman's syphilitic balanitis [14] is a clinical variant of chancre, the sign of which is spots with scales on the head of the penis, combustiform chancre - resembling a superficial burn, herpetiform chancre - in the form of a group of pinpoint microerosions [15], hypertrophic - simulating skin carcinoma [16] .
Syphilitic lymphadenopathy (enlarged lymph nodes) is a symptom of the primary and secondary periods of syphilis.
Syphilitic roseola (spotted syphilide) is a manifestation of the secondary early congenital and, less commonly, tertiary period of syphilis, occurring in 50-70% of patients.
Late roseola (erythema) of Fournier is a rare manifestation of tertiary syphilis, usually occurring 5-10 years after infection. It is characterized by the appearance of large pink spots, often grouped into bizarre shapes [17]. Unlike roseola, with secondary syphilis the spots peel off and leave behind atrophic scars [18].
Papular syphilide is a symptom of secondary and early congenital syphilis; it appears with relapse of the disease in 12-34% of cases. It is a rash of isolated dense nodules (papules) of a hemispherical shape with a smooth surface from pink-red to copper or bluish in color. There is no itching or pain, but if you press on the center of the papule, patients note sharp pain (Jadassohn's symptom).
Condyloma lata - observed in 10% of patients. The warty surface of the papules, which almost always merge into large conglomerates, is weeping, eroded and often covered with a gray foul-smelling coating. There is severe pain during sexual intercourse and defecation. In rare cases, condylomas lata can be located under the armpit, under the mammary glands, in the folds between the toes, or in the recess of the navel [5].
Pustular syphilide can most often be found in patients who abuse alcohol and drugs, are infected with HIV, and have hemato-oncological diseases [13].
Syphilitic alopecia (baldness) is characterized by untreated secondary and early congenital syphilis. Usually appears in 4-11% of cases a few weeks after the appearance of the primary rash (fresh roseola) and spontaneously regresses after 16-24 weeks [4].
Pigmentary syphilide ( change in skin color) is a manifestation of secondary syphilis in the first 6-12 months after infection. Clinically, it is an alternation of pigment and depigment spots (mesh form), and at first only hyperpigmentation of the skin is noted. Depigmented (white) round spots with a diameter of 10-15 mm in the neck area (spotted form) are traditionally called the “necklace of Venus”, and in the forehead area - the “crown of Venus” [15]. Without treatment, the rash spontaneously regresses within 2-3 months. More rare is the “marble” or “lace” form.
Syphilitic tonsillitis is a symptom of secondary syphilis, a sign of which is the appearance of roseola and (or) papules on the mucous membrane of the mouth, pharynx, and soft palate. If the papules are localized on the vocal cords, a characteristic “hoarse” voice appears. Sometimes syphilitic tonsillitis is the only clinical manifestation of the disease, and then it is dangerous in terms of the possibility of sexual (during oral sex) and domestic infection due to the high content of treponemes in the elements of the rash.
Syphilitic onychia (thickening and brittleness of the nail plates) and paronychia (inflammation of the periungual fold) occur at all stages of syphilis and with early congenital syphilis [16].
Tuberous syphilide (tertiary papule) is the main symptom of the tertiary period of syphilis, which can appear as early as 1-2 years from the moment of infection. But as a rule, it occurs after 3-20 years. It is characterized by the appearance of isolated brownish-red seals up to 5-10 mm in size, which rise above the skin level and have a smooth and shiny surface. The outcome of the existence of a tubercle is always the formation of a scar.
Syphilitic gumma (gummy syphilide) characterizes the tertiary period and late congenital syphilis. In this case, a mobile, painless, often single node with a diameter of 2 to 5 cm appears in the subcutaneous tissue. Gummas can occur in muscle and bone tissue, and on internal organs. Most often they are localized in the mouth, nose, pharynx and pharynx, resulting in perforation of the hard palate with food entering the nasal cavity and a “nasal” voice, deformation of the cartilaginous and bone parts of the nasal septum with the formation of a “saddle” and “lornette” nose [18 ].
Symptoms of neurosyphilis
- Ocular and pupillary symptoms result from damage to the optic and oculomotor nerves. These include: progressive loss of vision, ptosis - drooping eyelid, anisocoria - small pupils ("prostitute's eyes"), unequal pupil sizes (Baillarger's symptom), Argyll Robertson pupil - narrowing pupils when the patient focuses on a close object, and not narrowing in directed bright light, oblique deflection - in which one eye moves downward while the other deflects upward [16].
- Labyrinthine deafness is a manifestation of neurosyphilis and late congenital syphilis due to damage to the auditory nerve.
- Tabetic arthropathy occurs in patients with late neurosyphilis and is most often manifested by unilateral enlargement and slight hyperemia (redness) of the joints of the foot and knee (Charcot's joint), which are subsequently deformed with the possible appearance of ulcerative skin defects.
- Ataxic gait is staggering while walking with eyes closed due to decreased joint-muscular sensitivity.
- Instability in the Romberg position is a symptom of neurosyphilis, in which it is impossible to maintain balance in a standing position with your feet together and your arms extended along the body or forward with your eyes closed.
Symptoms of visceral syphilis (from the internal organs) depend on the localization of the process [16].
- Yellowness of the skin and sclera occurs with syphilitic hepatitis.
- Vomiting, nausea, weight loss - with gastrosyphilis.
- Pain in muscles (myalgia), joints (arthralgia), bones - with syphilitic hydrarthrosis and osteoperiostitis.
- Cough with sputum - with syphilitic bronchopneumonia.
- Pain in the heart - with syphilitic aortitis (mesaortitis).
Characteristic is the so-called “syphilitic crisis” - paroxysmal pain in the area of the affected organs [8].
Symptoms of early congenital syphilis:
- syphilitic pemphigus;
- syphilitic rhinitis;
- diffuse papular infiltration;
- osteochondritis of long bones;
- Parrot's pseudoparalysis is a symptom of early congenital syphilis, in which there is no movement of the limbs, but nerve conduction is preserved;
- Sisto's symptom - the constant cry of a child - is a sign of developing meningitis.
Symptoms of late congenital syphilis:
- Parenchymal keratitis is characterized by clouding of the cornea of both eyes and is observed in half of the patients.
- Clutton's joint (syphilitic gonitis) is a bilateral hydrarthrosis in the form of redness, swelling and enlargement of the joints, most often the knees.
- The buttock-shaped skull is characterized by enlargement and protrusion of the frontal and parietal tubercles, which are separated by a longitudinal depression.
- The Olympic forehead is an unnaturally convex and high forehead.
- The Ausitidian symptom is thickening of the sternal end of the right clavicle.
- DuBois's sign is a shortened (infantile) little finger.
- Saber shin is a characteristic symptom of late congenital syphilis in the form of an anterior bend of the tibia, resembling a saber.
- Hutchinson's teeth - dystrophy of the permanent upper middle incisors in the form of a screwdriver or barrel with a semilunar notch on the free edge.
- Gaucher diastema - widely spaced upper incisors.
- Corabelli's cusp is the fifth additional cusp on the chewing surface of the first upper molar.
Can syphilis be asymptomatic?
The latent stage of syphilis is a period when there are no visible signs of syphilis. Without treatment, an infected person continues to have syphilis, even if there are no symptoms.
Early latent syphilis is called syphilis in which the infection occurred within the last 12 months, late latent syphilis - more than 12 months ago. Latent syphilis can last for years [27].
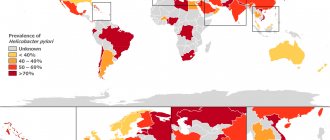
Helicobacter pylori and cancer
May provoke: stomach cancer.
How it is transmitted: fecal-oral route and through kissing.
How to prevent and treat: It is very difficult to protect yourself from Helicobacter pylori infection, which is why two out of three adults have it. Since this bacterium causes cancer in only a small number of people, it is not recommended for everyone to be tested for its presence. First of all, this should be done by people who have/had a stomach or duodenal ulcer (Helicobacter pylori is the cause of peptic ulcer). If bacteria are found, antibiotics are used. Testing everyone and prescribing antibiotics to people who have no symptoms but have Helicobacter pylori poses the risk of greater harm from the tests and medications. And this harm outweighs the possible benefits.
Signs of ulcer development
The appearance of a peptic ulcer is indicated by characteristic symptoms:
- Pain (burning, aching, cramping) is the most important symptom. Often bothered at night and between meals.
- Heartburn, burning and chest discomfort.
- Belching of air, unpleasant sour or bitter aftertaste.
- Nausea, heaviness in the stomach.
- Dark vomit and/or stool – occurs when ulcers are bleeding.
Perforation of the ulcer is accompanied by sharp cutting pain, nausea and vomiting, as well as painful sensations when tensing the abdominal muscles.
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)
May provoke: nasopharyngeal cancer, gastric lymphoma, Hodgkin's lymphoma, Burkitt's lymphoma. Its presence has been associated with an increased risk of developing these cancers in people living in Africa and Southeast Asia.
How it is transmitted: by airborne droplets, through dishes. When infected, some people develop infectious mononucleosis (prolonged fever, sore throat, enlargement of many lymph nodes), while others do not experience any special symptoms.
How to prevent and treat: Because of the mode of transmission, EBV infection is very difficult to prevent, and most teenagers in the United States have the virus. Like any virus from the herpes group, EBV remains with a person forever, so it is impossible to get rid of it by any means (including antiviral ones).
Hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus
May provoke: liver cancer.
How it is transmitted: through unprotected sex, contaminated needles, dental and manicure instruments.
How to prevent and treat: now children are already vaccinated against hepatitis B in the maternity hospital. However, many adults were born before this practice was introduced, so they should be vaccinated at least now. There is no vaccine for hepatitis C, so only simpler methods of prevention are relevant here: protected sex, use of disposable syringes. If a person becomes infected with hepatitis B or C, treatment is given to help reduce liver damage and reduce the risk of developing liver cancer.
How to cure an ulcer?
If you have stomach pain, consult your doctor for a diagnosis. Any gastrointestinal disease should not be treated on its own. For peptic ulcer disease, the doctor prescribes a treatment regimen for the patient, which depends on the causes of the disease:
- Antibiotics are prescribed to combat Helicobacter pylori - if it is detected.
- Drugs are prescribed that suppress the production of acid in the stomach.
- Pause or stop taking NSAIDs to reduce symptoms.
- A diet is prescribed and it is recommended to give up bad habits.
Take care of yourself and be healthy!
Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1
Can provoke: lymphocytic leukemia, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (namely, adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma - rare in Russia).
How it is transmitted: during sexual intercourse, through blood. In Russia, infections are recorded very rarely.
How to prevent and treat: prevention of infection is to use condoms and latex wipes, clean needles. If the virus does enter the body, it is no longer possible to get rid of it with the help of medications.
What diseases are transmitted by kissing?
As it turns out, kissing is not such a harmless activity. It turns out that in addition to herpes, which everyone knows about, there are more than ten diseases that are transmitted from person to person through a kiss. What are these diseases, how do they manifest themselves and who is at risk of catching them? Let's talk about the most common ones.
Infectious mononucleosis is caused by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). Basic signs . Entering the body with the saliva of an infected person, EBV provokes an increase in temperature to 39-40 degrees, which lasts about 10-14 days. At the same time, the patient’s cervical lymph nodes become greatly enlarged, the throat swells, and the nose is blocked. Another symptom of mononucleosis is abdominal pain caused by an enlarged spleen and liver (many patients have yellow skin and dark urine, as with jaundice). In severe form, this disease can result in rupture of the spleen, damage to the central nervous system, and the development of hepatitis or pneumonia. Risk group . The most vulnerable to this infection are children 3-10 years old, whose immune system is not able to fight back the insidious virus. Unfortunately, now adults who have experienced severe stress can also become victims of mononucleosis. How to insure yourself. As for adults, you can protect yourself from mononucleosis by refusing to kiss for 10-14 days after any illness , when the body’s immune status is especially low.
Cytomegalovirus infection The causative agent is cytomegalovirus. Basic signs. It is almost impossible to suspect cytomegaly yourself - it is very similar to an acute respiratory infection or a cold. Typically, this disease is manifested by fever, runny nose, sore throat and swollen lymph nodes. True, the virus disguised as an acute respiratory infection does not recede within 1-1.5 months, which should be alarming. Moreover, in men, cytomegaly is asymptomatic, but in women it most often settles in the genitourinary system, causing inflammation of the cervix or vagina. Risk group. Expectant mothers should be truly afraid of cytomegalovirus, because during pregnancy, a woman’s immunity is naturally suppressed so that immune reactions do not harm the fetus. Consequently, she becomes an easy target for the virus. And what’s most unpleasant is that once the infection enters the mother’s body, it is quickly transmitted to the child, causing birth defects. How to get insurance. To protect yourself and your child from this infection, future parents should be examined for TORCH infection before conception . If the insidious virus is not detected, you can breathe a sigh of relief and calmly enjoy kisses throughout the nine months of pregnancy. If the test is positive, the doctor will prescribe you medications to control the amount of virus in the body, inhibiting its development.
Gastric ulcer The cause is a bacterium of the genus Helicobacter pylori, usually found in patients with peptic ulcer. In Russia, about 80% of residents are infected with this bacterium. How to get insurance . Avoid contact with saliva. Eat food only in places with thoroughly washed or disposable dishes, do not drink from other people's glasses and do not kiss unexamined strangers on the lips.
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
Can provoke: Kaposi's sarcoma, invasive cervical cancer, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and many other types of cancer.
How it is transmitted: during sexual intercourse, through blood.
How to prevent and treat: HIV weakens the human immune system, which makes it easier for oncogenic types of HPV and herpes virus type 8 to provoke the development of cancer. Another important role is played by the fact that during HIV infection, the immune system fights mutated cells worse. Therefore, people with this disease need to take antiretroviral drugs, which will allow immune cells to work well. Also, everyone who does not know their HIV status should be tested for HIV at least once in their life: the infection may not make itself felt for many years, but the earlier it is detected, the fewer negative health consequences there will be.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Is stomatitis transmitted?
Allergic stomatitis
– one of the most common and intractable types of the disease.
The cause is an allergy, but what exactly is allergy is to be determined first. Allergens can be both food and medicine, as well as materials for dentures installed in the oral cavity. The typical course of stomatitis - the occurrence of painful ulcers - can be further complicated by difficulty breathing and swallowing, typical of allergies. Allergic stomatitis is not transmitted
except through hereditary means.
Viral (herpetic) stomatitis
- another popular type of this disease, especially common in small, close groups of people (schools, kindergartens, work groups, camps).
Its cause is the herpes virus, and its features are erosive spread (others may appear next to one ulcer) and the possibility of severe complications with fever, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. This is the most contagious variety; in 80% of cases, this stomatitis is transmitted both by airborne droplets and by contact
.
Aphthous stomatitis
– most often occurs in adults, and is associated with weakened immunity.
That is why outbreaks of aphthous stomatitis occur mainly in spring and autumn. It is characterized by the formation of aphthae - small ulcers, both single and occurring in clusters. This stomatitis is not contagious
and cannot be passed on to other people.
Fungal stomatitis (candidomycosis)
– is characteristic of both children (mainly infants) and adults, and mainly women.
It occurs due to Candida fungi, which multiply in the mouth due to weakened immunity or long-term use of antibiotics. It is characterized, in addition to the formation of ulcers, by a white “curdled” coating on the tongue, palate and inner surface of the cheeks. This stomatitis is contagious
: it can be transmitted through direct contact or through household and hygiene items (towel, toothbrush, dishes). A pathogenic fungus can remain in the body for some time and develop in an environment favorable to it.
Nicotine stomatitis
– as the name suggests, occurs in smokers as a result of a long-term addiction to cigarettes.
Tobacco smoke, affecting the oral cavity, actively promotes the growth of bacteria, and also irritates the palate, the tissues become denser, resulting in the formation of numerous ulcers. This type of disease is especially dangerous: although it is not transmitted to other people
, and generally goes unnoticed for a long time, it can develop into oral cancer.