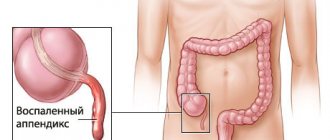
1.Treatment of appendicitis
The standard and, in general, the only method for treating appendicitis is surgery to remove the appendix.
Or as it is also called -
removal of appendicitis
, although this is not quite the correct name.
Even if appendicitis is not confirmed with 100% probability, doctors can play it safe (and rightly so) and still remove the appendix to avoid its rupture and the development of complications. If there is an abscess
, the whole procedure for treating appendicitis can become a little more complicated - first, the pus and fluid are drained, and then the operation itself to remove the appendix.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Operation technique
Removal of appendicitis can be performed under local anesthesia or general anesthesia. If, for medical reasons, intubation anesthesia with muscle relaxants cannot be used during appendectomy, then local infiltration anesthesia with a solution of novocaine is performed, which, if necessary, is combined with neuroleptanalgesia.
In mild cases of acute appendicitis (in which the operation is short), mask anesthesia can be performed using muscle relaxants. Excision of the appendix is performed traditionally or laparoscopically. Which access you choose depends on several factors.
As a rule, if the operation is performed urgently, then a wide access is necessary, which makes it possible to examine a large area of the abdominal cavity and exclude other pathologies that can cause similar symptoms. The choice in favor of laparotomy is made in the case of an atypical location of the process, as well as in cases of pronounced adhesions.
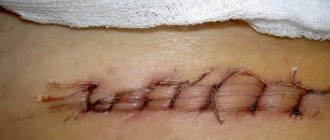
In the photo on the right is a scar from laparoscopy, and on the left is a scar from a traditional incision
Laparoscopy
If a laparoscopic approach is chosen to remove the appendix, then several small incisions are made on the anterior abdominal wall or (now it can be done through one puncture), through which endoscopic instruments are introduced into the abdominal cavity, allowing for medical manipulations and visual monitoring of the progress of the operation.
Although this method is less traumatic and requires less time for postoperative recovery, it limits access and does not allow examination of a large area of the abdominal cavity. Whether the operation can be performed in this way is decided by the doctor.
The operation includes several stages:
- examination of the abdominal cavity and identification of other pathologies;
- intersection of the mesentery;
- ligation and cutting of the appendix;
- treatment of the appendix stump;
- sanitation of the abdominal cavity;
- suturing the wound.
Traditional way
Most often, for uncomplicated appendicitis, an oblique Volkovich-Dyakonov incision is made. It is convenient in that it corresponds to the projection of the cecum and does not dissect nerves and muscles; accordingly, their trophism and innervation are not disturbed, which reduces the risk of hernia formation in this place; however, access with this incision is quite limited.
If the appendix is located atypically, purulent peritonitis has spread, or there is a possibility that purulent exudate will appear from other organs or a wider inspection of the abdominal organs is required, then a Lennander incision is made. The transverse approach can, if necessary, be extended medially by dividing the rectus abdominis muscle.
During pregnancy in the first trimester, the Volkovich-Dyakonov approach is usually chosen, and in the second and third trimesters this access is not always complete, therefore, the longer the gestation period, the higher the incision is made. In later stages of pregnancy, the incision is made just above the ilium. If the diagnosis is in doubt or diffuse peritonitis has developed, then lower-median laparotomy is indicated.
Laparoscopy can only be used up to 16-17 weeks of pregnancy.
For uncomplicated appendicitis, the surgeon makes an oblique (alternating) incision in the right groin area 7-8 cm long and opens the anterior dorsum of the abdomen in layers. First, the skin is dissected, then the subcutaneous tissue and superficial fascia. Pararectal laparotomy according to Lander involves an 8-10 cm long incision along the edge of the rectus abdominis muscle; the skin, subcutaneous tissue, superficial fascia, and vaginal walls are dissected.
Complications after appendectomy
The edges of the wound are pulled apart with sharp hooks. The aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle of the abdomen becomes visible, it is lifted with an instrument and a small incision is made in it to separate it from the muscles, and then the aponeurosis is dissected along the entire length of the skin wound.
After the muscle fibers are pulled apart, the peritoneum is grabbed with special tweezers and lifted to see if the organ is grabbed along with it, and then it is cut.
If the operation is performed under local anesthesia, then the parietal peritoneum is additionally pre-treated with novocaine. In the wound, the cecum is identified by its grayish color, absence of mesentery and omental processes, and ribbons. It is placed on the anterolateral wall of the abdomen and fenced off with gauze napkins.
The mesentery of the appendix is grasped with a clamp and, applying clamps, the mesentery of the appendix is cut off in a few movements. After this, the vermiform appendix, which is located between the two clamps, is cut off. The mucous tissue of the stump of the excised process is wiped with a disinfectant solution, and the stump itself is placed in the wall of the cecum using a previously applied purse-string suture.
Holding the ends of the purse string suture, an S-shaped suture is applied. If the appendiceal infiltrate is detected only during surgery, then the appendix is not removed, but drainage is done and antibiotics are administered into the abdominal cavity.
The ends of the abdominal wall wound are pulled apart with blunt hooks and the cecum is returned to the abdominal cavity. After this, an inspection of the abdominal cavity is carried out (it is checked whether the suture is airtight, whether there is bleeding from the mesentery, the abdominal cavity is examined for the presence of blood or contents) and the abdominal cavity is closed layer by layer.
Stages of surgery for appendectomy
Children under three years of age undergo ligature appendectomy, that is, the stump of the appendix is only ligated, but not immersed in the cecum. This method speeds up the operation time, reduces the risk of rupture of the wall of the cecum and changes in the ileocecal valve (when applying a purse-string suture, the thin intestinal wall may rupture, and the doctor may also touch the ileocecal valve located close to children).
Measures for complications
If purulent contents from appendicitis have penetrated into the abdominal cavity, then in addition to appendectomy it is necessary to carry out primary sanitation of the abdominal cavity, intestinal decompression, as well as drainage of the abdominal cavity for subsequent sanitation. A midline laparotomy or Volkovich-Dyakonov incision is performed.
After removal of appendicitis in the case of paralytic intestinal obstruction, nasointestinal intubation is performed. Then the abdominal cavity is washed, it is necessary to completely remove pus and fibrin films. After this, drainage is made to ensure unimpeded outflow of fluid from the abdominal cavity, and the surgical wound is sutured.
In most cases, the abdominal cavity during appendectomy is sutured tightly. However, for example, in case of perforated appendicitis, when there is effusion in the abdominal cavity, it is necessary to insert a thin rubber tube to administer intraperitoneal antibiotics.
3.Recovery after surgery
You can get up and move around for 12 hours after appendicitis surgery. Full recovery usually takes two to three weeks, but if the surgery was laparoscopic, the recovery period will be even shorter.
In general, appendectomy surgery is not considered very difficult and is performed in many medical institutions. But this does not mean that in the treatment of appendicitis you should rely on chance and go to any clinic where the ambulance team on duty will take you. Firstly, complications may arise with appendicitis, and this requires a higher level of surgical intervention. Secondly, if it is not contraindicated, it is better to remove appendicitis laparoscopically. But it is not a fact that a random doctor is fluent in this method of treating appendicitis or is in principle familiar with it. And thirdly, the operation to remove appendicitis, although relatively simple, is still a surgical intervention that is performed under anesthesia. And like any operation, it carries potential risks. Agree, it is much easier to undergo surgery when you are 100% confident in the qualifications of the doctor who will operate on you. Even if we are talking about simple appendicitis.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Appendectomy - removal of appendicitis
10.12.2021
This article describes what the appendix is and what its functions are in the human body. The article also describes what will happen if it becomes infected and what discomfort a person will experience after an appendectomy.
What is the appendix and its functions in the body
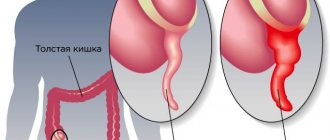
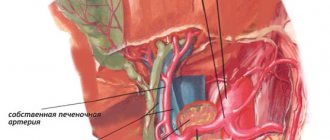
The appendix is a tube with a blind end connected to the cecum. The cecum is located at the junction of the small and large intestines . The average length of the process is 9 cm. It lies in the lower quadrant of the abdomen . In the abdominal cavity, its position corresponds to a point on the surface called McBurney's point.
- The most important function is to support the intestinal microflora , acting as a refuge for beneficial bacteria when recovering from diarrhea . The appendix is surrounded by immune tissue called gut- . This tissue helps provide immunity by supporting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria.
- Recent studies have implicated the appendix as an important component of mammalian mucosal immune function. It has been observed to initiate, in particular, B cell-mediated immune responses and extra-stimulated T cells. These cells cause movement and elimination of waste in the digestive system.
- The lymphatic vessels of the appendix regulate pathogens and induce protective responses against fatal diseases . It provides additional protection against invading pathogens and fights viruses and bacteria that infect this part of the intestine .
- The appendix is a vestigial structure that has lost its original functionality and developed a new function. It has developed a new function of rebooting the digestive system of new things and protecting against germs.
Appendectomy
This is the surgical removal of the appendix. This is a condition that requires immediate surgery . The surgery treats appendicitis , an inflammatory condition of the appendix. Appendicitis is an infection that causes an infection in the opening of the appendix, causing it to become clogged with bacteria and feces. The only way to cure this condition is to remove the appendix. This condition needs to be treated immediately. When the appendix ruptures, bacteria and fecal particles can spread throughout the abdomen and develop a serious infection called peritonitis .
Signs and symptoms of appendicitis include:
- Abdominal pain
- Muscle swelling
- Constipation
- Nausea
- Vomit
- Fever
Risks of appendectomy
Some of the risks of an appendectomy are:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Trauma to nearby organs
- Blocked intestines
Appendectomy procedure
Two types of appendectomy can be performed:
1. Open appendectomy: an incision is made in the lower right side of the abdomen . After this, the appendix is removed and stitches are made. This appendectomy is used when the appendix has ruptured and the infection has spread to other organs.
2. Laparoscopic appendectomy: The appendix is accessed through several small incisions in the abdomen. A narrow cannula is inserted to inflate carbon dioxide into the abdomen to provide a clear view of the abdomen . Once inflated, a laparoscope with a bright light and a high-definition camera at the front is inserted. The camera displays images and allows the surgeon to tie the appendix and remove it. The incisions are then cleaned and closed. Best suited for older people who are overweight. There are fewer risks than with an open appendectomy procedure.
Consequences of appendectomy
After an appendectomy, there is some discomfort and pain, which are known as short-term complications. However, there are never long-term complications with an appendectomy. They are classified below:
- Moderate pain in the incision area. This pain is caused by the stitches and goes away after a few days.
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Swelling and redness around the incision
- Wound infection: Despite taking antibiotics, infection can sometimes occur due to unsanitary conditions
- Bleeding under the skin, which can cause severe swelling . This bleeding usually goes away within a few days
- Scarring
- Collection of pus (abscess). In rare cases, an infection caused by a ruptured appendix can lead to an abscess after surgery
- A hernia can occur at the site of an open incision or in incisions made during laparoscopic surgery
- General anesthetics are used, but they may also carry some risks. The risk may be an allergic reaction or inhalation of stomach , which can lead to pneumonia .
If you experience symptoms such as fever above 38.3°C, vomiting, loss of appetite, stomach , diarrhea or constipation lasting more than two days, you should immediately consult a doctor . These signs can often be caused by an infection and require immediate medication.
Published in Surgery Premium Clinic