University
→ Home → University → University in the media → Psychological “roots” of peptic ulcer disease
Stomach and duodenal ulcers develop due to stress. It turns out that it is impossible to cure with drugs? For complete recovery, emotional stress must be eliminated. But in the modern world this is unrealistic... Answered by Associate Professor of the Department of Polyclinic Therapy of BSMU, Ph.D. honey. Sciences, general practitioner and psychotherapist Anatoly Bliznyuk (back in Soviet times, the doctor studied the relationship between the psychological and clinical-functional characteristics of patients with duodenal ulcers and now continues his research - as part of scientific work on psychosomatic diseases): - Peptic ulcer disease refers to classic psychosomatic ailments, which are the result of the interaction of mental and physiological factors. Local and general mechanisms are involved. The first is a violation of the regulatory functions of the gastroduodenal zone, motility disorders and a decrease in mucosal resistance. General – high level of psycho-emotional stress. Modern medicine copes well with local mechanisms. There are powerful medications - proton pump inhibitors and histamine H2 receptor blockers (they effectively suppress the acid secretion of gastric juice), as well as strong antibiotics (they eliminate the flagellated parasite - Helicobacter pylori; many consider it the main culprit of the pathological process). But the stress factor, alas, is underestimated and usually remains unattended.
Patient portrait
A long time ago, when I was a local therapist in a clinic, I noticed that people with stomach ulcers, stubborn, difficult to scar, persistent for a long time, usually got it after a conflict situation or a powerful emotional shock. This is especially true for older women who have experienced the death of loved ones. In patients with duodenal ulcers (these are 4 times more common), the stress was not so pronounced, although long-lasting, associated with professional fulfillment or family problems. All patients were united by an urgent need for love, care and protection, which, unfortunately, they did not have due to various circumstances. This thirst for care can be compared to what a small child experiences when abandoned by his mother. But this “does not suit an adult”, and therefore the feeling of defenselessness and dependence is suppressed by them. Having not received the desired attention, a person strives to compensate for this with professional success, sports victories, and other achievements; he often sets high standards and goes overboard with the load. But even having achieved the goal, he does not feel satisfied. This category of patients has a very painful sensitivity to failures at work, loss of a high position, and negative assessments of their activities. An inadequate violent reaction to events entails the inclusion of local mechanisms for the development of the disease.
Between emotion and body
When a person has a need, an acceptor of the result of an action is immediately formed in the brain, perceiving and evaluating the result of the efforts made. To achieve the desired, muscular and other mechanisms are launched that organize actions in the desired direction. If everything worked out - emotions of satisfaction and pleasure. If not, disappointment, aggression, indignation. In the latter case, a corresponding vegetative discharge occurs: breathing and heartbeat become more frequent, and blood pressure rises. Possible reactions from the gastrointestinal tract - pain, heartburn, increased secretion of gastric juice, reflux of acidic contents from the stomach into the esophagus. The endocrine glands turn on - the adrenal glands intensively pump the blood with stress hormones, in particular cortisol and adrenaline. The pancreas “starts”, which means insulin increases. It also stimulates the production of gastric juice. Increased acidity is favorable soil for duodenitis, ulcers, gastritis (it is no coincidence that they are called acid-associated diseases).
When a person has high demands on himself and sets extreme goals that do not correspond to physiological capabilities, the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system, which is responsible for resistance to stress, is activated. The stress response has been confirmed by animal experiments. The rats were subjected to immobilization stress—complete immobility; The thymus gland, which is responsible for cellular immunity, immediately decreased, hyperplasia of the adrenal cortex was observed, and gastroduodenal ulcers developed.
The connection between emotions and physiological processes is confirmed by the presence of peptides common to the gastroduodenal zone and the brain - substances involved in the self-regulation of body systems (endorphins, enkephalins, etc.). Therefore, the mood drops and changes occur in the gastrointestinal tract - motility, secretion, food digestion; appetite.
Ulcer from... demotion
Here's a case. A 37-year-old man had a periodically worsening stomach ulcer and was treated with medication twice a year. After a course of psychotherapy—working through a conflict situation in a group—the patient completely abandoned medications, and the pain stopped. An endoscopic examination of the gastrointestinal tract showed: there are scars in the stomach, no ulcers. No exacerbations were observed for 15 years. Another example. The military man was transferred to a lower position. He had many years of service behind him, he considered this unfair. In fact, translation became a powerful psychological trauma. After a couple of weeks, severe abdominal pain appeared. A fresh duodenal ulcer was diagnosed (some of the acute ulcers open literally the next day after a stressful situation). The man was treated with medication, the ulcer healed, but as soon as he returned to duty, it opened again. This time complicated by bleeding. The patient underwent gastric resection. After returning to work, he was again hospitalized with an anastomotic ulcer... The man turned to a psychotherapist in complete despair. A course of individual psychotherapy of 9 sessions was required (he refused group therapy), which included relaxation techniques, rational-emotive and hypnotherapy. The mental background of the severe course of the disease was revealed to the man. He did not immediately admit: his profession was everything to him; he wanted to constantly receive external confirmation that he was strong, successful and independent. And having lost his status, he experienced it as a life disaster. During therapy, the patient realized: life is not limited to success at work, especially in adulthood, when spiritual values are a priority. He has a wealth of experience, good intellectual baggage, he is organized and responsible, he has a lot of options to realize himself “in civilian life”, to be useful and interesting to his loved ones. The ulcer healed and a long-term remission was achieved.
It all starts with the desire to get to the bottom of things
An important condition for any psychotherapy is the patient’s awareness of his wrong attitudes and correction of his personal picture of the world. Unfortunately, few sincerely strive for this and show a willingness to open their souls, admit their own weakness, dependence, and serious internal problems. Advertising of pharmaceuticals and their abundance hinders the perception of the relationship between mental and physical factors: swallow a pill - and why get to the bottom of the problem by changing your worldview? The local mechanism for the formation of the disease is blocked, but incorrect attitudes and, as a consequence of this, periodically occurring or constant stressful situations and injuries remain. Therefore, today the so-called pathomorphoses, changes in the course of the disease. Instead of an ulcer, for example, GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease) appears, which is characterized by the reflux of acidic stomach contents into the esophagus. For those suffering from GERD, one of the characteristic psychological reactions is a strong internal protest against an unpleasant situation. Classic psychosomatoses also include nonspecific ulcerative colitis, myocardial infarction, arterial hypertension, rheumatoid arthritis, bronchial asthma, neurodermatitis, hyperthyroidism... Psychosomatic pathology rather requires rehabilitation measures, the purpose of which is to harmonize a person’s worldview and self-perception. Elena Kleshchenok Medical Bulletin , January 31, 2013
Share
Etiology and pathogenesis
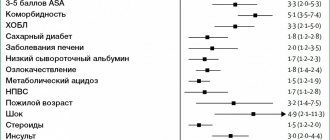
Unlike PU with its characteristic etiological factors (hereditary predisposition, Helicobacter pylori infection, neuropsychic overload, nutritional errors, etc.), OHSS are pathogenetically closely related to other (“background”) diseases or extreme exposures.
Leading importance in the ulcerogenesis of stress ulcers is given to ischemia of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum under conditions of microcirculation disorders, hypovolemia, plasma loss and hypotension; increased production of ACTH, corticosteroids, catecholamines, histamine during stress, which have an adverse effect on the protective barrier of the mucous membrane and increase the aggression of the acid-peptic factor; violation of gastroduodenal motility (paresis of the stomach and intestines, duodeno-gastric reflux).
The mechanism for implementing the ulcerogenic effect of drugs is diverse. NSAIDs primarily act on the protective barrier of the mucous membrane, damaging it, changing the quantitative and qualitative composition of mucus, and suppressing the synthesis of endogenous prostaglandins. Inhibition of prostaglandin production caused by NSAIDs is associated with inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX) activity. It turned out that selective suppression of COX type 2 (COX-2) can significantly reduce damage to the mucous membrane while maintaining the anti-inflammatory effect. Currently, drugs have been created (meloxicam, etc.) that selectively inhibit COX-2 without damaging the gastroduodenal mucosa.
Data on the ulcerogenic effect of corticosteroids are contradictory. Glucocorticoids enhance the production of HCl, change the qualitative composition of mucus, reduce the rate of renewal of the surface epithelium, thereby promoting ulcer formation. At the same time, a beneficial effect of steroid hormones on the gastric mucosa and duodenum is noted, associated with their lysosomal stabilizing effect and improvement of trophic processes.
OHS can occur against the background of other diseases and be pathogenetically related to them. An example is the formation of large gastric ulcers with atherosclerotic lesions of the abdominal aorta due to insufficient regional blood supply.
The reason for the development of duodenal ulcers in SZE is a neuroendocrine tumor that produces gastrin (gastrinoma), which leads to a sharp overproduction of hydrochloric acid. Ulcer formation in hyperparathyroidism is explained by an increase in HCl production and an increase in gastric motor function in response to hypercalcemia; Parathyroid hormone itself also has a negative effect on the mucous membrane.
Classification
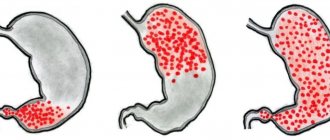
There is no detailed classification of OHS; usually only the type of ulceration is distinguished. We propose the following classification of SGDS. I. Main types: 1) stressful; 2) medicinal; 3) endocrine; 4) arising from diseases of internal organs. II. Morphological characteristics of ulceration: 1) erosion; 2) acute ulcer; 3) chronic ulcer. III. Number of mucosal defects: 1) single (1–3); 2) multiple (more than 3). IV. Sizes of ulcers (erosions): 1) small (less than 0.5 cm); 2) medium (0.5–1.0 cm); 3) large (1.1–3.0 cm); 4) gigantic (more than 3 cm). V. Localization:
Stomach - A: a) cardia, b) subcardial section, c) body of the stomach, d) antrum, e) pyloric canal; B: a) anterior wall, b) posterior wall, c) lesser curvature, d) greater curvature;
Duodenum – A: a) bulb, b) postbulbar region; B: a) anterior wall, b) posterior wall, c) lesser curvature (upper wall), d) greater curvature (lower wall). VI. Complications: 1) bleeding; 2) perforation; 3) penetration.
Diagnostics
Endoscopy. The most common and reliable method of diagnosis is endoscopy. The procedure is quite unpleasant for the patient, but it allows the doctor to get a complete picture of the condition of the patient’s internal organs.
Tests. Special testing methods are used to determine the presence of Helicobacter Pylori bacteria. They involve the examination of blood, vomit and feces, as well as material obtained from a biopsy.
X-ray. An important role in the diagnosis of duodenal ulcers is played by x-ray examination, which allows you to complete the picture of the disease.
Palpation. Palpation of the corresponding areas of the abdomen is one of the main methods for diagnosing ulcers.
Treatment
Treatment of duodenal ulcers is determined comprehensively depending on the general condition of the patient, the results of laboratory tests and a number of other conditions. It should be noted that the surgical method, which was popular earlier, is now used less frequently, only in cases of bleeding or perforated ulcers. Pharmacological therapy consists of destroying the Helicobacter Pylori bacterium, restoring the mucous membrane of the affected organ and preventing complications caused by the ulcer.
To make an appointment at the ABC-Medicine clinic for the diagnosis and treatment of duodenal ulcers, call +7 (495) 223-38-83.