Why might my right side hurt?
The causes of this symptom are usually associated with internal organs. “This is a sign that something located on the right side of the abdomen is suffering,” says Bulat Yunusov, a surgeon at GMS Clinics and Hospitals. “The cause of damage to these organs can also be different, for example, inflammation, oncological processes, trauma, consequences of previous operations, neurological disorders.”
However, this symptom may have other reasons. “An unpleasant sensation in the right side can be muscular in nature, especially if it occurs after physical activity. If a person falls on their right side, the pain may be associated with muscle contusion or injury, such as myositis. Gallstones can also cause an uncomfortable tingling sensation in your side. The stones close the ducts, which leads to swelling of the bladder and, as a consequence, to the occurrence of calculous cholecystitis, that is, an inflammatory process. All this, of course, is accompanied by pain,” commented an invited specialist from another medical center. Let's look at the main causes of pain in the right side.
When is a symptom not dangerous?
Yes, this happens. For example, with low mobility, physical activity increases blood circulation in the vena cava. And as a result of the release of adrenaline, heat occurs in the right hypochondrium. But stopping the load stops the burning sensation. Also, when the body bends, the tissues are compressed by the ribs, which causes an unpleasant symptom. It is temporary and does not continue to bother you after changing the position of the body.
In women during PMS, estrogen is released and a fever appears on the right side. Sometimes the pain is severe, causing nausea and a bitter taste. This is due to spasm of the bile ducts. Any discomfort that occurs in the body is evidence that a person may have health problems. A burning sensation in the ribs is a symptom that should not be ignored. It is imperative to identify the cause of the occurrence and take all measures to eliminate it.
Inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
Pain and cramps in the right side can be caused by a whole “bouquet” of inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract. “These are, for example, appendicitis, diverticulitis, colitis, gastroenteritis, stomach and duodenal ulcers,” says Bulat Yunusov.
Most often, with these diagnoses, the pain is felt as aching, moderate, with gradually increasing intensity. With appendicitis, pain may increase when walking, coughing, changing body position and decrease at rest. Also with this diagnosis, there is an increase in temperature, nausea, and vomiting.
With a stomach ulcer, the pain becomes more noticeable after eating fatty, spicy or fried foods, alcohol, and intense physical activity. Additional symptoms may include heartburn, nausea, and vomiting.
With colitis (inflammation of the intestines), the pain can be nagging or paroxysmal. The disease is also accompanied by diarrhea, fever, general weakness, headaches, and the presence of mucus in the stool.
With diverticulitis (protrusion of the intestinal walls), acute pain is felt to the right of the navel, the temperature rises, and diarrhea (with blood and mucus) appears.
With gastroenteritis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the stomach and small intestine), pain in the right side is accompanied by lack of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, etc.
With pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas), the pain begins suddenly and is constant and intense. Sometimes it can “give” to the left side or get worse after eating heavy, fatty or spicy foods.
Associated symptoms
If a burning sensation in the liver is caused by a violation of the structural and functional state of the gallbladder and the liver itself, the patient also notices a number of associated symptoms, including:
- fast fatiguability;
- recurrent headaches;
- poor appetite, and as a result - weight loss;
- insomnia;
- causeless skin itching;
- yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes;
- discoloration of stool;
- darkening of urine.
It is worth noting that liver dysfunction can occur covertly for a long time, without obvious manifestations. Typically, pain and burning appear only in the later stages of the disease.
Diseases of the urinary system
Often the side on the right side hurts due to the organs of the excretory system. “These include urolithiasis and pyelonephritis,” says Bulat Yunusov.
Pyelonephritis is an inflammatory disease of the kidneys, in which, in addition to pain in the right side, weakness, nausea, vomiting, “jumping” pulse, dry mouth, and high temperature may also occur.
Pain in the side due to urolithiasis can be constant or wave-like, dull or sharp, it can only bother you at rest or intensifies when walking. It depends on the location of the stone, but sometimes the pain may first be felt in the lumbar region (so-called “renal colic”), and only then “settle” in the right side.
What not to do
Many patients, trying to alleviate their condition, often warm up the sore spot. Doing this is strictly prohibited, since heat exposure only worsens many diseases. This poses a risk of complications. In the presence of certain ailments, suppuration may form after heating. Indeed, under the influence of heat, pathogenic microflora begins to actively multiply.
Experts do not recommend using medications with an analgesic effect. Such drugs can not only complicate the diagnostic process, but also change the composition of the blood. For example, the drug "Analgin" affects the test result and can change it in case of acute appendicitis. The drug "No-Shpa" is not classified as an anesthetic medication.
It is not recommended to take any choleretic drugs for burning in the right side. If the patient suffers from stones, then when using such drugs they can begin to move through the ducts. This can eventually cause the gallbladder to rupture.
Liver diseases
“Pain in the right side can occur with damage to the liver and organs of the hepatobiliary system,” notes Bulat Yunusov. “Such diseases include cholecystitis, obstructive jaundice, liver cysts, hepatitis, and cirrhosis.” All of these diagnoses are characterized by fairly sharp pain in the right side, which can “radiate” to the right shoulder, neck or shoulder blade.
Women often experience pain on the lower right side due to malfunctions of the pelvic organs. “Such work disorders include inflammatory diseases (salpingitis, salpingoophoritis) and non-inflammatory (corpus luteum cyst, ovarian tumors, endometriosis, ovarian cysts, ectopic pregnancy),” notes Bulat Yunusov.
With salpingitis (inflammation of the fallopian tubes) and salpingo-oophoritis (inflammation of the fallopian tubes and ovaries), the pain is most often felt as a pulling in the groin area, but it can also “radiate” to the right or left side. Accompanied by fever, nausea, severe headache, vaginal discharge and intensifies during sexual intercourse.
With ovarian or corpus luteum cysts, pulling or stabbing pain is mainly localized in the lower abdomen or lower back, but can also be felt in the right side.
With endometriosis, the pain is most often acute, cramping, and can disappear and return. It is felt, as a rule, in the lower abdomen, in the left or right side (closer to the lower back).
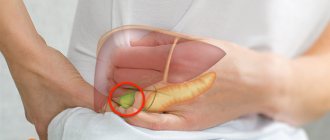
Right hypochondrium area
If we talk about localization, we should clarify which place in the human body is called the “right hypochondrium.” For this there is a classic definition from topographic anatomy - the area of the anterior abdominal wall that has:
- the upper border is the right dome of the diaphragm at the level of the V rib;
- lower - the inner edge of the costal arch;
- in the center - a conventional vertical line passing through the lowest edge of the rib;
- on the right side - the vertical connection of the XII rib and the right iliac crest of the pelvic bone.
As you can see, the anatomical definition is quite complex. In fact, we refer to the hypochondrium as everything that is located in the area of the right lower ribs and under them, starting from the spine (from the back) to the sternum joint.
The projection of the right hypochondrium includes internal organs:
- liver and gall bladder;
- bend of the ascending and transverse colon;
- upper pole of the right kidney with the adrenal gland;
- the peritoneal side of the dome of the diaphragm, separating the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity.
Response to physical activity
Sometimes the right side hurts not due to malfunctions in the internal organs (which we discussed above). If you feel pain on the right side during (or immediately after) physical activity, there is a chance that it is:
- Muscle spasm caused by weakness in the muscles of the back or abdomen.
- Diaphragm spasm. It is most often encountered while running: rapid breathing causes the diaphragm to contract faster, which can cause it to spasm and “give off” pain in the right side.
- Increased liver function. This organ is considered the “blood” depot of the body. During training, the liver may increase slightly in volume and “press” on its outer capsule, where there are many nerve endings, which will be felt as pain in the right side. And such discomfort can also arise due to an incorrect diet: for example, if before training you “got too much” with carbohydrates or fats. In this case, during exercise the liver will be forced to work under increased load, which can also provoke pain.
Features of pain localization
Uncomfortable stabbing sensations can occur in any area of the right side - above, below, to the right or to the left. It may hurt in one place, or the discomfort may spread to the back or chest.
If pain occurs below the ribs on the side, this indicates liver damage. Additional symptoms include nausea and vomiting. The pain may radiate to the neck and back. When a cyst ruptures in the liver, the pain intensifies and moves slightly downward.
Pain due to gallbladder dysfunction
The main reasons include severe stress (psychological or physical), dietary errors, smoking, and alcohol consumption.
The patient experiences pain on the right side, the pain may be in the back in the area of the scapula, or in the front - closer to the chest. The symptom is stabbing and tends to intensify during a deep breath. It does not last long - from 10 to 20 minutes, sometimes several minutes.
Typically, pain syndrome develops immediately if the patient has eaten fatty, sweet, starchy foods, or consumed alcohol or cold drinks. The severity of pain is weak when compared with the penetration of a stone into the bile canal.
Colic and fever
If the pain syndrome is accompanied by an increase in body temperature, this indicates an acute process. You cannot hesitate; the only way to avoid negative consequences is to call an ambulance. If pain and fever are severe, the person should be hospitalized. There are many reasons - acute form of hepatitis, appendicitis, peritonitis, cholecystitis.
Colic when inhaling and moving
In some cases, pain in the upper side is a consequence of physiological causes. It develops during fast walking, running or activity after eating.
Against the background of excessive production of adrenaline, the bile ducts relax and stretch. Due to the load, the liver fills with blood, the organ enlarges, which affects the nerve roots localized in the capsules.
For this reason, a person feels tingling and discomfort.
Increased stress on the body can provoke diaphragm spasm in an unprepared person. The pain syndrome appears when you inhale, and when you exhale it becomes easier. Doesn't last long - up to 10 minutes. The clinic leaves when breathing normalizes.
Pain due to hepatic colic
An attack of hepatic colic in patients always develops unexpectedly. Its duration varies from a couple of minutes to 2 hours, sometimes lasting a day (rarely).
Let's look at the symptoms and their etiology in the table:
| Symptom | Why does it appear |
| Acute stabbing pain in the upper right side of the abdomen. The pain increases over 10-50 minutes and persists for 2-6 hours. When the duration of pain is more than 6 hours, then most likely the cause is an acute form of cholecystitis | Nerve endings that are highly sensitive are located in the bile ducts. As the bile ducts stretch, they become irritated and pain develops. |
| Pain radiates to the right shoulder, upper limb, scapula, chest | The reason is that the nerve endings of the branches of the spinal nerves involved in the innervation of the hepatic and duodenal ligament are irritated. |
| Nausea, repeated vomiting, which does not bring relief to the person | Symptoms develop reflexively |
| Increased heart rate | This is a response to pain |
| Yellowing of the skin | If the common bile duct is blocked by a stone, the path for bile is blocked, pigment substances penetrate into the bloodstream, which gives a peculiar yellowish color to the skin. |
Against the background of hepatic colic, only in rare cases does the body temperature increase to 37-37.5 degrees.
How to determine why you have pain in your right side
Of course, you won’t be able to make an accurate diagnosis on your own. However, you can get some idea about it based on exactly how your right side hurts. “In acute diseases, pain occurs suddenly, increasing in intensity in a short period of time (hours, sometimes days),” notes Bulat Yunusov. “If the cause is some kind of chronic disease, then the pain syndrome is either constant or wave-like in nature, not very intense.”
It is also important to check for additional symptoms. “To correctly determine the cause of pain in the right side, you need to listen to the nature of this pain. For example, muscle pain is usually dull and aching,” the invited specialist commented. “However, muscle pain can also be acute, since in addition to the muscles in the right side there are intervertebral joints that can be a source of discomfort. In case of cholelithiasis or acute cholecystitis, the pain is accompanied by fever. This situation can be called “pain-plus” - pain and fever. Discomfort caused by renal colic can also be “pain-plus,” but pain plus frequent urination or the presence of blood in the urine. Pain caused by intestinal problems—pain plus diarrhea.”
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
To reduce pain in the right hypochondrium, it is recommended to follow a diet limiting fried, fatty, smoked foods, preserved foods and spices. Alcohol consumption is prohibited. The diet should consist of fruits and vegetables, lean fish and meat. If the pain syndrome intensifies, it is necessary to reduce physical activity and adhere to a gentle or semi-bed rest.
To stop an attack of spastic pain, you can use a warm (not hot!) heating pad, which is applied to the right hypochondrium. Cramping pain is well relieved with antispasmodics. Persistent pain is a reason to consult a doctor, since the symptom can be caused by dozens of different diseases that, without treatment, lead to serious complications.
Conservative therapy
Moderate pain in the right hypochondrium, arising from chronic diseases of the hepatobiliary tract, is treated on an outpatient basis. Hospitalization is required for patients with severe pain and severe general condition. In the hospital, narcotic analgesics are used to relieve unbearable pain, and detoxification therapy is carried out. To eliminate the causes of pain, several groups of medications are used:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
. They have an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect, so they quickly relieve pain. For functional biliary disorders, NSAIDs are combined with antispasmodics. - Cholekinetics
. Medicines that improve the flow of bile are necessary to relieve pain and discomfort and improve digestive processes. To enhance their effectiveness, they are combined with choleretics. - Antibiotics
. Medicines are prescribed for exacerbation of cholecystitis and cholangitis, which is caused by activation of pathogenic microflora. The selection of antibacterial agents is carried out taking into account the data of bacterial culture and bacterioscopy of bile. - Interferons
. Recombinant drugs are indicated for the treatment of chronic forms of viral hepatitis B and C. For the treatment of HCV, modern drugs from the group of protease inhibitors are effective, which provide complete cure. - Hepatoprotectors
. Products with UDCA and ademetionine are intended to protect healthy liver cells from damage and stimulate the regeneration of hepatocytes. The drugs increase the organ’s resistance to toxic factors and improve its detoxification function.
For chronic diseases of the gallbladder, courses of medicinal mineral waters are prescribed. Hepatobiliary pathologies in remission are an indication for physiotherapeutic treatment: reflexology, electrophoresis, SMT therapy. Herbal medicine methods are recommended to improve digestion. Sanatorium-resort treatment is widespread.
Pain in the lower abdomen on the right side in women
On the right side of women are the right appendages of the uterus: fallopian tube and ovary. With inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs, there may be pain in the lower abdomen on the right. Pain during the chronic process is aching, spreads to the lower back and suprapubic region, and is often combined with urinary disorders. Exacerbations may be accompanied by chills, nausea, sometimes vomiting, and discharge from the genital tract2, 14.
If the pain in the lower abdomen on the right begins suddenly and sharply, it may be a rupture or torsion of the cyst leg, or an ectopic pregnancy. The right lower abdomen hurts sharply, sometimes leading to fainting, the pain often radiates to the rectum. Patients try not to move so as not to increase the pain. Signs of intoxication and circulatory disorders may gradually appear: pallor, cold sticky sweat, nausea and vomiting, rapid heartbeat, and sometimes bloody discharge appears from the genital tract2, 14. Of course, if such symptoms appear, you must immediately seek medical help.
Pain in the right lower abdomen may periodically occur due to the connection with the menstrual cycle. Pain during menstruation can manifest itself as cramping or be aching and bursting. They often arise in the lower abdomen and then spread to the back, inner thighs, and rectum19-21.
Acute appendicitis
Perhaps this is the first pathology that a person thinks about when pain appears in the lower abdomen on the right. The pain in this case does not go away, arising near the navel, and eventually moves downwards1, 2, 15. The sensation may begin as dull, gradually becoming tugging, cutting, burning. A person’s health deteriorates and symptoms of digestive disorders occur: vomiting, bloating, constipation, and sometimes diarrhea15.
Acute appendicitis is treated surgically; if similar symptoms appear, you should immediately call an ambulance1.
Diagnostics
To understand the cause of stabbing pain, a thorough diagnosis is necessary. At the initial consultation, the doctor gets acquainted with the patient’s complaints, collects anamnesis, and conducts a physical examination. The doctor palpates the liver and uses percussion (to confirm or refute hepatomegaly). Afterwards, studies are prescribed.
Ultrasound of the liver and gallbladder
Ultrasound can rightfully be called the “gold standard” of diagnosis, since the technique has many advantages compared to other options.
These include high information content - from 95%, safety, accessibility, and no need for preliminary preparation.
Plus - low cost. This is relevant if a patient with a stabbing sensation in the right side seeks help from a private clinic.
Using ultrasound, you can diagnose deformation of the gallbladder, its wrinkling, narrowing or pathological expansion of the ducts.
The device helps to identify stones (single or multiple). An ultrasound of the liver shows the exact dimensions of the organ itself, its diameter, edges and contours of its lobes.
CT
When ultrasound provides an incomplete picture, CT is prescribed. This is a modern research method that allows you to identify minimal tumors in the liver, gall bladder and other organs.
CT scan examines the structure of the gland layer by layer. Based on the changes, it can identify focal or diffuse lesions, boundaries and structure of the organ. Any type of CT can detect an abnormal structure, tumors, inflammation, blockage of the bile ducts, and liver rupture. CT provides the opportunity to distinguish one tumor from another, and more specifically suggest what problem the patient has.
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
It is recommended to examine the gallbladder and bile ducts. Using special equipment, a contrast agent is injected, which is visible on an x-ray. Afterwards, a series of photographs are taken to identify defects and irregularities.
What happens in the hypochondrium during breathing?
Everything inside the human body is interconnected. The breathing process involves not only the lungs, but also other organs . At the upper border of the hypochondrium is the diaphragm, which takes an active part in breathing. Thanks to it, negative pressure is created inside the pleural cavity, due to which the lung tissue is greatly stretched and air enters it during inhalation.
How does a person breathe?
The muscles located between the ribs are also involved in the act of breathing. When they contract, the ribs move upward and the chest increases in volume. At this moment, the diaphragm descends towards the peritoneum and becomes flat.
Muscles of inhalation and muscles of exhalation
On a note! There are two types of breathing - chest and abdominal. The first is typical for women and occurs due to the muscles between the ribs; abdominal breathing is more often observed in men and its main participant is the diaphragm.
During movement, the diaphragm pulls along with it the internal organs located in the abdominal cavity. For example, the liver is connected to it by a special ligament. In turn, the gallbladder is attached to the liver. The intestinal organs are also involved in movement.
Respiratory system