Recurrent abdominal pain in children is not uncommon, but it is usually not associated with serious causes and goes away within 1-2 hours. As a rule, no organic cause is found during examination. Such pain is called functional: it is not associated with an organic disease, but often with stress. An attempt to correlate such pains with certain circumstances helps to determine their cause. It can be anxiety associated with attending school, emotional distress due to family troubles. If the child grows normally and the doctor finds no physical abnormalities, the pain is not localized in any specific place; there are no other symptoms of ill health - abdominal pain is unlikely to be associated with a serious illness that requires immediate attention. Chronic abdominal pain, accompanied by other symptoms of dyspepsia (stomach upset), can be caused, for example, by food allergies, intolerance to any foods, or worms. However, keep in mind that even if the cause is not found, the pain really exists and requires constant attention.
If a child experiences symptoms such as diarrhea, vomiting, or fever, you should immediately consult a doctor (call emergency help). Abdominal pain in children under one year of age - see the section “Colic in newborns”.
URGENT CARE
Call an ambulance if:
- the child woke up at night due to pain
- pain lasts longer than 2 hours; accompanied by vomiting that does not bring relief or diarrhea
- one place in the abdomen is very painful with slight pressure
- You find blood in your urine, stool, or vomit
THE DOCTOR'S CONSULTATION
Contact your doctor if:
- a child 4 years of age or younger has chronic or recurring abdominal pain
- The child has a decreased appetite and is not gaining weight well
ATTENTION!
Usually this aching pain is not very strong, but sometimes it is seriously disturbing. Too long attempts at diagnosis and treatment will most likely be ineffective and will only worry the child in vain.
| ASK YOURSELF A QUESTION | POSSIBLE REASON | WHAT TO DO |
| Have bowel movements become less frequent in the last 2-3 days? | Constipation | If the child's general condition has not worsened, see Constipation |
| Does pain occur in stressful situations, such as problems at school or in the family? | Functional pain | Contact your pediatrician . He will examine the child and, if necessary, prescribe examinations to exclude the organic nature of the pain. Try together to identify the cause - emotional, physical, diet violation. If the organic nature of the pain is excluded, consultation with a child psychologist . |
| In addition to pain, does the child complain of a feeling of bloating, cramps, or diarrhea? Skin rash? Do flare-ups occur several days hours or days after a certain food? | Food allergies | Consult your child's doctor . He will examine the child and recommend a specific diet, exclusion of certain foods and other measures to identify the cause of the allergy. |
| Does pain occur after your child eats ice cream or drinks milk? In addition, does he have a feeling of bloating, cramps, increased gas formation, or diarrhea? | Lactose intolerance (often develops after age 4, especially in children of Asian or African descent) | Make an appointment with your pediatrician . If he recommends, use rice or soy dairy substitutes for 1-2 weeks, then start giving milk again to see if symptoms return. There are other diagnostic methods. Consult your doctor about diet and treatment (enzymes); Before consultation, exclude dairy products from your diet |
| Exacerbations of pain are accompanied by bloating, cramps, increased gas formation, and diarrhea? Could a child drink unboiled water? | Parasitic infestation, such as giardiasis | An examination by a pediatrician is required , who will probably prescribe tests for Giardia and worm eggs. If the test result is positive, special treatment will be prescribed |
| Does your child have bloating, cramps, increased gas formation, or diarrhea? Did he eat a lot of apples or oranges, or chew sugar-free gum? | Excess intake of fructose or sorbitol | Reduce the amount of apples and oranges in your child's diet; do not give chewing gum. If there is no improvement within 2 days, contact your pediatrician . |
| Does your child have frequent headaches or nausea, with or without vomiting? Does sleep help? The pain is preceded by temporary blurred vision, spots before the eyes, etc. Does any of your relatives have migraines? | Migraine accompanied by nausea and vomiting (rare) | Place your baby in a quiet environment in a darkened room; You can give paracetamol. Contact your pediatrician , who may recommend migraine medication. |
| Attacks of pain always occur the same way and are accompanied by repeated vomiting (5 times or more) | Cyclic vomiting syndrome (rare) | Contact your pediatrician . Migraine medications are sometimes helpful for this rare condition. |
FOR INFORMATION
How to treat abdominal pain in a child
Even if no organic cause is found, the pain is real and bothers the child. In addition, children with functional abdominal pain are no less likely than other children to suffer from serious abdominal diseases, also accompanied by pain. Therefore, these pains should not be ignored. If new, unusual pain occurs, you should immediately contact your pediatrician.
Possible causes of vomiting and abdominal pain in a child
You must take your temperature!
Single vomiting and mild abdominal pain, as a rule, indicate food poisoning or minor disturbances in the functioning of the pancreas. However, constant vomiting and severe pain are an alarming sign. With frequent vomiting, the child loses fluid and suffers from dehydration.
Mom cannot reliably determine the cause of pain and vomiting, but she can suggest it. To do this, you need to accurately characterize the intensity and type of pain, remember what the child ate the day before and what other symptoms he has besides pain and nausea:
- If vomiting and pain are accompanied by diarrhea and a skin rash, we can talk about food poisoning. You should remember what the child ate that day and the day before before consulting a doctor. If the diet included products that had expired or were unusual for the child, we can talk about the body’s reaction to them.
- If the abdominal pain is cutting and not too severe, vomiting is not frequent, and the child has not gone to the toilet for several days, it may be constipation. However, despite the seemingly harmless diagnosis, constipation should not be underestimated. Sometimes severe constipation can be confused with intestinal obstruction, which requires immediate hospitalization.
- If a small child spits up so much every time after feeding that it looks like vomiting, has colic, bloating, problems with bowel movements, eats and sleeps poorly, the pediatrician may suspect lactose intolerance. It also occurs in older children. In this case, special medications or lactose-free formulas for feeding are prescribed.
- Vomiting and abdominal pain in a child, diarrhea can be a consequence of infection with parasites, for example, worms, Giardia. To clarify the diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo tests, after which the doctor will prescribe treatment. Similar problems often arise in children who are not accustomed to observing the rules of personal hygiene.
It is worth paying attention to the situations in which pain occurs: it can be functional or psychological. There are cases where a child vomited precisely in stressful situations, on the eve of tests, etc. In this case, a consultation with a child psychologist will be useful.
In rare cases, severe headaches (migraines) can also cause vomiting and stomach upset. Migraine often appears at school age: children report severe headaches, spots before their eyes, dizziness, and is often accompanied by vomiting.
What to do if you have severe pain and vomiting?
Vomiting and abdominal pain in a child is a reason to call an ambulance
Of course, the first thing parents should do is call an ambulance. In any case, vomiting and pain require examination. Before the doctor arrives, you can provide first aid. You can give your child something to drink, but in small quantities. There is no need to give him food or painkillers - they can blur the overall clinical picture.
The pain will subside, but the danger will remain. It is especially dangerous to relieve pain during appendicitis, as you may miss the moment when surgical intervention is necessary. If a child has a high temperature (38-40 degrees), you can give him an antipyretic that is appropriate for his age. However, you must definitely tell the doctor that you had a fever and you brought it down.
There is no need to put a small child to bed and cover him with warm blankets. If there is a fever, the temperature will rise even more. The position of the body should be such that the head is higher than the level of the stomach. This is necessary so that in case of vomiting the child does not choke or inhale the vomit. If the pain is unbearable, the child is screaming, and there is still a lot of time before the ambulance arrives, you can give a no-shpa tablet, but you must inform the doctor about this.
Exposure to sun and heat
While spending their vacation on the seaside, parents forget that not only acclimatization is harmful to the child, but also the unusual hot sun. At high air temperatures, the body overheats, and a lot of salts are excreted through sweat.
The child has a hard time with the loss of fluid and needs to constantly drink water. With insufficient compensation of electrolytes, heat stroke develops. Children complain that their head hurts a lot. Fainting can happen at any time. Overheating in the sun without a hat worsens the symptoms.
After a day spent on the beach, at night the following are observed:
- temperature rise up to 40 degrees;
- weakness, apathy;
- headache;
- nose bleed;
- The child has a stomach ache and is vomiting.
It is recommended that before the ambulance arrives, place the child in the shade, apply bottles of cold water to the neck and armpits, and cover him with a wet sheet. Give slightly acidified water to drink.
The baby can be comfortably placed under the awning
Methods for examining the digestive tract
Vomiting and abdominal pain in a child can also be due to worms
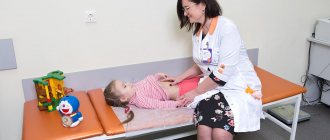
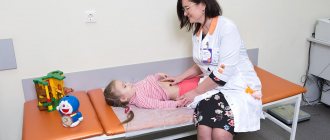
If abdominal pain, acute or chronic, or vomiting occurs, the child should be examined. All appointments are made by a pediatrician. As a rule, the local doctor listens to all complaints, collects anamnesis, examines the child, may palpate the abdomen, and then refers to a more specialized specialist - a gastroenterologist.
Tests are required: urine, feces and blood. They will help in making a diagnosis and indicate disruptions in the body and inflammatory processes. A stool test for worm eggs is taken separately. In addition to all of the above, the child may be prescribed the following procedures:
- Gastroscopy. This is a rather unpleasant procedure that involves examining the esophagus, stomach and duodenum using a thin tube that is inserted into the mouth. However, there is currently no more informative examination of the stomach. Using this procedure, you can quickly determine the presence of damage, tumors, bleeding, ulcers, and even immediately eliminate some of them. Children need to be prepared for this procedure, but under no circumstances should they be deceived. It is necessary to provide specific and understandable information, especially to older children. Before gastroscopy, you need to fast for 4-6 hours. If the child is so small that nothing can be explained to him, there is a danger that the child will move and damage the esophageal mucosa, so the procedure is performed under general anesthesia.
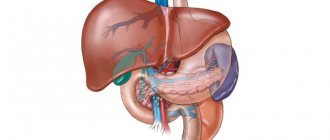
- Ultrasound. Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity helps determine the condition of many organs: stomach, liver, gallbladder, etc. However, sometimes the information obtained as a result of this examination is quite general, so further examination is prescribed (for example, FGS). 2-3 days before the ultrasound, it is advisable to keep the child on a non-strict diet: exclude everything creamy, carbonated, unhealthy, fried. It is not advisable for small children to be given vegetable and fruit purees on the day of the examination, since they take a long time to digest.
- X-ray or CT, MRI with contrast. Quite informative and painless examination methods. Unfortunately, it can be difficult for young children to remain motionless for long periods of time in an MRI machine. X-rays are done faster, but some radiation dose must be taken into account. If the intestines are examined, contrast may be injected into the rectum, which is quite unpleasant for the child.
Psychosomatics
Abdominal pain does not always have physiological causes. In childhood, painful sensations caused by various emotional experiences are very common (occurring in approximately 10% of children). We are talking about pain of a psychosomatic nature that appears against the background of severe stress, anxiety, and other psychological factors.
Symptoms:
- sudden attacks of dull pain in the navel area, which also end suddenly;
- Nausea, headache, general weakness, and pale skin are also possible.
The task of parents is to be attentive and monitor the condition of the baby. If these symptoms appear, it is necessary to exclude diseases of the internal organs. If there are no physiological causes of abdominal pain (confirmation of psychological causes), the pediatrician may refer the baby for consultation with a child psychologist or psychiatrist.
Diseases of the digestive system and their treatment
Vomiting and abdominal pain are common symptoms of food poisoning.
As mentioned above, the cause of pain and vomiting may be poisoning or lactose intolerance, but sometimes diagnostics reveals quite serious diseases that require constant medical supervision and comprehensive treatment:
- Appendicitis. The peculiarity of childhood appendicitis is that it is somewhat more difficult to determine, and this is where the main danger lies. Unfortunately, it is very easy to miss appendicitis in a child. The pain, as a rule, is not severe, the vomiting quickly stops, and the mother chalks it up to indigestion. As a result, the risk of complications increases. The only way of treatment is surgical, and the sooner the operation is performed from the moment the pain occurs, the better.
- Volvulus. A section of the intestine becomes twisted, the lumen closes, and feces cannot pass through. If left untreated, necrosis of part of the intestine may occur; the child’s condition quickly deteriorates, requiring emergency hospitalization. The treatment method is most often surgical, but sometimes an enema is sufficient if the volvulus is not severe.
- Acute diverticulitis. Diverticula are bulges in the intestine that can become inflamed. This causes severe abdominal pain and vomiting. This disease is easily confused with appendicitis. Just like appendicitis, diverticulitis can be life-threatening and requires immediate hospitalization and surgery.
- Acute gastritis. In some cases, acute gastritis in a child manifests itself in the form of severe pain and vomiting. More often, gastritis can be found in schoolchildren and the reason for it lies in nutrition. Acute gastritis is treated with gastric lavage, sorbents (Smecta or activated carbon), drugs to protect the stomach walls (for example, Almagel), enzymes, antispasmodics, and always diet.
- Acute pancreatitis. Acute pancreatitis is expressed in paroxysmal pain, nausea, and vomiting. This disease is dangerous because it can lead to necrosis of pancreatic tissue. If there are signs of a purulent process, surgical treatment is indicated. If there is no need for surgery, the child still needs to be observed in a hospital setting. He will be prescribed enzymes and a special diet.
This is not the entire list of possible diseases that can lead to vomiting and severe abdominal pain in a child. Mothers should be vigilant and not delay seeing a doctor for fear that the child will be admitted to the hospital.