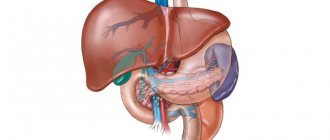
Spinal problems
Chest pain when inhaling often appears due to pathologies of the spinal column. The fact is that the spine contains a huge number of nerve endings, inflammation and/or infringement of which can lead to pain radiating into the chest, causing pain when inhaling.
Osteochondrosis
It is a serious disease that affects the cartilage tissue of the spinal column. The intervertebral discs thin out and become less durable, resulting in a decrease in the distance between the vertebrae. Because of this, nerve tissue is pinched, which leads to pain. If the pain intensifies when you inhale, this may indicate that the thoracic spine is affected.
Intercostal neuralgia
Sharp acute pain in the chest when inhaling occurs when compression or irritation of the nerve roots that are located between the ribs occurs. This condition can last literally a couple of minutes or drag on for a day, preventing the person from taking a deep breath and causing significant discomfort. The pain can come on suddenly, for no apparent reason, and often makes a person worry and think that the heart is stabbing, although the reason is completely different.
Fractured ribs
If you have recently been injured and experience pain in your chest when you inhale, you may suspect a rib fracture. This is a dangerous condition, and with a visit to a traumatologist
/
the surgeon
cannot hesitate, since, among other things, you may have damage to internal organs. The fracture itself, depending on its severity, can provoke additional damage.
Pain when taking a deep breath
Causes of pain when taking a deep breath
The following conditions lead to pain when taking a deep breath:
- inflammation of the pleura (pleurisy), often detected with pneumonia (the pain is more easily tolerated in a lying position, the general condition suffers, weakness and fever appear);
- intercostal neuralgia is a common cause of pain when inhaling, and they have a “shooting” character and sharp severity;
- deformation of the rib frame with limited mobility of the thoracic spinal column (this condition is typical for scoliosis and other postural disorders);
- shortening of the interpleural ligament, which is accompanied not only by pain when inhaling, but also by constant coughing;
- injuries or compression of the chest with damage to the cartilaginous or bony rib structures (the pain is sharp, intense, radiating to the surrounding areas and lower back);
- osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine (manifested by moderate pain of varying intensity, inhalation is difficult during exacerbation of the disease, which is caused by hypothermia, physical activity, and prolonged exposure to a static position).
As a rule, pain occurs not only when inhaling - the patient feels significant discomfort when coughing, sneezing, or laughing. If the discomfort is caused by intercostal neuralgia, numbness or burning of the skin along the branches of the affected nerve is added to the pain.
Treatment at the Posturology Clinic
The main task of a posturologist is to carefully release pinched nerve endings from compression by muscles, ligaments and the ribs themselves. Drug therapy is used according to strict indications and serves as an auxiliary method of treatment for acute, unbearable pain.
Using massage techniques, exercise therapy, reflexology, hirudotherapy, physiotherapy, the specialist achieves a number of effects:
- restores the anatomically correct configuration of the chest;
- relieves muscle blocks in the chest and back;
- restores normal curves of the spine;
- helps the internal organs of the chest to “fall” into place;
- improves blood circulation and nerve conduction in the affected area.
Complex treatment eliminates trigger pain points, relaxes the necessary muscle groups, forms the correct motor stereotype and consistently eliminates all links in the pathological chain of disorders.
There is no need to wait until the pain with a deep breath goes away on its own - it can and should be treated, and a competent doctor will not only relieve you of the pain syndrome, but will also bring all body systems into a state of harmonious balance.
Diseases and pathologies of the heart
Often, when inhaling, pain appears in the left chest if there is a heart problem. In this case, there may be quite a few reasons, and only an experienced pulmonologist
.
Pericarditis
Pericarditis is an inflammation of the heart sac - the outer lining of the heart, which is called the “pericardium”. The nature of such a disease can be infectious, rheumatic, or result from a heart attack. With pericarditis, not only does pain appear when inhaling on the right or left side of the chest; the condition is often accompanied by severe weakness, as well as shortness of breath if fluid leaks between the layers of the pericardium. Pericarditis with effusion can develop into suppuration and cause compression of the heart by accumulated secretions.
Pulmonary embolism
This is the name of the condition when the pulmonary arteries stop passing blood, i.e. clogged. This is a consequence of a blood clot (thrombus), drops of fat, bone marrow, catheter element or other foreign body entering the arterial bed. In this case, when inhaling, pain occurs in the left side of the chest, and the person needs urgent medical attention.
Pulmonary pathologies
There are many causes of pain in the sternum during inspiration, which are associated with pathologies of the respiratory system. It is worth considering some cases when pain may appear when inhaling.
Pneumothorax
It is an accumulation of gas in the pleural cavity, which leads to the collapse of lung tissue, from which the process occurs. In this case, the mediastinum shifts towards the healthy organ, the blood vessels are compressed, which leads to respiratory disorders, and blood circulation is also impaired. Often pneumothorax is traumatic, and can also be a consequence of spontaneous disruption of tissue integrity.
Pleuropneumonia
If chest pain appears when taking a deep breath, this may indicate progressive pulmonary pneumonia, when the pleura is involved in the pathological process. This disease is very dangerous; Along with pain when inhaling, a person notes the inability to take a deep breath and general weakness.
Pleurisy
Inflammation of the serous membrane of the lungs is called pleurisy and may be accompanied by pain when inhaling. In this case, a person not only has pain in the chest area when inhaling, but also shortness of breath, cough, pulmonologist
notes pleural friction noise when listening to breathing, and the temperature also rises.
Lungs' cancer
Pain in the middle of the chest when inhaling can occur if a malignant neoplasm has developed in the lungs. Pain syndrome is a consequence of tissue proliferation and compression of neighboring structures. To determine why your chest begins to hurt when you inhale and move, first consult a neurologist
, who, after a survey and examination, will refer you to a specialist.
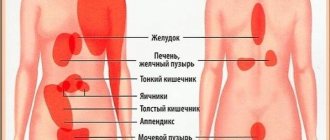
What pathologies cause abdominal pain when inhaling?
If pain when inhaling persists, despite changing body position, then this indicates serious disorders affecting the heart, lungs or abdominal organs. It happens that abdominal pain when inhaling is felt with inflammatory diseases of the gallbladder or cholelithiasis, stomach or duodenal ulcers, as well as with pancreatitis, splenic infarction or viral hepatitis.
Often pain in the right side when breathing occurs due to liver damage, but there may be other reasons, including:
Why does my lower abdomen hurt when I move?
- inflammation of the appendix;
- exacerbation of pancreatitis or cholecystitis;
- disruption of the cardiovascular system, for example, myocardial infarction or angina pectoris;
- renal colic;
- inflammation of the bronchi and lungs;
- kidney diseases, for example, pyelonephritis;
- pinched nerve, osteochondrosis.
Pain in the left side when inhaling can appear with the development of the following pathologies:
- hernia in the diaphragm and its pinching;
- damage to the nerves located between the ribs (intercostal neuralgia);
- appendicitis;
- cardiac ischemia;
- enlarged spleen (splenomegaly);
- exacerbation of pyelonephritis;
- osteochondrosis;
- stomach diseases;
- pancreatic dysfunction.
Pain when inhaling on the right side of the abdomen most often occurs with inflammation of the gallbladder or the formation of stones in it, as well as with progressive liver diseases. In the epigastric region, discomfort when inhaling appears if there are disturbances in the functioning of the stomach or intestines.
A deep breath can cause severe pain during renal colic; the sensation occurs in the hypochondrium and spreads to the shoulder and shoulder blade.
Pain syndrome when inhaling on the left side of the abdomen often appears with inflammation of the spleen
Stomach diseases that can cause the syndrome
Since the stomach is located in close proximity to the diaphragm, it can be compressed by it during the respiratory act. And if there is inflammation in the digestive organ, then any impact on the “exposed” nerve endings can result in pain. When you inhale, your stomach sometimes hurts if you have the following disorders:
Gastritis
The pain occurs after eating, because gastric juice begins to be released, which irritates the inflamed gastric mucosa, and also because the tissues are mechanically affected by food. As the food masses move into the intestines, the pain subsides.
In the chronic course of the disease, the pain in the upper abdomen is aching and not very pronounced. Acute gastritis can be recognized by lack of appetite, heaviness in the stomach, taste in the mouth, increased salivation, nausea, and belching. As the symptoms increase, severe pain in the stomach appears when inhaling, flatulence, diarrhea, and fever.
Ulcer
If an ulcer has formed in the stomach, then it makes itself felt with pain “in the pit of the stomach” about an hour after eating or due to hunger. The intensity of the symptom can vary: from mild discomfort to pain that makes it difficult to breathe.
The patient also suffers from heartburn, nausea and vomiting after eating, and sour belching. If a symptom of an “acute abdomen” occurs (severe spasmodic sharp pain, abdominal tension, stool disturbance), this indicates a perforation of the ulcer and urgent surgical intervention is required.
Benign neoplasms
These tumors do not threaten the patient’s life because they are not capable of metastasizing. But they can cause significant inconvenience during meals or when overeating due to the mechanical effect on education. Pain occurs due to the consumption of various foods, as a result of which the patient refuses to eat. Nausea and vomiting, pain on palpation, and bleeding may also occur.
Polyps are removed surgically, small formations can be removed by endoscopy
Malignant formations
As cancer grows, the pain is not very pronounced, but it is constant. Symptoms of intoxication also occur: lack of appetite, indigestion, heaviness in the stomach even after eating a small amount, chronic fatigue, anemia. As the tumor grows, the pain also increases, bleeding and vomiting appear.
Poisoning
When poisoned by chemicals, the gastric mucosa becomes inflamed, hence the signs of gastritis (pain, burning in the stomach, nausea and vomiting, lethargy, weakness). In severe cases, loss of consciousness occurs.
In food poisoning, pathological processes are provoked by putrefactive bacteria that entered the digestive tract with low-quality products. The patient feels severe spasmodic pain in the stomach when inhaling, nausea, dizziness, and weakness. As the body tries to remove toxins, vomiting and diarrhea occur.
Infection
Viruses and bacteria that have entered the digestive system can also cause stomach pain when inhaling. The most common infection is gastroenteritis, which is characterized by diarrhea and vomiting.
Expanding pain in the stomach when inhaling is disturbing when overeating, indigestion, frequent constipation, tension in the abdominal muscles, and can be caused by smoking or drinking alcohol.
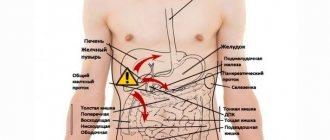
Diseases of the abdominal organs
Pain when inhaling also occurs with flatulence. The diaphragm lowers, the pressure in the abdominal cavity increases and the intestinal walls, filled with gas, contract. With renal colic, pain when breathing appears in the hypochondrium and “in the pit of the stomach”, then it spreads throughout the abdomen, radiating to the right shoulder blade and shoulder.
Colic appears due to a sudden disturbance in the passage of urine, renal ischemia and an increase in intrapelvic pressure. In addition to pain, there is pain when urinating, nausea and vomiting, flatulence, chills, and hyperthermia.
Splenic rupture is possible after blunt trauma to the abdomen. From the damaged organ, blood flows into the abdominal cavity. Increased innervation of the lymphoid organ causes severe pain, which becomes more intense with movement and even with a full breath.
The pain is characterized as shooting and is felt under the ribs on the left. With pathology, body temperature rises, chills appear, and the skin in the abdominal area becomes blue. A subphrenic abscess causes severe pain during breathing in the sides or under the ribs.
Severe pain can cause shock, so if symptoms appear, seek immediate medical attention
The sensation extends to the shoulder blades and collarbone. Symptoms of intoxication also appear (heat, fever, lethargy, nausea). The patient breathes shallowly, as a deep breath increases the pain. Unpleasant sensations are somewhat reduced if you lie on the sore side or are in a semi-recumbent position.
With a diaphragmatic hernia, the diameter of the esophagus increases, and part of the stomach rises several centimeters. This provokes the appearance of aching pain in the left hypochondrium and difficulty taking a deep breath; the pain intensifies when sneezing or coughing. Frequent regurgitation and heartburn indicate a hernia in the diaphragm.
Acute appendicitis. When the appendix is inflamed, bursting pain can affect the right or left side of the abdomen or the navel area. At the same time, it is difficult for the patient to take a full breath, the pain is more intense when sneezing, coughing, or laughing. As the pathological process develops, pain is concentrated in the right side.
The disease is accompanied by fever, single vomiting, and bowel dysfunction.
The gallbladder is not in contact with the diaphragm, but it is attached to the liver. When you inhale, both the liver and the gallbladder move, hence the pain in the inflamed organ. Inflammation of the gallbladder can occur in acute or chronic form. Acute cholecystitis is most often caused by the movement of stones blocking the bile ducts.
Pain appears in the right hypochondrium, radiates to the back and is felt in the lower abdomen. They intensify when you inhale. There is also a fever. Lack of therapy can lead to the spread of the inflammatory process to nearby organs.
With chronic cholecystitis, bile stops flowing into the duct, which causes stagnation of the secretion and it begins to damage the bladder tissue. The pathology develops slowly and is provoked by poor nutrition, stress, and infections.