- home
- Proctology Center
- Digital examination of the rectum
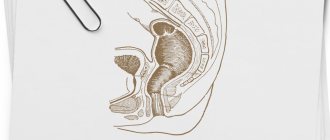
Digital rectal examination of the rectum is a diagnostic examination method that allows you to identify the presence of pathology in the intestine. The main advantage of this method is considered to be ease of implementation and the absence of the need for special equipment. Thanks to digital rectal examination, serious diseases can be detected at an early stage. A digital examination is performed by a proctologist.
Indications for the study
The rectal examination procedure is indicated for people who are concerned about the following changes in their health:
- bowel dysfunction: constipation, diarrhea, or alternation of these symptoms;
- pain in the anus;
- bleeding from the anus;
- there is a suspicion of a malignant or benign tumor.
Digital rectal examination precedes other diagnostic methods: anoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy. It allows you to assess the patency of the distal rectum and identify contraindications to instrumental examination.
general characteristics
Doctors recommend such studies for all men over 50 years of age, regardless of the presence or absence of signs of pathology of the genitourinary organs. This significantly increases the likelihood of diagnosing the causes of not only pronounced changes, but also poorly manifested, but serious and dangerous diseases in the early stages. Which sometimes preserves not only the health, but the life of the patient. The high information content of this study is due to the close anatomical relationship of the lower intestine and the prostate gland. It is directly adjacent to the rectum in its anterior section, where you can palpate the posterior surface of the prostate. Before palpation, the anal area is also examined, cracks, signs of inflammation and the presence of hemorrhoids are identified. This makes it possible to exclude concomitant intestinal pathology and identify the spread of the process beyond the gland tissue in certain diseases (neoplasms, abscesses).
What does it reveal?
Digital examination of the rectum helps to identify the following pathologies:
- pathological changes in the rectal canal: rectal fistula, cracks, changes in the consistency of the mucous membrane;
- rectal fissures;
- narrowing of the rectal lumen;
- dilatation of the veins of the lower part of the rectum, where nodes form;
- rectal tumors;
- presence of a foreign body;
- cystic formation.
This type of diagnosis also makes it possible to identify changes in the urological and gynecological parts: inflammation or oncology of the prostate gland in men and diseases of the internal genital organs in women.
What does the procedure show?
RIPC is prescribed to patients with complaints indicating pathologies of the PC or pelvic organs. Alarming symptoms include pain in the anus or lower abdomen, the appearance of blood during bowel movements, fecal incontinence, constipation, and other problems. A rectal examination (RI) can identify the following diseases:
- haemorrhoids;
- anal fissure;
- proctitis - inflammation of the intestinal mucosa;
- neoplasms (polyps, cancerous tumors);
- paraproctitis - inflammation of the fatty tissue surrounding the intestine;
- rectal and anorectal fistulas;
- cryptitis - inflammation of the anal crypts.
RIPC is also used in the complex diagnosis of BPH - benign prostatic hyperplasia. It is prescribed to women for gynecological purposes if there is no access to the vagina. It makes it easier to palpate the ovaries and assess their condition.
Preparation
To make the procedure less uncomfortable and more informative, it is recommended to prepare for it:
- Normalization of intestinal function. You need to avoid foods that are too fatty and spicy, as well as foods that contribute to flatulence and bloating. These include legumes and fresh fruits.
- Diet restriction. A digital rectal examination is performed exclusively on an empty stomach, so the last meal should be taken in the evening, at least 12 hours before the scheduled diagnosis.
- Drinking regime. In addition to maintaining proper nutrition, you need to drink plenty of fluids.
- Purgation. Immediately before the procedure, it is recommended to perform a cleansing enema.
- If the patient has problems with stool (constipation), then mild laxatives may be prescribed, which must be taken three days before the procedure.
Performing a digital rectal examination
Before carrying out the procedure, you need to relax the muscles of the anus as much as possible - only in this case can the information content of the technique be guaranteed. The procedure for conducting the examination is as follows:
- The patient lies down on the couch, bends his legs at the knees and brings them as close to his chest as possible.
- Before starting the manipulation, the doctor puts on disposable gloves, onto which a special lubricant is applied. Lubrication makes the procedure easier.
- Next, the rectum is examined: the doctor spreads the patient’s buttocks with one hand and inserts one or two fingers into the rectum.
The procedure takes no more than 5-10 minutes.
Parameters and their assessment
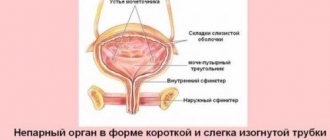
The prostate normally has a tight-elastic consistency, uniform throughout the organ; in the middle part, the median groove between its lobes is palpable; in the lateral areas of the gland, seminal vesicles are detected. The boundaries of the prostate are clear, the transverse size of the gland is 2.5-4.5 cm, and the longitudinal size is from 2.5 to 3.5 cm. All structures are painless, and the rectal mucosa above the prostate is displaceable, the tissues are not fused together.
- size of the gland (if enlarged, then evenly or in a certain area);
- shape of the prostate (in pathology – irregular, asymmetrical);
- boundaries of gland tissue and seminal vesicles (clear or unclear);
- density (during diseases, areas of sharp compaction or softening may appear);
- characteristics of the interlobar groove (during inflammatory processes of various natures it is smoothed out until it disappears);
- degree of sensitivity and pain (individual areas and the entire organ);
- mobility of the intestinal mucosa at the site of contact with the prostate (if the pathological process spreads beyond the gland, intestinal tissue may be involved and fixed);
- characteristics of the tissues around the gland, seminal vesicles (pain, consistency, size).
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
Advantages
- simplicity of the procedure;
- takes a little time;
- Every proctologist has the technique;
- no need to use additional tools;
- a minimum number of contraindications to the examination.
Flaws
- impossibility of identifying the etiology of the tumor (malignant, benign);
- discomfort for the patient when performing the manipulation;
- limited diagnostic scope.
Despite the presence of shortcomings, digital rectal examination is considered a necessary diagnostic method, which is carried out without fail if a proctological or urological disease is suspected.
Changes in various pathologies
A rectal examination of the prostate can suggest the inflammatory, tumor nature of changes in the organ, and reveal the extent of the spread of the pathological process and the involvement of surrounding structures. With acute inflammatory changes (prostatitis), an increase in size is observed, with sharp pain, the consistency becomes denser, and the boundaries are somewhat smoothed out. With a complicated course and the formation of an abscess, foci of a sharp decrease in density are added, up to situations where fluid is palpated in a limited cavity (focus of fluctuation). Chronic prostatitis is characterized by a slight enlargement of the prostate and its uneven consistency, slight pain is possible. Adenoma (benign hyperplasia) is characterized by an increase in the size of the prostate gland and a significant smoothing of the median groove while maintaining normal density. There is no pain.
- pronounced and uneven density (even rocky);
- increase in size;
- soreness when palpated;
- adhesion of the tissues of the gland and rectum, the inability to displace the intestinal mucosa at the point of contact with the prostate.
Thus, digital rectal examination of the prostate gland is a traditional method of direct examination of the patient, which allows one to determine the feasibility of further research during preventive examinations, as well as prescribe instrumental methods to confirm the diagnosis.
Other diagnostic methods
A digital rectal examination usually precedes more informative studies. These include:
- Anoscopy. The doctor performs a visual examination using an anoscope. This instrument resembles a gynecological speculum. When it is introduced into the rectum, only up to 8-10 cm of the anal canal can be seen. If this distance is not enough, a more informative type of diagnosis is used - rectoscopy.
- Sigmoidoscopy. Visual inspection of the condition of the rectum in real time. The procedure is carried out using a rectoscope. The instrument is inserted into the anus and air is supplied so that the rectum straightens and the diagnosis becomes more informative. This method allows you to assess the condition of the rectum along its entire length.
- Colonoscopy. The rectum is examined using a colonoscope. This device is a small rubber hose with a metal tip. The advantage of this type of diagnostics is the ability to display images on a monitor. The tip is inserted into the anus and the condition of the rectum is assessed. If indicated, the entire colon can be examined.
What are the RIPC methods?
RIPC can be either finger or instrumental. Depending on the chosen method, the proctologist can examine the condition of the PC visually or by touch. Each study has its own characteristics.
Finger examination
Palpation is the examination of the lower part of the PC and surrounding tissues using a finger inserted into the anus. Before the procedure, the doctor puts on medical gloves. To reduce discomfort, additionally lubricate the finger with Vaseline. He then inserts it into the anal canal and feels the surrounding tissue. The advantage of the method is the ability to assess the density of the intestinal wall and the muscle tone of the sphincter.
Mirror Study
A rectal speculum is a two-leaf instrument inserted into the PC cavity through the anus. With its help, the proctologist pushes the walls of the intestine apart and evaluates its membranes visually. A lamp can be installed inside the mirror to increase the information content of the procedure and the accuracy of medical manipulations.
Application of an anoscope
An anoscope is an optical instrument consisting of a hollow tube and an obturator (an oval-shaped tip). It is inserted through the sphincter, similar to a rectal speculum. Thanks to it, the proctologist receives high-quality visualization of tissues from the inside. During an anoscopy, the doctor may take a tissue sample for a biopsy and ligate or scleros the hemorrhoids. If an anal fissure is detected, he will block it. Found polyps will be removed.
What is sigmoidoscopy
Sigmoidoscopy is an endoscopic examination of the PC and distal sigmoid colon. It is carried out using a sigmoidoscope - an instrument in the form of a long tube. Its design resembles an anoscope. With its help, the doctor examines a section of the intestine up to 25–30 cm deep from the anus.
Procedure:
- The patient undresses and takes a knee-elbow position.
- The doctor probes the anal canal with a finger to assess its patency and pain.
- If there is pain, the proctologist administers a local anesthetic, then a sigmoidoscope with an oval obturator.
- First, the doctor advances the instrument 4–5 cm. Then he removes the obturator and continues inserting the tube without it.
- As the instrument moves, the doctor evaluates the color, degree of moisture, shine and surface relief of the mucous membrane. The results obtained are recorded.
- After completion of sigmoidoscopy, the instrument is carefully removed. The patient can then get dressed and leave the office.
All types of rectal examinations are carried out in the medical department. Make an appointment and come to an appointment with a proctologist at a time convenient for you, tell him about your symptoms. The doctor will prescribe the necessary tests for you, make the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment.