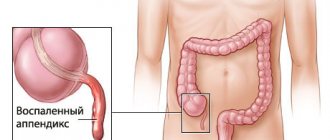
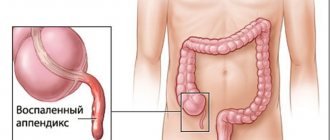
Appendectomy is one of the most common surgical procedures in the world. Postoperative complications include early (wound infection, intra-abdominal abscesses, postoperative intestinal paresis) and late (intestinal fistula, adhesive disease of the abdominal cavity). Stump appendicitis (stump appendicitis), which is a rare complication of appendectomy, is considered separately. It is understood as continued or recurrent inflammation in the remaining part of the appendix. Since the first description by T. Rose [1] in 1945, to date, only 61 cases of this complication have been described in the literature. A number of authors believe that the true prevalence of this complication is higher and a significant part of AK remains undiagnosed [2, 3]. When a clinical picture of acute appendicitis occurs in patients with a history of appendectomy, right-sided diverticulitis and inflammation of the uterine appendages are most often assumed. In this case, antibiotics are prescribed that relieve inflammation in the stump in most cases [3, 4].
AK can occur at different times after the initial operation: from several days, according to F. Chikamori [2], to 40 years or more, according to A. Mangi [5]. Leaving a stump longer than 5 mm is considered a risk factor for complications: according to A. Mangi and D. Berger, the length of the stump in repeated operations for AK ranged from 5 to 65 mm [5]. The main method of non-invasive diagnosis is computed tomography, which makes it possible to identify inflammatory changes in the appendix stump and surrounding tissues [3, 4, 6].
Analysis of a clinical case
In the clinic of general surgery of the pediatric faculty of the Russian National Research Medical University named after. N.I. Pirogov on the basis of City Clinical Hospital No. 4 of Moscow for 5 years, from 2011 to 2015, 1967 appendectomies were performed, among them 1941 (98.7%) laparoscopically, the number of conversions was 2.6%.
Here we present a clinical analysis of a single case of necrosis of the appendix stump with the development of anaerobic peritonitis on the 2nd day after laparoscopic appendectomy, which amounted to 0.05% of the total number of appendectomies we performed.
Patient,
A 25-year-old man who had not had any surgery on the abdominal organs was admitted to the clinic with a clinical picture of acute appendicitis 8 hours after the onset of the disease.
Ultrasound showed signs of acute appendicitis and empyema of the appendix. The patient was operated on urgently. Antibiotic prophylaxis was administered (ciprofloxacin 200 mg and Metrogyl 500 mg once intravenously before surgery). Laparoscopy revealed a small amount of transparent serous effusion in the abdominal cavity (30 ml), diagnosis: acute phlegmonous appendicitis. A standard laparoscopic appendectomy was performed using the ligature method with treatment of the appendix stump with coagulation and antiseptics. When a 15 cm long and 1 cm thick appendage was removed from the abdominal cavity, its lumen was opened, and the abdominal cavity in the area of contamination was sanitized with an antiseptic solution. No abdominal drainage was performed. Culture from the shoot revealed the growth of E. coli
, sensitive to amikacin, ceftazidime, ciprofloxacin and imipenem. The early postoperative period proceeded smoothly.
29 hours after the operation, the patient developed sharp pain throughout the abdomen, peritoneal symptoms, and intoxication was noted. Leukocytosis increased from 9.7 to 16.0 thousand per mm3. An ultrasound revealed fluid layers between the intestinal loops in the right iliac region and a fluid accumulation in the pelvis measuring 9x8x7 cm. A biochemical blood test revealed an increase in creatine phosphokinase to 957 U/l. Considering the clinical picture of diffuse peritonitis, the patient underwent relaparoscopy, which revealed diffuse fibrinous-purulent peritonitis with brown effusion and pus in the abdominal cavity with a volume of up to 300 ml, necrosis of the appendix stump, the length of which was 1 cm, retroperitoneal putrefactive phlegmon, pelvic abscess with a volume of 400 ml (Fig. 1 and 2).
Rice. 1. Necrotizing fasciitis. Phlegmon of retroperitoneal tissue.
Rice. 2. Necrosis of the stump of the appendix (circle), mesentery of the appendix (indicated by a dark arrow), paracolic tissue (indicated by a white arrow).
Laparotomy was performed. Laparotomy confirmed necrosis of the appendix stump; no signs of stump failure were identified. Putrefactive retroperitoneal phlegmon with purulent streaks along m. iliopsoas
and
m.
iliacus into the small pelvis and along
m.
quadratuslumborum to the subhepatic space and signs of necrotizing fasciitis. When opening the leaks, the entry of gas bubbles and brown exudate was noted. Necrosis of retrocolic fat tissue was detected. There was no necrosis of the intestinal wall. Resection of the appendix stump, immersion of the stump with a purse-string and Z-shaped suture, necrectomy, drainage of the retroperitoneal space and abdominal cavity (5 drainages) were performed. The patient was prescribed carbapenem antibiotics intraoperatively. The next day, a sanitizing intervention was performed, the signs of peritonitis subsided, the abdominal cavity was sanitized, sutured in layers, and the drains were replaced. Histological examination of the stump revealed necrosis of its muscular wall and colonies of microorganisms were found in the lumen of the stump. In the postoperative period, fever up to 37.6-38 °C and purulent discharge with fibrin flakes through drainages from the pelvis and retroperitoneum persisted for 7 days, while ultrasound showed no signs of fluid accumulations. For 5 days the patient was in the intensive care unit due to symptoms of a systemic inflammatory reaction. The postoperative period was complicated by the development of bilateral lower lobe pneumonia and bilateral hydrothorax. For 3 days after surgery, paresis persisted, which resolved with drug stimulation. A computed tomography study on the 10th day after surgery revealed signs of: myositis of the right iliac muscle, iliopsoas muscle; infiltration of paracolic fiber in the projection of the cecum and ascending colon with gas bubbles in it (Fig. 3); bilateral small hydrothorax; fluid in the abdominal cavity in small quantities.
Rice.
3. Computer tomogram (10th day after surgery). Increase in size m. iliacus, m. ileopsoas (indicated by white arrows), gas bubbles in paracolic tissue (indicated by a dark arrow). The patient underwent detoxification and antibacterial therapy, the drains were sequentially removed (the last one - from the right retroperitoneum - on the 11th day from the last operation). On the 22nd day from the first operation, the patient was discharged in satisfactory condition. The postoperative period was also due to initial hypoproteinemia.
Types of scars after appendicitis removal
We all experience the period of skin restoration and the scarring process differently - this directly depends on the regenerative characteristics of the body. Therefore, the mark from the operation looks different for everyone.
- Normotrophic - flat, almost invisible, white in color, visually similar to a strip. Such a scar is an ideal outcome of surgical intervention and does not require correction.
- Hypertrophic - forms a thick and hard scar. Difficult to remove. It is recommended to use the gel or ointment for a long period.
- Atrophic - characterized by retraction into the skin. In order to eliminate such a scar, it is necessary to destroy the deformed collagen fibers in the deep layers of the skin. This can be done with the help of special cosmetics and injections.
- Keloid is the most unpleasant scar of all. Rough, dense, red or bluish in color. Brings itching, burning, a feeling of tightness and discomfort. It tends to grow over several years and significantly exceed the original size of the wound. To combat such a scar, physiotherapy with medicinal solutions, laser resurfacing, hormone injections and anti-scar gels are effective.
Scar treatment after appendectomy
This problem worries people regardless of gender. How not to be embarrassed by an appendicitis scar? Is it possible? After all, both men and women want to get rid of scars as quickly as possible. Don’t worry, modern medicine is ready to offer effective methods for getting rid of scars.
You should be patient; correction may take a long time (from a month to several years, depending on the type of scar, its age and location). And especially in cases where several months or even years have passed since the operation. Such a popular procedure as laser resurfacing does not guarantee complete restoration of the skin in one session. Moreover, it has many contraindications and is very painful. To see the first results, you will need to undergo 2-3 procedures. Keep in mind that after resurfacing, a long recovery period is required - be patient and follow your doctor's recommendations.
Any medical procedures should be discussed with your doctor. And it doesn’t matter whether you select ointments, patches, vitamins or choose a clinic, pay attention to the competence and reputation of the medical center. You should not rely solely on pricing policy. The risk in this case is not justified.
Find out which method of correcting scars and stretch marks is optimal for you!
doctor Svetlana Viktorovna Ogorodnikova.
doctor
Discussion
In the given clinical example, there was necrosis of the appendix stump with necrotizing fasciitis, retroperitoneal phlegmon, pelvic abscess and widespread anaerobic peritonitis in the early postoperative period after laparoscopic appendectomy in the absence of signs of stump failure. A possible predisposing factor for the growth of anaerobic microorganisms is the anaerobic carbon dioxide environment during laparoscopic appendectomy. The triggering mechanism in the described clinical case was a rupture of the appendix with contamination of the abdominal cavity when it was removed during the primary operation.
AK is considered by most authors as a recurrence of appendicitis in the stump of the appendix at various times after surgery. In this clinical example, there was a reinfection of the abandoned stump of the appendix 10 mm long with anaerobic microorganisms from the lumen of the appendix with the development of the classic picture of anaerobic inflammation. Prevention of A.K. is to leave a stump of the appendix no more than 3 mm long, which requires clear visualization of the base of the appendix or immersion of the stump, as well as thorough sanitation of the abdominal cavity with antiseptics with anaerobic activity in case of its contamination [3, 6]. Tactics for uncomplicated appendicitis of the stump require further discussion.
Drug treatment or how to remove a scar after appendicitis
Sometimes a person does not stop at one method, but uses several at once. A quick effect is not always safe. Only your doctor knows which method of getting rid of a scar is right for you personally. Doctors base it not only on the external condition of the scar, but also on the characteristics of your body. Don't self-medicate! This may worsen the condition of the mark.
Ointments and gels
Such drugs are similar in the method of action, but different in the result. They reduce the density of connective tissue and its quantity. After the time specified in the instructions, the scar becomes less bright and convex. But there are several factors that influence the duration of treatment:
- condition of the scar (its age, location, size);
- your individual metabolism;
- tissue regeneration rate;
- susceptibility to external factors;
- degree of response to pathogens.
It is recommended to choose medications that contain collagenase. For example, using the anti-scar gel Fermenkol you can make a scar almost invisible. Fermenkol destroys pathological collagen, which is the basis of the scar, and restores a healthy skin framework.
Appendicitis and complications after it
23.06.2021
Almost every person knows about appendicitis
Problems begin when this part of the intestine becomes inflamed, leading to a dangerous acute condition that requires urgent medical attention.
It is noteworthy that due to a wide variety of reasons, medical assistance is often delayed, and the body has to cope with severe consequences.
The whole process has several stages, each of which is more dangerous and difficult than the previous one. If the patient does not consult a doctor time (and some rely more on painkillers), this will lead to the accumulation of pus, and due to the weak condition of the intestine, it can rupture at any time and then all this will fill the abdominal cavity, which will greatly complicate the situation and will create a health hazard.
There will be no consequences if a person manages to seek help in the first two days. A delay of 3 to 5 days can lead to the same intestinal ruptures, inflammation of the abdominal cavity and other problems.
If the inflammatory process continues for more than 5 days, then more serious consequences await the person:
- infiltration is a problem in which adhesions form between organs, which is why a person constantly feels pain, which also does not have a clear location. Ultimately, there may be two options: after the intervention, the adhesions will naturally resolve or the process will transform into an abscess;
- abscess - occurs when there is too much purulent accumulation in the appendix. As for the location, if the intestine is intact, then all processes take place in it, but if there is a rupture, then other organs also suffer;
- peritonitis or perforation - develop in acute appendicitis , but extremely rarely, however, with their development, the risk of death greatly increases, especially if surgical intervention is delayed;
- pylephlebitis is a problem in which the portal vein , which can result in the formation of a blood clot . Its symptoms include large bloating and general poor health. Also, due to an insufficient amount of blood the liver suffers , which is marked by unstable body temperature, and as a result, this can very well lead to death.
Moreover, even timely surgical intervention does not guarantee the absence of problems and consequences for the body, especially if it was carried out in the last stages.
consult a doctor if a person feels severe discomfort on the right side of the iliac region. Additionally, the temperature may rise, the digestion process may deteriorate, and sharp pain may be felt, which makes it impossible to move normally.
In such a situation, you can use only painkillers, after which you need to consult a doctor . If surgery , it is important to observe the recovery period.
Published in Surgery Premium Clinic
Hormonal drugs, patches or bandages?
Taking complex medications should be strictly under the supervision of a doctor. They are prescribed only after a careful diagnosis of the condition of your body and are used in the early stages of scar healing. The period of hormonal therapy can last from 6 to 12 months after the final epithelization of the wound.
The specialist injects 25–30 mg of the drug into the suture site. But if pathological symptoms develop, treatment must be stopped. And choose another method that suits you. If you are afraid of hormonal therapy or do not have the opportunity to be observed by a specialist, pay attention to silicone patches.
Patches are effective while the scar is fresh and just forming (up to six months), otherwise its use becomes ineffective. They relieve discomfort and moisturize scars. Under this influence, the injured area softens and gradually dissolves due to pressure on the damaged area. The patches do not destroy the scar, but prevent its growth, this is important. A bandage might be right for you.
This is an elastic medical belt that helps temporarily stop the formation of a scar. This is its spectrum of action. The bandage cannot reduce the scar or make it flat and less obvious. The belt is worn for no more than a year. Your doctor will give you exact recommendations.
Scar correction methods
For various reasons, for example, individual intolerance to the components, medications to remove the growth may not be suitable for you. What to do? Don’t go to the beach, always feel embarrassed about a flaw and have a complex? No, there are several alternative methods that can achieve very good results in the fight against scars.
Laser resurfacing
This procedure can only be used 6 months after the operation. Laser resurfacing will help even out the color of the damaged area and make the scar almost invisible. The downside is that this cannot be achieved in one session. It is necessary to undergo a course of several procedures. In some cases, scar recurrence is possible, so it is important to determine the type of scar in order to avoid unpleasant consequences.
Scar dermabrasion
The method is suitable for people with a low pain threshold. The procedure is carried out using abrasive substances. With their help, the top layer of damaged tissue is removed. In comparison, it looks like a very harsh peeling. Not everyone is able to withstand this kind of influence.
Tattooing
The method is popular among young people. This is an alternative method and easy camouflage of an ugly scar. The tattoo barely hides the skin damage and will not be able to cover the scar. If you want to get rid of the scar forever, then it is better to choose other correction methods.
Surgical intervention
Plastic surgery successfully copes with serious old scars. The doctor cuts the suture and creates a new one in the area where the appendix is removed. In some cases, adipose tissue is injected, this is necessary to obtain a thin cosmetic seam. After the operation, a thin, almost imperceptible strip remains.
The condition of the skin after removal of appendicitis depends, among other things, on the care, and not just on the work of the surgeon. It is important to monitor the scar, because its appearance directly depends on it.
You can purchase all Fermenkol products in our online store
Order online
Appendicitis in women: causes, symptoms, diagnosis
24.09.2019
Appendicitis occurs much more often in women This is due to the structural features of the body. The inflammatory process often begins during menstruation and is manifested by abdominal , nausea and vomiting. Every woman should know the symptoms of inflammation of appendicitis - this will help her avoid complications.
Reasons for appearance
The appendix is a lymphoid organ up to 5 cm long. It provides immune protection to the digestive organs. Most often, appendicitis occurs in women aged 20 to 40 years.
The causes of the disease may be the following:
- displacement of the appendix as a result of its compression by the abdominal organs. This situation occurs during pregnancy ;
- blockage of the organ with small debris (for example, seeds);
- clogging of the lumen with feces;
- poor nutrition;
- transfer of infection from the pelvic organs;
- inflammation of the lymphoid tissue in the appendix;
- infection through the blood or intestines ;
- individual structural features of the appendix.
To avoid the disease, women should:
- Healthy food. Foods high in fiber help eliminate the problem of constipation and improve digestion;
- support immunity . Taking vitamins, physical activity, hardening - protect the body from inflammatory diseases and prevent infection from getting into the appendix;
- fight allergies , which can greatly reduce immunity ;
- do not expose the body to emotional tension and stress.
First symptoms
The most common sign of appendicitis abdominal pain . It can intensify during movement, spread throughout the abdomen and radiate to the leg. The pain is pressing and pulling in nature, often moving from the right side to the left, and vice versa.
After some time, the woman begins to feel a low-grade fever. Typically it varies from 37 to 38 degrees. Feeling gradually worsens, nausea and vomiting appear.
Due to the fact that food is no longer digested normally, a person begins to experience diarrhea or constipation . of urination also increases significantly .
The first symptoms of appendicitis most often occur against the background of a normal condition.
Dangerous manifestations of appendicitis
Despite the fact that appendicitis is a common disease, it is not always possible to diagnose it yourself. Sometimes the symptoms of a disease manifest themselves differently and are interpreted incorrectly by a person.
A disease that is accompanied by complications can be recognized by the following signs:
- vomiting mixed with bile is a symptom of blockage of the bile ducts;
- black feces indicate the presence of blood ;
- increased gas formation - signals inflammation of the pancreas ;
- prolonged absence of menstruation .
The danger of these symptoms is that they can lead to serious complications and rupture of the appendix.
Diagnostics
As soon as a person has the first symptoms of the disease, you need to call a doctor .
Under no circumstances should you:
- drink water;
- carry out active movements;
- reduce the temperature with antipyretic drugs;
- use painkillers.
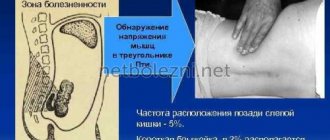
To make sure that the pain is a consequence of appendicitis , you can diagnose the pathology by palpation.
a flat surface and bend her knees . After this, she should gently press her fingers on the right side of her abdomen . If the pain intensifies during palpation, then the appendage is inflamed.
You can also detect inflammation of the appendix by loud coughing. If during a cough a woman feels pain in the area of the right ilium , this indicates confirmation of the diagnosis.
Appendectomy
It is impossible to cure inflammation of the appendix; the appendix is removed surgically .
There are two types of operations:
- emergency - carried out immediately after arrival at the hospital . The surgeon makes an incision on the right side of the peritoneum. After removing the appendage, a small scar remains on the body;
- planned - carried out a few hours after admission to the hospital . Elective surgery is performed on patients with any contraindications.
Further stay in the hospital is no more than 7-10 days. Rehabilitation after removal lasts until the doctor removes the stitches.
During this period, it is important to follow some recommendations:
- refuse to visit the bathhouse;
- do not expose the body to physical stress;
- do not lift weights weighing more than 2 kg;
- stick to a diet ;
- do not drink alcoholic beverages.
It is important for women to normalize their bowel movements, so they should drink as much clean water as possible.
Published in Surgery Premium Clinic