Encocution or fecal incontinence is a disorder in which the patient loses the ability to control the process of defecation. This condition does not threaten human life, but significantly worsens its quality. In most cases, the appearance of encoporesis in adults is associated with organic pathologies, including tumor processes and trauma. According to statistics, this disease is more often diagnosed in men.
What is fecal incontinence
Until recently, fecal incontinence was considered a common condition in old people in old age. However, upon closer examination of the problem, it turned out that they suffer from this disease at a younger age.
Interesting fact! About 50% of patients with this diagnosis are middle-aged men and women (over 45 years old). Less than a third of patients with encoporesis are elderly (75 years or older).
By this concept, doctors understand the inability to restrain the urge to have a bowel movement until the right moment arrives - going to the toilet. In this case, involuntary leakage of feces occurs, regardless of its consistency.
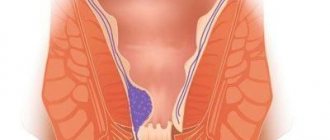
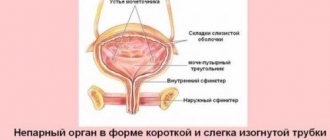
The mechanism of development of the disease is a disruption of the coordinated functioning of the sphincter and pelvic floor muscles, which hold feces in the rectum and maintain the intestines in tone. Normally, this occurs due to the activity of the autonomic nervous system, that is, the process of defecation without a conscious influence on the tone of the sphincter. It remains in a tense (closed) state during sleep and wakefulness. The average pressure in this area in men is slightly higher than in women, and the average values for this value are 50-120 mm Hg.
Stimulation of defecation occurs due to irritation of mechanoreceptors in the rectum. It occurs due to the filling of this section of the intestine with feces. In response to irritation, a person experiences a Valsalva reflex, in which he feels the need to take a position suitable for bowel movements (squatting), after which he begins to contract the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall. At the same time, the rectum reflexively contracts, pushing feces out.
If it is impossible for a healthy person to perform an act of defecation, the person voluntarily contracts the puborectal muscles and the anal sphincter. At the same time, the ampulla of the rectum expands, the urge to empty the bowel movement weakens. With encoporesis in adults, a failure occurs at one of the described stages, and feces freely exit the anus.
Types of fecal incontinence
There are several types of encocution in adult patients, depending on how exactly the stool leakage occurs:
- Constant (regular) incontinence without the urge to defecate. Most often, this type of disease occurs in children and elderly people who are in serious condition.
- Incontinence, in which, shortly before the leakage of feces, the patient feels the urge to defecate, but there is no way to delay this process.
- Partial incontinence, in which defecation occurs under certain stresses - coughing, sneezing, lifting heavy objects. In such situations, urinary and fecal incontinence is often observed.
Separately, age-related fecal incontinence is distinguished, which is diagnosed in elderly people due to degenerative processes in the body.
The classification of the disease also includes stages of progression of encoporesis. There are three in total:
Each type of encocution has its own characteristics. To begin treatment for this condition, the doctor will have to determine the causes of the pathology.
Types of disease
Encopresis usually develops gradually, passing through several stages. At the first stage, a person is not able to retain the gases accumulated there in the intestines. In the second stage, the rectal sphincter muscles become so weakened that they become unable to hold liquid stool. After this, the last stage develops, in which a person is unable to retain either solid or liquid feces in the rectum.
Also, during illness, one of the following disorders may occur:
- the appearance of feces without preliminary urges;
- strong urges arise, but the person cannot restrain them and feces are released;
- inability to contain the excretion of feces during moments of physical stress, coughing, sneezing.
Causes of encoporesis in adults
Various situations can provoke the development of fecal incontinence. In adults, the main causes of pathology are associated with diseases and dysfunctions of the pelvic organs, pelvic floor, rectum and other parts of the intestine.
The most common causes of incontinence in middle-aged and older patients are as follows:
- Constipation. If a person has bowel movements no more than 3 times a week, feces accumulate in the rectum, resulting in stretching and weakening of the sphincter muscles. The result of the process is a weakening of the holding capacity of the rectum.
- Traumatic changes in the sphincter muscles (external or internal). Occurs as a result of injury or after rectal surgery. As a result of such changes, muscle tone is completely or partially lost, and fecal retention becomes problematic or impossible.
- Failure of nerve endings and receptors in the rectum, as a result of which the patient does not feel that the rectum is full, or the body loses the ability to regulate the degree of tension of the internal and external sphincters. Childbirth, diseases and injuries of the central nervous system can lead to such problems. Often such disorders occur after a stroke or traumatic brain injury. Very often, such patients experience simultaneous urinary and fecal incontinence.
- Decreased tone of the muscles of the rectum as a result of the formation of scars on it and partial loss of elasticity of the walls of the organ. Such situations arise after surgery on the rectum, radiation therapy, ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease.
- Dysfunction of the pelvic floor muscles due to impaired nerve conduction or muscle failure. These may be disorders such as rectocele, rectal prolapse, postpartum weakening of the pelvic floor muscles in women. A common combination is episiotomy and fecal incontinence. The pathology is detected immediately after childbirth, which required dissection of the perineum, or several years later.
- Hemorrhoids often cause partial fecal incontinence. Hemorrhoids, especially if they are located under the skin around the anal sphincter, do not allow it to close completely. As a result, stool leaks. Over time, with a long and chronic course of the disease, progressive prolapse of hemorrhoids, the decrease in sphincter tone increases, and the symptoms of incontinence intensify.
Interesting fact! Experts have found that habitually holding back stool can weaken the anal sphincter and lead to stretching of the rectal ampulla. If you put off going to the toilet too often and wait for several hours at a time, you may eventually experience fecal incontinence.
A considerable proportion of diseases are caused by mental and psychological disorders. Loss of control over bowel movements occurs in patients with various forms of psychosis, schizophrenia, and neurosis. Sudden leakage of feces can occur during a panic attack or hysteria, or an epileptic attack. Patients with senile dementia also lose control over bowel movements.
Symptoms of true encopresis
True encopresis ( fecal incontinence ) occurs against the background of regular, independent bowel movements. The main symptom is stool anointing. Spotting occurs during physical or mental stress, and often for no apparent reason. The majority of the disease develops gradually, slowly progressing. In rare cases, it occurs quickly and ends in a short time. The clinical picture and course depend on the cause, the degree of change in the neuropsychic sphere, and the duration of the disease. Over time, the volitional act of defecation decreases and then disappears altogether. The child constantly has dirty underwear (underpants), the perineum is covered in feces, skin irritation in the perianal area (near the anus, anus) is often observed, and there is an unpleasant odor (stinks). On digital examination, the rectum is of normal size, the sphincter tone is reduced. Sometimes encopresis is combined with enuresis.
Diagnostics
To choose ways to treat fecal incontinence, the doctor will need to find out many things. To begin with, a survey is conducted during which the doctor finds out the characteristics of the condition:
- in what situation does fecal leakage occur?
- how long has this been observed and with what frequency;
- whether or not the urge to defecate is felt before leakage occurs;
- stool of what consistency cannot be held;
- the volume of excreted feces, with or without gas it comes out.
The specialist also needs to know whether there have been strong emotional shocks or traumas recently, whether there is confusion of thoughts or disorientation in space, what medications he is taking, what his diet consists of, whether there are any bad habits and whether incontinence is accompanied by additional symptoms.
To establish the exact picture and causes of incontinence, a complex of diagnostic instrumental studies is used:
- anorectal manometry to measure the sensitivity and contractility of the anal sphincter;
- MRI of the pelvis to visualize the condition of the pelvic day muscles and anal sphincters;
- defectography (proctography) to determine the amount of feces that the rectum is capable of holding, and to identify the characteristics of the bowel movement process;
- electromyography to study the correct functioning of the nerves responsible for the contractility of the anal sphincter muscles;
- sigmoidoscopy and ultrasound of the rectum, with which you can detect abnormalities in the structure of this part of the intestine, as well as detect pathological neoplasms (scars, tumors, polyps, etc.).
Additionally, patients are prescribed comprehensive laboratory diagnostics: blood, stool, and urine tests (general and biochemical). Only after this the doctor decides how and how to treat encoporesis.
Important! To eliminate fecal incontinence, it is necessary first of all to eliminate the diseases that cause weakening of the anal sphincter and pelvic floor muscles, and to get rid of associated pathologies.
Treatment methods for fecal incontinence
In adult patients, treatment of fecal incontinence requires a comprehensive approach. The patient is advised to review the diet, adjust physical activity, practice regular pelvic floor muscle training, take special medications, and avoid some medications altogether. Surgery is also used to eliminate this problem.
Drug therapy
Drug therapy is used mainly for incontinence, which occurs against the background of diarrhea. Several groups of drugs are used:
- anticholinergics, which include atropine and belladonna - to reduce intestinal secretion and slow down peristalsis;
- medications with opium derivatives (Codeine and painkillers) or Diphenoxylate - to increase intestinal muscle tone and reduce peristalsis;
- medications that reduce the amount of water in stool - Kaopectate, Metamucil, Polysorb and others.
Classic drugs like Loperamide and Imodium also have a good antidiarrheal effect. Prozerin injections and the drug Strychin help get rid of the manifestations of encoporesis. Taking vitamins (ATP, group B and others) will also be useful.
Important! To restore stool, patients with encoporesis are not recommended to take antacids, as well as medications that can cause diarrhea.
For mental and psychological problems, the patient is prescribed sedatives, sedatives and tranquilizers that help control behavior. They are released only with a doctor's prescription.
Diet
Doctors call diet therapy the basis of therapeutic measures for anal sphincter failure. Without compliance with certain nutritional standards, treatment will be ineffective. Main objectives of the diet:
- restoration of stool (exclusion of diarrhea and constipation);
- reduction in stool volumes;
- normalization of intestinal motility.
The first priority is to exclude from the menu foods that cause softening of the stool. These include sugar substitutes (sorbitol, xylitol and fructose), dairy products, especially whole milk and cheeses, nutmeg, alcoholic beverages, coffee. It is advisable to reduce to a minimum or completely eliminate hot spices, lard, fatty meats, and citrus fruits from the diet. You should also refrain from smoking.
Important! Patients are recommended to keep a diary in which they should record information about the foods they eat, the time they were taken and the volume of portions. It should also be noted at what moments incontinence occurs. This will help eliminate foods that irritate the intestines from the menu.
The basis of the diet should be cereals, fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grain bread or wholemeal flour. They contain a lot of fiber, which helps thicken stool. Fermented milk drinks without additives will also be beneficial. If there is a lack of fiber, the diet includes bran and whole wheat grain flakes. It is advisable to eat food often and little by little, up to 5-6 times a day. The intervals between meals should be equal.
Exercise therapy
A complex of special gymnastics (Kegl exercises) is used to strengthen the sphincter and pelvic floor muscles. It includes the following exercises:
- contraction and relaxation of the anal sphincter - repeat 50-100 times a day;
- retraction and protrusion of the abdomen - 50-80 repetitions per day;
- tension of the pelvic muscles in an inward and upward direction while sitting with crossed legs.
Such exercises strengthen the pelvic muscles equally well in men and women. They can be performed in several variations: quickly alternate between contraction and relaxation, hold the muscles in a tense state for 5-15 seconds and relax for 5-7 seconds, and so on. How to do exercise therapy using Kegl correctly is shown in the video:
At the initial stage, the doctor can connect special sensors to the patient’s body, which will indicate which muscles are involved in the work during exercises. This way you will be able to understand how to perform gymnastics correctly.
Patients recovering from a stroke are also shown a set of exercise therapy exercises, but in addition to the techniques described above, attention is paid to the development of fine motor skills. It will be useful for them to squeeze or roll small balls in their palms, do modeling, and put together mosaics from medium-sized elements. All this will allow you to quickly restore neural connections in the brain and get rid of the unpleasant consequences of the disease.
Important! Gymnastics does not give instant results. The effect becomes noticeable after a few weeks from the start of daily training, and is consolidated after 3-6 months.
Surgery
Surgical intervention is used when previously described methods are ineffective. This treatment works well after surgery on the rectum, which caused complications in the form of encoporesis, after injuries (including postpartum) and for incontinence caused by a tumor process in the rectum.
To eliminate the incompetence of the anal sphincter, use:
- Sphincteroplasty, during which the sphincter is reconstructed. This method is used for injuries to the muscle ring, its complete or partial rupture.
- Straight sphincter surgery, in which the sphincter muscles are attached more tightly to the anus.
- Installation of an artificial sphincter, consisting of a cuff that covers the anus and a pump that supplies air to the cuff. This device holds the anus closed, and if necessary, the patient deflates the cuff (releases air from it) to have a bowel movement.
- Colostomy, during which the large intestine is cut off and brought to an opening in the anterior abdominal wall. The stool is collected in a special bag called a colostomy.
The type of surgical intervention that will be applied to the patient is selected based on the causes of encoporesis. Only the attending physician can choose how to treat the disease.
How can a doctor help a child with colomasia?
The basis of treatment for retentional stool is to relieve the child of chronic constipation.
The methods have long been known and simple.
The main medications are laxatives (usually macrogol or lactulose) in sufficient doses for a sufficiently long period. The key word is enough !
The main mistakes of parents and even doctors:
- give a certain dose of laxative and not realize that the dose must be further adjusted according to the child’s reaction
- prescribe treatment for too short a period (unfortunately, constipation that has lasted for years cannot be cured in a month)
The value of other drugs (probiotics, choleretic drugs) is usually very small; their effect can be easily replaced with a slightly larger dose of a laxative.
Is diet (eating high in fiber) important?
I usually talk about a diet that is beneficial for stool (fruits, vegetables, whole grains), but in a real situation, when constipation is so severe that stools occur, the diet in treatment is of minimal importance. Talking about proper nutrition is more important for the future, when the stage of gradual abandonment of laxatives comes. Then nutrition will be part of the prevention of relapses, and then a component of the formation of a healthy lifestyle.
The defecation schedule is a very important part of working with stool.
The main recommendation is to put your child on the potty/toilet regularly soon after eating .
Why after eating?
We use for our own purposes the gastrocolic reflex , which everyone has to one degree or another. When food enters the stomach, a reflex signal goes to the large intestine - it’s time to make room for a new portion :-).
Schoolchildren are also advised to sit on the toilet after returning from school.
To consolidate your bowel habits, you can use a diary .
For parents of my youngest patients, I recommend using a beautiful, visual calendar. The child marks the day when he was able to fully relieve himself by gluing a smiley face or a star. If you collect a certain number of emoticons, you will receive a pre-agreed “bonus” from your parents. Motivation is awesome!
Treatment of non-retentive calomasia.
This option is much less treatable.
Laxatives are useless - there is no constipation at the heart of this type of constipation.
All that remains is the bowel movement regime and keeping a diary .
Sometimes medications that slow motility and improve the tone of the internal anal sphincter can be useful (they are often prescribed for diarrhea).
The most famous such drug is loperamide.
Unfortunately, experience with the use of loperamide in children is limited; close, confidential contact with the doctor is required when attempting to use it.
16, total, today
Tips for fecal incontinence in adults
The following tips will help you cope with the difficulties in everyday life that inevitably arise in patients with encoporesis:
- Before leaving the house, try to empty your bowels.
- It is worth planning walks and visits 1-2 hours after the main meal or later.
- Before leaving home, make sure that you have wet wipes and a change of clothes in your bag.
- If the risk of fecal leakage is high, it makes sense to use disposable underwear instead of regular underwear.
- When you are away from home, the first thing you should do is find out the location of the toilet room.
- Use special underwear or diapers.
Note! In pharmacies you can buy drugs that can help reduce the specific smell of feces and gases.
Anal sphincter incompetence is an extremely unpleasant disease that many patients prefer to keep silent about. The first step on the path to recovery is seeing a doctor. You can come to a therapist or proctologist with such a problem. If incontinence occurs after childbirth in women, they should consult a gynecologist. The sooner you pay attention to the pathology and take measures to eliminate it, the higher the chance of restoring the functions of the anal sphincter or at least preventing further progress of the disease.
There is no point in trying to correct the situation using folk remedies. Most of them are ineffective and sometimes downright dangerous. Even if you want to try to improve your condition through folk remedies, it is recommended to start taking them after consulting with your doctor.