General information
Nematodes are a type of multicellular animals belonging to protostomes and moulters.
There are more than 24 thousand species, which can be not only parasitic, but also free-living. At the moment, given the pace at which new species of nematodes parasitizing insects are being identified, it is estimated that there may be approximately a million species. In general, they are considered the most numerous type of roundworms, which are divided into 5 classes: the actual roundworms that parasitize humans, gastrociliary worms, kinorhynchus, hairworms and rotifers.
Features of the life activity of the free-living nematode
Free-living nematodes live mainly in soil, fresh water bodies and seas, where there are more than 25 of them per 1 cubic meter. They attach to the substrate using terminal tail glands, which also function as mechano-, chemo- and photoreceptors. The basis of nutrition is bacteria, algae and detritus. They are considered an important element of the saprophage complex of freshwater and marine biocenoses, and soil species take part in soil formation.
Representatives of free-living nematodes are an important link in ecosystems. Interestingly, individuals of the species Halicephalobus mephisto are the deepest living organisms on the planet.
The most common parasitic nematodes in humans
In addition to commensalism, nematodes have adapted to a parasitic type of coexistence with almost all large systematic groups and even protozoa. Thus, nematodes are known, not only from animals, but also from plants, in which roundworms lead to the death of roots, damage to root crops and the formation of galls.
Nematodes cause invasive diseases in humans and animals. The most common include ascariasis (ICD-10: B77), enterobiasis (B80), trichinosis (B75), and hookworm (B76).
Known animal nematodes
To date, it has been established that nematodes are capable of parasitism on all types of vertebrates. They penetrate into any tissues and organs, although most of them “populate” and parasitize in the thickness of the digestive tract. The greatest danger to humans is represented by domestic animals, which can become a source of nematode infection.
In cats, various types of nematodes can be identified - Toxocara mystax (feline roundworm), Ancylostomosis et uncinariosis, so it is very important in what conditions the animal is kept and whether it is wormed fairly regularly.
Golden potato nematode and other varieties of plant parasitic roundworms
Herbivorous nematodes are capable of infecting both shrubs and herbaceous and woody forms, regardless of whether they are wild or cultivated. As a result of the violation of the integrity of the root system by worms, favorable conditions are created for the penetration of pathogenic fungi, bacterial and viral infections into the plant. In addition, they slow down the process of emergence, growth and development of seedlings, leading to weak flowering, partial or significant death of young plants, reduction or loss of yield.
Golden potato nematode cysts
Golden potato, as well as beet and oat nematodes cause severe branching of the root system and rotting of small roots. There are also gall varieties of parasites that cause the appearance of various forms of galls and most often infect vegetable and industrial crops. Eels can provoke the development of “beaks” in the form of pointed swellings on the roots of wild cereals. Other manifestations of parasitic plant nematodes can be ulcers leading to the death of rhizomes, spindle-shaped thickenings of stems, underdevelopment and deformation of leaf blades, swelling of strawberry petioles, and the formation of dark spots of soft structure on potato tubers. There is no danger to humans.
Brief information about the structure and physiology of nematodes
The body size of nematodes, depending on the species and gender, can vary significantly - from 80 micrometers to 8.5 meters. The body structure is usually not segmented, filamentous, barrel-shaped, lemon-shaped or spindle-shaped. In general, they are distinguished by external sexual dimorphism; in the body of females there are 1 or 2 ovaries, an oviduct, a uterus, and they are capable of ovoviviparity or laying eggs, from which larvae hatch and molt several times. Species are known to be both dioecious and hermaphroditic. Males usually have a complex copulatory apparatus, supplemented by complementary organs for retention; the reproductive system consists of one or two testes, vas deferens and an unpaired ejaculatory duct.
Nematode organization diagram
Nematodes are roundworms, since in cross section their body is perfectly round, with bilateral or biradial symmetry, a developed musculocutaneous sac, covered with a multilayer cuticle of a smooth or annular type. Under the cuticle there is a symplast of the hypodermis and cords of longitudinal muscle fibers. There are known cases of syncytal structure of parasites, when there are no cell boundaries and the epithelium consists of cytoplasmic masses and nuclei included in them.
Cross-sectional structure of a nematode
The body is usually divided into a dorsal (dorsal), ventral (abdominal) and two lateral chords, nerve trunks, lateral sensory nerves, excretory canals, coelom and the primary body cavity - pseudocoelum. Inside there is a cavity fluid that creates a hydroskeleton and a container for organs. The digestive system is quite developed and consists of an oral cavity with three lips, as well as a pharynx, which can have various weapons, an esophagus, a foregut, a midgut and a hindgut, which opens with the anus in females and the cloaca in males. The oral capsule may be equipped with teeth, plates or other types of cutting elements.
There are no organs of the circulatory or respiratory system (the mode of existence is anaerobic by the type of fermentation) and most sense organs, as well as flagellar cell structures. The nervous system is represented by the peripharyngeal nerve ring and the ventral and dorsal nerve trunk extending from it, as well as longitudinal nerves not connected to it. The simplest tactile sense organs (sensilla) are tactile setae, labial or cephalic papillae, olfactory amphids, sensory glandular phasmids, etc.
What are nematodes
Nematodes are called roundworms that can live freely in nature or carry out parasitic activity in the body of humans, animals and plants. The most famous representatives of this class of helminths include:
- pinworms;
- roundworms;
- whipworms.
A large number of different nematodes are united into a separate group according to some characteristics specific to them:
- All representatives of nematodes have a round shape. Their body has respiratory, nervous, digestive, reproductive and nervous systems.
- When considering nematodes, it is possible to separate males and females based on shape and size. The first ones are usually smaller.
- All species develop through the same stages from larva to adult worm.
- Nematodes reproduce by laying eggs.
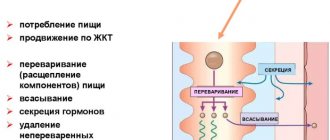
Pathogenesis
Parasites are able to penetrate and localize in most tissue structures and organs of humans and animals, most often in the gastrointestinal tract, muscles, lymph nodes and blood vessels, connective tissue, under the skin, in subcutaneous fatty tissue, in more rare cases - in the respiratory organs, in liver and kidneys. Worms are able to attach to the intestinal wall, damage its integrity, feed on its contents and blood, spread through the bloodstream, and also migrate throughout the body, thereby disrupting the structure of tissues. The clinical picture of helminthiases is caused by the mechanical, toxic and allergic effects of parasites, which:
- the enzyme produced - hyaluronidase, parasites are able to cause lysis of the walls of blood vessels and other structures;
- due to the mechanical effect on the intestinal mucosa, disturbances in the processes of parietal digestion, absorption and assimilation occur;
- the vital activity and migration of larvae causes inflammatory foci and hemorrhages in the small intestine, liver, bronchi and other tissues into which the larvae penetrate;
- intoxication with waste products.
The sexually mature stage usually occurs in the intestine. Females release a fairly significant number of eggs or larvae, for example roundworm up to 250 thousand per knock. They come out along with feces and can remain viable for years. For their further development, oxygen, a specific level of humidity and temperature are required.
Complications
If you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner and, accordingly, delayed treatment, complications are possible in the form of:
- intestinal obstruction, when a large number of parasites accumulate in its lumen;
- penetration of nematodes into the gallbladder and its ducts;
- intoxication of the body by waste products of parasites;
- appendicitis, when nematodes enter the appendix;
- entry of worms into the respiratory tract, resulting in possible mechanical asphyxia;
- peritonitis that occurs with liver abscesses and purulent cholangitis;
- helminthic infestation, which leads to various pathological processes in the body.
Classification
Depending on the characteristics of the life cycle, nematodes are divided into two groups:
- bionematoses - a group of diseases in which pathogens during their life cycle require vectors and a change of hosts, these usually include mosquitoes, midges, horseflies, crustaceans, etc.;
- geonematoses - when eggs or larval forms develop in the soil, water or on the surfaces of household objects.
There is also a separate group of contact helminths that are transmitted from person to person, for example, pinworms .
Characteristics of nematosis
Causes of helminth damage
The bulk of society infected with nematodes are mainly schoolchildren and preschoolers, because they do not follow the rules of their own hygiene. The helminth can infect a healthy person through manual contact, in a domestic environment, and orally. The main symptom indicating the presence of a parasite inside the body is severe itching of the anus. At night it becomes more intense and the infected person scratches it. Then the helminth eggs penetrate under the nail plates, then onto the bed, hands of a healthy person and other household objects. As a result, during a food meal, they move to a zone that is comfortable for them - the stomach - and begin to actively parasitize a healthy body.
Causes
The etiogenesis of nematodes in humans and animals is based on objects, soil, food, water contaminated with mature (invasive) eggs or larvae, which are ingested orally, that is, through the nutritional route. In addition, infection from vectors, for example from blood-sucking insects, from person to person is possible, for example, the spread of enterobiasis, especially in children's groups. For hookworms and strongylids , percutaneous penetration is also possible.
Symptoms of nematode
Single parasites may not cause symptoms for a long time and the disease is mild. But most often, various types of nematodes cause disturbances in organ systems such as digestive, nervous, reproductive, etc., but the most common symptoms are:
- indigestion;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- loss of appetite;
- fever;
- weight loss;
- itching in the anus;
- decreased performance;
- headache;
- restless sleep;
- dizziness;
- nausea with vomiting;
- weakness and deterioration in health;
- tachycardia and decreased blood pressure;
- allergic reactions and even anaphylactic shock .
Specific symptoms of necatoriasis
Necatoriasis caused by Necator americanus and hookworm (caused by Ancylostoma duodenale) are called hookworm disease and are characterized by significant disturbances of the circulatory system. Since worms of these species are hematophytes that feed on blood, they injure blood vessels with their cuticular teeth and secrete an anticoagulant, which causes ulceration, severe bleeding and, as a result, significant blood loss . Patients experience symptoms such as:
- chronic iron deficiency anemia ;
- dyspnea;
- lethargy;
- developmental delay in children;
- edema;
- diarrhea mixed with mucus and blood;
- representatives of the black race may develop depigmentation due to iron deficiency.
Treatment
Thanks to modern medicine, it is possible to cure most cases of nematodes in humans and animals, especially if the patient’s body is not in an extremely serious condition. For this, anthelmintics are used.
The doctors
specialization: Parasitologist
Fedosyuk Alexander Vasilievich
8 reviewsSign up
Find a doctor and make an appointment
Medicines
Piperazine Adipate
Dekaris
- Piperazine is a drug in tablets, usually prescribed for enterobiasis and ascariasis, as it has a paralyzing effect on pathogens. Daily dose 1.5-2 g - 2-5 days.
- Naftamon - the drug is used in cases of ascariasis, enterobiasis, trichuriasis, hookworm. The standard dose is 5 g per day, the duration of the course depends on the type of disease and can last from 1-2 days for ascariasis, and 5 days for trichuriasis.
- Decaris is a proven anthelmintic tablet that has a paralyzing effect on nematodes. Prescribed for ascariasis and strongyloidiasis 150 mg once.
- Mebendazole is a universal remedy for nematodes; the size of a single dose can range from 100 to 200 mg, depending on the severity of infestation.
Procedures and operations
For nematodes, pharmacological conservative treatment is usually prescribed, but in case of obstruction and swelling, for example, of the bile duct, the patient may need surgical intervention.
How to treat nematodes in humans
After diagnosis, the doctor, based on the test results, must prescribe therapy. The fight against nematodes in humans has a comprehensive approach, which includes:
- anthelmintics;
- special dietary regime;
- medications that normalize the body’s condition after the toxic activity of nematodes;
- folk remedies for helminths as prevention and additional assistance;
- tablets to cure nematodes in animals if a person has contact with them.
- Lytic mixture for children against fever. Composition and dosage of the lytic mixture in tablets and ampoules
- Knitted manicure - photo. How to make a sweater design on nails with gel polish step by step at home
- Washer and dryer - rating of the best with price. How to choose a washing machine with drying function with reviews
Medicines for helminths
An important and mandatory aspect of antiparasitic therapy is taking special tablets against nematodes, which should be prescribed by a doctor after determining the type of helminths. There are broad-spectrum and narrow-spectrum medications. The first group of tablets can kill several types of parasites, the second - a specific one. There are medications for nematodes that are used once, while others require a course of treatment. Any medicine for worms must be prescribed by a doctor so as not to cause negative effects.
Traditional treatment for helminths at home
Deworming tablets for humans are very toxic drugs. Many doctors recommend using enemas with soda or garlic, or herbal infusions. Among the variety of natural medicines for nematodes, we can highlight:
- An alcoholic tincture of ginger for helminths can be easily prepared by taking 0.5 kg of grated root and 0.5 liters of vodka. The ingredients must be mixed and left to infuse for 2 weeks. The process must take place inside a dry room. You need to take the infusion 1 tsp. three times a day, half an hour before meals. Treatment with the drug requires 14 days.
- Onion infusion is an effective remedy for human parasites. Peel 1 head and cut it into small cubes. Pour boiling water over the vegetable pieces. The deworming infusion will form overnight. It must be drunk in the morning on an empty stomach. Application cycle – 5 days.
- Tansy, wormwood and celandine are suitable for preventing the occurrence of worms in the body. Form a collection of these herbs: take celandine ½ tsp, tansy flowers - 1 tbsp. l. and the same amount of wormwood. Powder from plants against helminths should be taken a tablespoon in the morning and evening, on an empty stomach, with warm water.
Prevention
The main methods of preventing nematodes include:
- compliance with such simple hygiene rules as washing hands after walking outside and contacting animals, as well as before eating, changing clean underwear;
- preservation and sufficient processing of vegetables, fruits and others, preventing the possibility of penetration of cockroaches, flies and other insects;
- sanitary education work among the population;
- quality pet care;
- sanitary agrotechnical and household safety provision.
During pregnancy
Nematodosis during pregnancy is an extremely dangerous condition, both for the woman and for the unborn child, because invasion can occur through the placenta and even milk.
It is very important not to confuse the signs of helminthiasis and early toxicosis. Chronic nausea with vomiting, dizziness, fainting, and heart pain may be a cause for alarm. Most likely, these are signs of ascariasis or enterobiasis . They not only worsen a woman’s well-being, but also have a toxic effect on the fetus and can cause asphyxia and premature labor.
Peperazine is considered the safest drug for pregnant women , but an additional laxative can be prescribed to more quickly evacuate worms from the intestines.
FAQ
Are free-living nematodes dangerous for humans?
Worms living in an aquarium do not harm humans. This type of nematode is adapted to life only within the aquarium ecosystem.
Is it possible to become infected with parasitic nematodes?
You can become infected by eating contaminated raw fish or by ignoring hygiene rules.
Can purchased fish be immediately placed in an aquarium if it does not show signs of worm infection?
No, this cannot be done, even if the individual looks healthy. First, she is placed in quarantine, and only after making sure that she will not harm other residents is she moved to a permanent place.
Diet for nematodes
Diet for anemia
- Efficacy: no data
- Time frame: 3 months
- Cost of products: 2700-3200 rubles. in Week
Most nematodes significantly poison and weaken the human body, so the diet if such an unpleasant illness is detected should be aimed at improving health and restoring strength, while fully providing fats and carbohydrates in proteins. If someone in your family has helminthiasis, then in addition to worming you should:
- eat healthy food - do not fry it, do not eat spicy, smoked, etc.;
- give up street food, alcohol, caffeine and white sugar;
- calculate and consume the daily intake of dietary meat, vegetables and fruits, taking into account the patient’s body weight and physical activity;
- introduce porridge, whole grain baked goods or pasta, herbs, onions and garlic, high-quality vegetable oil, seafood, dairy products, dried fruits, nuts, seeds and other healthy ingredients into your diet.