It is a well-known fact that it is undesirable to eat fatty, spicy and salty foods. But, unfortunately, only a few try to adhere to the recommendations of nutritionists. The rest remember the rules of healthy eating only when it gets late or very late.
Girdle pain in the hypochondrium, general poor condition - this is a reason to urgently contact a medical facility. After all, similar symptoms are caused by pathologies of the pancreas.
Necrosis. Definition and reasons
The cause of necrosis is pancreatitis.
What is necrosis or pancreatic necrosis? This is the death of areas or an organ as a whole.
Necrosis is not a clinical diagnosis, since it is not established by the attending physician, but, as a rule, by a pathologist in the morgue.
This condition develops as a complication of the destructive form of pancreatitis.
The cause of the disease is pancreatitis, but the factors causing this pathology can be considered the cause of organ necrosis. What causes this pathology:
- alcohol in high doses and regularly;
- excess fatty and heavy foods in the diet;
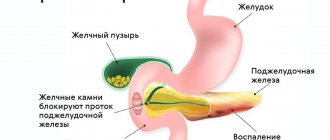
- pathologies of the bile ducts;
- surgical intervention on the peritoneal organs.
As a rule, an acute attack of the disease occurs spontaneously after libations and a belly celebration. It is extremely rare that pancreatitis develops due to other reasons:
Treatment with folk remedies
When a patient's pancreatic necrosis worsens, he experiences severe pain. Folk remedies that are used in parallel with the main treatment can help improve the condition a little. But, before practicing such methods, it is necessary to visit a doctor, establish a diagnosis and begin practicing the correct treatment regimen.
- The fruits of Japanese Sophora - a decoction is prepared from them. A spoonful of raw materials should be filled with 1 tbsp. boiling water and leave for 5 hours. Drink warm before every meal. The course of treatment is 10 days.
- Blueberry berries and leaves - a decoction is prepared from them by pouring boiling water over dried or fresh raw materials and boiling for 5 minutes. (2 tbsp. raw materials per 250 ml of water). Drink instead of tea.
- Immortelle herb - a decoction helps relieve pain and inflammation. To prepare the decoction, take 1 tbsp. l. dry herbs and a glass of water, cook for 5 minutes. Strain the resulting broth and drink throughout the day.
- Oat decoction helps relieve irritation and restore organ cells. To prepare the product, you need to soak the grains and wait a few days for them to sprout. Sprouted grains need to be dried and ground. Pour the mixture with cold water (1 tablespoon of oats per 1 glass of water) and leave for about half an hour. You need to drink 2 glasses of this product a day.
- Lemon – helps reduce pain. To do this, boil the lemon in water for 5 minutes, then squeeze the juice out of it and mix with raw yolk. Drink the product on an empty stomach and do not eat for three hours after it. Take it five times a day, once every three days. The course of treatment lasts several months.
- Licorice root - to prepare it you need to take 1 tbsp. l. chopped dry licorice root, the same amount of dandelion and burdock leaves. Pour the mixture with 2 cups of boiling water, drink the infusion hot, half a glass 3-4 times a day.
There are also special herbal mixtures used to treat the pancreas. But it is important to take into account that they bring benefits to the body if such preparations are taken regularly and according to the scheme approved by the doctor. Under no circumstances should you practice self-medication with folk remedies for such a terrible diagnosis as pancreatic necrosis.
Pancreatic necrosis. Classification
There are 3 types of pancreatic necrosis.
Pancreatic necrosis is an emergency.
Any predictions about the patient’s condition are made based on the type of pathology. The following types of pancreatic necrosis are distinguished:
- small, medium and large-focal - diagnostic criteria differ little and the diagnosis depends on the degree of damage to the gland;
- subtotal – almost the entire organ is affected;
- total - this diagnosis is made by a pathologist, since the patient dies in 100% of cases.
According to the degree of damage by pathogenic microflora, sterile and infectious necrosis are distinguished.
In the second type of necrosis, the prognosis is unfavorable, as toxins immediately enter the systemic circulation, and the patient develops sepsis and multiple organ failure.
Symptoms, diagnosis of acute pancreatitis, pancreatic necrosis
The disease begins with acute pain in the upper abdomen, radiating to the hypochondrium, often of a girdling nature. Patients are concerned about nausea, weakness, and often experience repeated vomiting. The general condition depends on the extent of damage to the pancreas: from satisfactory with edematous pancreatitis, to extremely severe with large-focal and subtotal pancreatic necrosis. On examination, tachycardia is characteristic, palpation in the upper abdomen is painful, with pancreatic necrosis there may be local tension in the abdominal wall muscles (defense) and a positive Shchetkin-Blumberg sign. In severe pancreatic necrosis, the symptoms of toxic shock quickly increase - pale skin, severe weakness, decreased blood pressure, etc.
A laboratory study reveals an increase in the number of leukocytes in the blood (leukocytosis), often with a shift of the leukocyte formula to the left, and a decrease in lymphocytes. Characterized by an increase in amylase in the blood and diastase in the urine.
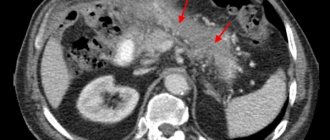
Ultrasound is considered an informative method for diagnosing acute pancreatitis. Ultrasound reveals an increase in the size of the pancreas, unevenness, and unclearness of its contours; there may be a small amount of fluid around the gland; in later phases, necrosis in the gland tissue and accumulation of pus can be seen with purulent complications. If the ultrasound picture is unclear, a computed tomography scan is performed.
Pancreatic necrosis. Mechanism of disease development
Speaking figuratively, the reason for the development of necrosis is the body’s digestion of itself. Due to excess alcohol and food, premature activation of digestive enzymes occurs. Normally, these substances begin to work only upon contact with bile.
The digestion process begins in the intestines. If the enzymes do not have time or cannot leave the pancreas, then they begin to break down the tissues of the organ.
The enzymes that break down fats begin to work first. Then - breaking down protein compounds. As a result, the pancreas dies.
Watch a thematic video about pancreatic diseases:
Symptoms and stages
Acute pancreatic necrosis is determined by the following signs:
- severe pain in the left hypochondrium, which can radiate to the side, shoulder, back or heart area;
- vomiting with blood and bile, which does not bring relief;
- severe intoxication;
- respiratory dysfunction;
- signs of renal and liver failure;
- unstable mental state: increased excitability, lethargy, inappropriate reactions.
Depending on the extent of the damage, three stages of the disease are distinguished:
- Focal - necrosis has a point nature, most of the gland retains functionality. The focal form is treated with conservative methods.
- Subtotal form - about 60–70% of the gland is affected. In such cases, doctors can resort to both conservative methods and surgical intervention.
- Total pancreatic necrosis means 100% damage to the organ; urgent surgical intervention is indicated.
Treatment of this pathology
Hospitalization in the surgical department is the best treatment strategy.
The recovery statistics for patients with this disease look unsightly. But the treatment must be carried out in full.
Then the patient has a chance of recovery. Therapeutic tactics for pancreatic necrosis:
- hospitalization in a surgical or intensive care unit;
- administration of drugs that block the release of digestive enzymes;
- complete refusal of food for several days;
- elimination of dehydration orally or intravenously;
- if liver function has not recovered and the bile ducts are blocked, then intravenous feeding is indicated for a long time;
- hemosorption – toxic substances should be removed from the blood;
- the drug “Somatostatin” is indicated for use;
- antibiotics for the infectious nature of the disease.
In severe cases, surgery is indicated. A strict indication for surgery is infection of the organ and lack of response to conservative therapy.
If the pathology is sterile, the indications for surgical treatment are the failure of drug treatment, a high probability of infection of the organ, and the spread of necrotic processes to other organs of the peritoneum. Surgical treatment is divided into 3 types:
- Emergency – within 24 hours from the moment the patient is admitted to the hospital.
- Urgent – carried out if the situation does not improve within 72 hours.
- Late - prescribed within 14 days of hospitalization if conservative therapy does not bring relief.
The complexity of surgical treatment lies in the lack of a unified method of indications for the intervention and its timing. Returning to normal life after surgery depends on the patient’s behavior, since the diet will have to be followed for life.
Often, patients with pancreatic necrosis develop diabetes due to impaired insulin production.
Pathogenesis
The basis of the pathogenesis of pancreatic necrosis is a failure in the mechanism of internal protection of the pancreas from the influence of pancreatic enzymes that destroy it. If a person drinks alcohol heavily and constantly overeats, external secretion increases significantly, the ducts of the gland are stretched, and the outflow of pancreatic juices is disrupted.
Necrosis of the pancreas develops against the background of pancreatitis - an inflammatory process of the pancreas, in which the death of part or the entire organ often occurs.
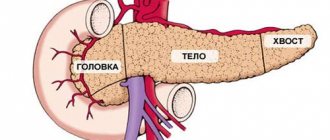
The pancreas is an organ important for the normal functioning of the body. Its main functions are the production of the main enzymes involved in digestion, as well as the regulation of blood sugar due to the production of the hormones insulin and glucagon . Accordingly, dysfunction of this organ leads to serious disturbances in the general condition of the body.
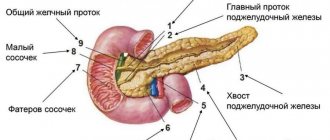
When a person feels hungry, juices and enzymes are transported through the connecting duct into the small intestine, which ensures enzymatic processing of food. Pancreatic fluid acts on the acidic environment of gastric juice, neutralizing it. In the intestines, digestive enzymes break down and process substances.
The pancreas produces the main digestive enzymes:
- lipase – breaks down fats;
- amylase – converts starch into sugar;
- chymotrypsin , trypsin - are involved in the breakdown of proteins;
- glucagon , insulin , polypeptide , etc.
If in healthy people the enzymes produced by the pancreas are active directly in the digestive tract, then in patients with damage to the ducts of the gland, the enzymes directly affect the pancreas. Against the background of increased pressure inside the ducts, edema of the parenchyma develops, the acini of the pancreas are destroyed, and proteolytic enzymes are activated prematurely. As a result, the gland “poisons” itself. Due to the activation of lipase, necrosis of fat cells occurs, under the influence of elastase, blood vessels are destroyed, and activated enzymes, as well as breakdown products, end up in the bloodstream. In this case, there is a toxic effect on all tissues and organs. First of all, damage occurs to the liver, kidneys, heart, and brain.
With pancreatic necrosis, three stages of tissue death are determined:
- Toxemic - toxins of bacterial origin appear in the blood, the gland actively produces enzymes.
- Development of an abscess - a purulent inflammatory process of tissues and organs that surround the pancreas develops.
- Purulent changes in tissues - if purulent sepsis develops, immediate surgical intervention is required, as this condition is life-threatening.
How is diagnostics carried out?
To diagnose the disease, doctors resort to the following methods:
- blood and urine test for alpha-amylase enzyme;
- Ultrasound of the pancreas, during which you can see swelling and affected areas;
- computed tomography, during which you can examine the heterogeneity of pancreatic tissue;
- Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive procedure during which it is possible to detect organ swelling, record the inflammatory process and differentiate the type of pathology.
Is surgery necessary for pseudocyst?
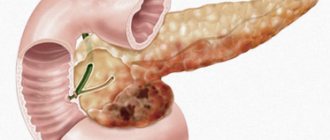
Pseudocyst is a consequence of an acute inflammatory process in the pancreas. From a physiological point of view, a pseudocyst is a cavity that has not received a formed membrane, and inside it there is pancreatic juice.
Some people mistakenly believe that such a diagnosis is cancer, but in fact, getting rid of it is much easier than when diagnosing oncology. This even applies to situations where impressive accumulations of up to 5 centimeters in diameter are discovered.
If you do not help the patient at this stage, he will soon face numerous complications, which are expressed in:
- compression of surrounding tissues or ducts;
- chronic pain;
- suppuration up to the formation of an abscess;
- vascular erosions with bleeding due to exposure to aggressive digestive enzymes;
- breakthrough of accumulations into the abdominal cavity.
Such sad scenarios are confirmed by numerous reviews from those who have already gone through such a difficult test. To alleviate their condition, they were prescribed:
- percutaneous external drainage;
- excision of pseudocyst;
- internal drainage, which is based on creating an anastomosis of the cyst with the stomach or a loop of the cyst.
One of the options presented above is selected solely on the basis of analysis results.
Popular questions about pancreatic necrosis
What kind of disease is pancreatic necrosis?
Pancreatic necrosis is a serious, life-threatening complication of acute pancreatitis, in which pancreatic tissue partially or completely dies. The condition is accompanied by severe intoxication and can lead to multiple organ failure and death.
How does pancreatic necrosis begin?
Pancreatic necrosis usually appears several hours after drinking alcohol or overeating. The first symptoms of the disease are pain in the left hypochondrium, radiating to the side, shoulder, arm, back or heart area. Acute pain is accompanied by severe intoxication, intestinal upset, and vomiting.
How long can you live after surgery for pancreatic necrosis?
Mortality during surgical intervention for pancreatic necrosis is about 50% of cases. If the patient undergoes the operation safely, he has a chance to live a full life, however, following a strict diet.
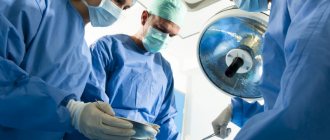
Surgery
The operation involves removing dead tissue and cleaning the abdominal cavity. Intervention is indicated if the patient has a total or subtotal infection of an infectious nature, a purulent abscess, false cysts, or peritonitis.
If the disease proceeds without infection, surgery is avoided.
Surgeons prefer to resort to minimally invasive techniques, since open abdominal surgery has a high mortality rate and is often accompanied by secondary infection.
What operations are performed for chronic pancreatitis?
Some patients believe that with diabetes mellitus, along with the concomitant destabilization of the gland due to chronic pancreatitis, only surgery will help. But experts warn that with such a pancreatic condition, one can only hope for relief, and not for a complete recovery without the risk of relapse.
To help victims of the chronic form of such a dangerous disease, doctors have developed several surgical practices:
- drainage of ducts, which is necessary in case of pronounced problematic patency;
- resection with drainage of the cyst;
- resection of the head, which is characteristic of obstructive jaundice, duodenal stenosis;
- pancreatectomy for large-scale lesions.
The stones that are deposited in the ducts deserve special attention. They partially or completely block the passage of secretions, which provokes acute pain. In case of severe pain and the impossibility of reducing its manifestations with the help of pharmacological substances, there is no other option other than classical surgery.
This technique is called virsungotomy. This means cutting the duct to remove the stone, or draining above the level of obstruction.
Causes of pancreatic diseases
A quarter of all cases of acute pancreatitis and pancreatic necrosis occur due to overeating and alcohol abuse. The causes are infections: viral, bacterial, fungal, parasitic.
Scientists have noticed an increasing trend in the incidence of chronic pancreatitis, with a decrease in the average age of patients, from 50 to 39 years. The most common causes of the disease:
- excessive consumption of protein and fatty foods;
- long-term use of a number of medications;
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract and liver;
- metabolic disorders;
- developmental anomalies;
- autoimmune diseases.
Acute and chronic pancreatitis lead to the formation of gland cysts - cavities inside which pancreatic juice accumulates. They disrupt digestive functions, cause inflammation and pain.
Pancreatic diseases can be congenital, appearing in infants. They occur in children due to food allergies and genetic disorders (cystic fibrosis, celiac disease).