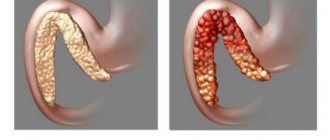
The quality of feces, like the process of defecation itself, is an indicator of human health. Ideally, everything should happen every day, at approximately the same time, quickly and without causing discomfort.
Any inclusions in the stool - blood, mucus, undigested pieces of food - a change in color should alert the patient. If the temperature rises, vomiting occurs and the general condition worsens, self-medication and self-diagnosis are inappropriate.
A little about blood and diarrhea
Diarrhea is a signal of disruption of the gastrointestinal tract
Minor diarrhea without additional symptoms does not cause significant harm to human health. If 4 episodes of bowel movements have passed within 24 hours and the condition has returned to normal without drug therapy, then there is no need to worry.
The appearance of inclusions in stool is a reason to think and pay attention to your own health.
A small amount of blood is excreted in the feces. The norm is considered to be up to 4 ml per day. But the appearance of visible impurities or clots in feces is a sign of a pathological process. If additional symptoms are added, then you need to urgently contact a medical facility.
Treatment
If this symptom occurs, timely treatment must be started. Otherwise, diarrhea can become chronic and lead to severe dehydration.
What to do
Treatment of diarrhea after alcohol involves complete abstinence from alcohol. It is necessary to help the body get rid of toxins and carry out high-quality detoxification. If vomiting does not occur after 2-3 hours after intoxication, you must induce it yourself.
What to drink
You should take the following medications:
- Enterosorbents: “Enterosgel”, “Activated carbon” or “Smecta”;
- "Regidron" to restore water-salt balance and combat dehydration.
It is important to drink plenty of fluids to remove toxic substances from the body.
How to stop
Avoiding strong drinks, taking enterosorbents, drinking plenty of water and an appropriate diet will help restore normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. If white feces, hallucinations, yellowing of the skin and hyperthermia appear, you should urgently call a doctor.
Diet
After the feast, it is necessary to limit food consumption for 12 hours. A diet containing strengthening foods (rice, crackers, etc.) will help normalize the condition of feces and alleviate the general condition of a person. The consumption of confectionery products, baked goods, tea, coffee, fried and fatty foods is prohibited.
Possible reasons
The appearance of impurities in feces always indicates pathological processes occurring in the body. Possible reasons:
- internal hemorrhoids;
- injury to the hemorrhoid during defecation;
- damage by pathogenic flora - such impurities in feces occur when infected with salmonella, the causative agent of dysentery;
- enteritis of various etiologies;
- colitis with the formation of areas of necrosis and ulceration;
- dysbacteriosis;
- ulcer in the upper gastrointestinal tract;
- carcinoma of the stomach, duodenum, other parts of the intestine, and rectum.
Examination of stool, examination by a proctologist, gastroenterologist, or surgeon will help make the correct diagnosis. During the examination, the doctor will take into account additional symptoms and the nature of bowel movements.
How to avoid diarrhea?
In order to prevent the above problems, parents need to know that careful adherence to basic preventive measures related to proper nutrition and hygiene will help to avoid them. The child should have a healthy diet appropriate for his age. Check the expiration date of products, exclude all products with artificial colors and additives, as well as sausages, especially smoked ones, mushrooms and seafood.
- Strengthen your children's immunity every day.
- Carefully observe the rules of hygiene and teach your child to follow them; wash your hands and fresh vegetables, berries and fruits before eating.
- The child should drink only boiled water.
- You cannot swim in prohibited areas.
- Avoid contact with infectious patients.
- Follow a diet for nursing mothers.
- Cook meat, fish, eggs and milk.
Therefore, parents should identify it as quickly as possible and seek help from a doctor who will promptly make the correct diagnosis and prescribe all the necessary treatment.
Blood color and diarrhea
When veins or clots of biological fluid appear, you need to pay attention to their color and quantity. During examination, this information is reported to the doctor, as this makes it possible to suggest the cause of the pathological process and speed up diagnosis.
| Color, quantity | Possible reason |
| Scarlet. | Injury. Haemorrhoids. Cracks in the anus, rectum. |
| Black, black clots. | Upper parts of the gastrointestinal tract. |
| Black in large quantities. | An open or perforated ulcer in the upper gastrointestinal tract. |
Mucus and blood in feces
Examination of stool will allow medical professionals to narrow down the list of possible causes of the disease. If, in addition to blood, mucus is found in the stool, this suggests:
- colitis with the formation of ulcers;
- neoplasm of malignant origin in the gastrointestinal tract;
- tuberculosis;
- Treponema pallidum infection;
- aggressive allergic reaction to food.
If you have this type of diarrhea, you should contact a medical facility. Taking a sufficient amount of fluid or using medications for rehydration is indicated on your own. You will have to give up food, at least for 1 day. This will reduce the load on the digestive organs.
Blood in vomit and stool
Diarrhea with blood is an alarming symptom
The appearance of such symptoms is not always a sign of damage to the gastrointestinal tract. What will the doctor suggest in this case:
- Poisoning, both food and pesticides, herbicides, household chemicals. The route of penetration of toxic substances can be inhalation or transdermal.
- Diseases of the nervous system.
- Infectious diseases - when additional symptoms appear and the temperature rises to 38 degrees.
- Rotavirus most often affects children, but adults are not immune from this pathogen. The temperature with rotavirus can reach critical values.
- Colitis - due to errors in nutrition. Accompanied by epigastric pain.
- Gastritis.
- Cholecystitis, pancreatitis, impaired motility of the bile ducts. These diseases, in addition to diarrhea with various impurities, are accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and a bitter taste in the mouth.
First aid for bloody diarrhea
What to do if a child has bloody diarrhea? First of all, you need to call a doctor or ambulance. Before their arrival, to alleviate the condition and prevent dehydration, older children should alternately be given a little sweet tea and salted water every 5-10 minutes. Infants need to be put to the breast more often. It is also important to limit your food intake until further instructions from your doctor.
* Among products based on Loperamide. Based on sales in money for February 2022 - January 2022, according to IQVIA (from English IQVIA).
Green feces and blood
A change in the color of stool is an additional sign of the presence of a pathological process in the gastrointestinal tract. Possible reasons:
- food poisoning;
- consumption of foods with food dyes;
- in rare cases, this shade of stool is caused by excessive consumption of green leafy salads and vegetables;
- dysentery - accompanied by an increase in temperature, vomiting, and blood in the stool;
- metabolic disorders;
- increased hemoglobin level;
- intoxication with glandular preparations, overdose;
- microflora disturbance during antibiotic treatment. In this case, flatulence and epigastric pain occur.
Causes of bloody diarrhea in a child
Loose stools with blood in a child are not an independent disease, but a set of symptoms that accompany the course of various pathological processes. In this situation, diarrhea, which has a number of age-related characteristics, may vary in the frequency of bowel movements and the volume of feces. This is primarily determined by the nature of the disease that caused it and the localization of intestinal bleeding.
The most common causes of bloody diarrhea in a child include:
- acute intestinal infections (dysentery, salmonellosis, escherichiosis, Proteus/staphylococcal/rotavirus infection, etc.);
- parasitic diseases (amoebiasis, giardiasis, helminthiasis);
- intolerance to cow's milk, soy (can develop in formula-fed infants);
- reaction to certain medications;
- internal hemorrhoids (a consequence of congenital dilatation of hemorrhoidal veins, prolonged sitting on a potty, strong prolonged crying, etc.);
- juvenile polyps (benign neoplasms). Identified at the age of 4–7 years. When introduced into the intestinal lumen, they can cause mild diarrhea with blood in a child;
- Crohn's disease (chronic inflammatory bowel disease);
- ulcerative colitis (inflammation of the colon mucosa). Usually occurs in school and adolescence, less often in children of the first year of life;
- systemic lupus erythematosus (autoimmune pathology of connective tissue and blood vessels). In some cases, it may be accompanied by diarrhea streaked with blood.
Scarlet blood
Hemorrhoids are the cause of bleeding
The addition of bright scarlet blood to diarrhea is a sign of bleeding from the lower gastrointestinal tract. The doctor will suggest:
- fissures in the anus;
- the appearance of fistula tracts, paraproctitis;
- damage to hemorrhoids;
- the presence of malignant neoplasms in the rectum, large intestine;
- erosion of various origins;
- perforation of the ulcer.
Depending on the intensity and volume of bleeding, the patient may complain of dizziness, weakness, and pain. As a rule, the temperature does not rise.
Causes of watery diarrhea
Faecating with water often indicates infectious or non-infectious intestinal diseases. Sometimes pregnant women complain about the appearance of liquid, unformed feces, which is caused by gestational changes in the digestive and endocrine systems. In children, watery stools can be a sign of a toxic form of dyspepsia or the initial stage of colitis. Water diarrhea with dyspeptic disorders, weakness, hemorrhages is characteristic of alimentary-toxic aleukia. Profuse diarrhea occurs in 90% of patients with toxic shock.
Bacterial infections
The entry of pathogenic intestinal microflora into the body is usually accompanied by watery diarrhea of the secretory type. Bacteria are capable of secreting a specific enterotoxin that affects the epithelial cells of the mucosa and causes the accumulation of adenylate cyclase, cAMP, in them. This contributes to an increased release of ions into the intestinal lumen with subsequent entry into the intestines along a concentration gradient of a large amount of liquid. The condition is aggravated by concomitant inflammatory lesions of the gastrointestinal tract. The following intestinal infections lead to water diarrhea:
- Cholera
. This infectious disease manifests itself with diarrhea, which quickly loses its fecal character and odor, becoming watery. After a few hours, repeated vomiting occurs, which aggravates the condition, causing severe dehydration. A distinctive feature is the complete absence of abdominal pain or moderate discomfort, detected in no more than 30% of patients. - Escherichiosis
. Watery diarrhea often develops when infected with enterotoxigenic strains of the microbe, when the disease proceeds like a mild version of cholera. In young children, water diarrhea is usually caused by enteropathogenic strains. Diarrhea is combined with vomiting, pain in the epigastrium, along the intestines. Body temperature may rise to subfebrile levels. The general condition of the patients is of moderate severity. - Salmonellosis
. Dyspeptic disorders are the main manifestations of the gastrointestinal form of infection. The first symptoms of salmonellosis are general intoxication and headache; after a few hours, severe cramping pain in the intestines occurs, profuse bowel movements, first with the release of unformed feces, and then water with food particles and mucus. Greenish foamy stools (“swamp mud”) are characteristic. - Botulism
. With the gastroenterological variant of the infection, dyspeptic symptoms come to the fore: watery diarrhea, repeated vomiting, cramping abdominal pain. Patients complain of dry mouth and a feeling of a lump in the throat. Botulism is characterized by ocular manifestations: double vision, flashing “spots” before the eyes, blurred vision. In severe cases, paresis and paralysis of facial muscles with facial asymmetry are observed. - Campylobacteriosis
. The disease begins acutely with a rise in temperature to 38° C or more, pain in muscles and joints. Repeated diarrhea immediately follows with the release of liquid, foul-smelling feces, in which streaks of mucus and blood are revealed. Patients often complain of abdominal cramps, while nausea and vomiting occur in only a quarter of patients with campylobacteriosis.
Viral infections
Dyspeptic disorders, in particular watery diarrhea, are considered the main manifestations of most viral intestinal infections. When viruses enter the gastrointestinal tract, they multiply inside epithelial cells, causing their death and desquamation from the surface of the mucosa, which leads to impaired parietal digestion and diarrhea. Pathogens also slow down the processes of reabsorption of water from the intestinal lumen, which causes profuse diarrhea. The most common viral diseases affecting the intestines:
- Rotavirus gastroenteritis
. Watery stools are the main manifestation of rotavirus infection. In the mild version, the frequency of defecation is up to 10 times per day, the stools are fecal in nature, in the severe case the leading one is profuse diarrhea with the discharge of a turbid, foul-smelling yellow-green liquid. Diarrhea is combined with cramping pain in the umbilical region, low-grade fever. - Norovirus infection
. Norovirus is characterized by simultaneous damage to the respiratory and digestive systems. The disease begins with a sore throat, nasal congestion, then dyspepsia occurs - watery bowel movements, vomiting, abdominal pain. Repeated defecation with the release of a large volume of fluid becomes a prerequisite for severe dehydration, which is manifested by dry skin and mucous membranes, decreased blood pressure, and oliguria. - Hong Kong flu
. With this type of influenza infection, symptoms from the gastrointestinal tract are combined with signs of damage to the respiratory system and general intoxication of the body. Along with headache and high fever, there is repeated diarrhea with water, moderate pain in the abdomen, nausea, and lack of appetite. Respiratory manifestations (dry cough, sore throat, nasal congestion) occur on the 2-3rd day of illness. - Marburg hemorrhagic fever.
The disease manifests itself acutely with the appearance of headache, myalgia, conjunctivitis, and erosions on the oral mucosa. Dyspeptic disorders in the form of watery diarrhea, vomiting, severe abdominal pain develop on the 3-4th day of hemorrhagic fever. Pathognomonic signs are maculopapular rash, uterine, nasal and gastrointestinal bleeding, appearing on days 5-6 of illness. - HIV infection
. AIDS is characterized by copious watery stools without pathological inclusions, caused by digestive disorders and the addition of a secondary infection against the background of severe immunodeficiency. In addition to loose stools, other nonspecific symptoms are determined - prolonged low-grade fever, increased sweating at night. Most patients lose more than 10% of body weight.
Protozoal and helminthic infestations
Helminths and protozoa have a direct pathogenic effect on the enterocytes of the mucous membrane, causing severe disturbances in the digestion and absorption of food components. Severe malabsorption syndrome in combination with increased secretion of water and electrolytes into the intestinal cavity provokes profuse diarrhea. With insufficient replenishment of fluid losses, dehydration syndrome of varying severity develops. Watery diarrhea is observed with infestations such as:
- Cryptosporidiosis
. Protozoa parasitize in the lumen of the small intestine, potentiating malabsorption and inhibition of the activity of digestive enzymes, resulting in watery stools with a foul odor. Diarrhea is accompanied by severe abdominal cramps, nausea, and vomiting. The disease most often affects people with immunodeficiencies. In such cases, there is a long course (up to 4 months) with severe dehydration. - Strongyloidiasis
. Intestinal manifestations are observed in the second phase of the disease, 2-3 weeks after the appearance of the first symptoms - urticaria, rashes and arthralgia. The development of diarrhea is associated with inflammatory damage to the small intestinal mucosa, the formation of hemorrhages, and erosions. In addition to diarrhea, epigastric pain, nausea, and vomiting are typical. Sometimes yellowness of the skin and pain in the right hypochondrium occur.
Non-infectious bowel diseases
Watery diarrhea often complicates the course of organic diseases of the digestive tract, especially in the initial stages. The increase in the volume of feces is due to both disturbances in the processes of parietal and cavity digestion, and the influence of various inflammatory mediators. Diarrhea can be associated with intestinal motility disorders of the hyperkinetic or hypokinetic type. With changes in stool frequency and consistency, the following non-infectious gastrointestinal pathologies occur:
- Enteritis
. Watery diarrhea is a symptom of non-infectious inflammation of the small intestine, which is allergic, drug-induced or autoimmune in nature. The appearance of liquid, foul-smelling feces is mainly caused by malabsorption and maldigestion syndromes. Stools are observed up to 10-15 times during the day, accompanied by flatulence, rumbling in the stomach, decreased appetite, nausea, and significant weight loss. - Enteropathy
. Chronic watery diarrhea occurs with non-inflammatory intestinal pathologies. A change in the consistency of stool can be caused by both fermentopathy and impaired gastrointestinal motility (for example, a hypomotor variant of diabetic enteropathy). The pain syndrome is mild; digestive disorders predominate, promoting weight loss and protein-energy deficiency. - Acute colitis
. Colitis is characterized by spasms in the left iliac region, painful urge to defecate, and the presence of pathological mucus and blood in the stool. The stool initially has a fecal character, a fetid odor, and as the disease progresses it becomes watery. The frequency of bowel movements reaches 25 times a day. Similar changes are observed in the pseudomembranous variant of colitis with exudative enteropathy.
Enzyme deficiency
In the absence of enzymes in the initial parts of the small intestine, the appearance of profuse diarrhea with water is associated with an osmotic mechanism. The presence of a large number of undigested large molecules, especially disaccharides and peptones, is a prerequisite for increased pressure in the intestinal lumen, the release of fluid and sodium ions. Diarrhea occurs with fibrosis of the pancreas and a decrease in its exocrine function by 80-90%, as a result of which the digestion of all types of food is disrupted. The condition is aggravated by the addition of the secretory mechanism of diarrhea associated with the activation of cAMP.
Watery stools are possible with gastrinoma, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. Increased secretion of gastrin and hydrochloric acid leads to the destruction of digestive enzymes and an increase in chyme osmolarity. Diarrhea is accompanied by intense epigastric pain and sour belching. In children, defecation of water becomes a consequence of galactosemia - milk intolerance due to the congenital absence of the enzyme. The symptom appears immediately after the start of breastfeeding and is accompanied by malnutrition, jaundice, and suppressed reflexes.
Antibiotics and blood in stool
Defecation disorders are a common side effect of taking antibiotics. Most often, such troubles arise during treatment with 1st and 2nd generation drugs.
Modern drugs injure the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract to a lesser extent, rarely provoke excessive gas formation, and treat beneficial microflora more humanely.
If diarrhea develops during treatment, you should inform your doctor. If diarrhea is relieved by taking probiotics, then therapy is continued. If any inclusions appear in the stool, there is a possibility of damage to the mucous membranes of the stomach and intestines. In this case, the drugs are discontinued.
When treated with several types of antibiotics, the microflora is completely destroyed. But there is a risk of developing a representative of the opportunistic clostridia flora.
This microorganism is insensitive to antibacterial agents. In this case, pus and blood clots are present in the stool. There may be up to 20 episodes of bowel movements during the day.
If such symptoms appear, the main treatment is reviewed and drugs to suppress clostidia are added.
Alcohol and bloody diarrhea
Blood in stool can be secretive
Excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages negatively affects the condition of all organs. But the gastrointestinal system suffers first.
Ethanol is a toxin. It affects the cells of the mucous membranes of the mouth, esophagus, and stomach. In addition, the main cause of inflammatory processes in the pancreas is excessive or frequent consumption of strong drinks.
Therefore, the appearance of blood clots in stool is not uncommon after heavy drinking. Often there are additional symptoms - nausea, vomiting, temperature rise to critical values. In this case, you should call an ambulance.
Diagnostics
- determines the inflammatory process;
- diagnoses anemia caused by blood loss;
- determines dysbacteriosis, worms, hidden blood;
- (CA 19-9, CA-50, REA) – establishes the presence of malignant processes in the body.
Diagnosis of diseases accompanied by bloody stools involves identifying the degree of anemia and inflammation, establishing the location and cause of bleeding.
At the medical center on Yauza you can undergo a full range of diagnostic tests: general analysis of urine, blood, stool, stool examination for dysbacteriosis, worms, occult blood, all types of biochemical and oncological markers.
Ultrasound diagnostics, intestinal radiography, computed tomography on a modern tomograph (including virtual colonoscopy) will help to visually determine the pathological process.
Experienced and qualified radiology and endoscopic diagnostic doctors, together with gastroenterologists, surgeons, and coloproctologists, will give an objective assessment of the health status of the patient with blood in the stool and help eliminate the threat as soon as possible and achieve good results in individually selected treatment.
Approximately 30-50% of people over 25 years of age have intestinal diseases, which subsequently develop into serious chronic pathologies. Don't be fooled by false modesty. Make an appointment with your doctor today for a healthy tomorrow.