The article was prepared by a specialist for informational purposes only. We urge you not to self-medicate. When the first symptoms appear, consult a doctor.
The reflex act of vomiting arose in the process of human evolution and is always preceded by nausea. Both nausea and vomiting are subcortical reflexes, therefore, they cannot be suppressed by willpower, and the human consciousness cannot control them. The main purpose of vomiting is to cleanse the body of toxins, poisons, and chemical compounds that have entered it from the outside or are produced by its own tissues and organs.
Various pathologies and conditions manifest themselves with nausea and vomiting. These may be the only symptoms of the disease, or reflex acts appear in combination with other symptoms. Vomiting is always preceded by nausea - a feeling that is difficult to confuse with other sensations. Symptoms of nausea - “sucks in the pit of the stomach”, salivation (secretion of saliva) increases, the person becomes pale, breaks into a cold sweat, the feeling of lightheadedness and faintness increases.
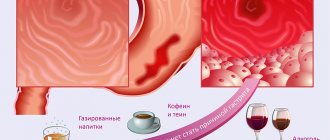
Vomiting is the release of stomach contents through the esophagus and oral cavity. It manifests itself in attacks that are caused by contractions of the abdominal muscles. Vomiting is accompanied by pain in the stomach, and the person becomes covered in sticky cold sweat. When vomiting, the larynx and soft palate rise, and the epiglottis descends, which protects the airways from vomit entering them.
The vomiting center, located in one of the ventricles of the brain, is responsible for the occurrence of this complex reflex. It is excited by an increase in intracranial pressure, exposure to impulses from the labyrinth of the inner ear, from mental stimuli, chemical reactions excited by the ingress of poisons, toxins, drugs into the blood, as well as by irritation of individual receptors in various parts of the body. The most sensitive receptors are located on the back wall of the pharynx; the peritoneum, mesenteric vessels, and bile ducts are also equipped with them.
Causes of nausea and vomiting:
- Pathologies and damage to various parts of the central nervous system;
- Food, drug, alcohol intoxication;
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Psychogenic causes;
- Very severe pain of any origin.
Vomiting is not a specific symptom, but assessing its characteristics in combination with other manifestations and studying vomit can greatly facilitate the diagnosis of diseases.
What disease may constant vomiting indicate?
There are various groups of diseases that occur with constant vomiting. Depending on the nature of its occurrence and characteristics, the disease is diagnosed:
- Central vomiting – meningitis, migraine, hypertensive crisis, encephalitis, glaucoma, brain tumors and abscess, damage to the inner ear;
- Psychogenic vomiting – hysterical neurosis, anorexia, attacks of cyclic vomiting in children;
- Hematogenous-toxic vomiting - uremia, acetonemic vomiting in diabetes mellitus, porphyria, carbon monoxide poisoning, alcohol, drugs, cytostatics, radiocontrast agents, exposure to viral and bacterial toxins in infectious lesions;
- Visceral vomiting – pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, peptic ulcer, duodenitis), diseases of the biliary and urinary tracts, acute appendicitis, pyloric stenosis, atony and gastric paresis;
- Vomiting with a putrid odor – stomach cancer;
- Vomiting with a fecal odor – intestinal obstruction;
- Bloody vomiting – gastrointestinal bleeding;
- Vomiting with bile – complications after surgery on the stomach, biliary colic, narrowing of the duodenum;
- Vomiting with undigested food - gastric achylia, achalasia of the esophagus.
To clarify the diagnosis, a bacteriological, chemical, cytological study of vomit is carried out, the relationship of vomiting with food intake is studied (morning, early, late, fasting, night and cyclic vomiting).
Classification
When systematizing the clinical variants of a symptom, its connection with gastrointestinal diseases, the frequency of manifestation, the mechanism of development, and the characteristics of vomit are taken into account. Vomiting associated with diseases of the digestive tract is called primary, and vomiting that occurs against the background of other pathological conditions is called secondary. Depending on the leading mechanism of development, the following are distinguished:
- Central vomiting
. It is observed in the presence of cerebral pathology (inflammation of the brain matter and membranes, increased intracranial pressure due to head injuries, brain tumors). In neuroses, panic attacks, migraines, hyperthermia, the symptom is associated with dysfunction of the central links of autonomic regulation. It often occurs repeatedly and does not alleviate the patient’s condition. - Hemotoxic vomiting
. It is caused by irritation of the receptor zone of the medulla oblongata during the circulation of various exo- and endotoxins in the blood. It is found in cases of poisoning with medications, toxic products and reagents. It is an unfavorable sign of intoxication in the presence of severe and terminal conditions (malignant tumors, renal, liver failure). - Reflex vomiting
. Caused by irritation of the visceral receptors of the arc of the gag reflex in various organs and tissues. It most often develops in gastrointestinal pathology, but can be provoked by pathological afferentation in diseases of the ENT organs, heart, lungs, bronchi and female reproductive system. Variants of reflex vomiting are psychogenic and vestibular.
The symptom can appear once (usually against the background of food errors, poisoning, intestinal infections), repeatedly (several times in a short time, up to uncontrollable vomiting in severe intoxication and cerebral disorders), periodically (with gastrointestinal diseases, other chronic pathologies). From a diagnostic point of view, it is important to take into account the nature of the vomit. According to the characteristics of the impurities, there are variants of vomiting of undigested food, blood (scarlet and the color of coffee grounds), bile, foamy mucus, and intestinal contents.
Why might there be water vomiting?
This type of vomiting is extremely rare, except for artificially induced vomiting during gastric lavage.
Causes of water vomiting in children:
- Runny nose;
- Colds;
- Teething;
- Pathologies of the ear, nose and throat.
All these reasons are due to large amounts of mucus entering the stomach. It flows from the nasal and oral cavities through the throat and esophagus into the stomach. Irritation of its mucous membrane causes vomiting. The consequence of this is vomiting of water without impurities.
In the absence of visible causes of the disease, this symptom manifests itself due to excessive dry air, exposure to air in frosty weather, and also due to an allergic reaction. In this case, the release of a large volume of mucus is the body’s protective reaction to the negative influence of the environment. Then everything happens according to the algorithm described above - the mucus irritates the gastric mucosa, where it enters in excess quantities.
It is not difficult to eliminate this symptom in children; you need to create optimal living conditions and cure the pathology of the ENT organs.
If vomiting water is diagnosed in an adult, this may be due to long breaks between meals. Gastric juice is secreted reflexively, and the longer the interval between meals, the more juice is formed in the stomach. If a large amount of juice causes vomiting, it may seem like you are vomiting water. Visually, these liquids are almost indistinguishable from each other.
For various reasons, a person does not feel that he is hungry, however, the body needs food. This condition leads to excessive production of stomach acid and vomiting that looks like water.
Diagnostics
The development of vomiting is most often caused by diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, so a comprehensive examination is carried out by a gastroenterologist. A diagnostic search involves studying the structural and functional features of the digestive system and excluding concomitant pathologies. The most informative for identifying the causes of vomiting:
- Endoscopy.
Using the method of visualizing the mucous membrane of the upper gastrointestinal tract, a specialist can see inflammatory changes, foci of epithelial destruction, and voluminous neoplasms. If necessary, during endoscopy, a biopsy of individual sections of the mucosa is performed for subsequent cytomorphological diagnosis. - X-ray methods
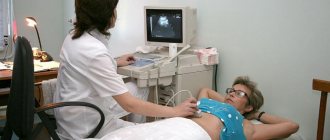
. Radiography with contrast is highly informative for organic diseases, which are often manifested by vomiting. The images can reveal deformation of the contours of the esophagus or stomach, and pathological shadows. The speed of contrast advancement is used to judge the motor function of the digestive tract. - Ultrasonography
. A survey ultrasound of the abdominal cavity is prescribed to all patients with dyspeptic disorders as a screening method. Sonography allows you to identify nonspecific signs of the inflammatory process and changes in the organs of the hepatobiliary system. The method is used to diagnose gastrointestinal pathologies in pregnant women at any stage. - Esophageal manometry
. Measurement of esophageal pressure is performed to exclude dyskinesia and dysfunction of the muscle sphincters, as the main cause of vomiting. If hyperacid diseases of the stomach are suspected, daily pH measurements are prescribed. Intraesophageal pH determination is indicated for the verification of GERD. - Lab tests
. In the coprogram, characteristic changes can be detected: undigested food components, the presence of fecal elastase. Stool culture is recommended to exclude intestinal infections. Biochemical blood test indicators are also assessed: acute phase proteins, levels of bilirubin and liver enzymes.
In case of damage to the hepatobiliary system, duodenal intubation with microscopic examination of bile and targeted ultrasound of the liver and gallbladder are recommended. If vomiting is caused by an infectious process, serological tests are performed to determine the type of pathogen and the amount of specific antibodies. A gynecologist is required to examine pregnant women. Once all organic causes have been ruled out, autonomic nervous system testing may be necessary.
For profuse vomiting, give oral or parenteral rehydration
Can there be vomiting with mucus and why?
An admixture of mucus occurs in many pathologies in both children and adults. Diseases for which vomiting with mucus is diagnosed:
- Flu;
- Rotavirus (“stomach flu”);
- Dietary disorders in chronic gastritis;
- Acute erosive gastritis;
- Damage to the mucous membrane by alkalis or acids (suicide attempt, accident).
Vomiting with mucus in infants is normal. However, in this age category, such vomiting may be the result of an accumulation of mucus due to inflammation of the bronchi. An infant cannot cough it up due to his age. When children consume foods of a special consistency (milk, jelly, fruit juices with pulp), vomiting with mucus is also observed.
Can there be black vomit and is it dangerous?
Black vomiting may be a sign of a serious pathology or have a physiological cause. Some foods turn vomiting black: chocolate, berries with dark pulp, etc. Knowing about their consumption on the eve of vomiting, you can only focus on relieving this unpleasant symptom.
Vomiting in the form of “coffee grounds” is a great danger. It indicates bleeding in the stomach or duodenum. The peculiar appearance of the blood indicates that it has oxidized and coagulated under the influence of gastric juice.
Diseases that cause bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract:
- Neoplasms of any etiology (tumors, polyps);
- Trauma to the mucous membrane of the stomach or intestines;
- Hemorrhagic disease;
- Ulcerative lesions of the stomach or small intestine;
- Side effects of drugs that can cause damage to the stomach or intestines (Indomethacin, Aspirin, Ibuprofen, drugs, steroid hormones);
- Alcoholism.
Stomach or intestinal bleeding is accompanied by dizziness and weakness. The patient's skin becomes pale, a feeling of apathy appears, and the person may faint. These symptoms are a reason to immediately call an ambulance, as delay can be life-threatening. If black vomit is the only symptom, you should still see a doctor as soon as possible.
What disease can cause a temperature of 38 and vomiting?
Diseases in which there is a combination of vomiting and high fever:
- Acute appendicitis;
- Acute respiratory viral infection;
- Acute gastroenteritis;
- Colds (bronchitis, tracheitis, pneumonia);
- Intestinal infection.
In the vast majority of cases, these symptoms are observed precisely during gastrointestinal infections. Children may react by vomiting to a rapid increase in temperature during any inflammatory process.
The initial manifestations of an intestinal infection and a viral disease are very similar: in both cases, hyperthermia, redness of the throat, and vomiting are observed. Specific symptoms appear a little later.
In any case, if vomiting is combined with a temperature of 38, you should urgently call “emergency help.” It is impossible to differentiate poisoning from an attack of appendicitis without a medical examination. Acute appendicitis requires urgent surgical intervention; serious poisoning requires treatment in a hospital.
On this topic:
How and with what to reduce the temperature of an adult?
When vomiting is scary
Any attack of vomiting is a very unpleasant experience. Even if a person experiences relief with the resolution of the attack, the vomiting itself is perceived as an extraordinary event, which should not normally occur. Shock to the body, everyday and social inconveniences - all this makes vomiting a process of a different order compared to other reflex actions, such as coughing or sneezing. We always react sharply to vomiting (we don’t ignore it), and rightly so.
However, in some cases, vomiting worries us especially strongly. This is vomiting bile , vomiting blood . Parents are concerned about cases of vomiting in children . Quite often, vomiting is observed during pregnancy , attracting increased attention.
These cases are worth mentioning separately:
- Vomiting bile
Vomiting blood
Vomiting during pregnancy
Vomiting in a child
Can antibiotics cause vomiting?
Antibiotic drugs have a large number of side effects, and vomiting occurs when using these drugs along with other symptoms.
Causes of vomiting while taking antibiotics:
- Vomiting is a side effect of a specific drug;
- There is incompatibility of the antibiotic with concomitantly taken medications from other pharmacological groups;
- Dietary disturbances or alcohol consumption occurred during antibiotic therapy.
The occurrence of vomiting directly depends on the form in which the drug is taken. Antibiotics in tablet form are more likely to cause vomiting than the same drugs given in injection form. You should not refuse a particular medication if oral use causes vomiting. It is worth trying intravenous or intramuscular administration. Adjusting the dosage to reduce the volume or frequency of taking the medication will reduce the risk of this unpleasant side effect, but at the same time the effectiveness of the treatment may suffer.
Antibiotics that may cause vomiting:
- Amoxicillin;
- Azithromycin (Sumamed);
- Tetracycline;
- Streptomycin;
- Ciprofloxacin (Tsiprobay, Tsiprinol, Tsiprolet);
- Ampicillin;
- Erythromycin;
- Metronidazole (Trichopol, Metrogyl);
- Neomycin;
- Cefpodoxime (Cefodox);
- Gentamicin;
- Doxycycline.
Drugs that cause vomiting when used simultaneously with antibiotics:
- NSAIDs (Ibuprofen, Aspirin, Diclofenac, Indomethacin);
- Cardiac glycosides;
- Estrogens;
- Potassium sulfate, ferrous sulfate;
- Antiviral agents.
Drinking alcohol and eating fatty foods during antibiotic therapy may trigger vomiting and increase this side effect.
Can the temperature rise after vomiting and why?
An increase in temperature after vomiting indicates that poisoning, hepatitis, or intestinal infection (salmonellosis, dysentery) are occurring. Poisoning with low-quality food products manifests itself as diarrhea, a combination of nausea and vomiting, and abdominal pain. An increase in temperature can be observed after vomiting. This indicates that toxins have entered the blood. Despite the fact that the attack of vomiting somewhat reduced the amount of poisons that entered the body, even a minimal amount can cause hyperthermia.
Measures to detoxify the body:
- Gastric lavage;
- Taking diuretics (Furosemide);
- Taking sorbents (Polysorb, Enterosgel).
If these measures do not give the desired effect and the temperature does not return to normal, most likely the cause of hyperthermia is an intestinal infection (dysentery, salmonellosis) or viral hepatitis. To clarify the diagnosis, you need to consult with an infectious disease doctor.
How can I prevent nausea?
There are a number of recommendations that can help prevent or relieve nausea.
- Reduce your food portions. This will help avoid overeating and excessive stomach fullness.
- Eat slowly and chew your food thoroughly.
- Avoid foods that are difficult to digest.
- Avoid foods that are too hot and eat foods that are slightly warm or at room temperature.
- Drink plenty of water between meals. Try not to drink food.
- Eat when you feel least nauseous.
Can worms cause vomiting?
Worm infestations provoke vomiting in both children and adults. Its appearance is specific - it is a foamy white discharge. It does not appear immediately after infection, but after 2-3 weeks.
At the first stage, a sick person may develop a dry cough and dermatitis, similar in appearance to hives due to allergies. At the end of the first stage, these symptoms are joined by nausea, excessive salivation, and signs of anxiety.
The appearance of vomiting with white foam is a reason to contact a parasitologist or infectious disease specialist. A more precise diagnosis is made after analyzing stool for worm eggs in a specialized laboratory.
general characteristics
At the time of vomiting, the patient experiences an uncontrolled contraction of the abdominal muscles and diaphragm, leading to a sharp release of gastric and, in some cases, intestinal contents.
The secreted masses may contain remnants of undigested food, mucous, bloody and bile inclusions, and other pathological impurities. Often the attack is preceded by nausea, profuse salivation, weakness, and sweating. Possible dizziness, unsteadiness of gait, rapid heartbeat. After an episode of vomiting, a sour, bitter, putrid taste or odor remains in the mouth and sometimes in the nasal passages. From the outside, the patient looks confused, pale, and beads of sweat are often visible on the forehead. The appearance of vomiting should always be regarded as a threatening condition that requires a medical examination. If the patient’s condition has improved after the vomit has passed, a visit to a general practitioner or family doctor may be scheduled. If indomitable vomiting occurs, blood, bile, mucus and feces are detected in it, the symptom is combined with hyperthermia, intense pain of any localization, diarrhea, stupor, disorientation and convulsions, you must call an ambulance.
Complications and consequences of vomiting
Short-term vomiting does not cause significant harm to the human body. Prolonged vomiting, on the contrary, causes serious metabolic disorders.
Complications and consequences of prolonged vomiting:
- There is a decrease in the volume of intracellular fluid, loss of hydrogen ions, and alkalosis develops - a change in the acid-base balance towards alkaline substances;
- Hypokalemia occurs as a result of potassium loss and excessive excretion by the kidneys;
- Metabolic disorders lead to loss of consciousness and paralysis;
- As a consequence of hypokalemia, arrhythmia, muscle weakness, nocturnal polyuria appear - an increase in the volume of urine excreted along with frequent urination at night;
- With severe vomiting, rupture of the mucous membrane of the esophagus, transmural rupture of the esophagus, rupture of the mucous membrane of the esophageal-gastric junction, accompanied by heavy bleeding, is possible.
These complications are especially relevant for children, weakened patients, and the elderly. Patients with impaired mental health can aspirate vomit into the respiratory tract. These complications lead to breathing problems and aspiration pneumonia.
Development mechanism
Vomiting is the result of a complex reflex reaction in which the uncontrolled contraction and relaxation of various muscle groups leads to the release of gastric chyme. The reflex is activated by influences on different links of the neural chain. Neuroreceptors that stimulate the vomiting center are located in the pharynx, stomach, intestines, bile ducts, peritoneum, coronary and mesenteric vessels, and a number of other organs. Their activation causes irritation of the mucous membranes with bacterial toxins, release of bioactive substances, pressure, vasospasm, and other visceral effects.
Impulses from peripheral receptors travel through vagal and sympathetic fibers to the vomiting center of the medulla oblongata. Neurons of the reticular formation can also be activated by the direct influence of toxic substances on the chemosensitive zone of the bottom of the fourth cerebral ventricle and by an increase in intracranial pressure. Less commonly, the gag reflex is triggered by impulses from the vestibular apparatus, exposure to mental stimuli, or intense pain of any origin.
The motor part of the reflex arc is represented by V, IX, X pairs of cranial nerves innervating the soft palate, larynx, pharynx, esophagus, stomach and diaphragm, spinal nerves providing contraction of the striated intercostal muscles and the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall. Since the vomiting center is located next to the cough, vasomotor, respiratory and other autonomic centers, their simultaneous activation causes hypersalivation, a drop in blood pressure, pallor and other parasympathetic reactions.
When efferent impulses arrive against the background of deep inspiration, the diaphragm lowers, the epiglottis closes the entrance to the respiratory tract, the larynx and palate rise, preventing the reflux of chyme into the trachea, bronchi and lungs. Tension of the diaphragmatic and abdominal muscles against the background of compression of the pylorus and relaxation of the cardia provides an increase in intra-abdominal and intragastric pressure, which ends in an attack of vomiting. In some conditions, antiperistaltic movements of the intestinal wall occur, causing intestinal contents to enter the stomach and then into the vomit.
First aid for vomiting
With the help of vomiting, the human body is freed from toxic substances.
An exception is vestibular disorders due to motion sickness, a condition after a traumatic brain injury, severe nervous strain, or stress.
First aid rules:
- You cannot stop the act of vomiting, you should wait until it is completed;
- After this, the person needs to be seated, cover the chest and knees with a towel or clean rags, place a bucket and basin at an accessible distance;
- If a person suffering from an attack of vomiting can only be in a lying position, you need to try to keep his head below chest level;
- An unconscious patient should tilt his head to the side so that he does not choke on vomit;
- After each attack, you need to rinse your mouth with cool water;
- Bed rest during such attacks is observed only when feeling unwell;
Particular caution should be exercised if there are blood impurities in the vomit; they look like coffee grounds. This is a sign of stomach bleeding and requires immediate medical attention. Losing large amounts of fluid through vomiting leads to dehydration. It is necessary to return lost fluid as quickly as possible by drinking plenty of fluids and restoring the optimal concentration of mineral salts.
Solutions for relieving mineral deficiency:
- Regidron, Trisol – normalizes water and electrolyte balance, prevents dehydration;
- Gastrolit - in addition to the above properties, it has an anti-inflammatory effect, since the drug contains chamomile extract. Gastrolit is poured with boiling water and left to cool completely;
- Homemade saline solution - add 1 tsp to 1 liter of boiled water. salt, 1/2 tsp. soda, 7 tsp. sugar, mix thoroughly until the components are completely dissolved.
Any saline solution should be taken in small sips every 5-10 minutes. You can alternate this drink with unsweetened tea or a 5% glucose solution. This technique will help avoid excess salts.
How to stop vomiting?
This symptom occurs for many reasons. Vomiting can be eliminated by applying in each specific case a specific etiotropic treatment aimed at combating the cause of the disease. If the cause cannot be identified, symptomatic drugs are used to stop vomiting.
Conservative therapy:
- Prokinetics.
Used for GERD and esophageal dyskinesias.
- Antisecretory drugs.
H2-histamine receptor blockers and proton pump inhibitors are used for long-term use of NSAIDs to avoid hematemesis.
- Antibiotics.
Used for vomiting with intestinal infections. Treatment is selected empirically, taking into account the suspected pathogen.
- Enzyme preparations.
They are used in the presence of pancreatitis and pathologies of the biliary tract.
- Antiemetics.
These drugs affect the vomiting center in the brain and are indicated for repeated painful vomiting. They have many side effects, so they are used only in extreme cases.
How to relieve vomiting after alcohol?
Abuse of low-quality alcohol or its excessive use in most cases causes severe vomiting. It is accompanied by extremely unpleasant sensations, as it is always combined with strong and painful stomach cramps. The breakdown products of alcohol in combination with semi-digested food, passing through the esophagus and oral cavity, irritate their mucous membrane. All these sensations leave the impression of vomiting after drinking alcohol as a painful and difficult to tolerate process.
Vomiting is a kind of protection of the body from the absorption into the blood of toxic substances formed as a result of the breakdown of ethanol. Therefore, there is no need to stop the process; on the contrary, in many cases it is vomiting that helps reduce the consequences of alcohol poisoning.
To alleviate the condition of a person with alcoholic vomiting, proceed as follows:
- Prepare a soda solution to soften the acidity of the vomit at the rate of 2 tbsp. l. soda per liter of water. You need to drink as much soda solution as possible before vomiting appears;
- After the first attack of vomiting, rinse your mouth with clean water with the addition of lemon juice;
- Prepare a mash of crushed activated carbon (2 tablespoons of carbon powder per 1 liter of water) and give it to drink as much as possible. If vomiting has ended, activated charcoal will bind remaining toxins in the gastrointestinal tract;
- If vomiting resumes after the charcoal drink, rinse your mouth and drink one of the enterosorbents available in your home medicine cabinet (Enterosorb, Polysorb, Polyphepan) to bind the toxins remaining in the stomach and intestines;
- Each episode of vomiting ends with rinsing the mouth and drinking mineral water.
Further treatment
After the doctors arrive, qualified assistance will be provided and therapy will be prescribed - in a drug treatment clinic, toxicology department, or in simpler cases - at home. In the latter case, the patient is given cleansing drips consisting of detoxification solutions, vitamins, drugs that support the functioning of the liver, kidneys, heart, brain, drugs that accelerate metabolism and restore mineral imbalance. Upon completion of the procedure, the patient’s relatives will be given all recommendations for continuing therapy.
If you managed to get by without calling doctors and your condition improved:
- Drink more fluids - this will help cope with dehydration that the body has suffered due to alcohol intoxication and vomiting. First of all, you need to drink water, but if you don’t want it anymore, make tea with honey.
- Take rehydration solutions and sorbent in the right dosage - even activated carbon will be useful, but it is better to use more modern and effective means. This will help remove toxins.
- Be sure to take a walk in the fresh air.
With this approach, the weakness and painful condition will finally disappear within a few days. But if there is no improvement and the vomiting does not stop, still seek medical help!
The text was checked by medical experts: Head of the socio-psychological service of the Alkoklinik MC, psychiatrist-narcologist L.A. Serova.
CAN'T FIND THE ANSWER?
Consult a specialist
Or call: +7 (495) 798-30-80
Call! We work around the clock!
Which doctor should I contact?
To diagnose a disease manifested by vomiting, you need to contact a gastroenterologist or therapist. If the symptom is central vomiting, it is quite possible that you will need to consult a neurologist, and for psychogenic vomiting, a psychotherapist.
Treatment of vomiting is impossible without a thorough diagnosis of the underlying disease and treatment of its manifestations. Manifestations of the gag reflex should not be ignored; they can be a symptom of dangerous pathologies.
Author of the article:
Alekseeva Maria Yurievna |
Therapist Education: From 2010 to 2016 practicing physician at the therapeutic hospital of the central medical unit No. 21, the city of Elektrostal. Since 2016 he has been working at diagnostic center No. 3. Our authors