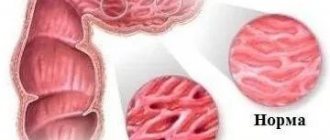
Classification
According to the type of course, acute and chronic colitis are distinguished.
The disease begins with an acute form, which is characterized by severe pain, nausea, and flatulence. If at this stage the patient ignores the disease, then it becomes chronic.
With chronic colitis, pathological changes begin in the intestinal mucosa. The reason for this is a long inflammatory process in which the functions of the organ are disrupted. After inflammation of the large intestine, a pathological process begins in the small intestine.
Colitis is divided into several types, based on the main cause of the disease:
- infectious;
- ischemic;
- nutritional;
- mechanical;
- drug;
- allergic;
- toxic.
When the disease is caused by several factors, combined colitis is diagnosed.
In addition, there is radiation colitis, which develops as a result of radiation damage, as well as ulcerative colitis of the intestine and Crohn's disease (etiology has not been identified).
Based on the location of the lesion, proctitis (inflammation of the rectum), typhlitis (inflammation of the cecum), and sigmoiditis (inflammation of the sigmoid colon) are distinguished. Pancolitis is observed when there is total damage to the intestine, and diffuse colitis is diagnosed when several parts of the intestine are affected.
Classification of the disease
Depending on the affected parts of the intestine, the following types of disease are distinguished:
- typhlitis;
- proctitis;
- transversit;
- pancolitis;
- sigmoiditis
Depending on the causes of occurrence, the following types of colitis are distinguished:
- toxic or medicinal;
- infectious;
- ray;
- ischemic (usually observed in elderly people);
- ulcerative is the most common type of disease.
Reasons for the development of the disease
Most often, patients are diagnosed with ischemic or infectious colitis.
Ischemic occurs due to disruption of circulatory processes. A decrease or complete cessation of blood flow to the large intestine can be caused by the formation of blood clots or atherosclerotic plaques. For this reason, ischemic colitis affects patients over 50 years of age.
The main causes of ischemic colitis include:
- decreased blood pressure;
- vascular atherosclerosis;
- embolism and thromboembolism.
The extent of the lesion depends on the size of the feeding artery and the duration of this condition.
Based on the nature of the lesion, a transient form is distinguished, in which the pathological processes are reversible, as well as a gangrenous form with the formation of ulcers and necrosis.
Infectious colitis is diagnosed with the development of opportunistic intestinal microflora, as well as after the entry of pathogens from the external environment. Thus, the following factors become the causes of the development of infectious colitis:
- fungi (candida, actinomycetes);
- protozoan microorganisms (giardia, amoeba);
- bacteria (salmonella, staphylococcus, proteus, shigella);
- viruses (rotavirus, enterovirus, adenovirus);
- pathogens of syphilis and tuberculosis.
The severity of the inflammatory process directly depends on the nature of the infection.
Other causes of colitis include: hereditary factor, constant emotional stress, autoimmune disorders. Based on the main cause of the pathology, the attending physician selects a treatment regimen for colitis.
Symptoms of colitis
| Type of pathology | Manifestations |
| Acute and chronic colitis |
|
| Ischemic colitis |
The chronic form of ischemic colitis is manifested by pain that is mild and occurs after eating. With a long course of the disease, which has become chronic, stricules (scar narrowing) appear. They may further promote the development of cancer cells. |
| Infectious colitis |
If the stomach is involved in the inflammatory process, then vomiting is added to the listed symptoms. |
For the initial assessment of the etiology of infectious colitis, the doctor takes into account the nature of the stool, its volume, frequency, appearance and other features of the stool. This is important, because with colitis caused by clostridia, the stool has a rotten smell, with an amoebic infection, the stool is crimson-colored with a jelly-like structure, and salmonellosis manifests itself in the form of stool that resembles swamp mud.
Page 4 of 10
Symptoms of Ulcerative Colitis
In most patients (75%), the disease begins gradually. Sometimes patients do not seek qualified help from a medical specialist for a long time, considering the presence of blood in the stool as a manifestation of chronic hemorrhoids. Between the appearance of the first symptoms of UC and the time of diagnosis can pass from 10 months to 5 years. Much less often, UC debuts acutely.
The severity of clinical manifestations of UC depends on the extent of the inflammatory lesion and the severity of the disease. Symptoms characteristic of UC can be divided into three groups:
- intestinal
- general (system)
- extraintestinal.
The most common intestinal symptoms are stool disorders in the form of diarrhea ( in 60–65% of patients with UC, the frequency of stool ranges from 3–5 to 10 or more times a day in small portions) or constipation (in 16–20% of cases, mainly with damage to the lower sections of the colon). More than 90% of patients have blood in their stool. Its quantity varies (from veins to a glass or more). When the lower colon is inflamed, the blood is usually scarlet in color and is located on top of the stool. If the disease affects most of the colon, then the blood appears in the form of dark cherry-colored clots mixed with feces. Often, patients also notice pathological impurities of pus and mucus in the stool. Characteristic clinical signs of UC are fecal incontinence, an urgent urge to have a bowel movement, a false urge with discharge of blood, mucus and pus from the anus, with virtually no feces (“rectal spitting”). Unlike patients with functional intestinal disorders (irritable bowel syndrome), UC patients also have stool at night. In addition, about 50% of patients complain of abdominal pain, usually of moderate intensity. More often, pain occurs in the left half of the abdomen; after passing stool, it weakens, less often it intensifies.
General or systemic symptoms of UC reflect the impact of the disease not only on the colon, but also on the patient’s entire body. Their appearance indicates a severe and widespread inflammatory process in the intestines. Due to intoxication and loss of nutrients along with loose stools and blood, the patient develops fever, loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting, increased heart rate, weight loss, dehydration, anemia (anemia), hypovitaminosis, etc. Patients often experience various disorders from the psycho-emotional sphere.
Extraintestinal manifestations of UC, occurring in 30% of patients, are the result of immune disorders. The severity of most of them is associated with the activity of UC. It should be noted that patients often do not associate these symptoms with intestinal pathology and seek help from various medical specialists (rheumatologists, neurologists, ophthalmologists, dermatologists, hematologists, etc.). Sometimes their appearance precedes intestinal symptoms. A variety of organs can be involved in the pathogenic process.
When the musculoskeletal system , patients complain of pain, swelling, decreased mobility of various joints (knee, ankle, hip, elbow, wrist, interphalangeal, etc.). As a rule, pain migrates from one joint to another without leaving significant deformities. Damage to large joints is usually associated with the severity of the inflammatory process in the intestine, and arthropathy of small joints occurs regardless of the activity of UC. The duration of the described articular syndrome sometimes reaches up to several years. Inflammatory changes in the spine with limitation of its mobility (spondylitis) and sacroiliac joints (sacroiliitis) may also appear.
Lesions of the skin and oral mucosa in patients with UC manifest themselves in the form of various rashes. Typical are painful red or purple subcutaneous nodules on the arms or legs (erythema nodosum), blisters in areas with a small thickness of subcutaneous tissue - legs, in the sternum, which spontaneously open to form ulcers (pyoderma gangrenosum), ulcers on the mucous membrane of the cheeks, gums, soft and hard palate.
When the eyes , patients with UC develop pain, itching, burning in the eyes, redness of the eyes, photophobia, a feeling of “sand in the eyes,” blurred vision, and headaches. Such complaints accompany the appearance of inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye (conjunctivitis), the iris (iritis), the white membrane of the eye (episcleritis), the middle layer of the eye (uveitis), the cornea (keratitis) and the optic nerve. For correct diagnosis, patients need to consult an ophthalmologist and conduct a slit-lamp examination.
Often, extraintestinal symptoms of UC include signs of damage to other digestive organs (liver and biliary tract (including primary sclerosing cholangitis, which is difficult to treat with medication), pancreas), disorders in the blood system (phlebitis, thrombosis, autoimmune hemolytic anemia).
- Back
- Forward
Pathogenesis
Long-term exposure to mechanical, toxic, allergic and some other etiological factors on the intestinal mucosa leads to the onset of the pathological process. These effects, through the development of dysbiosis, lead to disruption of the motor and secretory functions of the large intestine.
Dysbacteriosis develops in the colon after a decrease in the number of bifidobacteria and an increase in the number of opportunistic microflora. Dysbiotic microflora disrupts the normal activity of the gastrointestinal tract, is a source of the formation of toxic substances, they change the permeability of the intestinal wall, disrupt peristalsis, and suppress epithelial regeneration. This leads to a change in dyspeptic properties. Experts consider changes in motility and increased mucus production as a protective mechanism in response to damage.
The presence of dysbacteriosis causes the development of dyspepsia. As the disease develops and the body weakens, immune disorders develop, concomitant pathologies arise, and septic complications arise.
With radiation colitis, atrophy of the intestinal mucosa occurs immediately after irradiation. At the same time, the length of the villi decreases, and cell division, on the contrary, increases. Inflammatory processes begin with a neutrophil reaction. If the patient has been exposed to large doses of radiation, inflammation may occur for a long time after irradiation. This leads to the development of ulcers and stricules on the intestinal mucosa. In this case, all departments are affected.
Treatment of pseudomembranous colitis after COVID-19. MKSC patient history
A 63-year-old patient was admitted to the Moscow Scientific Research Center in serious condition . This hospitalization was not his first this year.
- He previously suffered from COVID -19 , which was treated with antibiotics and cytokine storm blockers.
- During the course of the disease, like 20% of all patients with COVID-19, the patient complained of diarrhea, but after recovery, the stool did not return to normal.
The diarrhea persisted, so the patient was readmitted to the hospital. The results of the examination revealed that toxins A and B Clostridium bacterium .
- After treatment, he was discharged with temporary improvement.
Pseudomembranous colitis is an inflammation of the colon that is most often caused by the toxigenic bacterium Clostridium difficile.
- Its characteristic symptoms are fibrinous deposits on the mucous membrane of the colon and diarrhea.
It should be noted that in a quarter of patients , after conservative treatment of clostridial pseudomembranous colitis, a relapse of the disease occurs.
So, after some time, our patient developed pseudomembranous colitis with renewed vigor.
- Diarrhea increased , along with fever and abdominal pain.
- Diarrhea led to severe water and electrolyte disturbances and the development of hypoalbuminemia - the patient’s condition noticeably worsened.
With such clinical, laboratory and instrumental data, death could have occurred with a probability of 46%.
In addition, against the background of multicomponent conservative therapy, the patient developed toxic dilatation of the colon.
- The doctors decided to perform an operation. There was a high risk of death (up to 80%).
- Thus, a favorable outcome in our patient was unlikely.
Surgeons urgently performed a colectomy - they removed the large intestine to form a small intestinal stoma.
The postoperative period proceeded without complications, and the patient was soon discharged from the coloproctology department of the Moscow Scientific Research Center.
- And after some time he returned to his usual way of life.
The well-coordinated work of the MCSC team - anesthesiologists-resuscitators, gastroenterologists, coloproctologists, as well as the patient’s will to recover - made it possible to successfully treat the fulminant form of pseudomembranous colitis, complicated by toxic dilatation of the colon against the background of a coronavirus infection.
Read our Facebook to stay up to date with the latest events.
Was the information useful?
Complications
Possible complications of colitis include the following conditions and pathologies:
- extensive bleeding;
- dehydration;
- osteoporosis;
- colon perforation;
- inflammatory diseases of the skin and mucous membranes;
- the appearance of stricula, fistulas and abscesses;
- fecal incontinence;
- intestinal obstruction.
In addition, there is a high risk of blood clots and colon cancer.
Diagnosis of colitis
Treatment of colitis should begin with a thorough diagnosis, which includes a comprehensive examination. Laboratory research methods for suspected infectious colitis include:
- general blood analysis;
- blood test for sterility (if a septic lesion is suspected);
- serological study;
- stool analysis to determine the pathogen.
Among the instrumental methods, ultrasound examination and sigmoidoscopy are considered mandatory.
For ischemic colitis, it is necessary to do irrigoscopy, colonoscopy and angiography, which will show not only the degree of vasoconstriction, but also the localization of inflammation. A differential diagnosis should be made and ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease, as well as malignant neoplasms, should be excluded.
In case of radiation colitis, when collecting anamnesis, the doctor takes into account the fact of radiation exposure. Sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy with biopsy are indicated. It should be noted that this form of the disease is combined with atrophy of the mucous membrane.
Do I have spastic colitis?
Elena
June 20, 2020
How it all started It all started more than a year ago. One day I felt a nagging pain in the middle of my stomach, as if something was stuck. I don’t remember exactly, but everything seemed to go away after the gases came out. The next day in the morning there was a feeling in my stomach that there was some kind of lump. There was no chair. Constipation began, there was no bowel movement for 2-3 days. Sometimes everything went away, stool appeared, but every time it was mushy and unformed, but after that there was no pain in the stomach or a feeling of incomplete emptying. During constipation, the stool was very thin, but not hard. In addition, during constipation, a dull pain was felt in the left lower abdomen, from the ribs to the navel. Start of treatment I did not see a doctor right away. I tried to add more fiber, vegetables, and fruits myself. No prunes or beets helped. I tried enemas, they helped, but then everything started all over again. I tried castor oil, magnesia, buckthorn and senna. The effect is one-time. I drank lactulose, it caused severe gas and unformed stools. After 3 days she stopped helping. I tried to take antispasmodics, the stool became of normal diameter, and not thin, as usual, the pain on the left went away, but I still didn’t completely empty my bowel movements. I did gymnastics and moved a lot. Examination I went to a proctologist, he did not reveal any pathologies. I went to a gastroenterologist, they did an irrigography, and as a result they diagnosed a violation of the evacuation function, spastic colitis, chronic constipation against the background of dolichosigma. Tests (blood, feces, urine) are normal. After FGS, gastroduodenitis was diagnosed, although I was never bothered by stomach pain, mainly by constipation. Helicobacter was not detected. They gave me trimedat, neobutin, something for gastroduodenitis (gastro...), prescribed microlax for constipation, drinking phytomucil (it stopped helping after 2 uses). Nothing helped, everything remained as it was. Remission Started introducing more processed, warm, oily foods. I excluded flour in any form, as well as dry, cold, and raw foods. I noticed that eating fresh halva always helps with constipation. After it, an excellent chair, but also unformed. Eating hulled sunflower seeds and sunflower oil helps relieve constipation. After meat there is also good stool. But as soon as you stop eating butter, seeds, nuts, sometimes halva, as well as warm soft food, the stool again becomes very thin from unformed, incomplete emptying appears, and the left stomach hurts. Please tell me, do I really have spastic colitis? And what measures should I take to eliminate intestinal spasms (which is probably why the stool is so thin when constipated)?
Age:
19
Chronic diseases:
No. They diagnosed an endemic goiter
The question is closed
constipation
spasms
Dolichosigma
Spastic colitis
Treatment
Treatment for infectious colitis includes:
- antibacterial, antifungal agents;
- solutions to replenish lost fluid and useful components;
- sorbents;
- probiotics and prebiotics;
- anti-inflammatory drugs and antispasmodics;
- enzymes.
For ischemic colitis, medications are added to improve blood flow, antiplatelet agents, and drugs that soften stool.
Treatment of ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease is similar to the treatment of intestines in adults with radiation damage. Antibacterial therapy and drugs that contain 5-aminosalicylic acid are indicated.
Therapeutic measures may include psychological support, nutritional therapy, and surgical treatment in complex cases. There are certain indications for urgent surgical intervention, for example, perforation, intestinal obstruction, and elective surgery is required when a stricule forms.
Intestinal diseases: colitis, IBS, their treatment
This article will talk about the treatment of intestinal diseases, such as chronic colitis, ulcerative colitis and IBS - irritable bowel syndrome . And today I will tell you about how to try to cure these diseases.
We will try to treat these diseases in 3-4 stages.
Stage No. 1
Colon cleansing with enterosorbents (3 days only)
Enterosorbents are drugs for cleaning the gastrointestinal tract, most often of natural origin.
Enterosorbents bind various harmful substances - poisons, heavy metal salts, ethanol, cholesterol, pathogenic bacteria and bacterial toxins - and remove all this from the body through the intestines.
In what form can you buy enterosorbents now: 1. These are lignin preparations - Polyphepan, Filrum or Entegnin. 2. If you were unable to buy lignin preparations, you can use Polysorb or Enterosgel.
Any of these listed drugs must be taken strictly according to the instructions for these medications, but not for as long as their manufacturers sometimes recommend, but only 3 days. If you take them longer, sometimes constipation begins.
But in general, lignin preparations have very few contraindications and almost no side effects, provided that you take them correctly and for a short time.
The first stage - cleaning with enterosorbents - lasts only 3 days. Then we move on to the second stage:
Stage No. 2
Chamomile + lemon balm
You need to buy 2 medicinal plants at the pharmacy - Chamomile and Melissa officinalis. We take them in parallel for 3 weeks.
We brew them like this: Chamomile: Chopped flowers. About 9 g (2 tablespoons) of chamomile flowers are placed in an enamel bowl, pour 200 ml (1 glass) of hot boiled water, cover with a lid, heat in a boiling water bath with occasional stirring for 15 minutes, cool at room temperature for 45 minutes , filter, the remaining raw materials are squeezed out. The volume of the resulting infusion is adjusted to 200 ml with boiled water. Take 2-3 tablespoons warm orally 2-3 times a day immediately before meals. The course of treatment is 3 weeks. It is recommended to shake the infusion before use.
Melissa: About 2-3 g (1 tablespoon) of chopped herb is placed in a glass or enamel bowl, pour 200 ml (1 glass) of boiling water, cover with a lid and heat in a boiling water bath for 15 minutes. Then cool at room temperature for 45 minutes, filter, and squeeze out the remaining raw material. The volume of the resulting infusion is adjusted to 200 ml with boiled water.
Take half a glass orally, warm, 3 times a day, about 1 hour after meals. The course of treatment is 3 weeks.
If the treatment did not eliminate the intestinal problems, proceed to the third stage:
Stage No. 3
We take an infusion of alder fruits for 3 weeks
How to take: About 10 g (2 tablespoons) of crushed alder fruits are placed in an enamel bowl, pour 200 ml (1 glass) of hot boiled water, cover with a lid and heat in a boiling water bath for 30 minutes, then filter without cooling, the remaining raw materials squeeze out.
The volume of the resulting decoction is adjusted to 200 ml with boiled water. Take 2 tablespoons orally 3 times a day 20–30 minutes before meals. The course of treatment is 3 weeks. The decoction must be shaken before use.
Stage No. 4
Methyluracil tablets for a month . How to take it is described here>>
***
The author of the article is Dr. Evdokimenko©. Published 10/12/2019. Attention! When copying or reprinting materials, be sure to indicate the source! All articles, news and book chapters are protected by copyright P.V. Evdokimenko©
Dietary nutrition for colitis
The goal of a diet for colitis is to stop the inflammatory process, as well as fermentation and putrefaction in the intestines, and restore its basic functions. The doctor prescribes diet No. 4 according to Pevzner, but in case of exacerbation of the disease, diet No. 4b is more suitable.
It is important to exclude prohibited products:
- rich broths;
- white bread and baked goods;
- fatty meats and fish;
- pickles, marinades, smoked products;
- spices;
- legumes;
- carbonated and alcoholic drinks, coffee;
- mushrooms, raw vegetables;
- canned food;
- fast food;
- fresh fruits;
- nuts.
Meals should be fractional - 5-6 times a day. The last meal is indicated a couple of hours before bedtime. Dishes should be warm so as not to irritate the mucous membrane. Products should be consumed baked, boiled or stewed. Fried foods are strictly prohibited. The amount of plant fiber should be reduced. Fluid intake of up to 2 liters per day is recommended. Failure to adhere to the diet is fraught with frequent exacerbations.
Proctitis, Colitis or Crohn's disease?
Marat
November 1, 2021
Hello, in August I fell ill with Covid 19. Mild form, fever for 2 days, sore throat on the left side, cough with sputum, took antiviral drugs, Stopangin spray, and after my neighbor’s horror stories, antibiotics Sumamed 5 tablets (this was a mistake), also took aspirin for liquefaction blood (also a mistake), after finishing taking antibiotics, I had diarrhea, once, took Polysorb a couple of times, the diarrhea went away, the stool returned to normal, a couple of days after going to the toilet, blood appeared, separate from the stool, 1-2 drops, stopped taking aspirin, I didn’t see any blood for 1 day) blood appeared mixed with feces and mucus, I bought suppositories with sea buckthorn and relief, since last year there was a similar situation, I had mild hemorrhoids, I’ll post a photo of the conclusion, but after one suppository everything stopped, this year a miracle did not happen, I passed the OAK, biochemical analysis, urine, feces (I will attach a photo) HP is positive, and I turned to a gastroenterologist who I saw last year, he said I have bloating, he prescribed me Creon, Festal, Neobutin and the probiotic Complexex and relief advance suppositories, sea buckthorn
Candles. I took all this for 10 days, but the result was the same blood, mucus, plus rumbling was added, the stool disappeared, only mucus and blood remained (if I was pushing thick), frequent urge to go to the toilet, gas with the smell of rotten fish .. tongue on the root of the tongue covered with a white coating and the papillae are also inflamed, he called a gastroenterologist, he prescribed Mesacol 3 tablets a day and sent him to a proctologist.., the proctologist gave a conclusion about chronic proctitis, recommendations for a colonoscopy, prescribed Salofalk 2p.d suppositories and Natalsid... I bought the suppositories, but did not use them , since I immediately signed up for a colonoscopy, 2 days of preparation and a colonoscopy was performed with a biopsy taken from as many as 4 places... I will attach a photo, Endoscopist: the conclusion is colitis. While I was waiting for the biopsy, I used Salofalk suppositories, after the first suppository I went to the toilet normally, the stool was soft, there was no blood, there was a little mucus, but it was the first day of the colonoscopy, I read what this could be, the next day the stool became normal without blood and mucus, color brown, once a day, went on his diet, rice, boiled meat, oatmeal, buckwheat but rarely, marshmallows, tea without sugar, bananas, removed bread, vegetables, fruits, nuts, etc. constipation appeared, in order to go, I had to drink a lot of water, I connected mucofalk, it didn’t help much, I need to drink a lot of liquid, I connected chamomile and chicory, the constipation went away, 1-2 times the stool was stable, in the morning, before breakfast, I always felt good, sometimes excellent , there were tingling sensations from the left to the right below the navel but practically unnoticeable, a biopsy came in, active inflammation, I thought it was strange that I felt good, there was no blood, in general I put suppositories for 2 weeks and took Mesacol 3, etc., I started reading this forum and saw that the dosages of mesalazine here they are prescribed much more than I drink, I called the gastroenterologist and asked if he could increase the dosage and whether to continue putting the suppositories, they had just run out, he said that if you feel well, then you don’t need to, you can reduce the dosage over time and the suppositories can be canceled .. that’s what he did felt good, mesacol eventually reduced to 1 td. started drinking coffee with cream), relaxed in short), followed the diet, but after three weeks I felt a tingling near the navel, then a little lower on the left and right, noticeable but tolerable not often, I didn’t feel it when walking, the burning sensation in the anus was tolerable, barely noticeable, I called the gastroenterologist explained situation, prescribed rebagit, I bought it later, took one tablet, half an hour passed, I had to go to the toilet, it was kind of mushy, but after that I felt some kind of weakness, fever, dry mouth, I wanted to drink constantly, my vision seemed to have a veil before my eyes , panic attack in general, the last time I had this was during Covid, especially in the evenings, and in 2022 I was diagnosed with VSD, osteochondrosis and narrowing of the spinal artery, I had the same symptoms, there were no sedatives at hand, I measured my blood pressure 115/68, pulse 80, the temperature was normal, but there was a fever, I called an ambulance, but it didn’t come, I drank strong tea with sugar, I seemed to feel better, but I was tired, I fell asleep, woke up in the morning in a terrible state, I decided to go and get blood Oak, I thought my hemoglobin had dropped, I felt bad all day , the tests came back, everything was normal... 2 hours before the test, I actually ate a banana and smoked... but they told me that it wouldn’t have much effect... I bought Normotim, it seemed to work at first, but it didn’t seem to help me... I noticed that the burning in the anus intensified, I decided buy suppositories with sea buckthorn and after that I felt better, and the burning went away and all the symptoms listed above)) I bought salofalk suppositories and tablets again and started treatment on my own, increased the dose to 6 tablets a day and 2 times suppositories, after a couple of days everything seemed to get better anxiety has gone away, vision has more or less normalized in the evenings, only there is some kind of veil again, but there is some unsteadiness when walking sometimes and a strain in the neck, I usually drink Cytoflavin in the spring and autumn, but with ulcerative colitis I can’t take it... I do exercises with three belts, it becomes easier, I also smoke , but my back hurts from smoking and a brown coating appears on my tongue, I tried to quit for 10 days and the coating goes away and my back calms down. And my weight before Covid was 75 kg. After 72, with nyak I now weigh 67, when I didn’t smoke 70, but because of the diet I couldn’t gain..., I want to gain weight, I want to quit smoking, but I read somewhere that I shouldn’t do this with nyak, but I’m not sure that this is a nyak, more like Crohn's, But I'm not a doctor, so I ask you for help in making the correct diagnosis based on colonoscopy, biopsy, tests and adjusting treatment Chronic diseases:
Psoriasis, VSD, anxiety disorder, osteochondrosis, narrowing of the vertebral artery..
The question is closed
UC
crown.
Prognosis and prevention
Even after effective treatment of colitis, there is a possibility of exacerbation. Therefore, it is important to monitor symptoms, respond to them in a timely manner, and begin treatment under the supervision of a doctor. In this case, the prognosis is favorable. A healthy diet is important. You should not abuse foods that negatively affect the gastrointestinal tract.
As a preventive measure, it is recommended to adhere to a healthy lifestyle - avoid drinking alcoholic beverages, monitor your weight, and engage in moderate exercise daily. It is worth keeping in mind that uncontrolled use of antibiotics can lead to colitis.
If you notice symptoms characteristic of colitis, it is recommended not to delay visiting a specialist. Make an appointment with a doctor at the Miracle Doctor clinic, where a full diagnosis and treatment of colitis is possible.