Staphylococcal infection in children
A staph infection can cause many symptoms. This depends on the location of the infection in the body and the severity of the primary inflammatory focus. Staphylococcal infection in children can be generalized or localized in form.
Most cases are localized mild forms, for example, nasopharyngitis or rhinitis. Minor inflammatory changes are observed, there is no intoxication. In infants, these forms may manifest as poor appetite and insufficient weight gain. Blood cultures can isolate staphylococcus.
But localized forms do not always go away easily; they can be accompanied by severe symptoms, severe intoxication and bacteremia, which is why it may be necessary to differentiate them from sepsis.
The disease can occur in an asymptomatic or erased form. They are not diagnosed, but are dangerous for the child and others, since an infected child spreads the infection. In some cases, another disease is added to the disease, for example, ARVI, which leads to an exacerbation of staphylococcal infection and complications, in some cases very severe.
For staphylococcal infection, the incubation period lasts from 2-3 hours to 3-4 days. The shortest incubation period for the gastroenteroscolitic form of the disease.
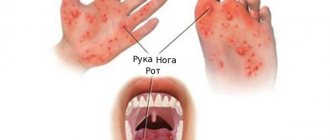
Most often, staphylococcal infection in children is localized on the skin and subcutaneous cells. With a skin staphylococcal infection, an inflammatory focus quickly develops with a tendency to suppuration and a reaction of regional lymph nodes such as lymphadenitis and lymphangitis. In children, staphylococcal skin lesions usually take the form of folliculitis, boils, pyoderma, phlegmon, carbuncle, and hidradenitis. Newborns may have Ritter's exfoliative dermatitis, neonatal pemphigus, and vesiculopustulosis. If the infection affects the mucous membranes, symptoms of purulent conjunctivitis and tonsillitis appear.
Staphylococcal tonsillitis in children as an independent disease is a rather rare phenomenon. This usually occurs against the background of acute respiratory viral infection, in some cases due to exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis or as a result of sepsis.
With staphylococcal tonsillitis in children, continuous overlays appear on the palatine tonsils, sometimes they also affect the arches and uvula. In some cases, tonsillitis is follicular. Overlays with staphylococcal tonsillitis in most cases are purulent-necrotic, whitish-yellowish, loose. It is relatively easy to remove them, as well as to grind them between glass slides.
There are extremely rare cases when, due to a staphylococcal infection, the overlays are dense, it is difficult to remove them, and removal causes bleeding of the tonsils. Staphylococcal tonsillitis is characterized by diffuse, bright hyperemia and hyperemia of the mucous membranes of the pharynx without clear boundaries. The child may complain of severe pain when swallowing. The reaction of regional lymph nodes is pronounced. Staphylococcal tonsillitis takes quite a long time to resolve. Symptoms of intoxication and elevated body temperature persist for about 6-7 days. The pharynx is cleared on days 5-7 or on days 8-10. Without laboratory methods, it is impossible to understand that a sore throat is staphylococcal.
Staphylococcal laryngitis and laryngotracheitis are common mainly in children 1-3 years old. They develop against the background of ARVI. The disease is characterized by an acute onset, elevated temperature, and laryngeal stenosis quickly appears. Morphologically, a necrotic or ulcerative-necrotic process in the larynx and trachea is noted. Staphylococcal laryngotracheitis often occurs with obstructive bronchitis and, in rare cases, pneumonia. The symptoms of staphylococcal laryngotracheitis in children are almost no different from laryngotracheitis caused by other bacterial flora. The disease is very different only from diphtheria croup, which develops slowly, with a gradual change of phases, a parallel increase in symptoms (hoarseness, aphonia, dry, rough cough and a gradual increase in stenosis).
Staphylococcal pneumonia is a special form of lung damage with a characteristic tendency to abscess formation. Young children are more susceptible to the disease than others. It begins in most cases during or after ARVI. As an independent disease not accompanied by others, staphylococcal pneumonia is extremely rare.
The disease begins acutely or violently, body temperature is greatly elevated, and severe symptoms of toxicosis are observed. In more rare cases, staphylococcal pneumonia in children may begin gradually, initially followed by minor catarrhal symptoms. But even in these rare cases, the patient’s condition quickly deteriorates sharply, the temperature “jumps” greatly, intoxication intensifies, and respiratory failure increases. The child is lethargic and pale, he is drowsy, does not want to eat, spits up, and often vomits. Shortness of breath, shortening of the percussion sound, a moderate amount of fine moist rales on one side and weakened breathing in the affected area are recorded.
With staphylococcal pneumonia, bullae form in the lungs. These are air cavities, the diameter of which is 1-10 cm. They can be identified by taking an x-ray. Infection of the bulla threatens lung abscess. Breakthrough of a purulent focus leads to purulent pleurisy and pneumothorax. Deaths are common with staphylococcal pneumonia.
, scarlet fever-like syndrome may appear . Most often this happens with staphylococcal infection of a wound or burn surface, lymphadenitis, phlegmon, osteomyelitis.
The disease manifests itself as a scarlet-like rash. It occurs on a hyperemic (reddened) background, is formed from small dots, and is located, as a rule, on the lateral surfaces of the torso. When the rash disappears, abundant lamellar peeling is observed. During this form of the disease, the child’s body temperature is high. The rash appears 2-3 days after the onset of the disease and later.
Lesions of the gastrointestinal tract by staphylococcus can be located in various places (in the stomach, intestines, on the mucous membranes of the mouth, in the biliary system). The severity of such diseases also varies.
Staphylococcal stomatitis mainly affects young children. There is a pronounced hyperemia of the oral mucosa, the appearance of aphthae or ulcers on the mucous membrane of the cheeks, on the tongue, etc.
Staphylococcal gastrointestinal diseases are gastritis, gastroenteritis, enteritis, enterocolitis, which occur when infected through food. In children under 12 months of age, enteritis and enterocolitis often occur as secondary diseases against the background of another staphylococcal disease. If the route of infection is contact, and enteritis or enterocolitis occurs, a small amount of the pathogen is in the body. Staphylococci cause local changes when multiplying in the intestines, as well as general symptoms of intoxication when the toxin enters the blood.
With gastritis or gastroenteritis of staphylococcal nature, the incubation period lasts 2-5 hours, followed by an acute onset of the disease. The most striking symptom is repeated, often uncontrollable vomiting, severe weakness, severe pain in the epigastric region, and dizziness. Most sick children have a fever. The skin is pale and covered with cold sweat, the heart sounds are muffled, the pulse is weak and rapid. In most cases, damage occurs to the small intestine, which leads to bowel dysfunction. Bowel movements occur 4 to 6 times a day, the stool is of a liquid consistency, watery, and contains some mucus.
The most severe manifestation of staphylococcal infection is staphylococcal sepsis. It occurs more often in young children, mainly in newborns; premature infants are at particular risk. The pathogen can enter the body through the umbilical wound, gastrointestinal tract, skin, tonsils, lungs, ears, etc. This causes the type of sepsis.
If staphylococcal sepsis is acute, the disease develops rapidly, and the patient’s condition is characterized as very severe. The body temperature is greatly elevated, and symptoms of intoxication are pronounced. Petycheal or other rashes may appear on the skin. Secondary septic foci appear in various organs (abscesses, abscess pneumonia, purulent arthritis, skin phlegmon, etc.). A blood test reveals neutrophilic leukocytosis with a shift to the left, ESR is increased.
There is a (very rare) fulminant course of the disease, which ends in death. But in most cases the course is sluggish, with low-grade fever and mild symptoms of intoxication. Children sweat, pulse instability is noted, abdominal bloating occurs, the liver and spleen may be enlarged, dilated veins are noted on the anterior abdominal wall and chest, and stool disorders are often among the symptoms. Sepsis in young children can manifest itself with various symptoms, which complicates its diagnosis.
Staphylococcal infection in newborns and children of the 1st year of life is associated primarily with maternal illness. Infection of a child occurs at any stage of pregnancy, during and after childbirth.
Causes of childhood staphylococcus disease
Staphylococcal infection is life-threatening for a child
Staphylococcal infection is a disease caused by bacteria of the same name. As with many infectious diseases, there are several reasons for a child to become infected. Staphylococcus comes in various types, among which it is customary to distinguish:
- saprophytic staphylococcus. The least common type of infection among children. Affects the genitourinary system. It poses a low risk to humans and, with proper treatment, can be cured within a few days.
- epidermal staphylococcus. This species often affects babies who have undergone surgery or have weakened immune systems. It is not dangerous for healthy children, and in case of skin lesions, local therapy is most often prescribed.
- Staphylococcus aureus. The most dangerous type of bacteria. It received this name because of the characteristic color of the colonies that microorganisms form. It affects the gastrointestinal tract and is often observed in the mucous membrane and on the surface of the skin.
One of the main reasons for infection of children with staphylococcus is considered to be weakened immunity. The good, effective functioning of the child’s body’s defense system is remarkably resistant to various pathogenic microorganisms, the danger of infection from which is encountered literally at every step. In some cases, the tests show the presence of bacteria in the body, but no infection is observed: this is explained by the successful protective function of a healthy baby.
But a child whose immunity is weakened is poorly protected from the negative effects of bacteria and therefore can get sick. However, the modern level of medicine makes it possible to avoid the negative consequences of staphylococcal infection if therapy is started on time.
Staphylococcus in a child's stool is a cause for concern
The second most common cause of infection of a child with staphylococcus is considered to be a banal failure to comply with hygiene rules. Pathogenic microorganisms live in dirty places, and since young children are often not accustomed to washing their hands before eating and like to put everything they can get their hands on in their mouths, they increase the risk of staphylococcus infection.
Another option for the spread of staphylococcal infection is direct infection of a child from an already infected person. Infection can occur through damaged skin or through the mucous membrane. When the carriers of the disease are catering workers or hospital employees, the baby can become infected through food in kindergarten or school, or after being in the hospital where he was subjected to certain procedures.
The disease can be spread by insects, so their bite sites should always be treated.
Staphylococcus is an infectious disease caused by staphylococcus bacteria. There are several types that affect different body systems, have different levels of danger and also respond differently to treatment. The main reason for the development of staphylococcal infection in a child is his low level of immunity.