In recent years, diseases such as gastric and duodenal ulcers, chronic gastritis and duodenitis are usually considered together, since the nature of their origin and symptoms are similar. The difference lies in the localization and severity of the inflammatory process.
The stage of simple inflammation is called chronic gastritis (when the inflammatory process is localized in the stomach), chronic duodenitis (when the pathology is in the duodenum) or chronic gastroduodenitis (when there is inflammation in both organs).
The peptic ulcer stage is a peptic ulcer of the stomach and (or) duodenum .
1
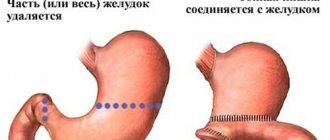
Comparison: healthy stomach and chronic gastritis. Causes of the disease
2 Gastric and duodenal ulcers
Treatment of the stomach should be comprehensive and individual, depending on the type and stage of the disease, as well as taking into account concomitant pathology. First of all, it is necessary to establish and eliminate the cause of the disease and relieve acute symptoms. Treatment of the stomach is most often carried out on an outpatient basis under the supervision of a gastroenterologist. In case of complicated gastritis, treatment in a hospital setting is required. An important component in the treatment of stomach diseases is adherence to a special dietary regimen.
General information
Chronic gastroduodenitis is a long-term pathology, which is characterized by inflammation of the pyloric part of the stomach and duodenum. The disease is more severe than gastritis or duodenitis individually.
Gastroduodenitis is a consequence of inflammatory, degenerative and dystrophic processes in the epithelial tissues of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract. As a result, the epithelium is rebuilt, dysfunction of the glands of the affected organs develops, and regenerative, secretory, and motor functions are disrupted.
Provoking factors
Systemic diseases, dietary errors and various external and internal factors can provoke the development of a chronic inflammatory process in the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum.
What diseases and pathologies can lead to the development of chronic gastroduodenitis:
- decreased production of gastric mucus;
- adrenal dysfunction;
- chronic gastritis, pathological processes in the liver, gall bladder, pancreas, peptic ulcer;
- colitis, enteritis;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine, cardiovascular, respiratory systems;
- kidney failure;
- helminthic infestations;
- food allergies;
- autoimmune diseases;
- poisoning with pesticides, acids, alkalis, salts of heavy metals;
- Helicobacter pylori infection;
- genetic predisposition.
One of the main provoking factors is violation of the rules of healthy eating. Long breaks between meals and constant overeating, excessive consumption of hot foods and drinks, fried, spicy foods, following a strict diet. Provoking factors include alcohol dependence and smoking, chronic fatigue, stress, unfavorable environmental conditions, long-term or uncontrolled use of medications.
What causes the disease?
There are several causes of inflammatory disease, which are divided into two groups:
- endogenous;
- exogenous.
Endogenous causes are the basis for focusing on acid formation, disruptions in hormonal regulation of secretion, and a decrease in the level of mucus formation. A predisposition to gastroduodenitis is observed in patients with the following diagnoses:
- diseases of the biliary tract and liver;
- endocrine pathology.
The most common exogenous etiological factors influencing the development of gastroduodenitis are:
- eating cold or hot, spicy food;
- chemical (exposure to pesticides);
- penetration of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori into the body.
Clinical manifestations
Symptoms of chronic gastroduodenitis include pain in the abdominal cavity of varying degrees of intensity and a feeling of heaviness in the stomach. 1-2 hours after eating, cramps and discomfort appear in the upper abdomen on the right side. The pain is most often aching, moderate, and can radiate to the back or shoulder blade.
Other manifestations:
- dark yellow or white coating on the tongue;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- constipation gives way to diarrhea;
- decreased appetite;
- nausea, vomiting, increased salivation;
- flatulence, belching;
- signs of dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system - weakness, increased sweating, finger tremor, tachycardia.
As the pathology worsens, the skin becomes pale, blood pressure and heart rate decrease. Sometimes the temperature rises to low-grade levels.
Exacerbation of the disease most often occurs in the spring and autumn months. The acute period can last up to 6-8 weeks, but the pain syndrome disappears after 7-10 days.
Symptoms
The chronic form of gastroduodenitis can make itself felt within six months. That is, during this time mild symptoms may be observed. Then an exacerbation develops. In this case, the symptoms become pronounced. An exacerbation attack can be triggered by stress, consumption of spicy, salty, fatty, fried foods, and alcohol. Moreover, exacerbation is observed in spring and autumn.
Superficial chronic gastroduodenitis during remission is characterized by aching pain in the stomach and navel. Pain is the main symptom. Nausea and vomiting may occur, especially if a person eats fatty or salty foods. Sometimes there is a violation of the stool - diarrhea is replaced by constipation. Heartburn and belching occur. If you follow a diet, pain and other symptoms will be less pronounced.
When an exacerbation occurs, the pain becomes sharp and sharp. They can be so strong that a person is twisted in half. The ulcerative form is characterized by vomiting with blood. This indicates internal bleeding. This condition requires immediate hospitalization because the ulcer may perforate. This is fraught with peritonitis. The condition is extremely life-threatening. During the period of exacerbation, a person not only experiences pain, but also the skin turns pale, bad breath appears, and belching with a sour or bitter taste appears. You may feel dizzy. Some patients even fainted.
Diagnostic measures
A gastroenterologist is responsible for diagnosing and drawing up a treatment plan. Additionally, you must make an appointment with an endoscopist.
Diagnostic methods:
- Examination with palpation of the abdomen, history taking.
- Clinical blood and urine tests, coprogram.
- EGDS - examination reveals hyperemia, atrophy or enlargement of the mucosa. Additionally, biomaterial is taken for histological examination.
- pH-metry is a method for determining the acidity of digestive juice.
- Electrogastroenterography, antroduodenal manometry - analysis of the motor and evacuation functions of the affected digestive organs.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs, duodenal intubation. Prescribed to identify concomitant diseases - pancreatitis, hepatitis, cholecystitis.
- X-ray with contrast. Erratic, hyperactive peristalsis and periodic spasms are observed. The folds of the intestine are reduced or enlarged. Sometimes congestion and signs of gastroesophageal reflux are observed.
- Tests for Helicobacter pylori - breath testing, polymerase chain reaction, stool enzyme immunoassay.
Differential diagnostics are carried out to exclude peptic ulcer, spasm of the sphincter of Oddi, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, cancer of the duodenal papilla, hiatal hernia.
Diet
General principles of proper nutrition in cases of dysfunction of the digestive tract include:
- Frequent meals of moderate temperature in small portions without swallowing hard or large pieces.
- Exclusion of spicy, fried, salty, smoked, alcohol, carbonated drinks.
- Consumption of vegetable soups and non-concentrated broths, lean boiled meat and fish, lactic acid products, eggs, boiled porridges, stale and unhealthy bread, boiled or raw grated vegetables and fruits.
Treatment methods for chronic gastroduodenitis
Therapy for the disease includes several stages - diet selection, drug and non-drug treatment.
Diet therapy
For chronic gastroduodenitis, diet is one of the important components of treatment. It is necessary to exclude from the diet foods that require prolonged digestion. All food should be boiled, pureed or mushy.
Authorized products:
- slimy or pureed first courses in vegetable or weak meat or fish broth;
- lean varieties of meat and fish, steam, boil, stew;
- buckwheat, semolina, rice, vermicelli;
- seasonal vegetables, stewed or boiled;
- butter and vegetable oils - add to prepared dishes;
- dried wheat flour bread, white crackers;
- steam omelette, soft-boiled eggs;
- jelly, jelly, sweet fruit compote;
- casserole, low-fat cottage cheese soufflé;
- dairy products;
- marshmallows, biscuits, honey, sweet jam;
- weak black or green tea with milk.
During an exacerbation of the disease with high and normal acidity, table No. 1 is prescribed. With low acidity - diet No. 2. After improvement of the condition - diet No. 15. For constipation - No. 3, with stool disorder - No. 4. In the first 24 hours after the onset of relapse Fasting is indicated; you can drink water or tea without sugar in small quantities.
If you have gastroduodenitis, you should not eat hot or cold foods, fatty or fried foods. The list of prohibited products includes any canned food, marinades, smoked meats and marinades, sauces and spices. Alcohol and carbonated drinks, raw vegetables, and mushrooms are contraindicated.
Pharmacotherapy
The goal of drug treatment of chronic gastroduodenitis in children and adults is the same - to relieve unpleasant symptoms, eliminate the causes of the pathological condition, reduce the risk of exacerbation of the disease and the development of complications.
Groups of medications:
- antimicrobial drugs, bismuth-based agents to eliminate Helicobacter pylori infection;
- antispasmodics;
- antacid drugs, proton pump inhibitors;
- dopamine receptor antagonists, enzymes;
- vitamin complexes;
- antidepressants.
When diagnosing a phlegmonous form of pathology, duodenal obstruction, surgical intervention is prescribed.
Non-drug therapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed during remission and exacerbation of the disease.
Effective physiotherapy:
- medicinal electrophoresis and galvanization;
- ultrasound therapy - for normal and increased acidity of gastric juice;
- treatment with diadynamic or sinusoidally modulated currents;
- DMV therapy;
- inductotherapy;
- laser or magnetic laser therapy;
- applications with ozokerite, paraffin, mud therapy;
- treatment with mineral waters, pine, pearl baths.
Physiotherapy has a beneficial effect on the main pathogenetic mechanisms of disease development. The procedures help normalize the functioning of the nervous, endocrine, and immune systems. The treatment helps to reduce the manifestations of inflammation and improve microcirculation, has a pronounced analgesic effect, and restores the trophism of the affected organs. The positive results obtained last for several months.
During remission, physical therapy is prescribed. The specialist selects exercises to improve blood circulation in the abdominal cavity and trophism of the gastric mucosa, accelerating reparative processes.
Additionally, patients are recommended a course of psychotherapy to learn methods of dealing with stress and nervous tension.
Duodenitis
Duodenitis is an inflammatory disease of the duodenum . There are acute and chronic forms. Acute duodenitis often occurs in combination with acute inflammation of the stomach and intestines (acute gastroenteritis, gastroenterocolitis).
Causes of the disease:
- heredity;
- poisoning with toxic substances;
- excessive consumption of spicy, rough foods in combination with strong alcohol, etc.
Symptoms:
- pain in the epigastric region;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- general weakness.
Acute duodenitis most often goes away on its own within a few days, but can become chronic. In some forms, complications are possible (intestinal bleeding, perforation of the intestinal wall, development of acute pancreatitis).
In the treatment of diseases of the stomach and duodenum, timely diagnosis and professional medical care are very important. Our clinic specialists work for you seven days a week and on holidays, using the most modern techniques.
The material was prepared with the participation of a specialist:
Prevention
To avoid exacerbation of chronic gastroduodenitis, doctors recommend adhering to the following rules:
- to refuse from bad habits;
- eat properly and balanced;
- do not forget about moderate physical activity;
- avoid stress and overwork;
- carry out anti-relapse therapy once every 2 months.
With chronic gastroduodenitis, it is impossible to completely cure the disease. Various factors can trigger a relapse - stress, dietary errors, overwork. But if you follow all the recommendations of the gastroenterologist, you can avoid systematic exacerbations.
Self-medicating chronic gastroduodenitis is dangerous. Without proper therapy, dangerous complications develop - peptic ulcer, gastric bleeding, cancer of the stomach or duodenal papilla, anemia, atrophic gastritis.
Causes of relapses
Treatment of chronic gastritis and chronic gastroduodenitis is not an easy task. This is due to its high prevalence, as well as the fact that many patients consider gastritis to be a simple disease and do not seek medical help in a timely manner. There are also difficulties in the treatment of gastritis due to the resistance of Helicobacter pylori to antibiotics.
Recurrence of the disease is associated with unauthorized cessation of treatment by patients, violation of diet and nutrition, and the development of resistance of Helicobacter pylori to antibiotics in prescribed treatment regimens. Psycho-emotional experiences during stress play a significant role in the occurrence of relapses. Today the statement “All diseases come from nerves” has complete scientific justification.