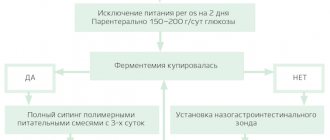
The cause of chronic gastritis in children is a number of factors. The greatest importance in the development of the disease is a violation of the regime and diet: irregular meals with long breaks, dry eating, fast food with insufficient chewing of food; systematic overeating, frequent intake of rough, difficult to digest, spicy, fatty foods; monotonous set of food products. Eating unwashed foods contaminated with bacteria can also lead to gastritis.
In some cases, the cause of the development of chronic gastritis may be a food allergy, that is, intolerance to certain foods.
Hereditary predisposition to stomach diseases plays a certain role. The cause of chronic gastritis can be diseases of other organs of the digestive tract (cholecystitis, colitis, hepatitis, pancreatitis, etc.), as well as other foci of chronic infection in the child’s body (sinusitis, tonsillitis, caries, kidney disease, pneumonia, tuberculosis, rheumatism, etc. ). In addition, chronic gastritis can develop against the background of neuroses and pathology of the endocrine system. It should be remembered that long-term use of certain medications can provoke chronic inflammation of the gastric mucosa. Such provocateurs include glucocorticoid hormones, salicylates, cytostatic drugs, antibiotics, reserpine and a number of other medications. The cause of the disease can be giardiasis and helminthic infestation in a child.
A negative emotional background is important in the etiology of the disease: conflicts in the family, unpleasant conversations and the environment during meals, etc. The onset of the disease in many children coincides with entry into school. This is explained by a sharp change in the child’s general and dietary regime, as well as increased emotional and physical stress associated with starting school. Cases of the disease in preschool children are also not uncommon.
General rules
In modern conditions, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, which were characteristic only of adults, began to be observed in children. Often the onset of the disease occurs in preschool age. gastritis , esophagitis and duodenitis have become not uncommon , and the number of children suffering from them has increased. If earlier erosive esophagitis was considered an “adult” disease and not typical for children, now it is often diagnosed in schoolchildren and preschoolers.
An important feature of gastrointestinal diseases in children is their combined nature, when several parts of the digestive tract are involved in the process. Acute gastritis , which is associated with the consumption of low-quality products, poisoning with household liquids (often in children under one year of age due to accidental intake of various detergents), proceeds rapidly, does not go unnoticed and often requires hospitalization. A peculiarity of chronic gastric diseases in children is the asymptomatic and mild nature of the course, and this complicates their diagnosis.
The reasons for the chronicity of the process are:
- Unhealthy diet and poor eating habits. Often the share of fast food in children's diets increases. Families do not always pay due attention to healthy eating. If you offer your child a bowl of soup and a burger, his choice will fall on the latter. From an early age, a child is accustomed to food with a high content of flavor enhancers, fats, sugar: carbonated drinks, juices with preservatives, sausages, semi-finished products, cakes with cream, shelf-stable confectionery. All these products have a detrimental effect on the condition of the gastric mucosa.
- Violation of the diet, which is very important for the harmonious functioning of the digestive system. Eating food at the same time teaches the digestive organs to develop a certain rhythm of secretion of enzymes and juices, work synchronously and digest food efficiently. In the absence of a regime, the digestive system cannot fully cope with incoming products, especially if it is loaded with fried or fatty foods.
- Helicobacter Pylori infection. It is generally accepted that this infection predisposes to a chronic inflammatory process. The bacterium is detected in children under one year of age and older. Children become infected from their parents, and treatment requires mandatory anti-Helicobacter therapy.
- Stress and anxiety, anxiety, overload at school and lack of sleep.
- Changes in hormonal levels during puberty.
With gastritis , a child experiences pain in the upper abdomen. Young children cannot indicate the location of the pain; they often characterize their condition as “stomach pain.” In some children, this symptom is not very pronounced, and nausea, poor appetite and vomiting predominate.
Older children may complain of heartburn or belching that is sour or has an unpleasant taste. General weakness and drowsiness and indigestion (diarrhea, bloating) may occur. vitamin deficiency develops .
Treatment of chronic gastritis and gastroduodenitis includes taking antacid, anti-Helicobacter and antisecretory drugs. Nutritional treatment for gastritis in children is considered the main method of rehabilitation.
Baby food should be clearly organized:
- Eating on a regular schedule.
- Eating only fresh and natural products prepared at home or in the kindergarten catering unit.
- Cooking food in accordance with the principles of nutrition. It is advisable for this disease to undergo culinary treatment in the form of boiling, stewing and steaming, and, if indicated, pureed. This provides mechanical and chemical sparing of the mucous membrane.
- Diversify the diet - include products of animal and plant origin so that the child receives all the necessary components.
- Establishing a daily routine - lessons, additional clubs, rest and outdoor games.
- Use a minimum of salt and sugar when preparing dishes.
- Exclusion from the diet of sweet fruit waters, fast food, sweets, chocolate, candies, semi-finished products, black bread, smoked foods, fatty and spicy foods, mushrooms, coffee, cocoa, sauces, ketchup, vinegar, mayonnaise and various spices.
Food in composition and quantity of all components must meet the needs of the body and meet age standards. Depending on the stage of the process, diets are used in which the degree of mechanical and chemical sparing is successively reduced.
During the period of exacerbation, if there is such a need, children are prescribed the most gentle Diet No. 1A . During this period, food is given only in liquid or mushy form. The amount of food consumed at one time is significantly reduced. Avoid eating bread and any vegetables. Since there are significant dietary restrictions and it is not balanced, it can only be used for 3-4 days.
The child can use:
- Slimy soups (decoctions of semolina, oatmeal or rice) with the addition of beaten eggs, cream, butter.
- Meat, poultry and fish in the form of puree, passed through a meat grinder several times and brought to a pasty state with boiled water.
- Milk, steamed fresh cottage cheese soufflé, cream for dishes.
- Steam omelet and soft-boiled eggs.
- Liquid pureed porridge (rice, buckwheat, oatmeal) with milk or porridge made from cereal flour with milk, butter or cream.
- Kissels made from sweet berries and jelly of sweet pureed fruits.
- Juices (carrot, apple, pumpkin) diluted, weak tea, herbal decoctions.
During the period when the manifestations of gastritis , the less gentle Diet 1B . The diet includes pureed soups and pureed milk porridges, pureed vegetables and fruits. Meat and fish dishes are enhanced with steamed quenelles and cutlets. In general, the amount of food consumed per day increases. A child can remain on this diet for up to one month. During the period of recovery and remission, it is recommended to switch to the main table, which will be discussed below.
It is recommended to adhere to these diets, replacing each other, from three months to 1 year. However, even an expanded version of a child’s diet should not contain lamb, pork, all kinds of smoked meats, canned meat, fish and vegetables, mushrooms, and ready-made confectionery products with preservatives and dyes.
Symptoms and manifestations
Gastroenterologists distinguish several stages of a health-threatening disease. Acute gastritis is characterized by a sudden onset, sharp pain in the upper abdomen (slightly above the navel), sometimes the pain radiates to the right hypochondrium. In this case, there may be nausea and vomiting, body temperature often rises (sometimes up to 39 ° C), upset stool, lethargy and lack of appetite are observed.
Very often, parents in these cases suspect that the child ate something wrong. And this is partly true. Even if the baby has eaten good quality food, it is quite possible that it is not appropriate for his age. In other cases, the disease may be caused by food toxins or disease-causing organisms.
If you consult a doctor on time, follow the timing and volume of therapy and all medical recommendations, then the disease will remain only an unpleasant episode in the child’s life and will not become chronic.
Chronic gastritis is a constant series of phases of recovery and exacerbation. In this case, the issue of baby food for gastritis comes to the fore. And the goal of treatment is to minimize periods of exacerbation (relapses) and increase periods of remission of the disease, that is, the time when painful symptoms are practically not observed.
Authorized Products
The diet for gastritis in children includes the use of:
- Lean meat and poultry. To prepare dishes, you can use beef, veal, chicken or turkey. Mostly dishes are prepared from minced meat or minced meat - soufflés, pates, cutlets, zrazy, meatballs, quenelles. Tender meat can be offered in pieces, or cooked in the oven using foil.
- Soups made with vegetable broths or water, to which oatmeal, semolina, buckwheat, cereals and rice are added.
- Soups can be pureed or not, and finely chopped vegetables can be added to them. To improve the taste, first courses are flavored with cream, beaten egg and butter are added, meatballs or rolled boiled meat are added.
- Fish in the form of steamed or stewed minced products: cutlets, meatballs, dumplings, lump fish. For cooking I use low-fat dietary fish (pike, pike perch, hake, cod, pollock, pollock, ice fish, blue whiting).
- Potatoes, young green peas, carrots, zucchini, pumpkin - they are prepared in the form of puree with the addition of cream and butter.
- Dried wheat bread, white bread croutons, savory pastries with cottage cheese or apples.
- Homemade sauces - milk, sour cream or cream.
- Cereals and flours made from buckwheat, oatmeal, semolina, and rice, from which porridge is prepared with milk or water, depending on the child’s preference.
- Milk, non-acidic cottage cheese in a semi-liquid state, cottage cheese soufflé, milk jelly. The child can drink warm milk if tolerated well.
- Soft-boiled eggs or steam omelet.
- Berry jelly and jellies, baked apples, which after cooking can be drizzled with honey.
- Butter.
- Weak tea with milk, diluted berry juices, carrot and pumpkin juice.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cauliflower | 2,5 | 0,3 | 5,4 | 30 |
| potato | 2,0 | 0,4 | 18,1 | 80 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| beet | 1,5 | 0,1 | 8,8 | 40 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
Fruits | ||||
| apricots | 0,9 | 0,1 | 10,8 | 41 |
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
| nectarine | 0,9 | 0,2 | 11,8 | 48 |
| peaches | 0,9 | 0,1 | 11,3 | 46 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Berries | ||||
| strawberry | 0,8 | 0,4 | 7,5 | 41 |
| raspberries | 0,8 | 0,5 | 8,3 | 46 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| semolina | 10,3 | 1,0 | 73,3 | 328 |
| cereals | 11,9 | 7,2 | 69,3 | 366 |
| white rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| noodles | 12,0 | 3,7 | 60,1 | 322 |
Bakery products | ||||
| white bread crackers | 11,2 | 1,4 | 72,2 | 331 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jelly | 2,7 | 0,0 | 17,9 | 79 |
| marshmallows | 0,8 | 0,0 | 78,5 | 304 |
| meringues | 2,6 | 20,8 | 60,5 | 440 |
| paste | 0,5 | 0,0 | 80,8 | 310 |
| Maria cookies | 8,7 | 8,8 | 70,9 | 400 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
| sugar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 99,7 | 398 |
| milk sauce | 2,0 | 7,1 | 5,2 | 84 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk | 3,2 | 3,6 | 4,8 | 64 |
| cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,7 | 205 |
| sour cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,2 | 206 |
| curdled milk | 2,9 | 2,5 | 4,1 | 53 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese | 17,2 | 5,0 | 1,8 | 121 |
Meat products | ||||
| boiled beef | 25,8 | 16,8 | 0,0 | 254 |
| beef liver | 17,4 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 98 |
| boiled beef tongue | 23,9 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 231 |
| boiled veal | 30,7 | 0,9 | 0,0 | 131 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| boiled chicken | 25,2 | 7,4 | 0,0 | 170 |
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
Eggs | ||||
| chicken eggs | 12,7 | 10,9 | 0,7 | 157 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
| ghee | 0,2 | 99,0 | 0,0 | 892 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| coffee with milk and sugar | 0,7 | 1,0 | 11,2 | 58 |
| black tea with milk and sugar | 0,7 | 0,8 | 8,2 | 43 |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| apricot juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,0 | 38 |
| carrot juice | 1,1 | 0,1 | 6,4 | 28 |
| pumpkin juice | 0,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 38 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
At the stage of unstable recovery
Dietary dishes of table No. 1b contribute to further normalization of the gastric mucosa, and are prescribed for a period of 5-7 days. Acidic foods (marinades, fruits and berries), rich broths and white cabbage - a powerful stimulator of gastric juice secretion - are excluded from the diet.
Food is prepared with a liquid and mushy consistency by steaming or boiling. Steamed cutlets and wheat crackers appear in the list of dishes, and pureed soups are served instead of slimy soups. The energy value is slightly reduced due to the restriction on carbohydrates, but at the same time it practically corresponds to the norm of 2600 kcal.
Sample menu for diet No. 1b
Fully or partially limited products
Exception required:
- Millet, pearl barley, corn barley, cereals, since they are coarse and difficult to digest.
- Broths, animal fats, fried foods, fatty meats, sausages, pickled and pickled vegetables, smoked meats, rough meats and rough vegetables, mushrooms.
- Irritating foods (onions, garlic, ginger, radishes, radishes), legumes and cabbage, which contain a lot of fiber and cause bloating.
- Fermented milk drinks, sour undiluted juices, which can irritate the mucous membranes.
- Carbonated drinks, cocoa, kvass, strong tea.
- Pepper and spices, hot sauces, ketchup, mayonnaise, vinegar in dishes.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| vegetables legumes | 9,1 | 1,6 | 27,0 | 168 |
| swede | 1,2 | 0,1 | 7,7 | 37 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| sauerkraut | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,4 | 19 |
| green onion | 1,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 19 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| canned cucumbers | 2,8 | 0,0 | 1,3 | 16 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| turnip | 1,5 | 0,1 | 6,2 | 30 |
| canned tomatoes | 1,1 | 0,1 | 3,5 | 20 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| corn grits | 8,3 | 1,2 | 75,0 | 337 |
| pearl barley | 9,3 | 1,1 | 73,7 | 320 |
| millet cereal | 11,5 | 3,3 | 69,3 | 348 |
| barley grits | 10,4 | 1,3 | 66,3 | 324 |
Confectionery | ||||
| candies | 4,3 | 19,8 | 67,5 | 453 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Cakes | ||||
| cake | 4,4 | 23,4 | 45,2 | 407 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| ginger | 1,8 | 0,8 | 15,8 | 80 |
| ketchup | 1,8 | 1,0 | 22,2 | 93 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
| ground black pepper | 10,4 | 3,3 | 38,7 | 251 |
| chilli | 2,0 | 0,2 | 9,5 | 40 |
Dairy | ||||
| kefir | 3,4 | 2,0 | 4,7 | 51 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
| ham | 22,6 | 20,9 | 0,0 | 279 |
Sausages | ||||
| dry-cured sausage | 24,1 | 38,3 | 1,0 | 455 |
| sausages | 10,1 | 31,6 | 1,9 | 332 |
| sausages | 12,3 | 25,3 | 0,0 | 277 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| dried fish | 17,5 | 4,6 | 0,0 | 139 |
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| bread kvass | 0,2 | 0,0 | 5,2 | 27 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Basic principles
Photo: Depositphotos.com. Author: inerika.
The purpose of dietary tables is to minimize further irritation of the gastric mucosa and reduce the load on its secretory functions. “Food should be gentle - thermally, mechanically and chemically,” this phrase is repeatedly repeated as a postulate by nutritionists and pediatricians when prescribing treatment. In other words:
- food is served only warm;
- irritating products are excluded: spicy, fatty, pickled, salty, sour, carbonated and smoked;
- Difficult-to-digest foods are prohibited: legumes, mushrooms, fatty or stringy meat, fruits with thick skin;
- Rich broths containing vegetables, meat and fish are contraindicated.
During treatment, strict adherence to a daily routine with a full night's rest, 6 meals a day strictly according to the clock (every day at the same time) and a favorable psychological atmosphere during meals is necessary.
Nutrition menu for gastritis in children (Diet)
The basis of the diet, depending on the severity of the exacerbation and the doctor’s recommendations, consists of unprocessed or pureed dishes: porridge, soups, meat and fish. For gastritis, you can often prepare milk soups and porridges if the child has previously eaten dairy dishes well.
You can steam souffles (meat or fish), omelettes, puddings, egg porridge, and sauces. Preference is given to dairy products and egg dishes, since their protein is easier to digest.
Eggs and cottage cheese can be included in the menu every day. For constant nutrition during the period of remission, you can prepare steamed or stewed meat and fish dumplings, cutlets, soufflé and zrazy (with mashed potatoes). Fish or meat dishes should be consumed twice a day.
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
Diet tables
A child's continued adherence to a diet often causes concern among parents. What to feed, how to cook, what foods are strictly prohibited for consumption?
For dietary therapy of gastritis, dietary tables No. 1, 1a, 1b, 2 are intended:
- No. 1 – for chronic gastritis with high acidity without exacerbation (for 6-12 weeks);
- No. 1a – for acute form of gastritis and chronic during the period of exacerbation (until the pronounced clinical manifestations of the disease disappear);
- No. 1b – in the stage of unstable recovery (until complete normalization of well-being)
- No. 2 – in the treatment of gastritis with reduced acidity.
Reviews and results
For children diagnosed with gastritis , dietary nutrition is of great importance in treating the disease. Reviews from parents indicate its necessity and effectiveness. The main table can be performed for a long time, since it includes the required amount of proteins, fats and complex carbohydrates. Parents should choose recipes for those dietary dishes that are more acceptable for their child, taking into account his preferences.
The only difficulty is the lack of factory-made confectionery products in the diet, which contain trans fats, preservatives, flavor enhancers and food coloring. You can replace them with homemade low-fat baked goods: biscuits, cookies, muffins, at least they will not contain chemicals.
- “... A 4-year-old child began to experience vomiting and poor appetite. Whatever he eats, he feels nausea and then vomits. They examined the stomach, did an ultrasound - the liver and pancreas were enlarged. For now we settled on gastritis. Before this, my daughter had not eaten sausage, mayonnaise, cookies with dyes or chocolate. I can say that I cooked 70% of it for her separately. The food was practically dietary: soups, porridge twice a day, boiled meat, purchased purified water, curds and juices for baby food. He goes to kindergarten - there is food for children. I ate sweets, but within reasonable limits. I can't imagine why this happened. Until the age of 8, every spring and autumn she was in the hospital, where she was given a strict diet and medications. At home I have been cooking in a double boiler all these years. Nothing has bothered her for two years now”;
- “... My daughter is 9 years old; on FGDS she was diagnosed with chronic gastritis of the proximal stomach. They did a test for Helicobacter - several times higher than normal. Immediately prescribed Diet No. 5 and treatment for 2 weeks. I started using a slow cooker, in which I immediately stewed vegetables, chicken or turkey, and prepared omelettes and biscuits. I cooked soups in the usual way. After 2 weeks, the condition improved significantly - there was no nausea or pain, and my appetite also improved. When testing for bacteria was repeated, the response was within normal limits. The diet was followed for 2 months. Now the doctor recommends a gentler diet in the autumn-spring period; if there is pain, then take De-nol and Lansoprozole. Everything needs to be done, since the child is only 9 years old and has his whole life ahead of him”;
- “... My son started having stomach problems in the fifth grade, when his workload increased and he had to stay at school for up to three hours. At school, the food at the buffet is dry, and he doesn’t want to take food with him. Even if I did, it would still not be soups or warm porridge. He also doesn't eat well in the morning. The doctor said the right thing when he recommended dietary nutrition. On those days when the son is at home (holidays or vacations), he manages to eat properly and follow the regime, and improvement is immediately noted. It is also important that he rests, sleeps well and is not in a hurry. He enjoys eating milk porridges, cottage cheese casseroles, cheesecakes in a slow cooker and soufflé. I steam the cutlets, but I prepare bechamel or sour cream sauce for them - this significantly improves the taste. I cook soups in water and do not fry them. During this period, the whole family adheres to proper nutrition.”
Why did the child develop gastritis?
Among the reasons that caused the occurrence of this serious disease in childhood, experts name the following:
- immaturity of the children's digestive system. Since the child’s digestive system is fully formed by about seven years of age, before this age children are most vulnerable to the effects of adverse factors on the gastrointestinal tract;
- period of intensive growth of the child. Usually this is 5-6 years and 10-15 years. During these periods, there is a higher incidence rate;
- food inappropriate for age;
- non-compliance with diet;
- taking certain medications;
- eating in a hurry, when food is swallowed almost without chewing;
- abuse of dry eating - eating raw vegetables and fruits;
- physical and emotional stress, stress.
A child may encounter unfavorable factors when moving from kindergarten to school. During this period, general and nutritional regimes undergo dramatic changes and are often disrupted. Parents are not always able to control their child’s diet in new conditions.
Other reasons may be no less important:
- the baby’s hereditary predisposition to gastrointestinal diseases;
- various infections, especially dangerous encounters with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori;
- helminthic infestations;
- endocrine pathologies;
- untreated acute gastritis that has become chronic.
Important! Only a specialist can identify and confirm the diagnosis based on tests and laboratory tests! Don't self-medicate! An incompetent person can easily make a mistake and miss more serious surgical pathologies - appendicitis, intestinal obstruction and others. At the first signs of acute gastritis in your baby, immediately call a doctor or go to the clinic! Do not refuse hospitalization if necessary.