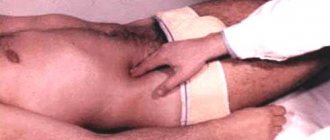
Gallbladder diseases are characterized by their manifestations, and one of them is Ortner’s symptom in cholecystitis. It appears during examination of the patient. If you hit the right costal arch with the edge of your hand, pain will occur. It is less pronounced in the chronic form and with biliary dyskinesia.
The gallbladder is located in the right lobe of the liver, in its lower part. Its dimensions reach 14 cm in length and 5 cm in width; in consistency it is a soft organ. In a healthy state, the gallbladder is practically not palpable, despite the fact that it protrudes slightly relative to the liver. If the doctor finds an organ during palpation, this indicates the development of pathology.
Relevance of palpation of the gallbladder (Murphy's symptom)
The doctor who developed this technique for diagnosing acute abdomen was born in 1857 in Chicago.
His name is John B. Murphy. Chicago physician D.B. Murphy is considered a leading figure in American surgery. He has also developed other methods that make it possible to quickly and effectively diagnose many acute pathological conditions of the abdominal cavity. His experience is valued by specialists and is being implemented in practical medicine. The symptom, the pattern of manifestation of which was established by an observant physician, made it possible to determine the cause of pain in many thousands of patients. By profession, John B. Murphy was a surgeon and diagnostician. He was lucky to study with a brilliant specialist of those years - Billroth. Murphy worked in his native Chicago. In addition to surgery, the doctor trained specialists, introducing the author’s methodology into practice. John B. Murphy is also the originator of the practice of treating tuberculosis using artificial pneumothorax.
The mere presence of gallstones does not prove that the cause of an episode of severe abdominal pain is cholecystitis, while maximum pain in the projection of the gallbladder confirms this diagnosis. The “ultrasound” Murphy’s symptom is detected as follows: the gallbladder is visualized and, by applying pressure with the device’s sensor, it is determined whether its projection is the zone of maximum pain.
The main method for determining intermittent inspiration when pressing in the right hypochondrium (Keur's point) is quite informative. With proper palpation during further diagnosis, acute cholecystitis is confirmed in almost 80% of patients. Additionally, the doctor conducts a survey and determines the presence of nausea, vomiting and pain in the upper right abdomen.
If during palpation the breath is intermittent, but the patient complains of pain in the lower back, then this is not cholecystitis, but most likely pancreatitis or kidney disease. Murphy's symptom is not indicative of pancreatitis. If inflammation of the pancreas is suspected, the Mayo-Robson symptom is noted (pain is concentrated in the costovertebral angle). Also informative are the symptoms of Bliss, Voskresensky, Kerte and many other specialists studying the pancreas.
The achievements of modern medicine make it possible to determine acute cholecystitis using hardware and instrumental methods. The most revealing can be considered MRI and ultrasound. Murphy's symptom serves as a reason for prescribing this diagnosis. Despite hardware methods, Murphy's symptom remains relevant, since treatment often needs to be started urgently; there is simply no time or opportunity to take the patient for a more accurate diagnosis.
For example, the patient is in a remote village, in a hunters' or shepherds' camp, where it is impossible to deliver medical equipment. Modern methods make it possible to identify the disease (acute cholecystitis) with an ultrasound Murphy sign. The accuracy of this method exceeds 90%. For diagnosis, a special probe is used to determine the location of the gallbladder.
In medical dictionaries you can also find a slightly different way of defining a disease according to Murphy’s symptom. In this case, the patient will not need to lie on his back. So, the doctor will need to clasp the patient’s torso with his left hand so that the thumb is located in the area of the right hypochondrium. Next, the patient will need to exhale, as a result of which the finger will have to plunge deep into the body.
Then you have to take a breath. If pain occurs at the moment, doctors tend to say that Murphy's symptom is positive. But in this case, it should be noted that this method of determining the positivity of a reaction is applicable to small people or children. With large-bodied patients, this diagnostic method will be completely irrelevant.
Diagnosis of cholecystitis
If gallbladder disease is suspected, the doctor initially examines the patient manually, without the use of various instruments. The reception begins with palpating and light tapping in different parts of the abdomen.
To diagnose such diseases in medicine, there are the following terms:
- Ortner's symptom is pain when tapping the side of the hand along the costal arches on the right.
- Murphy's symptom - the doctor presses lightly with his fingers on the area of the gallbladder, while the patient experiences pain when inhaling.
- Mussi's symptom - pressure is applied with two fingers in the area of the collarbones; if the patient experiences pain, then this is also considered a manifestation of pathologies of the gallbladder and its ducts.
Determining the symptoms of Ortner, Murphy, Mussi is an indication for further instrumental examination. As a rule, they prescribe: Ultrasound of the abdominal organs. General and biochemical blood tests. Analysis of urine. Tests for oncology, if necessary; Biopsy in some cases.
Video on the topic:
General symptoms of cholecystitis
Depending on the location of inflammation or changes in the structure of blood vessels and biliary tract, there are many symptoms of the disease:
- dull pain in the right hypochondrium, which spreads upward - to the area of the right shoulder blade, collarbone and shoulder; as the disease progresses, the pain becomes more acute and intense;
- nausea and vomiting caused by pain;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- the presence of bile in the vomit;
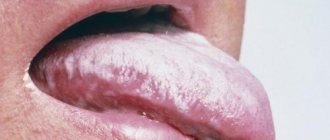
- the tongue is coated and dry;
- possible fever and chills;
- if the disease progresses, tachycardia and increased blood pressure are detected;
- if the lumen of the biliary tract is blocked (if there are stones in it), then the person develops pronounced jaundice;
- pain on palpation in the right hypochondrium.
In addition to those listed, the main symptom of the disease is Ker's symptom. It is expressed in pain upon palpation in the area where the diseased organ is located. As the disease progresses, the pain becomes more intense and spreads less localized.
What gallbladder diseases can be identified by checking symptoms
Bladder symptoms help with almost 100% probability to identify various diseases of the gallbladder, both acute and chronic. Dysfunction of the sphincter of Oddi is often accompanied by other diseases of the digestive tract.
Such as:
- impaired motility of the small and/or large intestine;
- inflammation of the gastric mucosa;
- hiatal hernia;
- ulcers of the stomach and duodenum;
- chronic pancreatitis.
The disease manifests itself as paroxysmal pain in the area of the stomach (often the duration of the attack reaches 30 minutes). In this case, ultrasound does not reveal any abnormalities in the gallbladder, pancreas and liver. And when cystic symptoms are detected, pain under the ribs on the right side is characteristic.
Lack of timely treatment for sphincter of Oddi dysfunction can provoke the development of gallbladder diseases - stone formation, cholecystitis and cholangitis.
The chronic form of cholecystitis is a disease of the gallbladder, in most cases it is diagnosed in women. An acute form of pathology occurs only if the diet is not followed.
In addition to cystic symptoms, the following signs indicate this disease:
- dull pain radiating under the scapula, to the heart, subclavian region, neck and back (becomes more intense when moving), often occurring at night, especially after breaking the diet (often accompanied by deep breathing and coughing);
- lack of appetite;
- quite pronounced intoxication and inflammatory syndromes;
- painful or difficult digestion;
- nausea and vomiting;
- sometimes yellowness of the skin (usually with cholangitis);
- increase in body temperature up to 38°C;
- feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- belching.
Chronic cholecystitis often occurs with regular intervals between exacerbation and remission. In some cases, this disease can lead to the formation of gallstones.
If you follow the treatment and nutrition regimen prescribed by your doctor, then attacks of cholecystitis may not bother you for quite a long time.
Gallstone disease is also more common in women over 35 years of age, especially those who tend to be overweight.
In addition to positive cystic symptoms, this disease is characterized by the following signs:
- jaundice, which appears within 24 hours after the end of the attack and gradually begins to disappear approximately 3 days after the attack;
- intolerance to fatty foods, manifested by mild abdominal pain, flatulence and diarrhea;
- paroxysmal pain in the right hypochondrium, which can last several hours and stop as suddenly as it began (while sitting, the pain increases significantly;
- signs of intoxication;
- a wave-like increase in body temperature up to 38°C, often allowing one to suspect acute cholecystitis occurring in parallel.
Also, cholelithiasis may be accompanied by atypical symptoms - nausea, vomiting, bowel dysfunction.
With this disease, attacks are most often provoked by non-compliance with the diet prescribed by the attending physician. In some cases, gallstone disease can lead to rupture of the walls of the organ or the accumulation of pus in its cavity.
For any disease of the gallbladder, not only examination and palpation, but also laboratory research methods are used to make an accurate diagnosis.
All cystic symptoms indicate various diseases of the gallbladder and its ducts, and the effectiveness of each of them is different. Only the symptoms of Kehr and Murphy indicate with almost 100% probability the development of cholecystitis.
Detailed examination technique
The patient is asked to lie supine on a firm couch, face up. The doctor places his thumb on the projection point of the gallbladder. He places his free fingers along the line of the ribs. The patient is asked to take one deep breath. The specialist presses forcefully on the designated area. If the gallbladder is inflamed, a sharp pain occurs, from which the body instinctively begins to collapse and breathing is interrupted.
If the patient is overweight, the tactics change slightly. Due to the large layer of fat, it is impossible to palpate the gallbladder. In this case, preference is given to the percussion (tapping) method. It is carried out as follows:
- The patient lies down on the couch.
- The doctor is located on the right.
- Places your index finger at the Kera point (it is located under the right hypochondrium, where the arch of the lower bone connects to the outer edge of the rectus abdominis muscle) and bends it.
- After this, the specialist asks the person to take a deep breath.
- In this position, the described organ rises as close as possible to the surface of the peritoneal wall.
- With the edge of the left palm, the doctor hits the phalanx of the finger of the right hand.
- If the blow causes pain, the diagnosis is confirmed.
Additionally, the doctor must conduct a survey, carefully collect and describe the anamnesis in the treatment protocol. Clinical manifestations help to navigate and establish the cause of the ailment. In the described situation, the patient may complain of the presence of dyspeptic disorders: the appearance of bitterness in the mouth, mild nausea that does not lead to vomiting, a feeling of heaviness in the stomach, flatulence and unstable stool.
If palpation of the gallbladder stimulates the interruption of a full breath, but at the same time there is severe pain in the lower back, and not in the hypochondrium, most likely the patient develops not cholecystitis, but pancreatitis or pyelonephritis. Murphy's symptom is not indicative for these diseases.
In case of exacerbation of the pancreas, another examination method is used - the Mayo-Robson symptom. His technique allows you to identify pain concentrated at the angle of intersection of the ribs and spine.
Symptoms of acute and chronic pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas. Pancreatitis is often associated with malnutrition, alcohol abuse, and hereditary pathology. Its symptoms upon objective examination are as follows:
- Sm Mayo-Robson. Pain is detected in the region of the costovertebral angle on the left.
- Sm Voskresensky - the pulsation of the aorta below the celiac trunk disappears.
- S-Kacha is a sign of chronic pancreatitis - hyperesthesia in the area of innervation of the Th8 nerve, which corresponds to the 8th intercostal space on the left and right. This symptom is related to the girdling pain during an attack of pancreatic pain.
Relevance of palpation of the gallbladder (Murphy's symptom)
Special manifestations of the disease include Kehr's and Ortner's symptoms. Further examination occurs after confirmation of the presence of these manifestations. To detect the first symptom, it is enough to carry out deep palpation of the right hypochondrium, in which case the patient will experience severe acute pain.
Ortner's symptom is detected by tapping the costal arch on the right side with the edge of the palm. If there is a disease, all manipulations will be accompanied by painful sensations of varying degrees, depending on how severely the disease has developed and the age and general health of the person.
In addition to them, there are also:
- Obraztsov’s symptom – when a person inhales during palpation and the pain intensifies;
- Murphy's symptom - inability to inhale during deep palpation in the right hypochondrium;
- Mussi-Georgievsky's symptom - upon palpation of the sternocleidomastoid muscle (in the area of its legs), the patient experiences painful sensations.
Laboratory blood tests may reveal neutrophilia, leukocytosis and lymphopenia.
No one will argue that Murphy's symptom in cholecystitis is not the only indicator of this disease. So, it is important to take other nuances into account. It is interesting to note that there are quite a lot of so-called cystic symptoms. These are indicators bearing the names of such scientists as Vasilenko (the symptom is useful in the early stages of the disease), Kera (pain on inspiration), Mussi-Georgievsky (pain on palpation of the muscle), Riesman (tapping along the edges of the costal arch is mandatory when holding the breath), Boas and Lepena.
Specific symptoms of acute cholecystitis include:
- Grekov-Ortner symptom - percussion pain that appears in the area of the gallbladder when lightly tapping the right costal arch with the edge of the palm;
- Murphy's symptom is an increase in pain that occurs when the gallbladder is felt when the patient takes a deep breath. The doctor places the thumb of the left hand below the costal arch, at the location of the gallbladder, and the remaining fingers along the edge of the costal arch. If the patient's deep breath is interrupted before reaching height due to acute pain in the right hypochondrium under the thumb, then Murphy's symptom is positive;
- Courvoisier's symptom - an enlargement of the gallbladder is determined by palpation of the elongated part of its bottom, which quite clearly protrudes from under the edge of the liver;
- Pekarsky's symptom is pain when pressing on the xiphoid process. It is observed in chronic cholecystitis, its exacerbation and is associated with irritation of the solar plexus during the development of the inflammatory process in the gallbladder;
- Mussi-Georgievsky's symptom (frenicussymptom) - pain on palpation in the supraclavicular region at a point located between the legs of the sternocleidomastoid muscle on the right;
- Boas's symptom is pain on palpation of the paravertebral zone at the level of the IX-XI thoracic vertebrae and 3 cm to the right of the spine. The presence of pain in this place during cholecystitis is associated with zones of Zakharyin-Ged hyperesthesia.
The inflammatory stage of gallbladder disease - cholecystitis - develops gradually, but can suddenly manifest itself in an acute form. It is important to know what symptoms are characteristic of the disease in order to contact specialists in time. An advanced condition can cause an acute attack requiring surgical intervention.
The disease is accompanied not only by severe pain. It is characterized by manifestations of the calculous form - a violation of the outflow of bile due to the appearance of stones. They are localized in the ducts and the bladder itself. Inflammation can provoke peritonitis; the situation requires urgent surgical intervention. Delay in providing assistance can result in death. It is necessary to know the first symptoms of cholecystitis. These include:
- heaviness in the right side;
- dull pain radiating to the arm, shoulder blade;
- nausea, vomiting;
- bitter belching;
- yellowish skin;
- lack of appetite.
There are types of acute cholecystitis - acalculous and calculous. The first one passes without the formation of stones. The second is a more severe case. It is characterized by the accumulation of pus inside the inflamed bladder due to the formation of stones. In addition, the nearby liver is affected, which can cause hepatocholecystitis. If, as a result of exacerbation of the processes, thinning of the walls and rupture of the gallbladder occurs, peritonitis and death cannot be ruled out.
Symptoms of acute inflammation are similar to other diseases. A number of doctors, studying their patients in detail in their clinics, proposed distinctive classification options. They help to accurately identify acute cholecystitis and distinguish it from other diseases with similar symptoms. Among such specialists: Murphy, Pekarsky, Ortner, Boas, Mussy, Courvoisier.
Grekov-Ortner - the occurrence of pain when the doctor taps the right costal arch with the edge of his palm at the site of the gallbladder;
Murphy - the patient is unable to inhale during deep palpation;
Mussi-Georgievsky - acute pain when pressing on a point above the collarbone in the area between the legs of the muscle - sternocleidomastoid.
What does a positive Kera and Murphy symptom mean together?
Ker's symptom is similar to Murphy's symptom, but differs in detection technique. Taken together, they speak of acute cholecystitis, most often in uncomplicated forms.
This disease manifests itself:
- paroxysmal pain in the right hypochondrium (most often after eating);
- muscle tension in this area;
- vomiting;
- pain on palpation.
In addition to the Kehr and Murphy symptoms, the development of acute uncomplicated cholecystitis is often indicated by the Grekov-Ortner symptom.
With their help, it is possible to preliminarily diagnose acute cholecystitis in complicated forms.
Often this pathology is accompanied by:
- inflammation of the bile ducts;
- obstructive jaundice;
- signs of intoxication (increased levels of leukocytes in the blood, rapid heartbeat, increased temperature).
In some cases, diagnosis using the Kera and Murphy symptoms are not effective.
These include:
- severe concomitant pathologies;
- mental disorder in the patient;
- old age;
- features of the anatomical structure (for example, the gallbladder is covered by nearby tissues).
In this case, other diagnostic techniques are used - laboratory and instrumental.
Symptoms of acute cholecystitis - the first signs and symptoms of inflammation of the gallbladder
Video on the topic:
- Grekov-Ortner symptom - painful sensations when tapping the edge of the palm on the right side of the costal arch;
- Murphy's symptom - heavy breathing during deep palpation of the right hypochondrium;
- Obraztsov’s symptom – increased pain during palpation while inhaling;
- Kera's symptom – pain in the right hypochondrium during deep palpation.
Murphy's symptom appears first. In most cases, it is accompanied by fever (increased body temperature), but its indicators are not too high. A clinical blood test revealed neutrophilic leukocytosis and elevated ESR.
Elderly people also experience symptoms of cholecystitis such as high fever, lack of appetite, malaise, apathy, irritability and even depression. If we are talking about acalculous cholecystitis, then in such cases the disease is accompanied by bloating and elevated body temperature.
The following symptoms of cholecystitis are often positive:
- Mussi-Georgievsky's symptom is pain when pressing in the supraclavicular region on the right between the legs of the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
- Murphy's sign;
- Obraztsov's symptom;
- Ortner's sign.
The liver is somewhat enlarged, has dense and painful edges on palpation. The gallbladder, as a rule, is not palpable, since it is usually wrinkled as a result of the scar-sclerosing process.
During duodenal intubation, it is often impossible to obtain a bladder portion of bile B (due to a violation of the bladder reflex and the concentrating ability of the gallbladder) or this portion is slightly darker than portions A and C, often cloudy. Microscopic examination of the duodenal contents shows a large amount of mucus, leukocytes and desquamated epithelium.
General description of Ortner's symptom
The gallbladder is located in the liver area, in its right lobe in the lower part. In healthy people, this organ is practically not felt during palpation, but protrudes slightly forward. If a doctor finds a gallbladder during an examination of a person, there is a high probability that the organ is inflamed.
In diseases affecting this area of the body, a number of painful points appear:
- Vesical: determined at the point of contact of the rectus abdominis muscle and the arch of the rib.
- Choledochopancreatic: upper abdomen to the right of the navel.
- Symptom or Ortner-Grekov syndrome: to determine its presence, the doctor taps on the right side of the costal arch.
- Acromial: when pressure is applied to the edge of the scapula, pain occurs.
- Scapular: discomfort is determined under the right shoulder blade.
- Boas zone: the appearance of severe discomfort in the area of the spinous processes in the thoracic region.
The appearance of pain upon palpation of the right abdominal region during diagnosis is explained by the effect on the inflamed gallbladder. If the same manipulations are performed on a healthy person, he will feel minor discomfort.
A similar test involves tapping the edge of the palm along the arches of the ribs in the right side, while the patient feels severe pain. If cholecystitis develops, the test or Ortner's sign will be positive.
In addition, there is irradiation of pain to the scapular region, the area above the collarbone. The severity of pain often depends on the scale of changes that have occurred in the gall bladder organ, how advanced the disease is and at what stage of development it is.
Differentiation of the disease
Acute cholecystitis can be differentiated from a duodenal or gastric ulcer, as well as acute pancreatitis, appendicitis or renal colic. In order not to confuse these diseases, it is important to be able to distinguish between them.
With peptic ulcers, the pain occurs sharply, and it is also quite sharp, while with cholecystitis in the liver area, the pain is dull and slightly intensifies over time. There is also a temperature around 38 degrees and vomiting with bile.
In acute pancreatitis, the pain is localized in the left hypochondrium and may also be accompanied by continuous vomiting.
Acute appendicitis does not include pain radiating to the shoulder and shoulder blade, and is not manifested by gagging. With appendicitis, the patient does not have the Coeur and Mussy sign.
With renal colic, there is no increase in temperature and no leukocytosis in the blood. The pain is localized mainly in the lumbar region and spreads to the hips and pelvic organs.
Since in most situations the identification of an acute form of pathology implies the initiation of immediate treatment, Murphy’s symptom continues to be relevant. There are cases when it is not possible to bring the patient for a more accurate diagnosis, for example, the patient is in a remote village, or at a construction site in the steppe, where it is impossible to deliver the necessary equipment.
Symptoms of appendicitis
We will start with the symptoms of acute and chronic appendicitis, which is dangerous by the development of infectious-toxic shock and peritonitis. With appendicitis, abdominal pain appears:
- At first the pain is aching, located in the center of the abdomen, gradually shifting to the right iliac region. This is the Volkovich-Kocher symptom. It appears at the beginning of the disease.
- Voskresensky's symptom is also recorded - when holding the hand from the right edge of the costal arch with the palm down, the pain intensifies.
- Rovsing's sign is determined by pressure on the left iliac region. In this case, gases move in the descending colon, which provoke increased pain on the right.
- Sitkovsky’s method - when the patient turns on his left side, the pain intensifies in the area of the ileocecal angle, that is, in the right iliac region.
- The Bartholomew-Michelson maneuver is similar to the previous one, however, here the area of the ileocecal angle is palpated with the patient positioned on the left side, as a result of which the pain intensifies.
- S. Dumbadze – there is pain in the umbilical region of the abdomen.
- Psoas symptom, or Obraztsov’s symptom, when when raising the right leg, abdominal pain intensifies upon palpation.
- Volkovich's syndrome is a symptom of chronic appendicitis - hypotrophy and even atrophy of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall appear in the right iliac region, and when palpating the cecum and retracting it outward, the pain increases.
Treatment of cholecystitis
Treatment of cholecystitis should begin before the patient is hospitalized. Drugs are administered intravenously that help reduce pain (the No-shpa injection solution is most often used) and reduce pressure in the gallbladder due to improved flow of bile into the small intestine.
Ker's symptom in cholecystitis is the reason for immediate hospitalization of the patient, followed by surgical or conservative intervention by medical staff.
Timely attention to the presence of the described symptoms and the ability to distinguish them from differential diseases helps to increase the chance of a quick recovery without surgical intervention.
Symptoms of gastric and duodenal ulcers
- S. Krymova talks about perforation of the ulcer - pain when palpating the navel with a fingertip.
- Boas's point - a pain point is determined in the back at the level of Th12 (12 pair of thoracic nerves, 12 segment of the thoracic spine) on the left.
- The “splashing noise” occurs when there is stenosis of the pyloric part of the stomach, that is, the part that is connected to the duodenum.
These are the most important symptoms of gastric and duodenal ulcers.
More about bladder symptoms
Murphy's symptom for cholecystitis is not the only method for determining the disease. A number of prominent doctors have made their contribution to medicine by developing techniques for identifying signs of gallbladder problems. For example, surgeon Vasilenko determined that at the early stage of cholecystitis, when tapping on the right costal arch at the point of projection of the gallbladder, pain occurs.
Ortner's symptom is considered indicative. He found that with cholecystitis, pain occurs if you tap along the edge of the costal arch. But it is necessary to carry out the manipulation on both sides in order to compare the patient’s sensations. The Mussi-Georgievsky symptom, also called the Phrenicus symptom, is still used. Using this method, pathologies of the organs of the upper abdomen are determined.
The manifestation of the Mussi-Georgievsky symptom is a painful sensation during palpation in the area of the legs of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Pain occurs with cholecystitis on the right side and radiates downwards. Doctor Lepen established the dependence of painful sensations in the area of the gallbladder during cholecystitis, if effleurage is performed with a bent finger. This symptom is called "Lepen's symptom."
Uncomplicated cholecystitis
Catarrhal (simple) cholecystitis can be calculous or acalculous, primary or as an exacerbation of chronic recurrent cholecystitis. Clinically, in most cases it proceeds calmly. The pain is usually dull and appears gradually in the upper abdomen; intensifying, localized in the right hypochondrium.
On palpation, pain is noted in the area of the gallbladder, with positive Grekov-Ortner and Murphy symptoms. There are no peritoneal symptoms, the leukocyte count is in the range of 8.0–10.0 G 109/l, temperature is 37.6 °C, rarely up to 38 °C, no chills. Attacks of pain continue for several days, but after conservative treatment they disappear. Acute destructive cholecystitis can be calculous or acalculous, primary or an exacerbation of chronic recurrent cholecystitis.
Destruction can be phlegmonous, phlegmonous-ulcerative or gangrenous in nature. With phlegmonous cholecystitis, the pain is constant and intense. Dry tongue, repeated vomiting. There may be a slight yellowness of the sclera and soft palate, which is due to infiltration of the hepatoduodenal ligament and inflammatory swelling of the mucous membrane of the bile ducts.
Symptoms of other equally important and dangerous diseases
Vascular lesions are quite a big problem and many people cannot decide to go to the doctor. We have collected several symptoms for some angiopathy that will help you decide on further examination and treatment.
- Trendelenburg's syndrome occurs with varicose veins, when the venous valves function poorly or do not function at all. The patient is asked to lie down and raise the affected leg up until the vessels are empty. Then the saphenous vein is clamped with a finger and the patient is asked to quickly take a vertical position. If pathology occurs, when the fingers are removed, the venous vessels immediately fill.
- Moshkovich's test - when removing the elastic bandage, the rate of increase in hyperemia and its intensity is much less on the sore leg than on the healthy leg. This test reveals obliterating angiopathy.
- S-Hackenbruch-Sicard - when coughing, a shock is detected during palpation of the femoral vein. This is a positive symptom that informs about the presence of valvular insufficiency.
- Hm, or Kazachescu's test. Using this test, thrombolytic pathology of the arteries is detected. A line is drawn along the entire leg with a blunt object. Where blood circulation is impaired, the redness of the line breaks off.
- Sm Delbe-Perthes. An elastic bandage is applied to the upper third of the thigh, which prevents the outflow of blood through the veins. When in this state for several minutes, usually from 3 to 5, if the filling of the veins with blood decreases, it means that the deep vessels are passable; if filling occurs, we can talk about deep venous pathology.
In fact, to determine venous and arterial insufficiency, there are many methods and symptoms that are less significant, so we will not describe them.
Summer brings us not only joy and fun, but also trauma. How to identify this or that damage? The symptoms below will help: Symptoms when injuries occur
- S-m balloting of the patella. This symptom indicates that there is fluid in the joint (synovitis, arthritis, hemarthrosis).
- Beler's syndrome occurs only with a meniscus injury located in the knee joint. It manifests itself as increased pain in the joint when walking backwards.
- Weinstein's S is determined by habitual dislocation of the shoulder. The patient is asked to abduct both shoulders 90 degrees and bend the arm at the elbow joints at a right angle. In this position, difficulties in outward rotational movements are identified.
- S-M Vereneya is a sign of a fracture of the pelvic bones. Pain appears when the pelvic bones are gently squeezed in the transverse direction (where the iliac crests are located).
- Sm Gorinevskaya, or the “sticky heel” symptom. This is a sign of a fracture of the superior ramus of the pubis. Its manifestations are that the patient cannot lift his leg in an extended position, but must certainly pull it towards the body. If someone else lifts the leg, the patient can easily hold it on his own.
- With the development of peritonitis, that is, inflammation of the peritoneum, pain appears on palpation of the abdomen. When you press on the stomach and suddenly remove your hands, the pain instantly intensifies. This is a symptom of an acute abdomen - the Shchetkin-Blumberg symptom.
- Valya's symptom indicates intestinal obstruction. Its essence lies in the appearance of local accumulation of gases in the intestine or protrusion of the proximal intestine.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=upload
That's all the information. We have given you only the most necessary and useful things, so after reading about these symptoms, you may suspect a particular disease. However, there is no need to exaggerate your strength and still, if necessary, you should consult a doctor.
Symptoms of renal pathology
Quite specific symptoms will be determined in diseases of the urinary system:
- S-Pasternatsky - when tapping the lumbar region on the right or left, pain is determined on the affected side, and also after this manipulation, blood cells, in particular, red blood cells, appear in the urine test.
- S-th effleurage - in the presence of kidney pathology, pain will be detected at the site of effleurage.
- Guyon's method - palpation of the kidney reveals its pathological mobility. This symptom in most cases indicates a tumor.