Bariatric surgery makes changes to the digestive system. This involves some changes in your diet, and therefore changes in your bowel habits (some positive, others not so pleasant).
It should be immediately noted that the problem of constipation after bariatric surgery mainly occurs after gastric bypass surgery. Resection or gastric banding does not make major changes in the functioning of the colon and such problems are much less common.
As your body adjusts to new eating habits, constipation is often an issue.
Why do defecation problems occur after the procedure?
After endoscopic examination, intestinal functions are disrupted for some time. This is due to irritation of the intestinal wall by the endoscope and the air that is used for better visualization. Another reason is to carry out manipulations, such as removing polyps or taking material for a biopsy.
All these reasons together lead to constipation, loose stools after colonoscopy and other consequences (the appearance of blood in the stool, bloating). The duration of these unpleasant manifestations is usually short; the functioning of the digestive system returns to normal 3-7 days after the study.
Risks and complications associated with the disease
Improperly treated constipation can eventually lead to rectal or colonic stool retention, which is the accumulation of compacted and hard feces in the distal part of the colon. Sometimes, despite the presence of stool in the rectum, the patient may experience diarrhea if liquid feces from the proximal colon bypass the stool site.
On physical examination, a hard fecal mass may be felt in the abdomen. Treatment of fecal retention requires restriction of dietary fiber, the use of an osmotic laxative and intestinal cleansing infusions. The best treatment for residual fluid is polyethylene glycol, administered at a dose of 100 g per 1 liter of electrolyte fluid orally in 4 portions per day for several days.
Sometimes it is necessary to manually pump out stool from the rectum. Retention of stool in the large intestine can cause intestinal obstruction and fecal ulcers. Fecal ulcers, due to necrosis of the mucosa from fecal pressure, are most often located in the left side of the colon and rectum and can lead to life-threatening intestinal perforation.
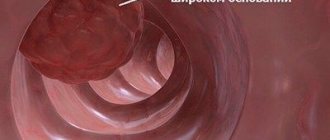
Colon cancer can also cause constipation. This disease is suspected when warning symptoms occur, which include rectal bleeding, “futile bowel movements,” onset of constipation later in life, alternating constipation and diarrhea, “pencil stools,” weight loss, iron deficiency anemia, and a strong family history.
What to do if you experience constipation after a colonoscopy
Short-term constipation (up to 1-2 days) does not require special action; this is a completely normal phenomenon after the endoscopic procedure. If there is a longer absence of the urge to defecate, it is necessary to take special measures to improve intestinal motility. These include:
- Drinking plenty of water (2-3 liters daily).
- Moderate physical activity.
- The right diet.
- Taking laxatives.
Forlax, Fortrans and other similar products are best suited as laxatives. It is important to consider that these drugs are contraindicated on the first day after the procedure. They can cause intestinal atony. After 2-3 days from the moment of examination, their use is completely safe.
Folk remedies
Regarding folk remedies in the treatment of constipation, therapy is based on proper nutrition and consumption of certain foods in higher concentrations. It is necessary to increase the level of fluid in the body. You are supposed to drink the universal norm of water or more (from two liters per day): boiled water, coffee and decaffeinated teas (the best option is a laxative). The consumption of carbonated drinks, fruit nectars, alcohol and energy drinks is prohibited.
Fiber in supplements softens stool and facilitates its movement through the gastrointestinal tract. Dietary fiber is consumed in different ways: in the form of capsules, chewing candies or powder - no more than twice a day with the permission of a doctor.
It is worth abstaining from foods that cause constipation:
- Foods with high concentrations of potassium and calcium.
- Milk (cheese, sour cream, yogurt, not including low-fat kefir).
- Fruits (grapes and bananas).
- Sweets (chocolate, caramel, etc.).
- Concentrated nectars.
- Flour and butter products.
- White bread and pastries (sweet and savory).
- White rice.
- Semi-finished products, etc.
Prunes are an essential component in the treatment of constipation, because their natural sugar sorbitol and fiber have a laxative effect. It is permissible to drink warm prune juice - a glass a day.
Traditional medicine suggests treating constipation with senna leaves and buckthorn bark, chamomile infusion, pumpkin or carrot juice. But no folk remedies will clear the congestion without clearly defined rules. In the case of nutrition, this is a strict diet.
What are the types of stool problems after colonoscopy?
In addition to constipation, other consequences are often encountered: loose stools, bloating, discomfort and pain after a colonoscopy with or without anesthesia. If during the study polyps were removed or other manipulations were performed, blood streaks may appear in the stool.
With the development of these unpleasant manifestations, you can use various medications that help restore the intestines. These include:
- Hilak Forte
. Helps eliminate toxins and improves digestion. - Lactobacterin
. Normalizes the microflora of the digestive system. - Linux
. Contains several varieties of live probiotic bacteria.
There are many other medications that will help normalize digestion after endoscopy. It is important to consult your doctor before starting treatment. Only a specialist can choose the right means to restore intestinal functions.
Complications of constipation in the postoperative period
Stool retention after surgery is characterized by difficulty or complete inability to empty intestinal contents. Fecal retention leads to intoxication of the body due to the processes of rotting and fermentation of intestinal contents. Toxic substances negatively affect a woman’s weakened body. Prolonged retention of feces leads to disruption of the beneficial microflora of the digestive tract, manifested by impaired absorption of nutrients and medications.
Fecal retention in the body leads to the following disorders:
- Absorption of toxins into the general bloodstream, which leads to intoxication of the body.
- Severe weakness increases, constant drowsiness appears.
- Hard and dry feces during evacuation can injure the intestinal mucosa, which will cause an inflammatory process.
- Severe straining leads to the appearance of anal fissures, which slows down the recovery process.
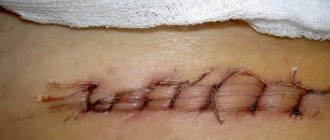
- During difficult bowel movements, the stitches may come apart.
Proper nutrition after endoscopic examination
One of the simplest and most effective solutions to the question “what to do if constipation or other problems occur after a colonoscopy” is a dietary diet. Meals should be divided, at least 4-5 meals daily. You should try to reduce the serving size so as not to create additional stress on the digestive system.
In the first days after the procedure, it is better to eat only liquid meals and drink plenty of water. The list of products that need to be completely excluded includes:
- Meat and fish with high fat content.
- Mushrooms, nuts, legumes.
- Spicy seasonings.
- Fresh vegetables (cabbage, radishes).
- Confectionery, alcoholic and carbonated drinks.
Among liquid dishes, preference should be given to low-fat broths (meat or vegetable); other dishes are best prepared by baking or boiling. Solid food should be started gradually, introducing it into the diet over 3-4 days.
Menu for the week
They are on a diet after surgery for about 3 months, so we have compiled a food menu for the week. All components can be swapped from week to week:
| Monday |
|
| Tuesday |
|
| Wednesday |
|
| Thursday |
|
| Friday |
|
| Saturday |
|
| Sunday |
|
If you plan your menu correctly, your diet can be more varied.
How to avoid serious consequences after surgery to remove the uterus in women
How to preserve the uterus and quality of life
Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Afanasyev Maxim Stanislavovich, oncologist, surgeon, oncogynecologist, expert in the treatment of dysplasia and cervical cancer
Historically, medicine has established the opinion that the uterus is needed only for bearing a child. Therefore, if a woman does not plan to give birth, she can safely resort to surgery.
Is this really true or not? Why, for example, in March 2015, Angelina Jolie had both ovaries and fallopian tubes removed, but left an “unnecessary” uterus? Let's find out together whether hysterectomy is dangerous. And if it’s dangerous, then with what.
From the surgeon’s point of view, a radical operation solves the issue “at its root”: no organ, no problem. But in fact, surgeons’ recommendations cannot always be perceived as objective. They often do not follow up with patients after discharge, do not conduct examinations six months, a year, 2 years after removal of the uterus, and do not record complaints. Surgeons only operate and rarely face the consequences of the operation, so they often have a false idea about the safety of this operation. Meanwhile, scientists from different countries independently conducted a series of observations. They found that within five years after hysterectomy, most women developed:
1. (previously absent) pelvic pain of varying intensity,
2. problems with the intestines,
3. urinary incontinence,
4. vaginal prolapse and prolapse,
5. depression and depression, up to serious mental disorders,
6. emotional and physiological problems in relationships with your spouse,
7. Some women who were operated on for severe dysplasia or in situ cancer experienced a recurrence of the disease - damage to the stump area and vaginal vault.
8. fatigue,
9. persistent increase in blood pressure and other serious cardiovascular problems.
The problem is not invented, because according to the Scientific Center for Obstetrics, Gynecology and Perinatology of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, various operations to remove the uterus account for from 32 to 38.2% of all abdominal gynecological operations. In Russia, this is about 1,000,000 uterus removed annually! The problem also has another side. Since all of these complications develop gradually, over the course of a year or several years after surgery, women do not associate the deterioration in their quality of life with the previous operation. I am writing this material with the goal that you yourself can evaluate all the pros and cons of the operation, weigh the pros and cons, and consciously make your choice. My practice shows that there are no extra organs. Even for older women, hysterectomy has negative health consequences, and I will discuss them in detail in the second part of this article.
I want to reassure those patients who are faced with a difficult choice - whether to agree to have the uterus removed or not. In some cases, hysterectomy can be avoided. Approximately half of those diagnoses that 10 years ago were considered direct indications for surgery are now treated without surgery or without organ removal.
Diagnoses that are no longer indications for hysterectomy
Thanks to the introduction of high-tech methods, some of the indications for genital removal have ceased to be absolute indications. Here is a list of diagnoses for which removal of the uterus in women can be replaced by other treatment methods and the organ can be saved.
1. Symptomatic, enlarged, rapidly growing uterine fibroids are today treated by embolization of the uterine arteries: the vessels feeding the fibroids are blocked. Subsequently, the fibroid gradually resolves.
2. Adenomyosis, or internal endometriosis, can be eliminated using the therapeutic method of photodynamic therapy (PDT).
With endometriosis, cells in the inner lining of the uterus grow in unusual places. PDT specifically destroys these cells without affecting healthy tissue.
Photodynamic therapy is an organ-preserving treatment method that is included in the federal standard of medical care (see Order of the Ministry of Health of Russia dated November 1, 2012 N 572n (as amended on June 11, 2015) “On approval of the Procedure for the provision of medical care in the field of obstetrics and gynecology”).
3. Precancerous conditions of the endometrium - complex endometrial hyperplasia, adenomatous endometrial hyperplasia, atypical endometrial hyperplasia - can also be treated with PDT. To date, I have successfully treated 2 patients with this pathology.
In cases where hyperplasia is predominantly viral in nature, treatment with PDT can eliminate the cause of the disease. In the treatment of cervical pathologies, the complete destruction of the human papillomavirus after one PDT session is confirmed in 94% of patients, and in 100% of patients after a second PDT session.
4. Precancerous conditions and oncological formations in the cervix. Grade 3 dysplasia, cervical in situ cancer and even microinvasive cancer can be completely cured using photodynamic therapy in 1 or 2 sessions.
The PDT method eliminates not only the disease itself, but also its cause – the human papillomavirus.
Therefore, correctly and fully performed photodynamic therapy is the only method that ensures lifelong recovery and minimal risk of relapse (reinfection is possible only in case of re-infection with HPV).
There is one more good news. Previously, a combination of age and several gynecological diagnoses was a compelling reason for organ removal. For example, a combination of cervical condylomas and uterine fibroids, or cervical dysplasia with adenomyosis against the background of a completed labor function. To justify the removal of an organ, the surgeon usually does not give rational arguments, but refers to his own experience or established opinion. But today (even if the attending physician tells you otherwise) a combination of several diagnoses is no longer a direct indication for removal of the uterus. Modern medicine considers each diagnosis as independent, and for each treatment tactics are determined individually. For example, dysplasia and adenomyosis regress after photodynamic therapy. And the presence of multiple fibroids is not a reason for oncological alertness. Numerous observations in recent years show that fibroids are in no way associated with cancer, do not degenerate into a cancerous tumor, and are not even a risk factor. In surgery, there is a concept of risks of therapeutic effects. The task of a good doctor is to minimize risks. When a doctor decides on treatment tactics, he is obliged to evaluate the indications, weigh the possible negative consequences of different treatment methods, and choose the most gentle and effective one. By law, doctors must inform about all possible treatment methods, but in practice this does not happen. Therefore, against the backdrop of the surgeon’s urgent recommendations for organ removal, I strongly advise you to consult several specialists or write to me to evaluate the possibility of performing organ-preserving treatment that is suitable for you. Unfortunately, not all diseases of the uterus can be treated with minimally invasive and therapeutic methods, and in some cases it is still better to remove the uterus. Such indications for removal are called absolute - that is, not requiring discussion.
Absolute indications for hysterectomy
1. Uterine fibroids with necrotic changes in the node. Preservation of an organ with such a diagnosis poses a threat to life.
2. Prolonged uterine bleeding that cannot be stopped by any other means. This condition is fraught with the loss of a large volume of blood and poses a serious danger to life.
3. Combination of large uterine fibroids and cicatricial deformation of the cervix.
4. Uterine prolapse.
5. Cancer, starting from stage I.
6. Giant size of tumors.
Depending on the indications, operations on the uterus are performed using different methods and in different volumes. First, we will get acquainted with the types of surgical interventions. Then I will dwell in detail on the consequences that every woman will experience to one degree or another after the removal of this organ.
Types of hysterectomy operations
In medical practice, abdominal and endoscopic removal of the uterus is performed.
- Abdominal surgery (laparotomy) is performed through an incision on the anterior abdominal wall. The method is considered traumatic, but it provides great access and in some cases there is simply no alternative. For example, if the uterus has reached a large size due to fibroids.
- The second method is endoscopic surgery (laparoscopy). In this case, the surgeon removes the uterus through punctures in the anterior abdominal wall. Laparoscopic hysterectomy is much less traumatic and allows for faster recovery after surgery.
- Vaginal hysterectomy is the removal of the uterus through the vagina.
Operations are classified according to the volume of intervention
1. High uterine amputation - only part of the uterus, its fundus, is removed.
2. Subtotal hysterectomy (uterine amputation) - complete removal of the uterus while preserving the cervix.
3. Total hysterectomy (hysterectomy) - surgical removal of the uterus along with the cervix.
4. Panhysterectomy - removal of the uterus with the cervix and appendages.
5. Radical removal of the vagina, cervix, lymph nodes.
Consequences and complications after hysterectomy are often a direct consequence of the volume of intervention. Let's talk about them.
Consequences after abdominal hysterectomy surgery
Abdominal surgery to remove the uterus through a large incision is one of the most traumatic procedures. In addition to the complications caused directly by the removal of the uterus, such an operation has other negative consequences.
1. After the operation, a noticeable scar remains.
2. High probability of hernia formation in the scar area.
3. Open surgery usually leads to the development of extensive adhesions in the pelvic area.
4. Rehabilitation and restoration (including performance) requires a lot of time, in some cases up to 45 days.
Consequences after laparoscopic hysterectomy
The consequences of laparoscopy are less traumatic. Laparoscopic surgery to remove the uterus is performed through punctures, so small scars remain on the skin of the abdomen, which over time become almost invisible. The risk of adhesions and hernias after laparoscopy is much lower than after abdominal surgery. In addition, the postoperative period after this operation is shorter and recovery is faster.
Removal of the uterus without the cervix. Consequences of supravaginal amputation of the uterus without appendages
Whether the cervix is left or removed during a hysterectomy depends on the condition of the cervix and the risks associated with retaining it. If the cervix is left, this is the most favorable situation possible. On the one hand, due to the preserved ovaries, the hormonal system continues to function more or less normally. But why do they leave the cervix when removing the uterus? Preserving the cervix allows you to maintain the length of the vagina, and after restoration the woman will be able to lead a full sex life.
Removal of the uterus without ovaries. Consequences of hysterectomy without appendages
Removal of the uterus without appendages, but with the cervix, is a more traumatic operation. By leaving the ovaries, the surgeon allows the woman to maintain normal hormonal levels. If the operation is performed at a young age, the ovaries can avoid menopause and all the associated health consequences. But even after removal of the uterus without appendages, the anatomical relationship of the organs is disrupted. As a result, their function is impaired. In addition, complete removal of the uterus, even with preservation of the ovaries, leads to shortening of the vagina. In many cases, this is not critical for sex life. But the anatomy of the organ is different for everyone, and not all women manage to adapt.
Removal of the uterus with appendages
This is the most traumatic operation that requires a lot of recovery time. It requires serious hormonal correction and usually causes all the most severe consequences, especially if performed at the age of 40-50 years - that is, before the onset of natural menopause. I will tell you more about the most common consequences of hysterectomy below. The most unpleasant thing is that all these consequences are irreversible and practically impossible to correct.
Consequence 1. Serious hormonal imbalances
Until now, when convincing patients to agree to surgery, surgeons utter the same monologue - supposedly, the uterus is needed only for the birth of children, supposedly it does not produce hormones, and its removal has almost no effect on the quality of life. It remains a mystery to me on what basis these surgeons believe that removing the uterus will not in any way affect the patient’s quality of life. Moreover, many surgeons are truly convinced that after 50 years a woman does not need organs such as the uterus and ovaries.
Meanwhile, a series of recent scientific studies in this area indicate the opposite. Even if the ovaries are preserved, removal of the uterus is an operation with a high risk of endocrine disorders .
The reason is simple. The uterus is connected to the ovaries and tubes by a system of ligaments, nerve fibers and blood vessels. Any operation on the uterus leads to a serious disruption of the blood supply to the ovaries, up to and including partial necrosis . Needless to say, in literally suffocating ovaries, the production of hormones is disrupted. Hormonal imbalances manifest themselves in a whole string of unpleasant symptoms, the most harmless of which is a decrease in libido. In the vast majority of cases, the ovaries are not able to completely restore or compensate for normal blood supply. Accordingly, the hormonal balance of the female body is not restored.
Consequence 2. Ovarian cysts after removal of the uterus
This is a fairly common complication in cases where the ovaries are preserved after removal of the uterus. This is how the negative impact of the operation itself manifests itself. To understand the nature of the cyst, you must first understand how the ovaries work. In fact, the cyst is a natural process that occurs every month in the ovary under the influence of hormones and is called a follicular cyst. If the egg is not fertilized, the cyst bursts and menstruation begins. Now let's see what happens to the ovaries after removal of the uterus. The uterus itself does not produce hormones. And many surgeons assure that after its removal the hormonal levels will not change. But they forget to say how closely the uterus is connected to other organs. When separating the ovaries from the uterus, the surgeon inevitably disrupts the blood supply and injures them. As a result, the functioning of the ovaries is disrupted, and their hormonal activity decreases. Unlike the uterus, the ovaries produce hormones. Disturbances in the functioning of the ovaries lead to disruption of hormonal levels and the process of follicle maturation. The cyst does not resolve, but continues to grow. It takes about 6 months to restore the full functioning of the ovaries and level out hormonal levels. But not always everything ends well, and the enlarged cyst resolves. Often, repeated surgery is required to remove an overgrown cyst - with large tumors there is a risk of rupture and bleeding. If, several months after removal of the uterus, pain appears in the lower abdomen, which increases over time, you should visit a gynecologist. The most likely reason why the ovary hurts is an overgrown cyst. The likelihood of developing this complication is only 50% dependent on the skill of the surgeon. Every woman's anatomy is unique. It is not possible to predict the location of the ovaries and their behavior before surgery, so no one can predict the development of a cyst after removal of the uterus.
Consequence 3. Adhesions after hysterectomy
Extensive adhesions after removal of the uterus often lead to the development of chronic pelvic pain. The characteristic symptoms of these pains are that they intensify with bloating, indigestion, peristalsis, sudden movements, and prolonged walking. Adhesions after surgery to remove the uterus form gradually. Accordingly, pain appears only after some time. At the initial stage, postoperative adhesions in the pelvis are treated conservatively; if ineffective, laparoscopic excision of adhesions is resorted to.
Consequence 4. Weight after hysterectomy
Body weight after surgery can behave differently: some women gain weight, sometimes even gain weight, while others manage to lose weight. The most common scenario after removal of reproductive organs is rapid weight gain, or a woman’s belly grows.
1. One of the reasons why women gain weight is due to metabolic disorders and the resulting fluid retention in the body. Therefore, strictly monitor how much water you drink and how much you excrete.
2. After removal of the uterus and ovaries, the hormonal levels change, which leads to a slowdown in the breakdown of fat, and the woman begins to gain excess weight.
In this case, a gentle diet will help to remove the belly. Meals should be fractional, small portions 6-7 times a day.
Should you worry if you have lost weight after having your hysterectomy? If the reason for the operation was a giant tumor or fibroid, there is no need to worry, you lost weight after removing the uterus. If there was no mass formation, but you are losing weight, most likely it is a hormonal imbalance. To return your weight to normal, you will need hormone therapy.
Consequence 5. Sex after hysterectomy
Women who have undergone vaginal hysterectomy should remain in sexual rest for at least 2 months until the internal sutures heal. In all other cases, sex can be had 1-1.5 months after the operation. Sex life after removal of the uterus undergoes changes. In general, women are concerned about vaginal dryness, burning after intercourse, discomfort, and pain. This occurs due to a drop in estrogen levels, which causes the genital mucosa to become thinner and begin to produce less lubricant. Hormonal imbalance reduces libido and interest in sexual life decreases.
- Removal of the uterus and appendages most strongly affects the intimate side of life, since the lack of female hormones leads to frigidity.
- Removal of the uterine body has little effect on intimate life. Vaginal dryness and decreased libido may occur.
- Removal of the uterus and cervix leads to shortening of the vagina, which makes sex difficult after surgery.
Consequence 6. Orgasm after hysterectomy
Does a woman have an orgasm after a hysterectomy? On the one hand, all sensitive points - the G-spot and the clitoris - are preserved, and theoretically a woman retains the ability to experience orgasm even after removal of the organ. But in reality, not every woman gets an orgasm after surgery. Thus, when the ovaries are removed, the content of sex hormones in the body drops sharply, and many develop sexual coldness. A decrease in the production of sex hormones occurs even if the ovaries are preserved - for many reasons, after surgery, their activity is disrupted. The best prognosis for orgasms is for those who still have a cervix. The consequences after removal of the uterus and cervix are manifested in a shortening of the vagina by about a third. Full sexual intercourse often becomes impossible. Research conducted in this area has shown that the cervix is of great importance in achieving vaginal orgasms, and when the cervix is removed, achieving it becomes extremely difficult.
Consequence 7. Pain after hysterectomy
Pain is one of the main complaints after surgery.
1. In the postoperative period, pain in the lower abdomen may indicate a problem in the suture area or inflammation. In the first case, the stomach hurts along the seam. In the second case, high temperature is added to the main symptom.
2. If the lower abdomen hurts and swelling appears, you can suspect a hernia - a defect through which the peritoneum and intestinal loops extend under the skin.
3. Severe pain after surgery to remove the uterus, high temperature, and poor health indicate pelvioperitonitis, hematoma or bleeding. Repeat surgery may be required to resolve the situation.
4. Pain in the heart indicates the possibility of developing cardiovascular diseases.
A large Swedish study of 180,000 women found that hysterectomy significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular disease, coronary artery disease and stroke. Removing the ovaries further aggravates the situation.
5. If you are concerned about swelling of the legs or an increase in local skin temperature, you need to rule out thrombophlebitis of the veins of the pelvis or lower extremities.
6. Pain in the back, lower back, right side or left can be a symptom of adhesive disease, cyst on the ovary and much more - it is better to consult a doctor.
Consequence 8. Prolapse after hysterectomy
After removal of the uterus, the anatomical location of organs is disrupted, muscles, nerves and blood vessels are injured, and the blood supply to the pelvic area is disrupted. The frame that supports the organs in a certain position ceases to perform its functions. All this leads to displacement and prolapse of internal organs - primarily the intestines and bladder. Extensive adhesions aggravate the problem. This is manifested by numerous increasing problems with the intestines and urinary incontinence during physical activity and coughing.
Consequence 9. Prolapse after hysterectomy
The same mechanisms cause the so-called genital prolapse - drooping of the vaginal walls and even their loss. If in the postoperative period a woman begins to lift weights without waiting for full recovery, the situation worsens. Intra-abdominal pressure increases, the walls of the vagina are “pushed” out. For this reason, lifting weights is contraindicated even for healthy women. When lowered, a woman experiences a sensation of a foreign object in the perineal area. Pain bothers me. Sex life becomes painful. To reduce the symptoms of prolapse of the vaginal walls after removal of the uterus, special gymnastics are indicated. For example, Kegel exercises. Constipation also increases intra-abdominal pressure, so to prevent the process, you will have to learn to monitor your intestinal function: bowel movements should be daily, and stool should be soft. Unfortunately, vaginal prolapse after hysterectomy cannot be treated.
Consequence 10. Intestines after hysterectomy
Intestinal problems after surgery are affected not only by the changed anatomy of the pelvis, but also by a massive adhesive process. Intestinal function is disrupted, constipation, flatulence, various defecation disorders, and pain in the lower abdomen occur. To avoid intestinal problems, you must follow a diet. You will have to learn to eat often, 6 - 8 times a day, in small portions. What can you eat? Everything, with the exception of heavy foods, foods that cause bloating, and stool retention. Improves the condition of the pelvic organs and regular exercise.
Consequence 11. Breasts after hysterectomy
Removing the uterus has no effect on the incidence of breast cancer. However, with one exception. If the cause of the operation was fibroids, then the mammary glands after removal of the uterus require special attention. The fact is that fibroids are a hormonal-dependent disease. And the trigger for the development of a tumor process in the mammary glands is often hormonal imbalances.
Consequence 12. Urinary incontinence after hysterectomy
This syndrome develops in almost 100% of cases as a consequence of a violation of the integrity of the ligamentous and muscular framework during surgery. The bladder prolapses and the woman loses control of urination. To restore bladder function, doctors recommend performing Kegel exercises, but even with exercise, the condition usually progresses.
Consequence 13. Relapse after hysterectomy
Uterine surgery is performed for various indications. Unfortunately, the operation does not protect against relapse if the uterus was removed due to one of those diseases that are caused by the human papillomavirus, namely:
- dysplasia 3 degrees,
- cancer in situ,
- leukoplakia of the cervix,
- stage 1A cervical or uterine cancer
- microinvasive cervical cancer, etc.
Regardless of the technique, surgery does not guarantee 100% recovery; it only removes the lesion. Traces of the human papillomavirus, which is the cause of all these diseases, remain in the vaginal mucosa. Once activated, the virus causes a relapse. Of course, if there is no organ, then a relapse of the disease cannot occur either in the uterus or in its cervix. The cervical stump and the mucous membrane of the vaginal vault are subject to relapses - dysplasia of the vaginal stump develops. Unfortunately, relapses are very difficult to treat with classical methods. Medicine can only offer such patients traumatic methods. Removing the vagina is an extremely complex and traumatic operation, and the risks of radiation therapy are comparable to the risks of the disease itself.
That is why, against the backdrop of a high risk of relapse, the only sure way to treat virus-associated cervical diseases is not to use surgery, but high-tech therapeutic treatment using photodynamic therapy. This method eliminates not only atypical epithelial cells, but also the virus itself.
According to various sources, relapses after surgery occur in 30 - 70% of cases. That is why, for the purpose of prevention, the Herzen Institute recommends performing photodynamic therapy of the vagina and cervical stump even after surgical removal of the uterus. Only eliminating the papilloma virus protects against the return of the disease. This is the story of my patient Natalya, who faced a relapse of cancer of the vaginal stump after removal of the uterus.
“Well, I’ll start my sad story in order, with a happy ending. After giving birth at 38 years old and my daughter turning 1.5 years old, I had to go to work and I decided to see a gynecologist. In September 2012, there was no sign of sadness, but the tests were not reassuring - stage 1 cervical cancer. It was of course shock, panic, tears, sleepless nights. In oncology I passed all the tests, where the human papillomavirus genotype 16.18 was discovered.
The only thing our doctors offered me was expiration of the cervix and uterus, but I asked to leave the ovaries.
The postoperative period was very difficult both physically and mentally. In general, a vaginal stump remained, no matter how sad it may sound. In 2014, after 2 years, tests again showed a not very good picture - grade 1 dysplasia, then six months later, grade 2. They treated her with everything - all kinds of suppositories, antivirals, ointments.
In short, a lot of money was spent, and after a year and a half of treatment for this dysplasia, it went into the third stage and again cancer. What did our doctors offer me this time: photodynamics.
After reading about her, I was delighted and gave myself into their hands. So what do you think was the result of their innovative technologies? And nothing has changed! Everything remained in its place. But I read so much about this method, studied various articles, I was especially attracted to the photodynamic method of Dr. Afanasyev M.S., and having compared the method and technology of treatment, I was surprised that everything that this doctor writes and tells was significantly different from how they did it me in our clinic. Starting from the ratio of the drug per kilogram of my weight, the methodology itself, the questions they asked me. After photodynamics, I was forced to wear glasses for almost a month, sit at home with the curtains closed, and not lean out into the street. I had no doubt that they simply did not know how to do this procedure! I contacted Dr. Afanasyev M.S., bombarded him with questions, told my story and he offered his help. I thought and doubted for a long time.
My doctor offered me radiation therapy, but knowing the consequences and the quality of life after this therapy, I still chose photodynamics again, but that Maxim Stanislavovich would do it for me.
Having gathered new strength, I flew to Moscow. The first impression of the clinic was, of course, pleasant, you feel like a person whom everyone cares about, attentiveness and responsiveness are the main qualities of these employees.
About the PDT procedure and recovery
The procedure itself took place under anesthesia, went away quickly, and in the evening I went to see my sister who was staying with me. I only wore glasses for three days. After 40 days I went for an initial examination to my clinic, but I had an eroded spot, apparently the healing was slow, but despite all this, the tests were good! The doctor prescribed healing suppositories. And when I came back after 3 weeks, the doctor gave me…….., everything healed, and I was very surprised - how did that happen! After all, during the entire practice of conducting photodynamics using their technology, there was not a single positive result! Now I will go for another examination in April. I am sure that everything will always be fine for me now!
This is my story. And I’m telling it to you so that you don’t give up, and during treatment choose the most gentle method of treatment, and not remove everything at once, apparently this is easier for our doctors. If I had found out about Maxim Stanislavovich earlier, I would have avoided these tears, a terrible operation, the consequences of which will strain my whole life! So think about it! No amount of money is worth our health! And most importantly, if you have the human papillomavirus of this particular genotype, which provokes cervical cancer under certain circumstances, you need to remove this cause. This is exactly what photodynamics does, but the technology and the doctor who does it must be masters of their craft. Who have extensive experience, scientific works and positive results in this area. And I think the only doctor who observes all this is Maxim Stanislavovich. Thank you very much Maxim Stanislavovich!!!”
The consequences described above after removal of the uterus affect different women to varying degrees. Young women of childbearing age have the hardest time undergoing hysterectomy.
Consequences of hysterectomy after 60 years
Removal of the uterus in old age, after menopause, is relatively easy to tolerate. In postmenopause, the main discomfort comes from the operation itself, as well as the adhesive process and the consequences of displacement and prolapse of organs. Removal of the uterus after menopause no longer leads to a severe hormonal disorder.
Consequences of hysterectomy after 50 years
Surgery during menopause also does not greatly affect the health and well-being of a woman. And if the operation was performed according to indications, then you made the right choice.
Consequences of hysterectomy after 40 years
If a woman did not have menopause before the operation, then during the recovery period it will be very difficult for her. The consequences of surgery during active childbearing years are experienced much more acutely than at the age of natural menopause. If the operation was caused by a huge fibroid or bleeding, removal of the uterus provides significant relief. Unfortunately, over time, almost all the long-term consequences that we discussed above develop. In medical language, this condition is called post-hysterectomy and post-variectomy syndrome. It manifests itself as mood swings, hot flashes, arrhythmia, dizziness, weakness, and headache. The woman does not tolerate stress well and begins to get tired. Within just a few months, sexual desire decreases and pain develops in the pelvic area. The skeletal system suffers - the level of minerals drops, and osteoporosis develops. If hormonal levels are not corrected, aging will begin immediately after surgery: 5 years after hysterectomy, 55–69% of women operated on at the age of 39–46 years have a hormonal profile consistent with the postmenopausal one.
Surgery to remove uterine cancer is not necessary in its early stages
Uterine cancer is adenocarcinoma and carcinoma is a malignant process. The choice of treatment method and extent of intervention depends on the stage of the disease. Previously, the initial stages of cancer (in situ cancer, microinvasive cancer) and precancerous diseases (grade 3 cervical dysplasia, atypical hyperplasia) were indications for hysterectomy. Unfortunately, oncological surgery does not eliminate the cause of the disease - the human papillomavirus - and therefore has a high rate of relapses. With the advent of photodynamic therapy for these diagnoses, it became possible to preserve the organ and eliminate the very cause of the disease. What is the essence of the technique? The patient is injected with a drug that increases the photosensitivity of tissues - a photosensitizer. Over time, this drug is removed from healthy cells and remains in atypical cells, including those that contain the human papilloma virus - the cause of cancer and precancerous conditions. 2-3 hours after administration of the drug, the doctor irradiates with laser light to activate the photosensitizer. The photochemical reaction that occurs in response to the interaction of light with a photosensitizer causes the formation of toxic substances harmful to them in pathological cells. Cells die and recovery occurs.
Photodynamic therapy is effective not only before removal of the uterus for dysplasia, in situ cancer, 1A cancer, endometrial hyperplasia, but also after surgery. The procedure allows you to exclude the development of relapse and at the same time preserve the organ .
Call and schedule a consultation, and together we will find a solution on how to preserve the uterus and avoid these problems. Send your test results by email [email protected] or make an appointment by calling 8 (800) 555-77-26 in Moscow.
The reception is conducted by Afanasyev Maxim Stanislavovich, oncologist, doctor of medical sciences, professor and member of the academic council of the First Moscow State Medical University named after. THEM. Sechenov Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, oncologist surgeon, gynecological oncologist, gynecologist-immunologist, expert in the treatment of dysplasia and cervical cancer.
The article uses the following sources, which we took the liberty of popularly adapting for non-specialists:
1. Erik Ingelsson, Cecilia Lundholm, Anna LV Johansson, Daniel Altman. Hysterectomy and risk of cardiovascular disease: a population-based cohort study. // European Heart Journal, Volume 32, Issue 6, 1 March 2011, Pages 745–750
academic.oup.com
2. Skorbach E. I., Shcherbina I. N., Lazurenko V. V., Mertsalova O. V. “Posthysterectomy disorders and prevention of their development.” // International medical journal. 2011, No. 2. pp. 27-31
dspace.nbuv.gov.ua
3. D.I. Gaivoronskikh, A.A. Koval, V.G. Skvortsov. “Posthysterectomy syndrome: clinical manifestations and methods of their correction.” // Bulletin of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences. 2012, 4(40). pp. 120-123.
www.vmeda.org
Principles of treatment
Therapy for defecation disorders consists of a comprehensive and individual approach to each patient. Before starting treatment, the doctor must collect complaints and examine the patient.
Treatment consists of the following steps:
- Diet correction.
- Performing special gymnastic exercises.
- Drinking enough liquid.
- Acupressure course.
- Drug therapy using laxatives.
- The use of therapeutic microenemas.
Drug treatment
To prevent suture ruptures in the abdominal cavity during defecation, doctors prescribe laxatives and carminatives.
Today, the drugs of choice are lactulose-based products. These drugs enhance intestinal motility and eliminate symptoms of dysbiosis. The advantage of drugs in this group is a laxative effect without irritating effects on the smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract.
List of drugs that are widely used in the postoperative period:
- Normaze;
- Duphalac;
- Good luck;
- Portalak.
Hysterectomy of the uterus is a complex operation, after which complications may arise not only from the digestive tract, but also from other organs and systems of the body.