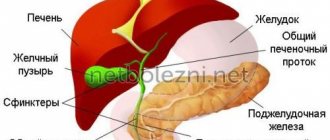
A polyp is a formation that arises from unchanged cells of the mucous membranes. Polyps are found in various organs: the nose, stomach, intestines, urinary and gall bladder. The reasons for the formation of polyps are diverse; inflammatory processes, hormonal and immune disorders, heredity, as well as the factor of chronic trauma play a certain role in their occurrence.
By their nature, polyps are benign formations, however, under certain conditions, they can degenerate into malignant tumors. This process is facilitated by frequent trauma to polyps and the presence of an aggressive environment. A high probability of malignancy is characteristic of polyps of the stomach, large intestine, and gall bladder. The surgical method is the only one that guarantees a complete cure for tumors in these localizations.
Minimally invasive endoscopic techniques are currently widely used to remove gastric polyps, allowing good treatment results to be achieved in a short time. In medical terms, endoscopic polypectomy is performed by experienced surgeons using modern equipment from the world's best manufacturers, which allows for constant visual monitoring of the progress of the operation.
Symptoms of polyps in the intestines and stomach
Polyps are benign neoplasms. The exact reasons for their appearance are still not fully understood.
The symptoms are different, and they can easily be attributed to completely different diseases. The intensity and severity of signs of the presence of polyps differ depending on the degree of damage and timing of formation.
With a large number of neoplasms, patients note the following symptoms:
- causeless weight loss;
- increased belching;
- constant heartburn;
- constipation alternating with diarrhea;
- pain in the stomach area, radiating to the back;
- bloating;
- weakness, fever.
With new single formations, symptoms may be completely absent. The diagnosis is made on the basis of gastroscopy or colonoscopy. Only a doctor can confirm the presence of polyps.
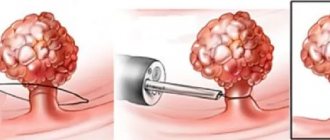
Endoscopic polyectomy
How the intervention will be carried out depends on the size of the tumor and its location. If the polyp has a long stalk, then the endoscope loop is placed as close as possible to the gastric mucosa. This manipulation should be carried out carefully, as there is a risk of injury to the stem of the formation. This will cause massive bleeding, which is quite difficult to stop. After the electrode loop is tightened, an electric current is passed through it.
At the same time, both the polyp is removed and the coagulation of the mucous membrane occurs. A scab will form at the site of the procedure. If the size of the polyp is small, but it has a wide base, then the maximum possible area is captured with a loop and the pseudo stalk is pulled out from the tissues of the mucous membrane. Next, the doctor passes an electric current through the loop electrode and removes the tumor.
How is surgery to remove stomach polyps performed in Moscow?
Polypectomy at the Yauza clinic can be performed immediately during a gastroscopic or colonoscopy. This is possible if the detected tumor does not exceed 0.5 cm.
If larger polyps are detected, additional examination of the patient will be required. The clinic uses gentle, minimally invasive methods for removing polyps in the stomach and intestines.
The procedure is performed under sedation. This takes 40-60 minutes. The doctor inserts the endoscope through the mouth or anus. When a polyp is detected, it is captured with a special loop with which the device is equipped, carefully removed and taken out. All obtained material is sent for histological examination.
Preparing for surgery
Polypectomy is preceded by a diagnostic stage, during which the patient undergoes all necessary types of examination. This stage includes:
- preliminary endoscopic examination with mandatory examination of the upper and lower gastrointestinal tract;
- general clinical blood and urine tests;
- study of indicators of the blood coagulation system;
- determination of blood group and Rh factor;
- ECG registration and blood pressure measurement.
The intervention is carried out on an empty stomach and does not require special preparation.
Rehabilitation after surgery to remove polyps of the stomach and intestines
After removal of a polyp of the stomach and intestines, our patients receive full information about the limitations during the rehabilitation period. If necessary, recovery can take place in a hospital setting under the constant supervision of doctors.
If the patient spends the rehabilitation period at home, he receives detailed recommendations. The doctor will tell you what you can eat after removal of a stomach polyp, explain acceptable physical activity, and warn about methods to prevent relapse.
After removal of polyps in the stomach, fatty and heavy foods should be avoided. A special diet involves the absence of spicy, fried, carbonated and alcoholic products in the diet. You will have to adhere to proper nutrition until the mucous membrane is completely healed.
There is practically no pain after removal of a stomach polyp. However, if necessary, the specialist will recommend painkillers. If an intestinal polyp is removed, the doctor will additionally advise on the specifics of hygiene procedures.
Nutrition after gastrectomy and gastrectomy (detailed version)
Gastric cancer continues to be one of the most common cancers. The main treatment method for tumors of this location is surgery.
Stomach surgery is a serious intervention that requires careful preparation carried out not only by medical personnel, but also by the patient himself and his relatives.
Preoperative preparation consists of general strengthening treatment - protein-rich food, sufficient fluids, vitamins, tonics. And if there is a narrowing of the outlet of the stomach and retention of food masses in it, eat only soft, sometimes pureed food for adequate evacuation from the stomach.
The postoperative period requires no less serious treatment. In the early postoperative period, patients are deprived of the opportunity to take water and food by mouth. Nutrition is carried out by intravenous administration of nutrient solutions, including protein and amino acids. The body's need for various substances is determined based on a blood test.
During this period, the patient is prescribed fasting for 2 days, and active aspiration of gastric contents is performed. From the 3rd day, if there is no congestion in the stomach, you can give “weak” tea, rosehip decoction, not very sweet compote without berries in small portions (20 - 30 ml) 5 - 6 times a day. To introduce protein products from the first days, it is recommended to use protein enpit (40 g per glass of water). Usually, in the first 2–3 days, 30–50 g of this solution is given through a probe, and later, after removing the probe, through the mouth. The diet is based on the principle of gradually increasing the load on the gastrointestinal tract and including a sufficient amount of protein. The specific type of enteral nutrition should be recommended by a physician.
The use of enpits allows you to bring the amount of animal protein in the diet to the physiological norm and provide the body with the necessary vitamins and mineral salts.
From the 3rd – 4th day after the operation, they begin to expand the diet and prescribe mucous soups, meat, fish and cottage cheese purees and soufflés, soft-boiled eggs;
from the 5th – 6th day – steamed omelettes, pureed porridge and vegetable purees in small quantities (50 g per serving). From the 5th day, if such nutrition is well tolerated, every meal should include protein foods. Gradually, portions of food taken at a time are increased (from 50 ml on the 3rd day to 200 - 250 ml on the 7th day and to 300 - 400 ml on the 10th day).
Thus, in the early postoperative period, patients will receive a sufficient amount of complete protein in an easily digestible form.
A gentle diet is prescribed to patients after 1 - 2 weeks. after surgery for 4 months. In the presence of complications such as gastritis of the gastric stump, anastomositis, peptic ulcer, patients must follow the diet for a longer period of time. The main purpose of the diet is to prevent or reduce the inflammatory process and prevent dumping syndrome.
Dumping syndrome (from the English dumping - dumping), dumping syndrome is one of the leading post-resection disorders. It occurs in some patients after partial or complete removal of the stomach due to disruption of the nervous and enzymatic regulation of the organs involved in digestion. As a rule, accelerated evacuation (“dumping”) of food from the stump of the stomach into the intestine, disruption of carbohydrate metabolism and the function of the remaining part of the stomach are observed. The attack begins after eating (usually after eating easily digestible food rich in carbohydrates) and is manifested by severe general weakness (sometimes with a disorder of consciousness), dizziness, profuse sweating, increased heart rate and decreased blood pressure, drowsiness, belching, regurgitation or vomiting, pain in the epigastric region , which is best consumed as a bite. Table salt 8-10 g. The diet is fractional - 5-6 times a day. Food temperature: no higher than 55-65° for hot dishes and no lower than 15° for cold ones.
This is a physiologically complete diet with a high protein content (meat, fish), a normal content of complex carbohydrates (cereals, cereals, vegetables, unsweetened fruits) and a sharp limitation of easily digestible carbohydrates (sugar, sweets, confectionery, fruit waters, canned juices), with normal fat content, limitation of mechanical and chemical irritants of the mucous membrane and the receptor apparatus of the gastrointestinal tract, with maximum limitation of nitrogenous extractives (especially purines), refractory fats (lamb), fat breakdown products obtained during frying (aldehydes, acroleins), with with the exception of strong stimulants of bile secretion and secretion of the pancreas and intestinal glands, foods and dishes that cause dumping syndrome (sweet liquid milk porridges, for example, semolina, sweet milk, sweet tea, hot fatty soup, etc.).
The meat is given in minced form, and the side dishes are not pureed (porridge, mashed potatoes). Salads, fresh fruits and vegetables, and black bread are excluded. All dishes are boiled, pureed or steamed. The third course for lunch is unsweetened (without sugar) or with the addition of xylitol (10-15 g per serving). The patient is given a strictly limited amount of sugar.
Complex therapy , aimed at compensating for the impaired functions of various body systems, begins after 2 weeks. after surgery and lasts 2 - 4 months. A diet high in protein (140 g), normal fat (110-115 g) and carbohydrates (380 g) with limited mechanical and chemical irritants to the mucous membrane and the receptor apparatus of the gastrointestinal tract.
Refractory fats, extractives, easily digestible carbohydrates, and fresh milk are excluded. Patients must follow a regimen of fractional meals. It is necessary to strictly limit the intake of easily digestible carbohydrates to avoid the development of hypoglycemic and dumping syndrome. At the same time, prescribing only a protein diet without a sufficient amount of carbohydrates is inappropriate, because under conditions of carbohydrate restriction, proteins may be wasted to cover energy expenditure, which leads to an increase in protein deficiency in the body. However, given the loss of peptic factor in such patients, preference should be given to protein products that are easily “attacked” by trypsin - fish and dairy. The intake of foods with coarse fiber and a large amount of connective tissue should be limited or they should be cooked.
Approximate diet for this period:
- Bread products – day-old wheat bread, wheat bread crackers, unsweetened cookies. Bread is allowed no earlier than 1 month after surgery.
- Soups - with vegetable and cereal decoctions, pureed, excluding white cabbage and millet.
- Meat and fish dishes - various dishes from lean beef, chicken, turkey, rabbit, veal with tendons removed, lean fish (cod, pike perch, carp, pike, bream, silver hake, carp, ice) in chopped form (puree, soufflé, dumplings, meatballs, rolls, cutlets). These dishes are boiled, steamed, baked (after preliminary boiling).
- Eggs and egg products – soft-boiled egg, no more than one per day, white omelet.
- Milk and dairy products - milk with tea and other products or as part of various dishes: if tolerated - whole milk. Kefir is included 2 months after surgery. Sour cream is only used as a seasoning. Non-sour cottage cheese, freshly prepared, pureed.
- Vegetables and herbs – boiled, pureed. Cauliflower only, boiled with butter, zucchini and pumpkin stewed; carrot, beetroot, mashed potatoes.
- Fruits, berries, sweets - natural fruits in limited quantities.
In the future, even in the absence of signs of disease in the operated stomach, you should adhere to a split diet for 2-5 years (4-5 times a day), limit the use of foods and dishes containing easily absorbed carbohydrates and fresh milk. The diet should be sufficiently varied, taking into account individual food tolerance. Patients with a good result of the operation and following a split diet, as a rule, do not need drug therapy.
If there are symptoms of post-gastroresection disorders, their treatment can be conservative and surgical. Diet therapy occupies a leading place in the conservative treatment of disease of the operated stomach. Food should be varied, high in calories, high in protein, vitamins, normal fat and complex carbohydrates with a sharp limitation of simple carbohydrates. Individual tolerance to foods and dishes should also be taken into account. Patients usually tolerate boiled meat, lean sausage, cutlets made from lean meat, fish dishes, soups with weak meat and fish broths, fermented milk products, vegetable salads and vinaigrettes seasoned with vegetable oil. The worst tolerated foods are sugar, milk, sweet tea, coffee, compote, honey, sweet liquid milk porridges, and baked goods, especially hot ones. Meals should be small, at least 6 times a day.
In case of dumping syndrome, it is recommended to start eating with hearty dishes; after eating, it is advisable to lie in bed or recline in a chair for 30 minutes. The products are used unprocessed, their chemical composition and energy value are 138 g of protein, 110–115 g of fat, 390 g of carbohydrates, total energy value is 3000 kcal. The diet is split - 5-6 times a day. In terms of the range of products, the diet differs significantly from pureed diet.
List of recommended dishes:
- Bread products – gray wheat bread, day-old baked goods, savory and unsweetened varieties of bakery products and cookies. Rye seeded bread.
- Soups - with vegetable broths and cereals, vegetarian. Borscht, cabbage soup, beetroot soup made from fresh cabbage. Low-fat meat soup once a week.
- Meat and fish dishes - various products from lean beef, chicken, turkey, rabbit, veal, lean fish (cod, pike perch, carp, navaga, pike, carp, etc.). These products are boiled, baked, stewed; can be cooked in pieces.
- Eggs and dishes made from them - soft-boiled egg, no more than 1 per day, white omelet.
- Cereals and pasta – crumbly and viscous porridges, puddings, cereal casseroles – unsweetened; boiled pasta and in the form of casseroles. Buckwheat, rolled oats and rice porridges are recommended, semolina is limited.
- Vegetables and herbs - raw, boiled, baked, stewed. Non-acidic sauerkraut, boiled cauliflower with butter, stewed zucchini and pumpkin, salads, vinaigrettes, green peas are allowed. Tomatoes with vegetable oil. Early raw, finely chopped greens can be added to various dishes.
- Fruits and berries, sweet and sugary products - not very sweet fruits and berries in their natural form and in the form of unsweetened compotes, jelly, mousses. Limit grapes and grape juice, which causes bloating. Sugar, honey, sweets, jam - extremely rarely.
- Milk and dairy products - milk with tea and other drinks or as part of various dishes, if tolerated - whole milk, curdled milk, kefir, acidophilus milk. Sour cream as a seasoning and in salads. The cottage cheese is not sour, fresh.
- Fats – butter, ghee, olive, sunflower.
- Snacks - mild cheese, low-fat herring, doctor's sausage, diet sausages, homemade meat pate, ham without lard. Salads, vinaigrettes, jellied fish in gelatin, jelly from boiled legs in gelatin.
- Sauces and spices - vegetable broth, sour cream, with the addition of butter.
- Drinks and juices - “weak” tea, weak coffee with milk, unsweetened, fruit and berry juices, vegetable juices, rose hip decoction.
It is prohibited to consume the same foods and dishes as when prescribing the pureed diet, except for white cabbage.
An approximate one-day menu when using an unprocessed diet:
- 1st breakfast: boiled meat, salad of tomatoes and cucumbers with sour cream, oatmeal porridge without sugar, tea with milk.
- 2nd breakfast: cheese 50 g, apple.
- Lunch: vegetarian borscht, boiled meat stew with mixed vegetables, xylitol jelly.
- Afternoon snack: boiled fish, boiled beets.
- Dinner: meat soufflé, stewed carrots, cheesecake with sugar-free cottage cheese.
- At night: a glass of kefir, fresh cottage cheese 100 g.
- For the whole day: rye bread – 150 g, white bread – 150 g, sugar – 30 g.
All dishes must be boiled or steamed and not pureed. Separate baked dishes without a rough crust are allowed, the third dish for lunch is unsweetened or with xylitol (10-15 g per serving). Sugar is given to the patient in a strictly defined quantity.
Drug therapy for dumping syndrome is much less effective, so reasonable dietary recommendations are more helpful.
Read about stomach cancer on the website www.gastriccancer.ru
SIGN UP FOR A CONSULTATION by phone +7 (812) 951 - 7 - 951
Share link:
Which clinic is used to remove polyps in the stomach and intestines?
The clinic on Yauza performs operations to remove polyps of the large intestine and other gastrointestinal organs at an expert level. The medical center is equipped with modern high-precision endoscopic equipment. This allows for removal as accurately as possible, avoiding injury to the mucous membrane.
Our specialists have enormous knowledge of polyp removal techniques, acquired in the best clinics in Russia and Europe. Based on patient feedback, we have created the most comfortable conditions for them in the hospital. With us you will be surrounded by attention and care throughout the entire treatment period.
The polyp removal service may include a full examination or is carried out on the basis of previously obtained data.
Sign up for the procedure
What is a stomach polyp, symptoms and causes of appearance
Polyp is a growth of cells on the mucous membrane of an organ.
A polyp is a proliferation of cells on the mucous membrane of an organ. These tumors can appear in the sinuses, stomach, uterine cavity, bladder and gall bladder. Any organ that has a mucous membrane is at risk of developing such growths. Gastric polyps are growths of cells inside the stomach. The disease is quite rare. Causes of growths:
- Age – persons over 50 years of age are at risk
- Bacterial infections – Helicobacter pylori promotes the formation of polyps
- Hereditary oncopathologies of the gastrointestinal tract system
- Taking certain medications
- Radiation exposure
- Chemical effects on the gastric mucosa
Stomach polyps rarely manifest themselves. They are often discovered during a comprehensive examination or during the treatment of other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms of gastric polyposis:
- Stomach pain
- Pain when palpating the epigastric region
- Nausea
- Vomit
- Feeling of fullness
- Bleeding
- Impaired evacuation of food from the stomach
- Defecation disorder
- Intractable anemia
- Halitosis, possible foul-smelling vomiting
These signs are characteristic of many pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract. To confirm the diagnosis of polyposis, he uses various types of gastroscopy - examination of the stomach cavity using an endoscope and simultaneous collection of material for histological examination. The attending physician decides what to do next. Polyps measuring less than 1 cm are recommended to be observed; those larger than this should only be removed. If histology has determined the presence of malignant cells, then removal of such a formation is mandatory, regardless of its size.
Even with a benign polyp, surgical intervention is recommended, since there is a high probability of its degeneration into a cancerous tumor.
Is surgery necessary?
It is necessary to remove polyps, as they can provoke the development of quite serious complications.
Among them:
- strangulation of polyps with accompanying severe pain;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- infection;
- stomach bleeding.
Among the most dangerous complications: transition from a benign neoplasm to a malignant one. Degeneration into cancer occurs in 90 percent of total polyposis (a case where the number of polyps cannot be counted).
The more gastric mucosa is covered with polyps, the higher the likelihood of degeneration into cancer. Polypous stomach cancer is called carcinoma. The presence of risks of degeneration into a malignant tumor, as well as damage to a large area of the gastric mucosa, is an automatic indicator for surgical manipulation.
It is worth understanding that carcinoma is formed not only from large polyps; therefore, during the removal process, small tumors should not be ignored. In medicine, there are cases when apparently benign tumors turned out to have malingia of the villi (already degenerated into malignant ones).
Cancer is a very unpredictable disease, therefore, it is important to completely remove the polyposis during surgery.
Polyps can be identified during:
- Ultrasound diagnostics with contrast;
- x-ray diagnostics;
- MRI;
- CT;
- gastroenteroscopy.
Patients who have a chronic or congenital form of gastrointestinal diseases are at risk of polyposis and need regular endoscopy in order not to miss the onset of neoplasms. The doctor can finally say whether this formation is benign or malignant only after surgery, as well as histology and cytology of cells and tissues.
Prices
Price (rub.)In installments* (rub.) Consultation with a surgeon on the operation (SPECIAL)0—Online doctor’s opinion on the operation (SPECIAL)0—Endoscopic removal of polyps from the esophagus, stomach, duodenum, category I. complexity (polyp up to 1 cm) 6050—* You can read more about the conditions here - Treatment on credit or in installments
The cost is preliminary. The exact cost of the operation can only be determined by a surgeon during a free consultation.
Doctors performing polypectomy – endoscopists:
Gerasimets Viktor Alexandrovich
Endoscopist
22 years of experience
Make an appointment
Danyushin Vladislav Mikhailovich
Endoscopist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
Experience 37 years
Make an appointment
Why choose CELT clinic?
- Medical personnel. The high level of qualifications and many years of experience of our specialists indicate that you can trust us with your health.
- Manufacturability. Advanced medical technology allows all diagnostic and therapeutic procedures to be carried out at a very high level.
- Accuracy. You can be confident in the reliability of the results of histological examination of the collected material.
- Save time. The entire course of treatment, starting with a clinical examination, examination of the patient and ending with a series of therapeutic measures, including highly specialized care, takes a minimum amount of your precious time.
Postoperative complications
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
If removal is performed incorrectly, 5 percent of patients experience gastric bleeding. In order to avoid complications, the patient is given an injection of adrenaline before the procedure.
Approximately 13 percent of patients experience recurrence of the disease, most of which occurs within the first 24 months after the removal procedure. Approximately 35 percent of patients experience classic postoperative complications.