Pregnant women experience a variety of pain sensations, and it is sometimes difficult to know which pain is normal and which is a symptom of a serious illness. Very often, pregnant women experience pain in the right side of the lower abdomen. When a woman feels such pain, she should first consult a doctor to understand the cause. For almost all reasons, it is necessary to call an ambulance or see a doctor.
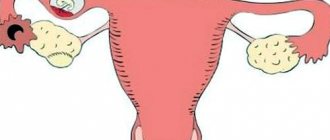
What organs are located on the right?
When they say “stomach hurts” or “stitches in the side,” they do not mean any one specific organ. After all, the “stomach” is a complex system of internal organs with its own tasks and functions. What can hurt on the right side? In diagnosing the problem, it is very important to understand where exactly the pain is localized. To do this, let’s divide the right side of the abdomen into the upper and lower halves:
- At the top are: liver, bile ducts, gallbladder, intestines, stomach and diaphragm, kidney, duodenum, pancreas;
- in the lower – ureter, fallopian tubes, appendix, ovary with appendage, small and large intestines;
Pregnancy leads to changes in the functioning of almost all organs. Their activity weakens, blood circulation is impaired, and immune status decreases. The result is an exacerbation of chronic diseases and the emergence of new problems that have never bothered a woman before.
Why does pain occur?
Before diagnosing the disease yourself, it is necessary to find out the exact symptoms and be sure to contact a leading specialist. After all, the occurrence of pain can portend various serious illnesses that threaten the child.
| Cause | Brief description of the problem |
| Uterine muscle strain | As the fetus grows, this leads to strong pressure on the uterus, especially on the muscles. The pain is localized in the lower abdomen and increases significantly with sudden movements. The main thing is that such discomfort is considered normal and does not pose a threat to health. |
| Fetal location | Depending on the position of the fetus, pain may occur either in the left side or in the right side, radiating down the abdomen. Discomfort is felt only when the fetus begins to move. Also not a pathological cause of pain |
| Appendicitis | The main thing is to determine the nature and location of the pain and immediately consult a doctor. An alarming sign is acute, prolonged pain. To eliminate this problem, surgical intervention is required, since lack of action is fraught with suppuration. Therefore, having identified all the risks, surgical treatment is prescribed. |
| Ectopic pregnancy | In the early stages, pain may occur in the lower abdomen on the right side, which sometimes becomes a confirmation of an ectopic pregnancy. This occurs when the fertilized egg attaches in the wrong place, that is, in the fallopian tube. As the fetus grows, there is strong pressure on the tube, which can lead to its rupture. Quite a dangerous phenomenon for women's health. The painful sensations may be similar to the signs of appendicitis, but the characteristic difference is bleeding. If such pain occurs, you must call an ambulance |
| Ureteral entrapment | The occurrence of pain in the lower abdomen can occur due to the process of pinching due to the growth of the uterus |
| Stones in the kidneys | The sensation of renal colic causes pain in the lower back, which radiates to the groin area; the symptoms are complemented by problems with urination, as well as the appearance of bloody spots in the urine. This case requires urgent hospitalization |
| Infection that is sexually transmitted | Various pathological ailments, which can be obtained through unprotected sexual intercourse, can provoke painful sensations. In this case, a doctor’s diagnosis followed by emergency treatment is necessary. |
| Ovarian rupture | The symptoms are very similar to an ectopic pregnancy. According to statistics, pathology most often occurs in the right ovary, which causes severe pain in the lower abdomen. The phenomenon is accompanied by heavy bleeding, which often leads to anemia in a pregnant woman. The treatment method will be determined by the severity of the bleeding. For minor blood loss, drug therapy can be used |
| Cyst rupture | Severe pain occurs suddenly and can even result in loss of consciousness. Additional symptoms: intestinal disorders, painful urination, high fever. Pathology is eliminated exclusively through surgery |
Diagnosis and treatment
Consultation with a gynecologist
Study of anamnesis and complaints, gynecological examination, preliminary diagnosis, planning of examination and treatment.
Additional examination
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs (to exclude ectopic pregnancy with delayed menstruation, assess the condition of the uterus and fertilized egg, exclude other gynecological pathologies);
- 3D - 4D ultrasound during late pregnancy;
- colposcopy (examination of the cervix under magnification);
- hysteroscopy (examination of the uterine cavity) if necessary;
- gynecological smears (examination for hidden sexually transmitted infections);
- general blood and urine tests;
- bacteriological urine culture (exclude urinary tract pathology);
- diagnostic laparoscopy (if indicated);
- puncture of the abdominal cavity through the posterior vaginal fornix (if indicated - to exclude intra-abdominal bleeding);
- X-ray, CT, MRI of the abdominal cavity and pelvis (if indicated);
- If necessary, consultations with doctors of related specialties are prescribed.
It is unacceptable to use painkillers for abdominal pain of unknown origin. This not only blurs the picture of the disease, but can also lead to a deterioration in health. If you are experiencing pain in the lower abdomen and do not know its cause, immediately make an appointment with a specialist. Perhaps a visit to the doctor will not only keep you healthy, but save your life.
Treatment
In our hospital you can undergo both conservative and surgical treatment of diseases that are the cause of pain in the lower abdomen.
Pain at different times
Unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen can rarely be avoided during pregnancy. These sensations can occur not only with pathology. Physiological pain is a manifestation of physiological changes that occur to a woman during pregnancy.
1st Trimester
The first trimester of pregnancy is the period of time from conception to the end of the 12th week of pregnancy. During the 1st trimester of pregnancy, the fertilized egg becomes an embryo, and the embryo becomes a fetus. The first trimester is exactly the time when you need to be especially careful towards your unborn baby and attentive to yourself if you really want to become the mother of a healthy, joyful baby.
During the first twelve weeks, almost all the vital organs of the unborn child are formed, and the body of the expectant mother “gets used” to her pregnancy and begins to “work” for the child. It’s amazing that so many important life events happen in such a short period of time.
2 Trimester
At this stage of pregnancy, the uterus begins to significantly increase in size, which leads to strong pressure on all organs located in the abdominal cavity. The pain can be explained by compression of the intestines, thus making it difficult to pass stool and can lead to constipation and pain. Also, pressure is exerted on the bladder with subsequent squeezing of the ureters, as a result, this leads to the accumulation of urine.
At the same time, during this period, the fetus begins to move more and more actively in the uterine cavity. The movement can cause impacts to various organs in the abdomen.
3 Trimester
Abdominal pain most often develops in early pregnancy, when hormonal changes provoke nausea and vomiting - symptoms that usually occur in the morning. In the middle of the second trimester, that is, at about 20 weeks of pregnancy, abdominal pain usually goes away. In the third trimester, it may appear due to the fact that the uterus begins to constrain other organs. During this period, some women experience heartburn or a feeling that the skin on the abdomen is stretching.
Causes of pain in the lower abdomen
Pain in the lower abdomen is caused by gynecological pathology, pregnancy, or can occur with diseases of other organs.
There are sharp and aching or nagging pain in the lower abdomen.
Acute pain is caused by:
- Ectopic pregnancy - against the background of a delay in menstruation and a positive pregnancy test, acute pain is caused by a rupture of the fallopian tube;
- Ovarian apoplexy—rupture of ovarian tissue and intra-abdominal bleeding—is diagnosed in 0.5–2.5% of women with lower abdominal pain;
- Torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian cyst or tumor formation is accompanied by tissue necrosis, severe pain, nausea and vomiting;
- Acute adnexitis (inflammation of the appendages) - severe pain and signs of intoxication. 55–75% of pain in the lower abdomen is associated with inflammatory diseases of the genital organs, a quarter of which in the future leads to ectopic pregnancy;
- External endometriosis - can cause severe pain, often associated with the menstrual cycle;
- Necrosis of the myomatous node, birth of a submucosal node (pathologies associated with benign formations of the uterus);
- Imminent miscarriage, beginning miscarriage - cramping pain, bleeding. According to statistics, 10–20% of all pregnancies end in miscarriage in the first trimester;
- Threat of premature birth - periodic cramping pain, uterine hypertonicity;
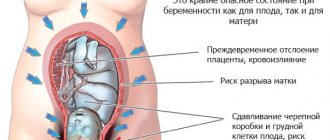
- Premature placental abruption - very intense pain, possible bloody discharge from the genital tract, hypertonicity of the uterus.
In case of acute pain, it is unacceptable to postpone a visit to the doctor. If you feel severe abdominal pain, immediately make an appointment with a specialist. Otherwise, you risk getting many serious pathologies. Ignoring abdominal pain can lead to the death of the patient.
Aching/pulling pain provokes:
- Chronic adnexitis - periodic aching pain (in autumn and spring during exacerbation), intensified by sexual intercourse and movement;
- Chronic endometritis (inflammation of the uterine mucosa) - dull pain, profuse leucorrhoea with an unpleasant odor, possibly mixed with blood;
- Algodismenorrhea - pain during menstruation;
- Internal endometriosis - nagging pain during menstruation, intensifies before it begins, disappears after it ends;
- Adhesive disease - often develops after surgery on the abdominal and pelvic organs. Aching pain, intensified by coitus, sudden movements, and heavy lifting.
If the pain is accompanied by an increase in temperature, it is unacceptable to postpone visiting the doctor. Hyperthermia may indicate the development of an inflammatory process in the body. If you have abdominal pain, immediately make an appointment with a doctor to identify the cause of the discomfort.
Pain in the lower abdomen with other diseases:
- Acute appendicitis - pain in the right lower abdomen, nausea, vomiting, fever;
- Intestinal colic, intestinal obstruction - very sharp pain, signs of intoxication;
- Acute cystitis, pyelonephritis (inflammation of the bladder, kidneys), urolithiasis - pain in the lower abdomen, lower back, frequent and painful urination;
- Digestive disorders during pregnancy - the growing uterus lifts the diaphragm and stomach, compresses the intestines, which leads to increased gas formation and abdominal pain.
Make an appointment
Phantom pain in the right iliac region of the abdomen
Oddly enough, so-called phantom pain can occur during pregnancy. In fact, the body is in perfect order, there are no pathologies, but the pregnant woman has a far-fetched feeling of discomfort.
This all happens exclusively at the psychosomatic level, when the psyche affects the sensations of the body. The reasons for the occurrence of such conditions during pregnancy are very different:
- Panic fear for the condition of the fetus.
- Unconscious desire to attract attention.
By virtue of maternal instinct, a woman will create all the most favorable conditions for the development of the fetus, therefore, if any pain occurs, the question of why the pain appeared, if everything was done correctly, is it not a threat? In order to rule out all sorts of ailments, it is best to seek advice from a leading gynecologist, because the pain may be obvious.
Pain in the upper segment of the right side
What can get sick in the upper segment of the abdomen
? Pain in the upper right segment of the abdomen can be caused by diseases:
- liver (fatty hepatosis, hepatitis);
- gallbladder (severe attack of pain due to inflammation, the presence of stones, bending of the bile ducts, excess bile, poor functioning of the sphincter that releases bile, rare pain due to a violation of the diet);
- upper right part of the diaphragm (hernia);
- the right part of the intestine with the duodenum (ulcer);
- the upper part of the right kidney with the adrenal gland.
Heartburn can be caused by hepatic or renal colic
Diaphragm diseases
The most commonly diagnosed hernia is diaphragmatic hernia. The uterus that has squeezed the diaphragm, frequent coughing or even constipation contribute to the development of the disease, which is confirmed by examining the esophagus using a flexible endoscope - esophagogastroscopy. Its symptoms:
- pain in the upper hypochondrium, aggravated in a horizontal position and with sharp bending of the body;
- intestinal disorders in the form of vomiting and burning in the esophagus, gas formation, frequent regurgitation;
- increased salivation;
- anemia.
The diaphragm is a dome-shaped structure consisting of muscles and connective tissue that separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity.
If the hernia is sliding, then it does not pose any harm to the child and is treated with diet and gentle medications, and if the hernia is strangulated, an urgent operation is required to eliminate it.
Pancreatic diseases
The pancreas (or pancreas) is an organ of the digestive system that produces juice with enzymes for digesting food and hormones for metabolism, including insulin.
Pancreatitis
In case of sudden attacks of pain that instantly arises and rolls down the back, it is recommended to pay attention to the pancreas. Inflammation of this organ manifests itself as follows:
- the attack is unbearably painful, with frequent vomiting and profuse sweating;
- the pain begins in the upper quadrant of the abdomen, but then, as if taking it in a ring, it encircles. It intensifies when taking a horizontal position, and subsides if you sit down and lean forward slightly;
- the stomach is swollen from accumulated gases;
- frequent stool discharge, which is not formed and contains particles of undigested food;
- against the background of irritable intestines, dysbiosis with accompanying skin rashes and candidiasis.
Gallbladder diseases
The most common dyskinesia of the gallbladder and ducts and cholelithiasis occur in pregnant women.
Dyskinesia of the gallbladder and bile ducts
Biliary dyskinesia is a disease associated with stagnation of bile due to compression of the bile ducts by the enlarged uterus. Manifests:
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- esophageal disorders (repeated belching, dryness and bitterness in the throat, burning in the chest, feeling of fullness);
- decreased appetite;
- increased nervousness.
If left untreated, it will lead to inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis) and stone formation (cholelithiasis).
Gallstone disease (cholelithiasis)
Gallstone disease is a violation of the functional movement of bile and cholesterol or bilirubin metabolism with the formation of stones (calculi) in the bile ducts and gallbladder. Pain is caused by poor diet, nervous exhaustion, or prolonged work with a bent back. Characteristic features:
- single, pulsating pain sensations reach their peak during the first hour due to biliary or hepatic colic. A barely bearable attack of pain lasts about six hours, then gradually fades away to a state of aching pain, which can continue for a long time;
- pain follows a path from the abdomen to the back or down the arm from the right shoulder;
- in the acute stage, vomiting and fever.
Liver diseases
If the pain is constant and does not subside, then this may be due to liver or intestinal diseases.
Hepatitis
Pain in the right quadrant of the abdomen during inflammation of the liver - hepatitis A, B, C, sometimes manifests itself only towards the equator of pregnancy, when the woman’s body is weakened and susceptible to infection through water or products due to viral hepatitis A. It is easy to diagnose:
- urine turns brown, skin turns red or yellow (jaundice);
- signs of a viral infection appear: chills, weakness, lack of appetite.
Fatty liver
More often develops towards the end of the second trimester of pregnancy and manifests itself:
- itching of the skin, sometimes jaundice;
- frequent nausea;
- lack of appetite;
- drowsiness;
- sudden change in mood;
- convulsions up to loss of consciousness.
In this case, we are talking about a real threat to the health of the unborn child and his mother, so the woman requires urgent resuscitation care.
Liver colic
The liver moves sideways and upward relative to its normal position and cannot cope with the outflow of bile. Sometimes such short attacks of pain are caused by the child, hitting the expectant mother’s liver. Such pain occurs most often after a diet violation in women with a weakened gallbladder. Unlike painful attacks of appendicitis, during which the pain radiates more to the groin, the liver hurts in the area of the right hypochondrium, and does not allow you to take a deep breath. If you have low-grade body temperature with sudden onset of intestinal disorders, you should seek help from a doctor.
Kidney diseases
With an inflammatory process in the right kidney, the pain will accumulate on top of the abdomen, radiating under the ribs. Often it can “escape” to the perineum in wave-like attacks.
Video: nephrologist, doctor of the highest category about kidney diseases during pregnancy
The danger of nephritis (kidney inflammation) lies in its ability to lead to kidney failure, which requires comprehensive treatment.
Nephritis of the right kidney
If the right kidney becomes infected, pus or stones form in it, which, when leaving the kidney, descend into the ureter and provoke repeated wave-like attacks of pain, targeting the groin.
In acute nephritis, a woman experiences the following symptoms:
- chilling and sweating, dry mucous membranes with subsiding thirst;
- body temperature reaches 40 degrees, increased blood pressure, sometimes dizziness;
- pain with frequent urination;
- puffiness of the face due to the accumulation of fluid in the body, which the kidneys cannot cope with;
- vomiting even without eating;
- increased pain in the lower back when tapping in the area of the projection of the kidneys;
- flakes and sat in the urine.
Why is pain dangerous?
But there are also dangerous obstetric pains that arise from the following problems in the body:
- Threat of miscarriage
. At the same time, there is aching and pulling in the lower abdomen and lumbar region. Bloody discharge is also added to the pain. You can avoid an unfavorable outcome only by seeking medical help in a timely manner. If no measures are taken, the pain becomes cramping, bleeding increases and spontaneous miscarriage occurs. - Ectopic pregnancy
. If the embryo begins to form not in the uterus, but, for example, in the fallopian tube, then we are talking about an ectopic pregnancy. This is a dangerous pathology for a woman’s health due to the high risk of internal bleeding, requiring urgent surgical intervention. Every woman of childbearing age should know the signs of an ectopic pregnancy in order to consult a doctor in time and prevent complications. - Premature placental abruption
. It can be triggered by gestosis, injuries in the abdominal area, a short umbilical cord and other pathologies. In this case, the pain in the abdomen is very severe, internal bleeding may occur without external discharge. In this case, only forced delivery and stopping the bleeding can save the woman and child. - Uterine tone
. “Uterine hypertonicity” can more often occur in the early stages of pregnancy. Uterine tone during pregnancy is contractions that appear before the expected due date. They are felt as pulling, aching pain in the lower abdomen (a similar condition during menstruation), sometimes pain in the lower back.
Among non-obstetric abdominal pains during pregnancy, surgical pathologies or certain diseases most often occur. The danger of intestinal infections during pregnancy is that, together with intestinal tone, they cause uterine tone.
Abdominal pain during pregnancy
Abdominal pain during pregnancy can be of different localizations and in most cases there is nothing threatening in itself. This is basically a normal reaction of the body to the increasing weight and growth of the uterus. The most troublesome period of pregnancy is the first trimester, because ectopic pregnancy, spontaneous abortion, and the like can occur here. Anxiety is greatly contributed to by the disruption of hormones in the body. After all, during this period they need to quickly adapt to a new way, which will allow them to carry and give birth to a healthy child without any problems, and even set up proper lactation. Moreover, at each of these stages a certain hormonal surge occurs, during which the emotional state of the pregnant woman is often changeable.
It is quite common to experience pain in the lower abdomen during early pregnancy. If they do not cause much discomfort, there is no bleeding, or other symptoms of a possible pathology or disease, then treatment is not required. At the beginning of pregnancy, such pain can be associated with hormonal changes, in the middle - with the rapid growth of the uterus, and at the end - with the preparation of the uterus for childbirth.
Abdominal pain in the first trimester
If your stomach hurts during early pregnancy, this does not always indicate some kind of pathology. If the pain is mild, rarely occurs and passes quickly, do not worry. But for greater confidence, as soon as the test shows two stripes, you should contact a gynecologist as soon as possible. This will not only save you from hassle, but will also set you up mentally for the upcoming event. If you experience frequent aching, intense and cramping pain, you must urgently find time and be sure to see a doctor. After all, this may indicate an ectopic pregnancy, which will require urgent surgical intervention. In addition, spontaneous abortion (miscarriage) can also be the cause. However, abdominal pain is often, but not always, accompanied by lower back pain and bleeding. If all indicators of pregnancy are normal, but your stomach still hurts, this can be explained very simply. The body is rebuilt, the tissues supporting the uterus become softer, looser, and the uterus itself grows and shifts, which contributes to tingling and pulling pain in the lower abdomen.
Pain in the lower abdomen
Pain in the lower abdomen during pregnancy, and especially in the later stages, is often due to internal pressure, that is, the growing uterus puts pressure on the internal organs, thus disrupting their full functioning. The intestines react very sensitively to pregnancy hormones with decreased motility and impaired peristalsis, which is a common cause of constipation, bloating and colic. To avoid this, you need to move more often, eat foods rich in fiber (fruits, vegetables, whole grain bread) and, of course, drink more fluids. Also, pain concentrated in the lower abdomen can be caused by sprained ligaments due to the rapid growth of the uterus, or can be triggered by premature placental abruption. In the latter case, urgent medical attention is necessary, because irreparable harm can be caused to the mother and child. In this case, rapid delivery and immediate stopping of bleeding are indicated. In addition, during pregnancy, new or worsening chronic diseases may develop, which can also send signals in the lower abdomen. These are cholecystitis, intestinal dysbiosis and others. In some cases, emergency surgery is indicated, and therefore it is worth paying attention to the slightest changes in the nature of the pain. If you have even the slightest doubt, you should urgently consult a doctor, otherwise it may be too late. In addition, problems with the genitourinary system are quite possible, which can also cause pain in the lower abdomen.
Uterine tone
Uterine tone is painless or slightly painful contractions of the uterus. If a pregnant woman feels a spasm in the lower abdomen, the stomach becomes like stone (this is especially noticeable in the second half of pregnancy) - this is tone. Tone is diagnosed by a gynecologist during an external examination. The fact that tone was detected on ultrasound, contrary to popular belief, is not an indication for treatment and hospitalization. The uterus is a muscular organ, and it is quite normal that it contracts periodically. The key word here is periodically, and, of course, painlessly and short-term. If the uterus is toned, doctors recommend taking a horizontal position, lying on your side, you can take an antispasmodic tablet and use a Papaverine suppository.
Preliminary contractions
As a rule, minor pain in the lower abdomen occurs during late pregnancy - these are preparatory contractions. In this way, the uterus prepares for the upcoming birth. In some women, the uterus begins to “prepare” like this at 32 weeks, in others in 1-2 weeks, and some either do not notice these weak contractions, or consider this to be the norm, and therefore do not pay attention. It is very important to learn to distinguish between preliminary contractions and true contractions, those that begin during labor. Preliminary contractions last for several seconds, and they are not regular, unlike true contractions, and do not intensify. It has been observed that primiparous women experience preliminary contractions more often than multiparous women. This kind of pain can be relieved very easily using non-medicinal methods - you can simply breathe deeply, lie down and relax. In many cases, taking a warm (not hot!) bath helps.
Gynecological pathologies
The 4 reasons that we described above are variants of the norm. However, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor if these conditions are accompanied by bloody or brown vaginal discharge, clear or greenish vaginal discharge (this may be amniotic fluid), if the pain lasts for several minutes, is not relieved by antispasmodics and only increases when weakness appears, dizziness, spots before the eyes, etc. In a word, if the condition worsens. Such symptoms may indicate a threat or beginning of spontaneous miscarriage, frozen or ectopic pregnancy (when early pregnancy, pain in the lower abdomen), premature or urgent birth, etc.
Other reasons
However, abdominal pain in expectant mothers does not always arise precisely because of gynecological problems and is a consequence of pregnancy. Let's list other probable reasons.
1. Cystitis and other diseases of the female excretory system. The ureter is located next to the internal genital organs, which is why this pain is often confused with “gynecological”. Usually the pain occurs suddenly in such cases and has a “stabbing” character. Pain in the lower abdomen is accompanied by frequent and painful urination. A urologist treats the genitourinary system. The disease should not be neglected, because it is caused by an infection that is unsafe for the child. Folk remedies, such as bearberry, do not help much, but the doctor can prescribe effective medications approved for use by pregnant women.
2. Intestinal problems: diarrhea, constipation, bloating. It should be noted that the last 2 are common phenomena in expectant mothers. Constipation is caused by a decrease in physical activity, displacement of internal organs due to the growth of the uterus, poor diet, and drinking insufficient amounts of fluid. Bloating is caused by consuming appropriate foods, as well as carbonated water. Sometimes it is enough to go to the toilet for the stomach pain to go away if the problem is constipation.
3. Poisoning or rotavirus infection. Their symptoms are very similar. Usually it all starts with cramping pain in the lower abdomen, sometimes the pain moves to the navel area. Then diarrhea and/or vomiting begins.
4. Appendicitis. If you are pregnant, nagging pain in the lower abdomen does not always indicate tone or minor ailments, this may be a symptom of appendicitis, especially if the pain is on the right side, accompanied by an increase in temperature. The correct diagnosis can be made by a surgeon. If the pain does not go away within an hour or two, but only increases, you should not attribute everything to an intestinal disorder and take drugs like “smecta”, this is very dangerous. If surgery is not carried out in time, it can lead to peritonitis.
And these are not all the reasons. Women who are pregnant not for the first time can quite easily distinguish painful sensations arising from uterine spasms from other types of pain. But in any case, it doesn’t hurt to see a doctor.
Pain in the upper abdomen
Pain in the upper abdomen during pregnancy mainly occurs in the later stages. Their cause is the same uterus, which is constantly increasing and begins to slowly reach the upper organs of the peritoneum. This primarily affects the liver, gall bladder, stomach, and pancreas, disruptions in the functioning of which lead to symptoms such as belching and bitterness in the mouth. In addition, very often in the last trimester of pregnancy, the stomach throws gastric juice up the esophagus, causing considerable discomfort. To avoid these unpleasant moments, you need to eat a balanced diet, which should be eaten in small portions. It is advisable, of course, to exclude fried, spicy, too salty and too sweet.
Stitching pains
Stitching abdominal pain during pregnancy occurs for many reasons. This may be stagnation of feces in the intestines, which also provokes flatulence and constipation. By the way, the latter, in the future, can become one of the causes of hemorrhoids. It is also necessary to pay attention to the intensity of the pain. If it is weak and rarely occurs, then you should not focus on it. But if the pain is severe, especially sharp, you need to consult a doctor. Acute pain can be a consequence of the development of appendicitis, inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis), and pancreas. Often, during filling of the bladder, expectant mothers complain of nagging pain in this area, which turns into stabbing pain, and becomes more painful when urinating, which indicates cystitis. In addition, stabbing pain may indicate the presence of infectious diseases, which are most often sexually transmitted.
Abdominal pain on the left
Abdominal pain on the left side during pregnancy can be caused by various diseases of the internal organs. They can signal various lesions of the stomach and pancreas, the splenic flexure of the colon and, in fact, the spleen itself, as well as the left kidney. In addition, pain localized in the left side of the abdomen is possible when a hiatal hernia occurs.
Abdominal pain on the right
Abdominal pain on the right side during pregnancy most often occurs with diseases of the gallbladder, liver, duodenum, and right kidney. If the pain is accompanied by other symptoms, you should consult a doctor. For example, symptoms of gallbladder inflammation include not only pain in the right side of the abdomen, but also nausea and vomiting (which are often confused with toxicosis). As a rule, following a salt-free diet with the complete exclusion of fatty, fried and spicy foods helps to cope with this problem. Possible formation of sand or kidney stones. Basically, during pregnancy they try not to affect this organ, because it is of great importance when bearing a child. But if the doctor sees some pathology or the hopelessness of the current situation, which may affect the further course of pregnancy, then measures will be taken to eliminate the cause of the pain, with maximum benefit for the fetus and the woman.
Abdominal pain when walking
A pregnant woman’s stomach often hurts when walking, causing some discomfort. This problem mainly concerns the second and third trimesters of pregnancy, that is, those periods when the uterus begins to actively grow, thereby causing a change in the center of balance. This is one of the reasons for the so-called duck gait. Many pregnant women are ashamed of this and stubbornly try to walk the same way they walked before, which causes pain. The second reason is the softening of the joints located between the pelvic bones. Thus, the body prepares for the passage of the baby through the birth canal. To reduce or even get rid of pain, you should pay attention to the position of your body when walking. The correct position of the body during pregnancy is to move the shoulders back, shifting the center of gravity from the toe to the heel; the use of a special bandage for pregnant women, which will not only reduce the load from the abdomen, but also remove tension from the spine, will also be invaluable.
Severe pain
The stomach hurts severely during pregnancy during some, at least not very good, changes. Normally, there should be no severe pain. But if they have already arisen, then you should not tolerate them; you must definitely consult with your local gynecologist. Severe pain can result from ectopic pregnancy, placental abruption, miscarriage, premature birth, as well as diseases associated with inflammation and chronic diseases of internal organs. In principle, in any of these cases, it is necessary to call an ambulance as quickly as possible, because untimely assistance can lead to disastrous consequences. The most important thing in this matter is not to miss precious time, which can give life to a small miracle, and maybe more than one.
Abdominal pain can be of different localization, intensity and etiology. If you have any doubts about this, you should immediately consult a doctor. If abdominal pain is accompanied by other symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, dizziness, loss of consciousness, etc., you should urgently, without delay, call an ambulance.
OSTEOPATHY AND ABDOMINAL PAIN
We recommend that you use our services and prevent abdominal pain without the use of medications harmful to the expectant mother. Osteopathy will help you not only get rid of pain, but also prevent its occurrence. Our specialists will carry out the treatment very carefully and effectively, absolutely safely. As a rule, the osteopathic treatment method is an excellent alternative to surgery in the treatment of many gynecological diseases.
Osteopathy is a generally recognized scientific method of treatment, the main medical instrument of which is the hands of a specialist.
An osteopathic doctor, with just gentle touches, will be able to determine the cause of the pain and, if possible, eliminate it. Osteopathy treats the human body very carefully, believing that the basis of health is its balanced activity, which means this method will not harm either the expectant mother or the baby.
How to alleviate the condition?
Moderate physical activity during pregnancy is a necessary measure for targeted stretching of the muscles and ligaments of the perineum. Regular gymnastic exercises prepare the body for childbirth. Here is an approximate complex that every pregnant woman can take note of:
- Get down on your knees, spread them shoulder-width apart and sit between them on your buttocks. This is a classic pose for stretching the perineal ligaments. If physical fitness permits, the woman can slowly and carefully lower herself from this position onto her back—this position is known as the fish position.
- Sit on a flat surface, bend your knees and pull your legs towards you, grabbing your heels. Now rest your feet against each other, and try to reach the floor with your knees apart. This exercise is called the butterfly.
- To relieve pain in the lower abdomen during pregnancy, a woman needs to learn to relax and contract the muscles of the perineum. It is enough to master the following exercise: imagine that you really want to go to the toilet in a small way, but there is no way to empty your bladder, so you have to endure it. To do this, you need to force your willpower to tense the muscles of your perineum for 10 seconds and then relax. Repeat the exercise several times in a row, it is especially important to do this when there is very little time left before giving birth.
Obstetric pain
Pain in the lower abdomen during natural pregnancy that occurs while carrying a child is called obstetric. They are associated with restructuring occurring in the uterus. For example, at the moment of implantation of a fertilized egg to the wall of an organ, a woman, as a rule, feels discomfort (pulling or tingling pain) of a short duration. This may release a small amount of blood.
Closer to the “equator” of pregnancy, when the belly becomes large, the ligaments and muscles that support it experience severe tension. This may result in brief bouts of pain.
From about 35 weeks (or even earlier), a woman begins to have training contractions. They are expressed in sensations of heaviness and pain in the lower abdomen. In a mild degree, training contractions do not cause alarm, but if they are severe and occur frequently, it is necessary to inform the doctor under whose supervision the pregnant woman is, as they can be a harbinger of premature birth.
Towards the end of pregnancy, the fetus begins to put pressure on the pelvic bones, which can lead to spasm of the pelvic floor muscles and result in pain. Normally, such discomfort is moderate, but if it intensifies, you should inform your doctor about it without delay.
Thus, obstetric pain in the lower abdomen during pregnancy is not intense or prolonged.