The gallbladder is an important organ that is directly involved in the digestion process. If the functionality of an organ is disrupted, the entire process of food digestion is disrupted.
This ultimately leads to the development of characteristic symptoms and is a very dangerous condition that threatens human health. That is why, when the first signs of gallbladder dyscholia are detected, it is necessary to consult a doctor as soon as possible and begin treatment.
At the same time, it is important to eliminate the very cause of the development of the disease, and only after that begin symptomatic treatment, only in this case the therapy will be complete and the result will be positive.
There can be many reasons for the development of pathology, but most often the provoking factors are poor nutrition, excess weight, and impaired metabolic processes in the body. About 20-30% of people who have problems with the gallbladder suffer from dyscholia.
Principles of treatment
Dycholia itself does not require treatment. Problems arise when pathology leads to various diseases. In this case, treatment will be symptomatic, and the drugs and methods chosen depend on the disease.
Diet food
Food should not overly burden the gallbladder and liver. Therefore, patients with dyscholia are recommended diet No. 5 with some indulgences. With dyscholia, it is not necessary to completely give up foods prohibited in the diet, but it is worth limiting their use. Such foods include:
- fatty and fried foods;
- strong coffee, cocoa, tea;
- sweets, baked goods;
- heavy food - mushrooms, legumes.
Eat 4-5 times a day, in small portions. Dishes from the prohibited list cannot be included in the diet more than 2 times a week; it is not advisable to eat them at night.
Drugs
The list of medications for dyscholia depends on the severity of the provoked disease and its symptoms. May be prescribed:
- Painkillers - No-shpa, Drotaverine, Papaverine for inflammation of the walls of the gallbladder.
- Choleretic drugs – Ursodeoxycholic acid, Betaine, Phenipentol.
- Antibiotics for bacterial infections are selected depending on its type.
- Hepatoprotectors to improve liver function - Essentiale, Heptral, Phosphogliv.
Operation
For dyscholia, surgery is not required. It is carried out when emergency conditions arise, for example, blocking of the bile duct with a stone. In all other cases, doctors prefer conservative treatment, since it is impossible to surgically remove the suspension from the bile.
Other methods
With dyscholia and the pathologies it leads to, it is important to change your lifestyle. Necessarily:
- Avoid nervous situations, especially before meals. Psycho-emotional arousal disrupts the production of bile.
- Quit smoking, alcohol, drugs. They injure tissues and organs, which leads to increased negative effects of dyscholia.
- Prevent stagnation in the body. A sedentary lifestyle will not bring benefits, so it is worth including sports in your daily routine. This could be walking, running, swimming, aerobics, etc. It is best to consult with your doctor before choosing a sport. He will give recommendations taking into account all existing diseases and contraindications.
Diagnosis and treatment
A preliminary diagnosis can be made based on clinical symptoms. An ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity, gastroduodenoscopy, and a biochemical blood test will help confirm the doctor’s concerns. The specialist will certainly examine the patient, establish his neurological status, collect information about the diseases of his close relatives, and also learn about the individual characteristics of the body.
Therapy for dyscholia should be comprehensive and includes a correct daily routine, dietary nutrition, physical activity and medication. The following drugs will help relieve pain, eliminate the cause of the disease, improve the functioning of the digestive tract and cleanse the body:
- enzymatic agents;
- antispasmodics;
- analgesics;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- antibiotics for bacterial infections.
Preventing dyscholia is much easier than treating it. Preventive measures include the following:
- avoid stressful situations;
- periodic examination;
- a balanced diet, including the consumption of vegetables and fruits;
- playing sports;
- giving up bad habits: drugs, smoking and alcohol abuse.
Stressful situations and emotional overload can cause an exacerbation of the disease, so try not to be nervous
Treatment of dyscholia
Pancreatic cancer: 10 early symptoms that cannot be ignored
Effective treatment of dyscholia in children and adults is primarily aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease.
In general, pathology therapy includes the following measures:
- Dieting. For patients with dyscholia, table No. 5 would be suitable.
- Treatment of bile stagnation and other pathologies of the biliary tract.
- Normalize your psycho-emotional state, avoid stress.
Diet
The key importance in the treatment of biliary dyscholia is compliance with the diet. Proper nutrition will normalize bile production and reduce the symptoms of pathology.
If the normal functioning of the gallbladder is disrupted, it is recommended to completely eliminate fatty and fried foods. Food should be boiled, baked or steamed. Vegetable fats should be used in cooking: sunflower and olive oil. Fatty meats and fish should be excluded.
You need to eat in small portions 5-6 times a day. It is better to eat strictly at the same time.
Traditional treatment
Gallbladder diseases can be treated using folk remedies, especially when it comes to treating children. This treatment has a gentle effect on the child’s body, does not cause side effects and does not have a toxic effect. Choleretic and anti-inflammatory drugs are used.
- Bran. Wheat bran will help reduce the concentration of cholesterol in bile. Bran is added to food by first pouring boiling water and draining it. Begin treatment with half a teaspoon three times a day. After two weeks, the dosage is increased to one teaspoon three times a day and taken for another two weeks.
- Strawberries. Has a mild choleretic effect. For therapy, tea made from wild strawberry leaves is used. Fresh or dried leaves are brewed in boiling water (1 tablespoon per 200 ml) and drunk instead of regular tea. The fruits of this plant also have a healing effect. 1 tbsp. l. steam in 400 ml of boiling water, infuse, filter and drink 80 ml (children) or 150 ml (adults) before each meal.
- Cabbage. Drink sauerkraut juice, 1 tbsp. l. three times a day half an hour before meals. This treatment is not used if dyscholia is associated with gastritis or peptic ulcer.
- Rose hip. A decoction of the berries of this plant strengthens the human body. Steam 2 tbsp in 400 ml of boiling water. l. berries, leave in a thermos for 2 hours, then filter. Drink the entire broth in small portions throughout the day.
- Sandy immortelle. A decoction of the inflorescences of this plant normalizes the composition of bile and has a choleretic effect. To prepare the decoction, steam 3 tbsp in 600 ml of boiling water. l. dried immortelle flowers, leave for half an hour and filter. Take 200 ml of infusion before meals three times a day.
- Angelica officinalis. A tincture of the roots of this plant is prepared. The roots are thoroughly washed, crushed and filled with alcohol in a ratio of 1:10 (10 g of roots per 100 ml of alcohol). Infuse in a dark, warm place for two weeks, shake regularly, then filter. Drink 30 drops of tincture, dissolved in a small volume of water, 2-3 times a day before meals. Treatment lasts a month.
- Corn. In the treatment of dyscholia, corn silk is used, which has a choleretic effect and normalizes the composition of bile. The stigmas are crushed and a decoction is prepared. Steam 1 tbsp in 200 ml of boiling water. l. stigmas, boil over low heat for 5 minutes, then cool and filter. Drink 100 ml of decoction three times a day before meals.
- Mint. Mint decoction has an anti-inflammatory effect, relieves pain and improves blood circulation. Steam 2 tbsp in 400 ml of boiling water. l. mint, leave for 2 hours, then filter. The entire infusion is drunk in small portions throughout the day.
- Beet. 2 peeled beets are poured into 3 liters of water and cooked in a large saucepan over low heat for 5-6 hours. The resulting syrup is poured into a separate container, the beets themselves are crushed and the juice is squeezed out of the pulp, which is mixed with the syrup. Take 1/3 cup of this drug three times a day half an hour before meals. Treatment lasts two weeks. This remedy has an anti-inflammatory effect and normalizes bile secretion.
Diet
Compliance with dietary nutrition is key in the treatment of dyscholia. It will help relieve the symptoms of the disease and normalize the production of bile secretions. All dishes must be cooked in the oven or steamed. Frying food is strictly prohibited! Stewed and boiled dishes are also recommended. Patients should eat fractionally, in small portions. The last meal should be no later than three hours before bedtime.
The basis of the diet of patients with dyscholia is porridge. You can add steamed wheat bran to them; they will help lower cholesterol and speed up the healing process. The following products are strictly prohibited for consumption:
- rich broths;
- alcoholic drinks and sodas;
- spices, herbs;
- smoked meats, canned food, marinades.
Important! Berry and fruit compotes, as well as rosehip decoction, will help normalize the composition of bile.
An active lifestyle plays a big role in preventing dyscholia
How to improve the contents of the gallbladder
Pancreatitis: symptoms of inflammation of the pancreas and treatment measures
To adjust the composition of bile in children, doctors prescribe choleretic drugs:
- choleretics with natural bile – Allochol;
- choleretics with lektravas - Holosas, Flamin, Holemaks, Chofitol, Febichol;
- synthesized choleretics – Osalmid, Nikodin, Oksafenamide;
- cholespasmolytics - Spasmonet, No-shpa, Atropine, Drotaverine, Spazoverine, Metacin, Ple-Spa, Platyfillin;
- cholekinetics – Magnesium sulfate, Cormagnesin, Valerian, Magnesia, Valerianahel.
Their dosage is calculated based on the body weight of the small patient. Drugs for dissolving stones are given to children for a long time - up to 8 months.
Among the folk remedies, the condition of the bile ducts quickly improves with tea made from wild strawberry stems. The twigs are collected during the flowering period of the crop. The raw material is brewed fresh or dry and given to children as regular tea.
To enhance bile secretion, the drink is prepared from dried strawberries. 1 tbsp. l. berries are thrown into a thermos and poured 400 ml of boiling water. After some time, the product is filtered and given to children before meals, 80 ml.
Dyscholia will disappear in a short time if you give your child sauerkraut juice. Let the baby drink it 3 times. per day in 30 minutes. before meals 1 tbsp. l. But if he suffers from arrhythmia, gastritis, kidney disease or stomach ulcer, such juice therapy is not carried out.
During the treatment of the gallbladder, give children alkaline mineral waters.
Natural hydrocholeretics are Essentuki No. 4 and No. 17, Borjomi, Slavyanovskie Vody. With bile dyscholia, it is important to strengthen the baby’s immunity. Steam rose hips by brewing them in a thermos
Proportion – 2 tbsp. l. fruits for 2 cups of boiling water. To detect gallstones in a timely manner, take your baby for an ultrasound examination at least once a year. Dycholia is a serious disorder. Often it begins the development of pathologies that distort the activity of the entire digestive system.
For any changes in the functioning of the biliary system organs, a visit to a specialist is necessary. If the correct therapeutic effect is absent, this is fraught with the appearance of not only unpleasant symptoms, but also the development of various dangerous consequences and complications.
Gallbladder dyscholia is a pathological change in the composition of bile. This problem can be triggered by various diseases and poor lifestyle choices; in particular, with an unbalanced diet and poor nutrition, the first symptoms of dyscholia appear.
Symptoms of the disease
Pancreatic lipomatosis
Any disturbances in the functioning of the liver and gallstones are manifested by dull pain on the right side of the abdomen, under the ribs. If stones have already formed, the pain may be severe. Symptoms depend on which components of the bile are in excess or insufficient quantities. Their intensity may vary, but when pathology occurs, unpleasant sensations visit the sick person regularly.
In addition to pain, the following may periodically appear:
- heaviness in the abdomen, a feeling of fullness (especially with stagnation of bile);
- bitter taste in the mouth due to the reflux of bile into the stomach;
- nausea;
- bowel disorders - constipation, diarrhea;
- vomiting (rarely) streaked with bile;
- general weakness, lethargy due to poor digestion of food and the presence of an inflammatory process.
After eating high-calorie, fried and fatty foods, symptoms usually worsen.
For a more accurate diagnosis, an ultrasound examination of the gallbladder is performed, and, if necessary, other abdominal organs. An analysis of the composition of the fluid taken during probing of the bladder is performed, as well as a blood and urine test. An increase in cholesterol and alkaline phosphatase is often found in the blood, and bilirubin in the urine. To identify parasites, the patient's stool is examined.
Often dyscholia is detected already at the stage of stone formation
It is very important to pay attention to pain and other symptoms in time in order to begin therapeutic treatment. This will help avoid the formation of large stones, which may lead to the need to remove the gallstone.
Symptoms
Thickening of bile may not manifest itself in any way. Even as the pathological process progresses, some complaints never appear. This only happens if the flow of bile is not impaired. A pronounced clinical picture appears late, which indicates the development of cholelithiasis.
But a completely different situation occurs when there is a violation of the outflow of bile secretions. Let us highlight the main symptoms of dyscholia:
- pain in the right hypochondrium, which intensifies after eating. It can be sharp and dull. The attack subsides under the influence of thermal procedures. Alcohol, as well as fatty, fried and spicy foods can cause a severe outbreak of pain;
- reflux of bile into the stomach from the duodenum manifests itself in the form of bitterness in the mouth, heaviness in the stomach, nausea, vomiting and belching;
- increased formation, diarrhea or diarrhea. Changes in the structure of feces. All this indicates a violation of the intestinal digestion of food;
- fever;
- loose, foul-smelling and green stools;
- the skin becomes jaundiced;
- weakness, loss of appetite, dizziness.
Important! Painkillers only temporarily relieve an attack. After a few hours the pain will return again.
Functions of bile and its composition
The main function of bile is to participate in the digestion process. It is carried out in the following directions:
- breakdown of fats, absorption of cholesterol in the intestines;
- activation of enzymes for subsequent absorption of proteins;
- stimulation of pancreatic enzymes.
Its other functions are no less important:
- regulation of motor activity of the small intestine;
- stimulation of mucus formation in the intestines;
- reducing the aggressive action of gastric juice.
The composition of bile is represented by the following components:
- bile acids (cholic, deoxycholic, chenodeoxycholic);
- bile salts (glycocholic and taurocholic compounds);
- bile pigments (bilirubin, biliverdin);
- cholesterol;
- water.
Most often, cholesterol concentration increases. Normally, it should be half as much as bile acids. If cholesterol levels increase, it begins to accumulate in the gallbladder and settle on its walls. As a result, the risk of developing gallstone disease increases.
The reasons for this violation come down to:
- poor nutrition;
- being overweight;
- endocrine diseases, including diabetes mellitus;
- hereditary predisposition.
JP can also be manifested by an increase in the concentration of the bile pigment bilirubin. In this case, dietary habits are not particularly important, since this phenomenon is caused by hemolytic anemia or bacterial infection.
Pathogenic microorganisms (staphylococcus and Escherichia coli) multiply quickly and produce lithocholic acid during their vital activity, which leads to dyscholia. They can enter the body in different ways:
- from the external environment;
- through blood from any internal source of inflammation (appendicitis, periodontal disease, tonsillitis);
- through lymphatic vessels.
Diseases of the stomach and intestines can provoke dyscholia. A sedentary lifestyle also plays a negative role, as it negatively affects the neuromuscular apparatus of the gallbladder. As a result, pathologies such as hypotension (low tone) and atony of the muscles of the organ (lack of tone) develop.
All diseases of the gallbladder and its ducts are interconnected. Due to metabolic disorders, neuroses, and parasitic infestations, dyskinesia of the gallbladder develops with disruption of its peristalsis, which leads to dyscholia, which, in turn, leads to the development of cholelithiasis.
Characteristics of the disease
Dyscholia is a fairly common disease
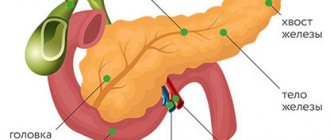
Gallbladder dyscholia is a disease in which a change in the composition of bile, its physical and chemical characteristics occurs.
Bile, necessary for digesting food, has a rather complex composition, which includes various types of bile acids, bilirubin, cholesterol and other components.
With dyscholia, the cholesterol content in the bile increases, which causes the formation of solid compounds in the cavity of the gallbladder, which settle on the walls of the organ. And this, in turn, contributes to the development of gallstone disease and the appearance of corresponding symptoms.
Historical reference
This is a relatively young disease, the first information about which dates back to the middle of the last century. This is due to the fact that recently the quality of nutrition has changed, the pace of life has changed, people who are constantly in a hurry are more likely to snack on the run, and more and more people are overweight. All of these reasons lead to increased cholesterol, and as a consequence, to the development of dyscholia.
Prevalence and significance
About 20-30% of the total number of calls for gallbladder diseases are due to gallbladder dyscholia. In this case, the age of the patient is not particularly important, however, it has been established that in children, due to the imperfect development of the organs of the digestive system, this disease is diagnosed somewhat more often.
Risk factors
The provoking factors for the development of dyscholia are considered to be:
- unhealthy diet (in particular, eating large amounts of fatty foods and processed foods);
- bad habits;
- excess body weight (we are talking about a pathology such as obesity);
- childhood;
- diseases associated with metabolic disorders (for example, diabetes).
In addition, people who have a family history (that is, if the person’s immediate relatives have also encountered this problem) are at risk.
Complications of cholecystitis
With a long course of the disease, the inflammatory process spreads to neighboring organs of the abdominal cavity. As a result, complicated cholecystitis occurs (pneumonia, pleurisy, pancreatitis develops). With the latter, a peri-vesical abscess is formed. Cholangitis also often occurs against the background of cholecystitis. If the pathology is diagnosed too late, gall bladder empyema may occur.
There is a risk of bile leaking from the diseased organ into the abdominal cavity. This process is caused by the melting of purulent tissue or concrete perforation of the bladder wall. When the secretion leaks, peritonitis develops, which can be fatal. When pathogenic microorganisms enter the bloodstream, sepsis begins.
Functions of bile and its composition
The causes of gallbladder dyscholia are also associated with the fact that certain changes occur in the biliary organs. The reasons for the stagnant process in the gallbladder lie in the following exogenous and endogenous factors:
- consumption of harmful products, as a result of which biliary disease develops;
- constant sedentary work, lack of load;
- frequent overeating;
- chronic inflammatory processes of the digestive system;
- infectious and inflammatory processes in the liver.
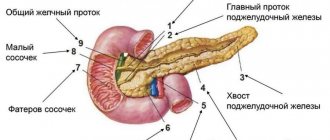
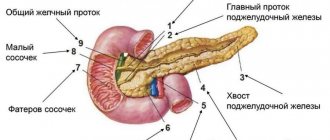
Bile is produced in the liver, from where it enters the gallbladder. It consists of bile acid, which is its basis, proteins, amino acids, vitamins, sodium and potassium ions, phospholipids.
The role of bile is to envelop and absorb fats in the digestive system. Thanks to it, chemical reactions in the digestive organs are accelerated, vitamins and cholesterol are absorbed. It participates in metabolic processes and contributes to the creation of synovial fluid located in the joints.
Violation of its chemical composition leads to the development of diseases, including dyscholia. This happens for many reasons:
- dysfunction of the endocrine system due to age-related disorders;
- weight gain;
- hereditary hypercholesterolemia;
- hemolytic anemia;
- the development of pathogenic microorganisms in bile and, as a consequence, the formation of lithocholic acid, which causes the disease;
- helminthic infestation.
Provoking factors
Changes in the composition of bile can occur under the influence of a large number of reasons, including:
- lymphogenous infection from chronic foci of infection;
- overeating, radical diets, too long breaks between meals;
- diseases of the digestive organs;
- metabolic disorders;
- alcoholism;
- passive lifestyle;
- infection of the gallbladder;
- stress, depression;
- mental disorders;
- overweight;
- diseases of the central nervous system;
- genetic factor;
- endocrine disorders;
- parasitic diseases;
- hypotension of the gallbladder.
Poor nutrition can lead to dyscholia
What is gallbladder dyscholia?
› Gallbladder
The process of dyscholia develops at any age, even in childhood
It is important to identify this pathological condition in time. To do this, you need to know how gallbladder dyscholia appears, what it is and how to deal with this problem.
This information will make it possible in the future to prevent serious and irreversible diseases that may result in surgical intervention.
Functions of bile and its composition
The main function of bile is to participate in the digestion process. It is carried out in the following directions:
- breakdown of fats, absorption of cholesterol in the intestines;
- activation of enzymes for subsequent absorption of proteins;
- stimulation of pancreatic enzymes.
Its other functions are no less important:
- regulation of motor activity of the small intestine;
- stimulation of mucus formation in the intestines;
- reducing the aggressive action of gastric juice.
The composition of bile is represented by the following components:
- bile acids (cholic, deoxycholic, chenodeoxycholic);
- bile salts (glycocholic and taurocholic compounds);
- bile pigments (bilirubin, biliverdin);
- cholesterol;
- water.
Physiology of the digestive process
A change in the composition of bile leads to a pathological condition. First of all, the ratio of bile acids and cholesterol is disrupted (in favor of the latter), the content of pigments increases, and the amount of water decreases. Due to this, the bile thickens - this process is called dyscholia. The thicker the bile, the higher the risk of stone formation.
Dycholia is provoked by the following factors:
- an infectious process in the gallbladder (its source can be any source of infectious inflammation in the body);
- excess nutrition (abuse of fatty, fried foods, overeating);
- alcohol;
- lack of physical activity;
- liver diseases (fatty hepatosis, hepatitis, cirrhosis);
- liver parasites (giardiasis, opisthorchiasis);
- disruption of the activity of internal secretion organs (thyroid gland, pancreas);
- hereditary causes.
Consequences of impaired bile formation
Treatment
If gallbladder dyscholia is diagnosed, treatment includes:
- adherence to a diet (exclude the consumption of fatty, fried foods, overeating);
- physical activity mode to prevent stagnant processes;
- psycho-emotional peace;
- drinking alkaline mineral waters (Essentuki No. 4, No. 17, Naftusya);
- use of medications.
Drug treatment is aimed at eliminating unpleasant and painful symptoms and normalizing the composition of bile. It is recommended to prescribe drugs from the following drug groups:
- stimulants of bile formation (Allohol, Cholenzym, Holosas, Flamin, Hofitol);
- antispasmodics (Papaverine, Drotaverine, Platiphylline).
In the presence of dyscholia, eating wheat bran has a positive effect. One teaspoon of bran should be poured with boiling water, left for 10 minutes, drained and consumed three times a day before meals. The course of treatment is one month; after a ten-day break, treatment must be repeated.
Drinking rosehip infusion, tea from berries and strawberry leaves also helps normalize the composition of bile.
Prognosis and possible complications
With timely diagnosis and correct understanding of what gallbladder dyscholia is, the prognosis is favorable. If all recommendations and treatment prescriptions are followed, the composition of bile usually normalizes after a few months.
However, if the diet is violated and treatment is not carried out, there is a risk of gallstone formation. The development of this process is fraught with exacerbation of pain, blockage of the bile duct with a stone and surgical intervention.
For more information about what symptoms are the result of gallbladder problems, watch the following video:
Conclusion
Gallbladder dyscholia can be successfully corrected with diet, an active lifestyle and medication. It is very important to solve this problem in a timely manner, since advanced cases can lead to stone formation and surgical intervention.
What is gallbladder dyscholia? Link to main publication
Causes of the disease
The main reason for the development of pathology is an infection in the organ that occurs against the background of stagnation of bile. Pathogenic bacteria (streptococci, E. coli, staphylococci), viruses, parasites, protozoa penetrate into the gallbladder from the intestines, as well as through lymph or blood from foci of infection in the body (purulent otitis media, periodontal disease).
Problems with the outflow of bile from gall bladder tissues arise against the background of:
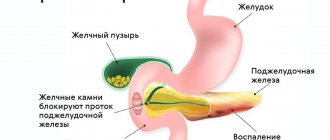
- gallstone disease. Pathology occurs in 80–90% of diagnosed cases. Formations in the gallbladder do not allow the secretion to drain normally, because they injure the mucous membrane and block the exit. Against this background, an adhesive process occurs, and the inflammation does not subside;
- congenital anomalies. If the organ is constricted and scarred from birth, it has narrowed ducts due to abnormal intrauterine development of the fetus, the risk of the disease increases. Pathological conditions lead to impaired bile outflow and stagnation;
- biliary dyskinesia. Pathology occurs due to a functional disorder of organ motility. In addition, the tone of the biliary system leads to it. As a result, not all of the gallbladder is released; part of the secretion remains. Against this background, inflammatory processes occur, stones and deposits form on the walls. Cholestasis may occur;
- other disorders of the system of bile excretion from the body. Neoplasms can also have a negative impact on the functioning of the gallbladder (polyps, cysts, benign and malignant tumors). Bile stasis worsens the condition of the biliary system. This happens due to compression of the ducts, deformation of the bladder due to Mirizzi syndrome, dysfunction of the valve system of the biliary tract.
The likelihood of the disease increases in certain conditions that affect secretion output and a change in composition from normal to pathological:
- Dyscholia refers to similar non-functional disorders (when the consistency of bile is not normal).
- Hormonal changes in the body during menopause or pregnancy also provoke the development of inflammation in the gallbladder.
- The enzymatic type of pathology develops with the constant flow of pancreatic enzymes into the cavity of the bladder. Gastroenterologists call this condition pancreatobiliary reflux.
- Poor diet, drinking alcohol and smoking are other common causes of the disease.
Forecast
With proper and timely treatment, the process of production and excretion of bile, as well as its composition, is normalized within several months. If the patient has not received the necessary medical care, dyscholia, as a rule, leads to the development of cholelithiasis, which provokes blockage of the bile ducts and stagnation of bile in the organ cavity. In this case, the patient will feel constant sharp pain. Without surgical intervention, this pathology cannot be eliminated.
Basic rules of diet for ADHD
The purpose of therapeutic nutrition for biliary dyskinesia is to ensure gentle functioning of the liver, improve the outflow of bile, normalize the functioning of the biliary tract, liver, and other digestive organs.
It is important that the diet is complete: it must contain a physiological amount of proteins and carbohydrates, but, at the same time, it must contain some limitation of fats, especially refractory ones. According to Pevzner’s classification, the diet for biliary dyskinesia corresponds to treatment table No. 5
According to order No. 330 of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, for this disease, it is recommended to adhere to the basic diet (OVD), which includes treatment table No. 5
According to Pevzner’s classification, the diet for biliary dyskinesia corresponds to treatment table No. 5. According to order No. 330 of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, for this disease, it is recommended to adhere to the basic diet (BD), which includes treatment table No. 5.
The daily content of nutrients in medical nutrition is as follows:
- proteins – 85-90g, of which up to 45g of animal proteins;
- fats – 70-80g, of which 25-30g vegetable oils;
- carbohydrates - 300-330g, simple sugars - up to 30-40g.
The daily calorie intake is 2170-2400 kilocalories.
Basic principles of the diet
diet; In therapeutic nutrition for diseases of the biliary tract, fragmentation is implied: food intake should be frequent and in small portions, up to 5-6 times a day
It is important to avoid overeating and eat at the same time; this tunes the gallbladder to produce bile, and the bile ducts release it into the intestines at certain hours. This helps to normalize the flow of bile, better digestion and absorption of food in the intestines
Frequent eating in small portions does not allow bile to stagnate in the bladder, does not allow the bile ducts and bladder to contract excessively, which usually provokes pain. culinary processing; All dishes for patients with biliary dyskinesia should be prepared boiled or baked. It is allowed (rarely) to stew food. Frying is prohibited, since frying partially destroys polyunsaturated fatty acids and forms toxic substances (aldehydes, ketones), which increases the load on the gallbladder and bile ducts, irritates the liver parenchyma and gastric mucosa. Only meat with a high content of connective tissue (stringy varieties) is rubbed. temperature regime; There are no strict restrictions on the diet for bile duct disease. Dishes are served warm (15-60 degrees Celsius), only cold foods that cause spasms of the biliary tract are excluded, violating the temperature principle of the gentle functioning of the digestive system. salt and liquid; It is necessary to slightly reduce the consumption of table salt (to 6-8g): an excess of sodium chloride contributes to fluid retention in the body, which causes thickening of mucus and complicates its evacuation from the gallbladder. The amount of fluid consumed should reach 2-2.5 liters per day. This volume helps to liquefy bile, prevent stone formation in the gallbladder, and remove cholesterol and toxins from the body. alcohol; You should avoid or at least limit your intake of alcoholic beverages. Strong alcoholic drinks cause spasm of smooth muscle muscles and, accordingly, the bile ducts, which leads to impaired outflow and stagnation of bile. In addition, the breakdown of ethanol occurs in the liver, and an excess amount of this substance increases the load on it and provokes the development of liver diseases. alimentary fiber; Fiber, which contains dietary fiber in large quantities, must be included in medical nutrition for diseases of the biliary tract. Firstly, it normalizes the secretion of bile, reduces the level of cholesterol in it and removes “bad” cholesterol from the body. Secondly, dietary fiber softens stool and activates intestinal motility, which prevents constipation. And thirdly, fiber alkalizes bile, which prevents the formation of gallstones.