Constipation
- a digestive disorder characterized by the absence of stool for more than two days or incomplete bowel movement.
According to medical statistics, today it is one of the most common phenomena, which is considered an independent disease by the World Health Organization. This fact may seem interesting, since a number of gastroenterologists consider intestinal constipation
a symptom of certain pathological conditions.
Be that as it may, constipation requires timely seeking professional medical help, as it can cause the development of serious proctological diseases. In itself, it affects the patient’s quality of life, significantly reducing it. At the same time, it is important for patients to know that the normal frequency of bowel movements varies from three times within 24 hours to three times a week (and not every day, as many believe). This must be taken into account when deciding to contact a specialist.
What is constipation?
Constipation (constipation) is a symptom that has different meanings for different people.
Most often it refers to irregular bowel movements, but may also describe a decrease in stool size and weight, the need to push to pass a bowel movement, a feeling of incomplete bowel movement, or the need for enemas, rectal suppositories, or laxatives to maintain normal bowel movements. For most people, the normal frequency of bowel movements is three times a day to three times a week. Some people may not have a bowel movement for a week or more without experiencing any discomfort. The frequency of bowel movements directly depends on diet. The average person's daily diet contains 12-15 g of fiber. And for normal functioning of the intestines, you should consume at least 25-30 g of fiber and 1.5-2 liters of liquid per day. Adequate physical activity is also necessary to maintain normal bowel function.
To ensure you get enough fiber from your diet, you should include fiber-rich foods in your daily diet, such as bran, cracked grains, whole grain breads, and certain fruits and vegetables.
About 80% of people suffer from constipation at some point in their lives, and such short periods of constipation are quite normal. The diagnosis of constipation is made when the frequency of bowel movements is less than three per week. The common belief that everyone should have a bowel movement every day has led to the overuse and dependence of many people on laxatives.
Constipation - from mild distress to alarm bells
Class Clinic
What causes constipation? They may be a sign of illness or a dangerous condition of the gastrointestinal tract. It can also be a symptom of an eating disorder or a manifestation of side effects from taking medications. It is important to determine what problem is associated with constipation. Robiya Damirovna Arabova, a practicing gastroenterologist at the Kaliningrad medical center Class Clinic, spoke about its most common causes and what needs to be done.
How often do you have to deal with chronic constipation, and for what reasons does it occur?
Patients with chronic constipation occur in almost all age groups. It is natural that the frequency of constipation increases with age. This is due to a sedentary lifestyle, the presence of concomitant diseases, especially in old age: for example, diabetes, hypothyroidism, heart failure, etc. Sometimes constipation occurs due to taking various medications that slow down intestinal motility.
However, it cannot be said that constipation is not typical for young people. They also occur quite often in young people, and, as a rule, this is a manifestation of irritable bowel syndrome.
What is irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)?
With this disease, there are no organic lesions of the intestinal mucosa (inflammatory, erosive-ulcerative, tumor), but functional disorders occur, manifested by abdominal pain, changes in the frequency and shape of stool, and bloating. In patients with IBS, there is an increase in the level of pain sensitivity to stretching and impaired motor activity (motility) of the large intestine. As a result, when intracavitary pressure increases in the intestines, pain occurs, and intestinal motility disorders lead to stool disorders (constipation or diarrhea).
Basically, irritable bowel syndrome occurs under the influence of psychogenic factors: severe stress, prolonged psycho-emotional stress, anxiety and depressive disorders. People can remain in this condition for years without significant improvement, which seriously affects their quality of life.
Irritable bowel syndrome is a diagnosis of exclusion. That is, it is established only after excluding other probable causes of intestinal pathology, including infections, parasitic infestations, inflammatory diseases, and tumors.
What complaints do patients most often present with? Is there a specific criterion that can be used to diagnose constipation?
Each patient understands something different by the term “constipation,” but in fact it is a complex of symptoms associated with impaired bowel movement.
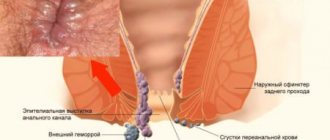
We diagnose constipation when the patient has bowel movements with a feeling of complete bowel movement less than 3 times a week. It also makes sense to talk about constipation if there is a feeling of incomplete emptying, there is difficulty in defecation, scanty fecal discharge or the discharge of hard, fragmented feces.
Another characteristic sign of constipation is excessive and ineffective straining, discomfort during bowel movements, which force the patient to spend more than 3-5 minutes in the toilet without a satisfactory result.
What accompanying symptoms of constipation are the most alarming?
Regular, intense, progressive pain and other symptoms that bother you at night should seriously alert you. Signs of serious problems are the release of blood, mucus, pus with feces, an increase in body temperature, a decrease in the level of hemoglobin and red blood cells, as well as an increase in ESR in a general blood test.
All these signs, combined with constipation, may indicate the possibility of severe cancer and other diseases, for example, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease and other life-threatening conditions.
In what cases with constipation is it necessary to urgently consult a specialist?
You should immediately consult a doctor if constipation is accompanied by alarming signs - intense pain, blood in the stool, nausea, vomiting, increased body temperature.
Unmotivated, sudden weight loss, especially after the age of 50, can be a sign of cancer and is also a reason for an urgent visit to the doctor.
What are the risks of self-medicating constipation with laxatives?
Regular and improper use of laxatives, especially irritating ones, causes intestinal dysfunction, which can be quite difficult to cope with. I see patients under the age of 25 who have not had a single independent bowel movement without taking laxatives for a year.
Currently, a special term has been introduced - “laxative disease”. This is a condition that occurs due to the abuse of irritant laxatives. It manifests itself as chronic diarrhea, and as a result - metabolic and absorption disorders in the intestines. Another of its manifestations is “lazy gut” syndrome, when the intestines are not able to function normally without taking laxatives.
We treat laxative disease, but it is much easier to prevent it by using laxatives strictly as prescribed by the doctor and following his recommendations. From the illiterate use of these medications, constipation develops into more serious problems, and the patient ends up in a vicious circle.
Make an appointment with Robiya Damirovna Arabova on the website or by phone.
What causes constipation?
There are several reasons that explain the development of constipation, including insufficient fiber and fluid intake, a sedentary lifestyle and changes in the usual environment. Travel, pregnancy, or dietary changes can cause constipation. In some people, constipation may occur following repeated volitional refusals to defecate when the urge to defecate appears.
More serious causes of constipation may be tumors or narrowing of the intestinal lumen. Therefore, if you have persistent constipation that cannot be corrected on your own, you should consult a coloproctologist. In rare cases, severe diseases such as scleroderma, lupus, disorders of the nervous and endocrine systems: thyroid diseases, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, stroke, spinal cord injuries can lead to the development of constipation.
What are the dangers of constipation in a child?
Normally, a healthy child’s stool leaving the colon should contain about 70% water, the remaining 30% being “waste” material. If the normal movement of intestinal contents through the colon is disrupted for some reason, additional absorption of water from it occurs. In addition, along with water, the body begins to “absorb” those “processed products” that should have been removed from its borders a long time ago.
Doctor, pediatric surgeon at the National Children's Specialized Hospital "OKHMATDET"
In a child, visually (what parents can notice) this is manifested by a predisposition to frequent viral infections (decreased general immune status), periodic nausea, vomiting, acetonemic syndrome, headaches, periodic (for no apparent reason) increase in temperature, rashes in the buttocks , thighs on the temporal areas and forehead skin.
Chronic exposure to such intoxication in younger children leads to disruption and delay of psychomotor development: impaired motor skills (spectrum of manipulative activities); impairment of static development (ability to hold head, sit, walk); disturbances in sensory reactions (reactions to light, sound and touch); language development (expressive speech and language understanding), that is, to generalize, to a violation of emotional and social development.
In older children - drowsiness, fatigue, loss of attention, delayed mental and physical development (for example, falling behind in school). Also, stool retention leads to the formation of hard feces and an increase in the diameter of the stool, which in turn leads to painful bowel movements.
The information is stored in his memory that every trip to the toilet “mostly” causes pain and discomfort, and therefore the child begins to deliberately restrain the natural act of defecation.
Consequently, chronic stool retention in a child leads to expansion and overstretching of the large intestine in the lower sections, which in turn leads to loss of muscle tone of the intestine (the strength of the peristaltic wave depends on it) and already triggers a cascade of irreversible changes, which are very difficult to influence with drug treatment and often you have to turn to surgeons for help.
What specialists should you contact if your child has constipation?
In this case, it is necessary to clearly understand that constipation, as I already mentioned, is just a symptom of the disease, but this one must be determined by a specialist. Based on the above classification, the child must be shown to a pediatrician, gastroenterologist and surgeon.
Can medications cause constipation?
Yes, many medications, including painkillers, antidepressants, tranquilizers and other psychiatric medications, blood pressure medications, diuretics, iron supplements, calcium supplements, and antacids containing aluminum, can cause or worsen constipation.
Moreover, some people who are not constipated in normal life may become dependent on laxatives, which they take to achieve daily bowel movements. For many of them, constant use of laxatives causes significant harm.
How can you determine the cause of constipation?
Constipation can be caused by various reasons, and it is very important to identify them in order to prescribe the correct and most effective treatment. The treating doctor will definitely prescribe special studies to exclude anatomical causes of constipation, such as tumors and areas of narrowing of the intestinal lumen.
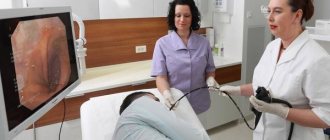
Digital examination of the rectum is often used as the first method of examination. This method is simple and can answer many questions about the causes of constipation. Examination of the intestines using a flexible, lighted instrument or a barium X-ray can help clarify the cause of constipation and rule out serious conditions such as polyps, tumors, or diverticular disease.
Other research methods help determine the functional state of the intestine. For example, to conduct a marker study, the patient swallows capsules containing certain biological markers, which are visible in an X-ray examination taken several days later. The results of the study show the presence or absence of dysfunction of the intestinal muscular system. Other studies are aimed at assessing the condition of the anal canal and rectum. These include a study using a small plastic balloon of the reflexes of the anal sphincter muscles, which controls the process of defecation, as well as an x-ray study during the process of defecation.
In most cases, neither anatomical nor functional disorders of the intestine can be detected and the causes of constipation are considered nonspecific.
Conducting an adequate study is a very important point, especially when the cause of constipation is: a decrease in the rate of movement of food through the intestines, difficulties in evacuating feces, or other conditions.
Diagnosis of constipation
Treatment of constipation
selected individually exclusively after diagnostic studies. They are prescribed by a gastroenterologist to find out the exact cause of the problem. First of all, he will listen to the patient’s complaints, collect anamnesis and determine whether there is a connection between the patient’s usual lifestyle and constipation.
Further actions include an examination: during the process, palpation will be carried out and its swelling, if any, will be determined. To identify anal fissures, hemorrhoids, and intestinal polyps, a proctological examination is performed. Further tactics of diagnostic studies are determined based on the results of the above examinations and data from general tests. Instrumental studies may include the following:
- Colonoscopy - allows you to obtain data on the condition of the intestinal mucosa and take samples for histology if neoplasms are detected;
- Rectoscopy - makes it possible to examine part of the sigmoid and the entire rectum in order to exclude the presence of polyps, other tumors and inflammation;
- Anorectal manometry - allows you to determine the functionality and tone of the sphincter muscles, their contractility;
- Electrogastroenterography is aimed at determining the motor-evacuation function of the gastrointestinal tract by recording the biopotentials of its departments.
Treatment of constipation
Most patients with constipation can be successfully treated by adding fiber-rich foods such as bran, whole grains, whole grain bread, vegetables and fruits to the daily diet, as well as adequate fluids. Your doctor may also recommend lifestyle changes. Eating foods that contain dietary fiber that is indigestible in the intestines, such as bran, has a positive effect not only on constipation, but also on digestion in general. With their regular use, cholesterol levels in the blood are reduced, the risk of developing polyps and colon cancer is reduced, and the development of hemorrhoids is prevented.
To achieve the full effect, you should consume sufficient amounts of fiber over several weeks, possibly months. However, its constant use does not create dependence, unlike stimulant laxatives. Other types of laxatives, enemas and suppositories should only be used as directed by a doctor and under the supervision of a coloproctologist.
Setting a specific time each day to have a bowel movement may be helpful for some patients. In certain cases, with disturbances in the activity of the anal sphincter, “positive bio-feedback” therapy can have a good effect. Only in very rare cases is surgery required to solve constipation problems. You can discuss all possible examination and treatment options in more detail with a coloproctologist surgeon.
Classification of constipation
If the question is how to get rid of intestinal constipation
, is also relevant for you - seek professional medical help. A specialist will find out the cause of the problem and help you deal with it. He will determine the type of constipation and will be able to select adequate treatment, which will definitely give the desired result.
| Classification of constipation | |
| Type of constipation | Distinctive features |
| By the nature of development | |
| Spicy | May be caused by:
|
| Chronic | Lasts about six months and is manifested by the following symptoms:
|
| According to the mechanism of generation | |
| Nutritional | Due to diets, lack of water, too small portions of food. |
| Dyskinetic | Triggered by dysfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract or their innervation. |
| Mechanical | There are tumors or strictures in the intestine. |
| Neurogenic | Due to disorders of neuroreflex function. |
| Psychogenic | Stress, constant psycho-emotional tension. |
| Proctogenic | Pelvic floor muscle dysfunction. |
| Spastic | Triggered by spasms of intestinal smooth muscles. |
| Iatrogenic | After surgery or uncontrolled use of medications. |
| For pathologies of the anus | Cracks, hemorrhoids, inflammatory processes. |