pH-impedansometry
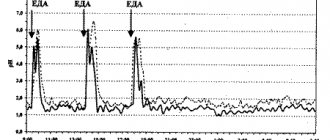
Daily pH metry is a study of the functional reactions of the upper gastrointestinal tract, in particular measuring the level of acidity directly in the esophagus, stomach or duodenum. In addition to the pH (acidity) level, impedance metry is carried out during the study, that is, measuring the level of resistance of the gastrointestinal tract environment.
Sufficient production of hydrochloric acid, as well as proper muscular function of the gastrointestinal tract, ensure a normal level of acidity. If this system fails, acid-dependent diseases develop. These include gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), the formation of ulcers, and gastritis. If symptoms of any of these pathologies appear, it is important to seek advice from a gastroenterologist, who, based on the collected history, for GERD, gastritis and other diseases, can prescribe daily pH measurements of the stomach and esophagus with monitoring of acidity (pH) for 24 hours.
Purpose of the study
Daily pH impedance monitoring of the esophagus and stomach with acidity monitoring sets the following objectives:
- Assessment of the process of daily production of gastric juice under normal operating conditions of the body, taking into account the influence of external factors (smoking, physical activity, body position, medication) on acidity;
- Diagnosis of gastroesophageal or duodenogastric reflux, the frequency and severity of their manifestation, as well as the degree of aggressiveness of the influence of the contents thrown from the duodenum and stomach onto the mucous membranes of the stomach and esophagus, respectively;
- Detection of factors that provoke the formation of reflux;
- Assessing the effectiveness of prescribed therapy;
- Assessment of the condition of the stomach and esophagus during periods of preparation for surgery and after surgical treatment;
- Designing a schedule of individual acidity rhythms and adjusting the patient’s daily diet taking into account the data obtained;
- Selection of long-acting medications to reduce and control acidity levels.
Indications for intragastric pH measurement:
- apnea;
- heartburn;
- chest pain;
- cough;
- hoarseness and hoarseness of voice;
- widespread recurrent caries;
- bad breath, subject to regular hygiene procedures.
Indications for GERD:
- nonerosive type of disease;
- extraesophageal symptoms (hoarseness of voice, sore throat, chest pain, paroxysmal shortness of breath, dental diseases, association with bronchial asthma);
- refractory form of GERD;
- functional heartburn;
- esophageal hypersensitivity;
- individual selection of antisecretory treatment;
- the period before and after surgery, for example, during gastric resection or elimination of hiatal hernia (hiatal hernia), a disease in which the lower part of the esophagus or stomach is displaced relative to the diaphragm.
Influence of pH on the properties of the medium
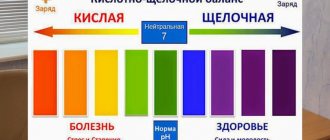
Using simple mathematical calculations, you can prove that the sum of the pH and pOH indicators for water is a constant value and equal to 14. For example, if pH = 5, then pOH = 9; for pH = -2 pOH = 16. In pure water without impurities (distilled) and in aqueous solutions formed by non-electrolytes, pH = 7, and therefore pOH = 7, i.e. the acidic and basic (alkaline) indicators balance each other , and a neutral environment is obtained.
When many chemical compounds enter water, they hydrolyze. The solute breaks down into cations and anions, which can combine with ions resulting from the dissociation of water. This results in a shift in the equilibrium of water dissociation. The pH value determines in which direction it occurred. If pH < 7, then the environment is acidic; when pH > 7, it is alkaline.
The pH indicator influences the course of chemical reactions both in production and in nature and is a universal indicator of the state of the environment. With the help of its control, all types of fuel, paints, fertilizers, personal care products and cosmetics are produced. In the food industry, the quality of production of drinks, dairy products, and cereal products is checked. All living inhabitants of natural soils and waters can live only at certain pH values, and the productivity of many plants also depends on it, so pH is monitored in soil science and agriculture, especially in hydroponics.
In this case, it is usually necessary to maintain a constant pH value over a long period of time. For this purpose, so-called buffer solutions are used. They are mixtures of a weak base and its salt or a weak acid and its salt, in which the measure of activity of hydrogen ions is constant and stable.
Contraindications to the procedure
The possibility of conducting daily pH -impedance measurements of the esophagus and stomach is determined individually at an appointment with a gastroenterologist at the UNION CLINIC in St. Petersburg. Absolute contraindications include:
- aortic aneurysm;
- severe maxillofacial injuries;
- gastric bleeding and 10 days after it stops;
- strictures (narrowings), diverticula (pathological protrusions), burns of the esophagus;
- nasopharyngeal obstruction;
- severe coronary insufficiency and hypertension;
- severe coagulopathies (blood clotting disorders).
Where to do daily pH measurements of the stomach and esophagus in St. Petersburg
You can do pH measurements (impedance measurements) of the stomach and esophagus in the comfortable conditions of the UNION CLINIC day hospital. When you first contact our specialists, you undergo a full examination. The gastroenterologist determines a number of indications and contraindications for the study and helps you prepare for it. Additional tests may be performed before prescribing daily monitoring. During the consultation, you will be able to clarify all the details of the procedure. To make an appointment for pH testing, you can use the online form on the “Make an Appointment” website.
UNION CLINIC uses a modern ambulatory pH recorder to conduct 24-hour pH impedance measurements of the esophagus and stomach. The compact, lightweight device simultaneously records acidity and impedance values, allowing you to classify reflux into acid, gas and mixed, as well as acid and non-acid. This method is especially convenient in determining the specificity of causeless symptoms that occur against the background of non-acid reflux during treatment with proton pump inhibitors (PPIs).
Human acid-base balance
The human body produces different fluids, each of which must have a certain pH value. Deviation in one direction or another can lead to the development of many serious diseases. Changes detected in time can be corrected by increasing or decreasing the acidity of consumed foods and drinking water. The mechanism for regulating the proportional ratio of acids and alkalis in cellular and intercellular fluids is called acid-base balance (equilibrium). The pH value can be used to determine the state of many human organs.
The pH of the kidneys and liver is influenced not only by metabolic processes in the body itself, but also by food and water. The body removes excess acidity from consumed foods through urine. A low urine pH level indicates that the kidneys are working at their limit. When excess acid cannot be eliminated from the body naturally, it accumulates in the subcutaneous fat layer, which has an acidic pH. This leads to excess weight. Alkaline water helps combat this phenomenon by reducing the load on the kidneys.
The environment in the stomach is sharply acidic; at the time of digestion, the pH is 1.8−3. Contrary to popular belief, the cause of such unpleasant symptoms as heartburn and stomach discomfort is low, not high, acidity of gastric juice. A normal pH level creates favorable conditions for the development of the right bacteria and triggers the digestion mechanism of food, and pathogens and helminths are broken down by digestive enzymes.
The body maintains blood pH at a constant level of 7.4-7.45. The slightest deviation from the norm can lead to serious consequences for a person. When the pH drops below 7.35, acidosis occurs . If the norm is exceeded, alkalosis occurs. These are not independent diseases; they indicate disturbances in the functioning of the lungs, kidneys, and liver. Such conditions are accompanied by very dangerous symptoms, sometimes even leading to coma. According to doctors, acidosis is easier to tolerate than alkalosis.
Blood vessels feed the salivary glands, so the pH level of the blood can be monitored by the pH of the saliva. Maintaining the acid-base balance in the circulatory system is the most important function of the human body. External factors do not affect blood pH; it is regulated only by the internal mechanisms of the human body:
- Blood buffer systems maintain the stability of the environment.
- The pulmonary (respiratory) system removes excess carbon dioxide from the blood.
- Excretory system (kidneys). The slowest, but also the most powerful mechanism, can completely restore the body's pH by removing hydrogen ions through urine.
Thus, although the blood acid level is completely unaffected by external influences, the mechanisms for maintaining it at the required level depend on what a person eats and what kind of water he drinks. Meat and milk increase the overall acidity of the body, while greens and green vegetables are best at neutralizing it. The acidity and alkalinity of various foods can be found in special tables. The optimal pH value for water is between 6 and 9.
By adhering to the principles of proper nutrition to maintain acid-base balance in your body, a person will maintain youth, beauty and health for a long time.
How is pH testing performed?
Conducting intragastric and esophageal pH measurements is the main method for diagnosing acid-related diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. A probe with a thickness of 1-2 mm is used for the study. It is carefully and painlessly inserted through the nose into the esophagus and further, without interfering with natural breathing and food intake. A new, sterile, disposable probe is used for each patient.
Research stages:
- After insertion, the end of the probe is left in the stomach or moved lower to the duodenum, if required by the initial diagnostic purpose.
- To record data, the probe is attached to a compact recorder, which is attached to the patient's shoulder or belt for the entire duration of information collection (24 hours).
- An electrode is fixed on the collarbone, which helps to capture and record control signals.
- During the entire study, you adhere to your normal rhythm and lifestyle so that the recorder’s readings are as objective as possible.
- Upon completion of data collection, the probe is easily and painlessly removed, after which you can continue your normal lifestyle without restrictions.
The results of the study are usually ready within 1-2 days after removing the probe and removing the recorder. You can discuss the collected indicators during a follow-up consultation with a gastroenterologist.
Theoretical basis
Water is a medium in which organic and inorganic chemicals dissolve and has the ability to break down into ions. One molecule donates its proton to another, so water constantly contains a certain amount of positively charged hydrogen ions H and negatively charged hydroxide ions OH. This process is called electrolytic dissociation.
When talking about the hydrogen ion, this is a simplification because the positively charged ion in water is actually the hydronium ion H3O. It is formed from a whole water molecule and a proton removed from another molecule. The more such ions in water, the greater its acidity.
Ions are very mobile and constantly move from one molecule to another. Thus, the process of disintegration and the process of joining into a new molecule are constant and balance each other, i.e., the dissociation of water is in equilibrium.
The number of H+ ions and the measure of their activity in most solutions are very small; they are written as a number with a negative power, which is very inconvenient. Therefore, the Danish biochemist Søren Sørensen in 1909 proposed expressing this number as an indicator of acidity (hydrogen index) pH, which is calculated as the decimal logarithm of the measure of activity of H+ ions with the opposite sign: pH = - log [H+].
S. Sørensen led the chemical-physiological laboratory at the Carlsberg brewery, where he developed a scale for measuring pH. On its basis, special instruments were created: pH meters, which are used to measure the acidity of solutions and liquids in industry, and acidogastrometers for diagnosing gastrointestinal diseases in medicine.
The indicator of the basicity of a solution, expressed as a decimal logarithm with a negative sign of the concentration of hydroxide ions in the solution: pOH = - log [OH-], is used much less frequently. pH and pOH values can be either positive or negative.
It is important not to confuse pH with the concepts of acidity and alkalinity. The main difference is that pH is a measure of activity rather than quantity.
It reflects the degree of acidity or alkalinity of the environment, and not the quantitative content of chemicals in the water. In dilute solutions, the measure of activity is equivalent to concentration, so under certain assumptions one term is replaced by another.