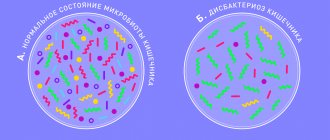
Vaginal dysbiosis is a change in the composition of the microflora of the mucous membranes of the external genital organs in a woman. Under normal conditions, the vaginal microbiome is formed by various strains of bacteria: bifidobacteria, lactobacilli, propionic acid bacteria, acetic acid bacteria, fungal flora, etc. The absolute majority of these microorganisms belong to beneficial flora, but a certain percentage also consists of opportunistic microbes.
Under the influence of aggressive factors (diseases, taking antibiotics, poor hygiene), the balance of microflora is disrupted, which leads to the active proliferation of pathogenic and opportunistic bacteria and fungi. Most often, the number of bacteria Gardnerella vaginalis increases and bacterial vaginosis (Gandnerellosis), or microscopic fungi Candida albicans develops, which causes candidal vaginitis (thrush).
The most important link in the complex treatment of vaginal dysbiosis is the use of probiotics, which effectively restore the microflora. In case of vaginal dysbiosis, specialists of the Research and Production Company “O.D. Prolisok recommend the use of multiprobiotics SIMBITER-2®, as well as functional food products SIMBIVIT®.
Why does microflora disorder occur in women?
Vaginal dysbiosis develops for a number of reasons:
- Changes in hormonal status - during puberty, pregnancy, childbirth, after termination of pregnancy, in premenopause and menopause;
- Infectious diseases – both of the reproductive system and other systems;
- Concomitant diseases - associated with stool disorders, diabetes mellitus, systemic connective tissue diseases;
- Irregular hygiene;
- Frequent change of sexual partners;
- Stress;
- Hypothermia and so on.
Dysbacteriosis in the vagina is usually associated with several factors at once, since a woman’s immune system has been able to independently regulate the composition of the microbiome for a long time.
Vaginal dysbiosis after antibiotics
Gynecologists often identify vaginal dysbiosis after antibiotics as a separate pathology. In this case, the disruption of microflora in women is directly related to the aggressive action of antibiotics and antifungal drugs that have a wide spectrum of inhibitory activity.
The severity of dysbiosis depends on the type of antibiotic, the woman’s immune status, nutrition, hygiene and other factors. In most cases, symptoms can be quickly eliminated with the help of a multiprobiotic with live bacteria, such as SYMBYTER-2®.
Complications of BV
One of the main concerns of gynecologists when identifying BV is the fact that this disease increases the susceptibility of STDs, as it reduces local immunity and is even considered a local acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. According to some data, with a deficiency of lactobacilli in the vagina, the risk of contracting HIV infection increases almost three times, and the risk of contracting gonorrhea and herpes type II almost doubles. With BV, the risk of developing infectious diseases after surgical interventions on the pelvic organs significantly increases. Vaginosis can also lead to cystitis, chronic endometritis and cause abnormal uterine bleeding.
Many scientific studies have confirmed the connection between BV and preterm birth, low birth weight of the newborn, premature rupture of membranes, postpartum endometritis and intra-amnial infection. Treatment of pregnant women is usually difficult due to the limited choice of medications that are allowed to be used during therapy for expectant mothers.
Symptoms of vaginal microflora disorders
Vaginal dysbiosis is accompanied by various unpleasant symptoms:
- Pathological vaginal discharge - white, yellow, gray, which gradually becomes more viscous;
- Unpleasant odor;
- Burning, itching in the vagina;
- Urinary problems;
- The appearance of pain during sexual intercourse.
In some cases, vaginal dysbiosis may be asymptomatic, which poses a potential threat to a woman’s reproductive health. Due to chronic dysbiosis, the menstrual cycle is disrupted, hormonal status changes, which causes difficulties in conceiving a child.
Diagnosis of vaginal dysbiosis
Dysbacteriosis in gynecology is diagnosed based on an examination by a specialist, who determines the presence of the main symptoms of the pathology, as well as laboratory methods:
- Microscopy - a quick examination by staining the resulting smear;
- Bacterioscopy is a longer study in which the flora from a smear is placed on a nutrient medium, and after a few days/weeks it is examined under a microscope;
- The amine test is a quick diagnostic option in which potassium hydroxide is added to the secretions. If a “fishy” odor appears, the test is considered positive;
- PCR is an additional method that is used when simpler ones are ineffective;
- pH measurement, rapid tests for flora.
In most cases, vaginal dysbiosis is quite easily confirmed in the laboratory, after which a course of treatment is immediately prescribed.
What does vaginal dysbiosis lead to?
Vaginal dysbiosis is not just a change in the balance of flora, it is a serious pathology that, if not treated in a timely manner, can lead to various complications and even chronic diseases in a woman.
Complications include:
- Cervicitis – inflammation of the cervical canal;
- Urethritis – inflammation of the urethra;
- Endometritis – inflammation of the endometrium (inner lining of the uterus);
- Salpingoophoritis - inflammation of the ovaries and fallopian tubes;
- Infertility is a decrease in reproductive function against the background of acute and chronic inflammatory processes in the female genital organs.
If you notice the first symptoms of vaginal dysbiosis, we recommend that you immediately seek help from a specialist, and also start using multiprobiotics for women SIMBITER-2®, which significantly weaken the manifestations of dysbiosis even before starting to use antibiotics.
Medicines
To restore the balance of microflora, it is not enough to simply purchase the drug at the pharmacy and take it in a course.
It is important to receive complete treatment in several stages from a gynecologist with mandatory control smears both at the beginning and at the end of therapy.
4.1. Clindamycin
This is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that successfully works against opportunistic and pathogenic vaginal flora.
It allows you to significantly reduce its quantity and gives beneficial lactobacilli a chance to multiply. Contraindicated in the first trimester of pregnancy.
It has different trade names in the pharmacy chain and is available in the form:
- 1 candles – Klindacin, Dalatsin.
- 2 Kremov – Clindamycin, Dalatsin, Clindacin Prolong.
- 3 capsules for oral administration and solution for intramuscular administration.
4.2. Metronidazole
It is active not only against pathogens, but also against protozoa, for example, Trichomonas.
Contraindicated in the first trimester of pregnancy and while breastfeeding. List of release forms for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis:
- 1Suppositories – Mistol, Flagyl, Metronidazole, Metrovagin.
- 2Vaginal tablets – Trichopolum.
- 3Vaginal gels – Metrogyl.
- 4Tablets and capsules for oral administration – Metronidazole, Klion, etc.
- 5Combined drugs - Vagisept suppositories (metronidazole + fluconazole), Vagiferon (with the addition of interferons), Metromicon-Neo, Neo-Penotran (metronidazole + miconazole), vaginal tablets Klion-D (metronidazole + miconazole).
4.3. McMirror
Nifurantel actively destroys bacteria, protozoa and fungi. In combination with nystatin, which has an antifungal effect, its effectiveness increases even more.
In the pharmacy chain, the combination of nifurantel and nystatin is known as Macmiror Complex (these are soft vaginal capsules). The drug is widely used at the first stage of normalization of microflora. Contraindicated in the first trimester of pregnancy.
4.4. Terzhinan
These are vaginal tablets containing ternidazole, neomycin, nystatin and prednisolone.
Ternidazole and neomycin successfully destroy Gardnerella and other microorganisms that predominate in dysbiosis.
Thus, the drug changes the ratio in favor of beneficial lacto- and bifidobacteria. Nystatin has an effect on yeast fungi, and prednisolone eliminates the inflammatory response.
Terzhinan is indicated at the first stage of restoration of microflora in cases of bakvaginosis and vaginitis.
4.5. Antiseptics
Chlorhexidine has a detrimental effect on many bacteria, including gardnerella, chlamydia, bacteroides and others.
When applied topically, it is practically not absorbed into the blood and does not have a systemic effect.
For use in gynecology, chlorhexidine is available in the form of suppositories (Hexicon, Hexicon D) and combination preparations (Depantol suppositories - dexpanthenol + chlorhexidine), which can be used for treatment during pregnancy and lactation.
Fluomizin also has a similar effect.
Dequalinium chloride (the main active ingredient of the drug) is an antiseptic that is active against most gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, fungi of the genus Candida and Trichomonas.
Polyvidone-iodine is a complex of iodine and polyvinylpyrrolidone, which has a detrimental effect on many pathogens, including yeast.
It is also used in the first stage of restoring the vaginal microflora. Povidone-iodine is often prescribed to prevent candidiasis.
The most common forms of release used in gynecology are Betadine and Iodoxide suppositories.
4.6. Clotrimazole
Has antibacterial and antifungal activity. Used to treat bacterial vaginosis and thrush. Contraindicated in the first trimester of pregnancy.
It has different release forms, of which the most often prescribed in gynecology are:
- 1Vaginal tablets – Candibene, Canesten, Clotrimazole.
- 2Gels, vaginal creams – Candide, Clofan.
- 3Combined suppositories – Vagiclin (clotrimazole + clindamycin), Clomegel (metronidazole + clotrimazole).
4.7. Natamycin
This is a natural antibiotic that has a detrimental effect on pathogenic fungi, including candida.
Its distinctive feature is the almost complete absence of allergic reactions. Can be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Prescribed to restore microflora in cases of thrush, as well as mixed forms of dysbiosis.
In gynecology, its dosage forms are used in the form of pessaries (Natamycin) and vaginal suppositories (Pimafucin, Pimafungin).
4.8. Econazole
Prescribed for thrush and combined bacterial-fungal infection.
Contraindicated in the first trimester of pregnancy. Release forms - creams and suppositories (Gyno-Pevaril, Ekalin, Econazole, Ifenek).
Prevention of vaginal dysbiosis
“It is better to prevent a disease than to cure it” is a legendary quote from Hippocrates, an ancient Greek physician, which is still relevant today. Prevention of vaginal dysbiosis consists of following simple but very effective methods:
- Probiotics - preparations with live bacteria should be used by a woman during “critical periods” when the risk of developing dysbiosis increases significantly, for example, during pregnancy, lactation, when taking antibiotics, during menopause;
- Maintaining normal hygiene - with irregular hygiene procedures on the mucous membranes, the number of pathogenic microorganisms increases;
- Nutrition and sugar control – daily consumption of prebiotics (food for bacteria) significantly reduces the risk of vaginal dysbiosis. Prebiotics include: lactic acid products, bread, cereals, fruits, vegetables, beans. High sugar levels are also factors in the development of dysbiotic disorders; its level must be regularly monitored;
- Constant sexual partner - a violation of the vaginal microflora often develops with frequent changes of partners, as well as refusal of barrier contraception;
- Regulation of intestinal function – intestinal dysbiosis = vaginal dysbiosis. These pathologies are closely related, therefore, following a diet and establishing regular bowel movements is the key to successful prevention of dysbiosis.
How is dysbiosis treated in gynecology?
Vaginal dysbiosis must be treated when the first symptoms appear; delaying therapy can aggravate dysbiotic and metabolic disorders and lead to chronicity of the process.
Dysbacteriosis in gynecology is treated comprehensively:
- Elimination of the provoking factor - that is, changing lifestyle, improving nutrition, sexual life;
- Antibacterial, antifungal therapy - the use of drugs that suppress genital tract infections;
- Probiotic therapy is an effective method of restoring normal vaginal microflora.
Pathogenesis of the disease
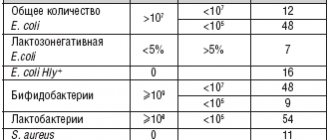
The composition of the microflora in most women is almost the same and is in stable balance. Approximately 90% are beneficial lactobacilli (Doederlein bacilli), 10% are bifidobacteria, less than 1% are opportunistic flora (leptothrix, gardnerella, candida fungi, mobiluncus, etc.). If immunity or the balance of flora is disturbed, opportunistic microorganisms are activated, begin to multiply intensively and lead to the development of dysbacteriosis. The disease can be provoked by pathogenic microorganisms, including sexually transmitted ones (streptococci, E. coli, Proteus, staphylococci, gonococci, Trichomonas, etc.). In such a situation, the number of beneficial bacteria is significantly reduced, and pathogenic microflora begins to predominate in the smear.
The beneficial bacteria that live in the vagina do not cause inflammation or tissue damage. They are antagonists of pathogenic flora. Protection is also provided by local and general immune reactions. Thanks to a healthy immune system, normal vaginal flora is restored.
Any pathogen that causes dysbacteriosis can provoke a serious inflammatory disease of the vagina - vaginitis or colpitis. The risk of inflammation increases with a large infectious dose of the pathogen and impaired immune defense mechanisms. At the initial stage, the immune system copes with and controls the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. But without timely and correct therapy, the process progresses and leads to the manifestation of the inflammatory process.
Multiprobiotics SIMBITER-2® to eliminate vaginal dysbiosis
Multiprobiotic SIMBITER-2® is a unique complex of living bacteria, ideally balanced and adapted to the needs of the female body.
SIMBITER-2® includes:
- Lactococci, lactobacilli;
- Bifidobacteria;
- Propionic acid bacteria;
- Acetic acid bacteria.
SIMBITER-2® has been actively used in obstetrics and gynecology for the prevention and treatment of vaginal dysbiosis for more than 20 years. Signs of vaginal dysbiosis are effectively eliminated from the first days of SIMBITER-2® probiotic therapy, and the total recommended course duration is from 14 to 30 days.
You can buy SIMBITER-2® multiprobiotics for the treatment of dysbiosis directly on our website or at partner pharmacies. We deliver products throughout Kyiv and the Kyiv region. If you would like to consult a specialist on probiotic therapy, please contact us by phone or visit the office of Scientific and Production Company “O.D. Prolisok" in Kyiv.
Frequently asked questions about vaginal dysbiosis:
✅ What are the main causes of microflora disturbance in the vagina?
Vaginal dysbiosis occurs mainly due to infectious diseases, hormonal imbalance, promiscuity, and also after taking antibiotics.
✅ Is it necessary to use probiotics if the vaginal microflora is disturbed?
Clinical studies show that vaginal dysbiosis must be treated using a complex of drugs: antibiotics, antifungals to eliminate infection, probiotics to restore normal flora.
✅ How is SIMBITER-2® different from other probiotics?
SIMBITER-2® is a balanced multiprobiotic that is specially designed to restore female microflora. It contains all the necessary types of live bacteria, can be used in parallel with antibiotics, and is also suitable for pregnant and lactating women.
✅ How long should you use medications for vaginal dysbiosis?
Dysbiosis of the cervix and vagina is treated on average from 10 to 14 days with antibiotics and/or antifungal agents. Probiotics are used in conjunction with the main therapy for at least 14 days, and for better effect – up to 4 weeks.
Bacterial vaginosis and STDs
Infections that are sexually transmitted have a direct connection with vaginal dysbiosis. Pathogenic microorganisms change pH and provoke inflammation, which further complicates the course of the disease.
Sexual infections are always accompanied by opportunistic flora. This must be taken into account when selecting therapy for STDs. Sometimes an antibiotic has an excellent effect on the causative agent of a sexually transmitted infection, but opportunistic microorganisms remain resistant to it. After the main pathogen is eliminated, they begin to multiply intensively.
The final stage of any STD therapy is the restoration of the vaginal microflora. In case of severe infections or mixed forms of STDs, it is necessary to first carry out adequate antibiotic therapy, and only then correct the dysbiosis. If the infection is not too severe and is caused by a single microorganism, you can simultaneously treat the patient with antibiotics and restore the flora. But before this, a comprehensive diagnosis must be carried out.