Inflammatory diseases of the stomach can have different etiologies and symptoms. Typically, the cause of gastritis is bacterial damage to the stomach tissue against the background of irritation of the mucous membrane, but doctors also identify other sources of the disease.
A separate cause of the disease can be considered the reflux of bile and pancreatic juice from the small intestine into the stomach, which leads to damage to the organ. Diet for reflux gastritis is an additional treatment method.
What is gastritis?
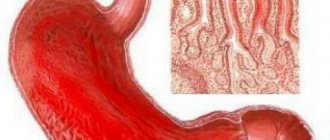
Gastritis is an inflammatory disease of the stomach.
In the mucous membrane of the stomach there are special glands that produce acidic gastric juice and other substances necessary for digestion.
Pepsin is one of the enzymes in gastric juice. Pepsin breaks down protein while stomach acid breaks down food substrates and protects the body from infections.
The hydrochloric acid in the stomach is strong enough to cause damage directly to the tissues of the organ. The cells of the stomach secrete special substances that protect the stomach from the aggressive environment of its own contents. Chronic gastritis is characterized by inflammation of the stomach tissue.
The disease can be triggered by bacteria, drinking alcohol, taking certain medications, chronic stress and poor diet. When an inflammatory process occurs, the mucous membrane changes and loses protective cells.
Sometimes this process is accompanied by a feeling of early satiety - when a person feels fullness in the stomach after eating a small portion of food. Since gastritis develops over a long period of time, the tissues of the organ gradually wear out and lose their protective properties.
This can cause cellular metamorphosis, metaplasia and dysplasia. Such changes are a precancerous condition characterized by a high risk of malignancy. Gastritis can be acute or chronic:
Reviews and results
Therapeutic nutrition can be carried out for a long time because it is balanced. Anyone who has encountered the problem of GERD knows that the diet must be followed. By reviewing your diet, you can avoid the discomfort associated with this disease. Reviews from patients confirm this. A light diet relieves belching, heartburn and heaviness in the stomach.
- “...Frequent reflux caused inflammation of the esophagus. I had to strictly follow the diet and treatment prescribed by the doctor. I stuck to it strictly for 2 months (mashed steamed dishes), and then switched to baking and didn’t puree it anymore. I excluded foods that cause heartburn in me (tomato paste, lemon, pickled vegetables and, oddly enough, sweets). I immediately felt an improvement, and, of course, the pills help. If you had the will to eat like this all the time, it would be great. I lost 4 kg in 3 months”;
- “... Lately, heartburn has begun to bother me; they discovered erosions in the esophagus. I had to go to the hospital because I needed sick leave. I don’t regret it, because at home I wouldn’t be able to take my mind off everything, eat right and take pills regularly. After 2 weeks, no erosions were found. At home I continued to follow the diet, but expanded it slightly compared to the hospital. As a result, 4 months of diet. I feel very good, it seemed that I got rid of heartburn forever. But after fried cutlets with buckwheat porridge, I again felt discomfort and belched. It turns out that you need to maintain proper nutrition all the time - this is the main thing”;
- “... I have been suffering from this disease for many years, I periodically take treatment and resort to diet. For me, the trigger for exacerbation is the consumption of sour fruits (lemon, currants and even apricot and peach), also jam and honey. Once you regularly eat jam and tea for a week, heartburn and belching begin, and constipation sets in. I also noticed that you should not overeat and work in the dacha in a bent position. It turns out that I always have an exacerbation in the summer - work plus berries and fruits. But somehow I endure it, I connect the pills, how can you give up fruit during the season? We have to put up with it and endure the heartburn.”
Causes of gastritis
Helicobacter pylori is the main cause of gastritis.
The most common causes of gastritis include the following:
- Infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori.
- Damage to the walls of the stomach, leading to reactive gastritis.
- Autoimmune organ damage.
Helicobacter pylori infection is the most common cause of gastritis. The vital activity of this bacterium leads to damage to functionally important cells of the organ. In this case, gastritis is usually characterized by a non-erosive form of inflammation. The bacterium can cause both acute and chronic gastritis.
Infectious gastritis is especially common in developing countries. The infection often begins in childhood and remains asymptomatic for a long time. Many people infected with Helicobacter never complain of gastrointestinal problems. The appearance of anxiety usually appears with age, when the organ is already sufficiently damaged.
Modern science does not have precise data on how the infection spreads, although there is evidence that food, water and utensils can transmit bacteria from person to person. The bacterium is also found in the saliva of some patients suffering from infectious gastritis.
Reflux gastritis is a separate etiological form of the disease, somewhat similar to gastroesophageal reflux disease. The pyloric sphincter separates the stomach from the duodenum.
Isolation is necessary to ensure that the alkaline contents of the small intestine do not enter the stomach. The walls of the stomach are not protected from the environment of intestinal juice, so reflux may cause damage to the organ. Reflux gastritis can occur due to disruption of the sphincter.
Proper nutrition for GERD
The key to solving many problems with the gastrointestinal tract is proper nutrition. Gastroenterologist at the Leninsky Clinic Katerina Chesskaya tells what those who suffer from reflux disease can and should eat.
What is GERD?
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a chronic, relapsing disease in which spontaneous, regularly repeated reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus occurs. As a result, the lower esophagus is affected. The reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus is considered normal if it occurs occasionally and is not accompanied by negative factors. The disease is indicated by frequent recurrence of reflux and inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract.
GERD is usually manifested by belching and heartburn that occurs after eating or bending forward, as well as at night. Pain behind the sternum, radiating to the interscapular region, lower jaw, and left half of the chest, may also indicate the presence of GERD. There are also signs of GERD that are not directly related to the esophagus - cough, shortness of breath, which often occurs in a lying position, hoarseness, dry throat, rapid satiety, bloating. The cause of chronic inflammatory diseases of the nasopharynx (pharyngitis, laryngitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis) in 30% of cases is GERD. It has been proven that against the background of GERD there is a risk of developing obstructive pulmonary diseases, including bronchial asthma.
Proper nutrition for GERD
As with many other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, the main principle of treatment for GERD is proper nutrition. There are foods that relax the lower esophageal sphincter, which leads to the reflux of acidic stomach contents into the esophagus, that is, reflux. These include; strong tea, coffee, chocolate, citrus fruits, tomatoes, bitters (garlic, onion), freshly brewed mint. As well as fatty fish, meats and products that cause gas formation: baked goods, hot pastries, legumes, brown bread, cakes, pastries, grapes, cucumbers, carbonated drinks. Alcohol and smoking also reduce the tone of the lower esophageal sphincter.
Here is a list of products that you need to consider when creating your menu for the day. Exclude:
1. Bread: fresh rye bread, butter pies and pancakes. 2. Meat: stewed and fried meat dishes from fatty meat and poultry. 3. Fish: fatty fish, fried, smoked, salted dishes. 4. Vegetables: white cabbage, turnips, rutabaga, radish, sorrel, spinach, onions, cucumbers, salted, pickled and pickled vegetables, mushrooms. 5. Fruits: Raw, sour, unripe fruits, dried fruit puree. 6. Cereals: millet, pearl barley, barley and corn cereals, legumes. 7. High acidity dairy products, sharp and salty cheeses. 8. Sweets: halva, chocolate, ice cream, cakes. 9. Drinks: sour, carbonated, fruit drinks, strong tea, coffee and alcohol.
Recommended:
1. Bread: made from first or highest grade wheat flour, yesterday's bread, dry, inconvenient baking. 2. Meat: Beef, veal, chicken, rabbit, turkey, all in the form of cutlets, meatballs, soufflé, puree and quenelles. 3. Fish: boiled river fish - pike perch, pike, perch, any low-fat varieties. 4. Vegetables: carrots, cauliflower, potatoes, beets, pumpkin and zucchini. 5. Fruits: Sweet berries, ripe fruits. Preferably pureed or baked. 6. Cereals: oatmeal, semolina, buckwheat (mashed), rice porridge, in water with milk, boiled vermicelli. 7. Dairy products: milk, lean cheese and low-fat sour cream. Curd dishes made from pureed cottage cheese, for example, cheesecakes, casserole. 8. Sweets: jam, marshmallows, honey, marshmallows, cream and milk puddings. 9. Drinks: weak tea or cocoa with milk, sweet juices and decoctions.
It is also important to adhere to your diet:
— Fractional meals in small volumes and often up to 5-6 times a day. - Do not lie down immediately after eating, the last meal is 2-3 hours before bedtime. — Do not work in a tilted position, avoid the “gardener” pose. — Do not wear tight belts and limit abdominal exercise. — People with obesity need to normalize their body weight.
Remember that only a gastroenterologist can accurately diagnose GERD (as well as any disease). At the appointment, the doctor, together with the patient, will find the cause of the disease, outline a treatment plan and further supportive therapy to avoid relapses.
The Clinic on Leninsky provides receptions for:
- pediatric gastroenterologist Natalya Medvedeva;
- gastroenterologist Ekaterina Chesskaya.
You can make an appointment with a gastroenterologist at the Clinic on Leninsky by phone +7
.
Symptoms of reflux gastritis
Heartburn is an essential symptom of gastritis.
Reflux gastritis differs from other forms of the disease in that it has more severe symptoms.
In some patients, the disease is accompanied by pain and discomfort in the upper abdomen, in the epigastric region.
In addition, pain can appear on an empty stomach - this phenomenon is called “hunger pain”. Asymptomatic reflux gastritis also occurs. Other possible symptoms:
Possible complications of the disease
A complication of gastritis can be ulcerative lesions of the stomach or duodenum.
The following complications of reflux gastritis can occur if treatment is not timely: The occurrence of peptic ulcers.
These ulcers occur in the area of the mucous membrane of the stomach or duodenum. Taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and Helicobacter infection increases the likelihood of ulcers.
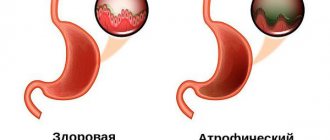
Atrophic gastritis. This form of gastritis occurs when chronic inflammation of the stomach walls causes the destruction of functionally important glands. Reflux gastritis and chronic gastritis of other etiologies often develop into the form of atrophic gastritis.
Anemia. Erosive gastritis often causes chronic bleeding in the stomach. Long-term constant blood loss leads to anemia. Anemia is a condition in which there is a deficiency of red blood cells, affecting the transport of oxygen in the blood.
Red blood cells contain hemoglobin, which is rich in iron and protein. Research suggests that Helicobacter pylori gastritis and autoimmune atrophic gastritis can affect the body's ability to absorb iron from food, which can also cause anemia.
Vitamin B12 deficiency and pernicious anemia. Patients with autoimmune atrophic gastritis do not have enough of a special intrinsic factor that helps absorb vitamin B12 in the stomach.
The body needs this vitamin to produce red blood cells and nerve cells. Insufficient absorption of vitamin B12 can lead to a separate type of anemia called pernicious anemia.
Hyperplasia of stomach cells. Chronic gastritis increases the risk of developing benign and malignant stomach tumors. Chronic infectious gastritis can lead to the development of gastric lymphoma - cancer of the organ's lymphoid tissue.
In addition to the above, you need to keep in mind that the acute form of gastritis can cause dangerous bleeding.
Thematic video will tell you about the symptoms of gastritis:
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of esophagitis is made on the basis of anamnesis, characteristic complaints and clinical signs. Often the main method for making a diagnosis is endoscopic examination, but in the acute period it is not done so as not to injure the mucous membrane of the esophagus. X-ray contrast study helps to detect signs of impaired motor function of the esophagus and areas of erosive and ulcerative process. The diagnosis of chronic esophagitis is also based on medical history, clinical symptoms, and the results of endoscopic and x-ray studies.
What foods can you eat?
For gastritis, it is recommended to drink fruit juices.
There are certain foods that should be consumed to relieve the symptoms of gastritis and stomach ulcers.
These foods can have a soothing effect on tissue and reduce signs of inflammation. Below is a list of recommended foods specifically for a diet for reflux gastritis.
Broccoli sprouts contain a beneficial chemical called sulforaphane. This substance helps destroy Helicobacter in the body due to its antibacterial properties.
A 2009 study published in the journal Cancer Prevention Research found that a group of patients who ate broccoli sprouts every day for two months had less significant signs of stomach inflammation.
Yogurt is an excellent choice for a gastritis diet. The product restores intestinal flora and improves the balance of the stomach environment. It is best to consume yogurt that contains beneficial bacterial cultures and a small amount of milk fat. You can add honey to regular yogurt to improve its anti-inflammatory properties.
Fruits help relieve reflux gastritis. Apples, bananas, pears, peaches, grapes, melon and kiwi are especially useful. Many vegetables are recommended for gastritis. These include broccoli, potatoes and tomatoes. Fruit juices, skim milk and cream cheese are also helpful.
What foods to exclude from the diet for reflux gastritis?
The following products should be excluded:
- Coffee.
- Alcohol.
- Black and green tea.
- Spicy foods including chili and curry.
- Black and red pepper.
- Fatty foods.
- Onion and garlic.
- Oranges, grapefruit, figs, berries and dried fruits.
- Fried food.
- Oil.
- Soft drinks or drinks with added sugar.
- Carbonated drinks.
- Citrus and pineapple juice.
This is not a complete list of products as some substances may cause individual reactions.