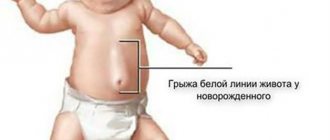
If the abdominal muscles are weak and the umbilical ring has not yet closed, then the internal organs that normally lie in the abdominal cavity may move beyond the anterior abdominal wall. Loss can be a consequence of pathology (for example, muscle separation), or caused by natural causes. This is how an umbilical hernia forms in children, especially often plaguing babies under one year old - according to statistics, it is diagnosed in approximately 20% of newborns.
Why do children develop an umbilical ring defect?
Medical systematization by type of origin umbilical hernias are defined as congenital
or
purchased
.
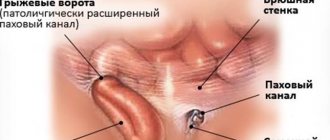
- A congenital hernia in a child is visually identified by a doctor immediately after birth - in the navel area there is a spherical (or cone-shaped) protrusion with a wide base, which passes into the umbilical cord.
- An acquired hernia can occur up to the age of three. Its visual identification is similar to that of a congenital hernia.
What is the cause of congenital umbilical hernia
A few days after the baby is born, the umbilical cord falls off. The umbilical ring consists of two parts. The lower part, where the umbilical arteries and urinary duct pass, contract well and form dense scar tissue. The umbilical vein runs in the upper part. Its walls are thin, do not have a muscular membrane, and subsequently contract poorly, which, with weak peritoneal fascia and an open umbilical vein, contributes to the formation of an umbilical hernia.
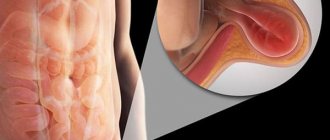
The contents of an umbilical hernia are usually intestinal loops. With light pressure, the hernial protrusion is freely retracted inward. With a very wide umbilical ring and a large hernia, intestinal peristalsis is sometimes visible outwardly, that is, contraction of the intestinal muscles and the movement of food through it, which is very frightening for many parents, but this does not cause inconvenience to the baby.
An important reason contributing to the occurrence of this pathology is the frequent increase in intra-abdominal pressure. It can be caused, for example, by frequent crying of a child, gas, constipation. The hole at the top of the umbilical ring may be wide and not cause distress to the baby. But in the case of a small defect with hard edges, the child may be worried. When a baby screams or cries, a hernial protrusion appears, which usually alarms parents.
Parents often associate the child’s increased anxiety with a strangulated umbilical hernia, but such developments of umbilical hernia pathologies in infants are extremely rare (in these cases, the hernial contents are fixed by adhesions to the inner wall of the skin of the anterior abdominal wall). As a rule, an umbilical hernia in children is always reducible. A strangulated umbilical hernia can be found more often in adult practice.
The main cause of umbilical hernias is a hereditary predisposition to weakness of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall due to connective tissue dysplasia. This means that if the father or mother of the child themselves had this pathology in childhood, then the probability that their child will have a hernia is about 70%.
Misconception about umbilical hernia in newborns
There is a persistent misconception among parents that an umbilical hernia in a child often occurs due to an error by the obstetrician, who cut the umbilical cord incorrectly. Today, this superstition has no objective conditions because in obstetric practice the technique of applying an umbilical bracket , which leaves no chance for error even for a young obstetrician.
The direct cause of an umbilical hernia in newborns is an anatomical feature determined by the physiological weakness of the connective tissue in the navel area.
How to “earn” an acquired umbilical hernia
A preliminary diagnosis of “umbilical hernia” can be made during examination by the pediatrician observing the child. In the future, the doctor should refer the baby for a consultation with a surgeon to receive additional recommendations for monitoring and treating this condition.
The main causes of acquired hernia in a child:
- Due to the frequent and prolonged crying of the child, when the abdominal muscles are constantly tense, the internal organs are under pressure.
- Constipation and flatulence provoke periodic short-term but intense increases in intra-abdominal pressure and, as a result, the umbilical ring does not contract as effectively as it should, and, consequently, intestinal loops or the omentum can prolapse beyond the abdominal wall, forming a hernia.
- Early walking can also cause a hernia. During this period, the abdominal muscles receive a new unusual load and may not be strong enough.
Relapses
The probability of a reoccurrence of a hernia when using mesh endoprostheses is less than 10%.
Secondary hernia may occur due to:
- Incorrectly performed operation;
- The size of the mesh endoprosthesis is incorrectly selected;
- The mesh is incorrectly installed in the hernial orifice;
- The patient did not comply with all the requirements and instructions of the doctor regarding behavior and lifestyle in the postoperative period;
- Obesity;
- Prolonged cough;
- Constant constipation;
- Getting injured;
- Excessive physical activity.
How not to be mistaken that your child has an umbilical hernia
The following signs are sufficient to accurately identify the disease:
- a protrusion in the navel area that decreases in size or disappears when lying down.
- abdominal pain that occurs with exercise and coughing.
- umbilical ring expansion
Diagnostic methods
Diagnostic methods for children are not numerous and are limited to the following list:
- examination by a pediatric surgeon;
- hernial protrusion;
Diseases with similar symptoms
There are not many diseases with similar symptoms; their list can be limited to the following:
- Hernia of the white line of the abdomen;
- Endometriosis of the navel;
- Oncological diseases and metastases of tumors of the stomach and duodenum (mainly in adults);
Rehabilitation period
With open surgery, the patient's recovery period lasts longer than with laparoscopy, since the operation affects more tissue.
After open surgery:
- The patient remains in the hospital for one to two weeks.
- For the first 5-7 days, the patient is treated with stitches and bandaged.
- The patient wears stitches for 2 weeks.
- For the first six months, the patient is prohibited from physical activity, standing for long periods of time, or lifting and carrying loads of more than 5 kilograms.
- After 8 months or later, the patient is prescribed physical therapy to restore and strengthen the abdominal muscles.
After laparoscopic surgery:
- The patient remains in the hospital for 3-7 days.
- Within 3-7 days, the patient’s wounds are treated and bandaged.
- The stitches are removed after a week.
- For the first six months, the patient is prohibited from physical activity, standing for long periods of time, or lifting and carrying loads of more than 5 kilograms.
- After 8 months, the patient is prescribed physical therapy to restore and strengthen the abdominal muscles.
Prevention of acquired umbilical hernia
Prevention of the occurrence of an umbilical hernia is, first of all, the prevention of excessive straining of the child and bloating, which is usually caused by increased gas formation and constipation.
To prevent excessive intestinal bloating in a child and the development of constipation, the most favorable option for young children is breastfeeding, but the mother must follow a diet. We can advise mothers to temporarily exclude the following foods from their diet: whole milk, white cabbage, legumes, nuts, sweets, smoked meats, sausages. It is preferable to consume fermented milk products, bran, whole grain cereals, fresh vegetables and fruits. During breastfeeding, prunes and dried apricots (no more than 3-5 berries per day) are useful for preventing constipation.
If the baby is bottle-fed, in order to avoid constipation, bloating, colic, or an allergic reaction, the formula should be selected by a pediatrician. The doctor observing your baby may recommend medications: SAB-SIMPLEX, ESPUMIZAN, PLANTEX, BABY-CALME, etc.
To prevent constipation, which can occur in a baby due to improperly selected artificial nutrition, due to errors in the diet of a nursing mother, as well as in dysbacteriosis and other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, in which excessive straining occurs, pediatricians recommend taking DUPHALAC among medications. , as well as the introduction of GLYCERIN SUPPLIES and microenemas - MICROLAX. Your pediatrician will tell you the dosage and specifics of administering these medications, since the prescription of drug therapy is purely individual and can only be done by the doctor monitoring your baby’s development.
Children with lactose intolerance (lactase deficiency) quite often have umbilical hernias. Lactase deficiency occurs in children who were born prematurely or at term, but remain functionally immature. In this condition, breast milk is partially or completely not digested, resulting in fermentation in the intestines and bloating. In addition, one of the forms of lactase deficiency may be a tendency to constipation. The most effective means of prevention for such children is a rational selection of feeding; during breastfeeding, additional administration of the lactase enzyme is often recommended.
At an early age, many children suffer from intestinal dysbiosis, that is, a violation of the intestinal microflora, which can occur against the background of lactase deficiency and other conditions. At the same time, constipation, as well as bloating, which accompanies dysbacteriosis, quite often provoke the occurrence of an umbilical hernia in babies. Treatment in this case should be aimed primarily at eliminating the symptoms of the underlying disease.
Complications
Possible complications when using meshes for surgical treatment of a hernia can arise in cases where the operation was performed incorrectly - an infection got into the wound, the endoprosthesis was poorly installed, the mesh was chosen of the wrong size.
If the operation is performed incorrectly, the following complications may occur:
- possible occurrence of extrusion and adhesions when the mesh is displaced;
- development of infections, suppuration and fistulas when germs or bacteria enter during surgery;
- discomfort when installing a larger mesh than necessary;
- relapse when installing a mesh that is smaller than necessary;
- bleeding due to insufficient wound suturing and improper installation of the endoprosthesis.
If the mesh endoprosthesis was installed correctly, then there should be no complications after the operation.
Despite the fact that the mesh endoprosthesis is hypoallergenic, in very rare cases the patient’s body may not accept the mesh and react to it with inflammatory and allergic reactions. In this case, the patient may experience vomiting and general intoxication of the body.
How umbilical hernia in children is treated in Russia
Traditional treatment
Traditional methods of treating umbilical hernia in children have taken root well in the historical consciousness of the Russian population. From generation to generation, grandmothers and aunts of children with umbilical hernia syndrome tell their mothers encouraging stories about “miraculous” deliverance from hernias with the help of village healers. Among these inventive and resourceful healing methods, three methods stand out:
- Conspiracies with manual-tactile actions in the navel area;
- Applying a piece of an alloy of non-ferrous metals to the navel, in common parlance: “copper coins”;
- The use of a mixture of dried herbs in the form of tea leaves, the authorship of which is pretentiously attributed to hermits from the Christian-church pantheon.
Common sense ignores the empirical content of these “methods,” finding no reason to discuss the impossible. It is known that such social phenomena are the subject of study by specialists in legal law and social psychiatry.
Doctors explain the phenomenon of the existence of these wild superstitions in modern educated society by the ability of the child’s body to independently get rid of the symptoms of an umbilical hernia (so-called self-healing). In classical medicine, this fact is a scientifically based guarantee of parents’ hope for self-healing from a hernia, but for healers it is a reason to replace the true cause with their home-grown techniques.
A good recommendation for responsible parents is to definitely visit a pediatrician if you suspect the first signs of an acquired umbilical hernia. If your baby was diagnosed with an umbilical hernia in the maternity hospital, then in a few weeks make an appointment with a pediatric surgeon at your municipal medical institution (the referral is given by the pediatrician at the first visit).
So that you don’t miss anything from the specialist’s valuable recommendations, take your baby’s dad with you. Men cope better with new information and his additions to your memory will be useful. Strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations, remember that your diligence, together with parental love, is a reliable guarantee of the expected treatment result.
Today in our country, the system of medical patronage for children's health allows us to effectively treat many diseases in the early stages. And it is the pleasant duty of parents to take full advantage of this civilizational advantage over past generations.
Conservative treatment – or treatment of umbilical hernia without surgery
Up to 5 years of age, an umbilical hernia is not operated on, since it is possible to close the defect on its own. Many doctors believe that hernias that had the potential to heal themselves disappear in children under the age of 3, maximum 4 years; some authors talk about the possibility of closing PG before 6 years of age. But both experts agree that it is imperative to operate on umbilical hernias in children 6 years of age and older.
Surgical treatment of pediatric umbilical hernia at the Laser Medicine Center
or why you shouldn’t be afraid to go to a pediatric surgeon
If the time allotted by nature to your baby’s health for self-healing is coming to an end, if all your conscientious efforts to help your child cope with this harmless pathology have not yielded results, then you should not hesitate and gather your courage and make a decision on surgical treatment of the hernia.
Please note that the uniqueness of a child for parents does not apply to his illness for a doctor. If a pediatric surgeon has several dozen operations to repair an umbilical hernia, then his professional experience is a sufficient guarantee of the success of the operation. When you are dealing with a doctor who has performed hundreds of similar operations, the child’s parents have an objective reason to be completely confident in the successful surgical treatment of their child.
Dear Parents.
You can get qualified help regarding the treatment of an umbilical hernia, as well as hernial protrusions of other origins, in the pediatric surgery department of the multidisciplinary clinic “Laser Medicine Center”.
We widely use modern effective treatment methods to achieve positive results. The department is equipped to the most modern standards, so your stay in the hospital will be as comfortable as possible.
Features of application
Instructions: how to apply the plaster
When using the medical adhesive plaster for the first time, it is better to entrust the application of a medical adhesive plaster to a doctor. If the hernial sac is small, you can perform the procedure yourself. All patches are rectangular in shape; all you need to do is apply the adhesive base tightly to your stomach. The middle of the tissue base should be at the navel, thanks to which optimal support will be provided to weak muscles.
Before gluing, the adhesive base is slightly stretched and pressed tightly against the skin to ensure the required pressure.
The therapeutic belt for babies is fixed in a special way. Before use, a skin fold is formed on the peritoneum that supports the muscle, and it is fixed on top with adhesive tape.
If the instructions for use seem too complicated, it is better to watch the video.
How to remove a patch without pain
To avoid causing pain to the newborn, the patches should not be removed dry. Even with careful and slow removal, the adhesive backing will cause discomfort.
The newborn needs to be bathed in a warm bath, allowing time for the adhesive plaster to absorb moisture. Next, it is carefully and slowly torn off from the surface of the skin.
As a rule, after using adhesive medical belts, redness forms on the child’s skin in the places of fixation. This is within normal limits, but they cannot be left unnoticed, otherwise open wounds may form. For several days, the redness is treated with baby cream or herbal decoctions.