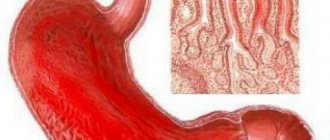
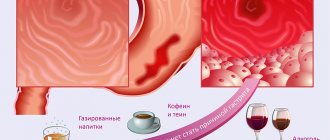
Gastritis is a process of inflammation of the gastric mucosa, characterized by periods of exacerbation and temporary weakening of the manifestations of a chronic disease.
The disease occurs as a result of:
- Bacterial activity (Helicobacter Pylori).
- Nervous stress and chronic fatigue.
- Improper diet and unhealthy food (excessive diets that do not spare the body or, conversely, gluttony).
- Alcohol or nicotine addiction.
- Intolerance to medications (possibly due to frequent use or due to the immunostimulating function of the drug).
- Non-compliance with the temperature regime when eating food.
- Harsh chemicals used in cooking (vinegar).
Gastritis occurs in acute and chronic forms.
The acute form of the disease occurs as a result of a one-time exposure to a strong irritant: poor-quality food, strong medicine or a chemically active substance. If the patient is not treated, the disease develops into chronic gastritis. Statistics show that this happens in the majority of those suffering from the acute form. If relief occurs and symptoms no longer appear, you should not stop taking medications and ignore your diet. The doctor decides how long the treatment will take.
Acute form of gastritis
The chronic form leads to pathological changes in the gastric mucosa and death of the glands that produce gastric juice. The causes are the activity of bacteria, stress, harmful addictions, and regular poor nutrition.
To identify the stage of development of the disease, it is necessary to consult a doctor and undergo an examination (ultrasound, endoscopic diagnosis, intragastric ph-metry, blood and stool tests).
Inflammation leads to improper functioning of the stomach, which will affect the digestibility of food. If left untreated, gastritis can progress to ulcers and stomach cancer.
What is gastritis like?
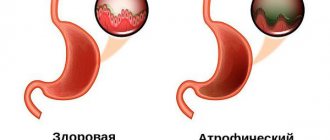
The most common form of chronic gastritis (CG) is bacterial, it occurs in almost 70% of patients. Most often it is provoked by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori (Fig. 1). Resistant to stomach acid, it is spread by the oral-fecal route. The enzymes secreted by H. pilory contribute to the destruction of the protective mucus of the stomach, which protects the tissues from the aggressive effects of gastric juice. Helicobacter is represented by various strains - from relatively harmless to extremely dangerous, causing the formation of chronic ulcers and even stomach cancer.
Figure 1. Helicobacter pylori bacterium, which causes gastritis. Micrograph using SEM. Photo: Yutaka Tsutsumi
Harm and benefits of Helicobacter
Important! H. pylori does not always lead to gastritis and can be beneficial for our body. In recent years, the positive effect of this bacterium on the functioning of the immune system has been proven. H. pylori is able to interact with T lymphocytes, suppressing inflammation, and reducing the risk of developing allergies and asthma.
Other types of gastritis include:
- Autoimmune (15% of cases). Caused by aggression of the body's own antibodies, attacking the cells responsible for the secretion of acid in the stomach. This form of gastritis is characterized by elevated pH levels and constant release of the hormone gastrin, which leads to the formation of microtumors in the stomach.
- Chemical (10% of cases). It is caused by the action of various drugs (acetylsalicylic acid, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibacterial and other drugs) that irritate the gastric mucosa or reduce its protective properties.
- Reflux gastritis (5% of cases). They develop if bile enters the stomach. The cause of reflux gastritis can be inflammation of the duodenum or surgery to remove part of the stomach.
- Special forms (less than 1%). These include Crohn's disease, radiation, eosinophilic and other types of gastritis.
Important! The development of hCG is facilitated by the absence of teeth, foci of chronic infection in the oral cavity and pharynx (caries, inflamed tonsils), smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, stress, serious injury or surgery.
There are many classifications of gastritis: by localization (gastritis of the body of the stomach, antrum of the stomach, fundus of the stomach, pangastritis), by the degree of tissue damage (superficial, gastritis with damage to the glands without atrophy, atrophic, hypertrophic gastritis).
Treatment of gastritis and special nutrition for gastrointestinal diseases
To treat gastritis, your doctor may prescribe the following medications:
- Antibiotics that act on the bacteria that provokes the development of gastritis;
- Medicines that reduce the amount of hydrochloric acid secreted and thereby normalize the acidity of the stomach;
- Prokinetics, which help a sore stomach digest food gently and quickly;
- Medicines that neutralize excess hydrochloric acid and help relieve symptoms of gastritis (pain, heartburn).
In order for the effect after treatment to be long-lasting, it is important to adjust your diet and stick to the diet even after the acute phase of inflammation has passed.
The menu should include simple and healthy products: boiled meat, cereals, fermented milk products (if your doctor allows it). Chemical food additives, processed foods, and alcohol will have to be avoided so as not to provoke a new attack of stomach pain.
Other preventive measures will also be beneficial: stop smoking, move dinner to an earlier time, etc.
Why is gastritis dangerous?
Left unattended, gastritis can develop more and more severe consequences. Over time, the superficial inflammatory process can cause deep tissue damage - erosions and ulcers, which can lead to life-threatening gastric bleeding. Certain strains of Helicobacter significantly increase the risk of developing stomach cancer. The same complications occur in patients with chemical gastritis. Autoimmune gastritis is more characterized by mucosal atrophy and pernicious anemia with vitamin B12 deficiency.
Symptoms
Gastritis pain appears during an exacerbation of the disease.
Photo: Fantastic Studio / freepik.com For many people, gastritis occurs with virtually no symptoms.
Obvious signs of the disease usually appear in the acute phase (Table 1). In this case, the leading symptom of gastritis is pain in the upper third of the abdomen (in the pit of the stomach): dull, burning, aching, gnawing, sucking, sharp. Table 1. Symptoms of chronic gastritis in the acute phase and in the remission phase
| Chronic gastritis without exacerbation phase | Chronic gastritis in the acute phase |
| Mild pain in the epigastric (epigastric) region | Pain in the epigastric (epigastric) region of varying intensity |
| Feeling of fullness, distension and heaviness in the stomach after eating | Feeling of fullness in the stomach |
| Attacks of nausea | Nausea |
| Belching of air or food eaten | Belching |
| Heartburn | Unpleasant taste in the mouth |
| Unstable stool (alternating constipation and diarrhea) | Drooling after eating |
| Bloating | Vomiting, which provides temporary relief |
| General weakness, headache, temperature may rise to 37.5 degrees | |
| Symptoms are clearly expressed 2-3 hours after eating |
Important! If you find at least some signs of hCG, consult a doctor. Before the examination, it is not recommended to use heating pads, enemas, or take medications.
Duration of exacerbation of gastritis
The duration of exacerbation of gastritis is estimated by the strength of the symptoms. The period of exacerbation can last up to a month, provided proper treatment and diet are followed. If treatment and diet are violated, the exacerbation is delayed for an indefinitely long time.
Exacerbation of chronic gastritis occurs in a similar way: it all begins with bloating and slight pain, then fullness after a small portion of food, belching, and a change in the consistency of bowel movements are added. It is already becoming clear that digestion is impaired. Then the attacks begin. In acute gastritis, they last a little more than an hour; in chronic gastritis, they can last throughout the day.
Clinical examination is carried out after an exacerbation once every 2 months (3 times), then every 3 months for 3 years, then every six months. In spring and autumn, treatment is carried out with courses against seasonal exacerbation.
Seasonal exacerbation of gastritis occurs due to the body adjusting to the rhythm of life familiar in the fall: vacations end, hard work begins, depression appears due to a lack of vitamins and sunny days, nutrition changes, and it is not always possible to eat on time. With the beginning of summer, nutrition normalizes, berries and fruits ripen, and the symptoms of exacerbation disappear.
Diagnostics
Gastritis is much easier to treat if it can be diagnosed in the early stages of the disease.
Who to contact
Gastroenterologists, doctors specializing in diseases of the digestive system, are responsible for the diagnosis and treatment of chronic gastritis. Gastritis often becomes an accidental finding during a routine examination or search for other diseases. Gastroenterology is a broad branch of medicine that requires the doctor not only highly specialized training, but also interdisciplinary knowledge and good erudition.
What tests should I take?
The classic method for diagnosing gastritis is gastroscopy (esophagogastroduodenoscopy, endoscopy), which is combined with a biopsy if a malignant process is suspected. During the procedure, a special device is inserted into the patient’s stomach through the mouth - a gastroscope, consisting of a long tube with a built-in camera. It allows the endoscopist to examine in detail the condition of the mucous membrane of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum (Fig. 2).
Figure 2. Performing gastroscopy. Photo: CC0 Public Domain
Since most cases of CG are associated with the presence of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori in the body, when gastritis is detected, a urease breath test is often performed (for the enzyme urease secreted by Helicobacter), as well as a blood test for antibodies to this bacterium or a stool test for the presence of its antigens in it.
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging help answer the question: is it really gastritis and does the patient have stomach cancer (Fig. 3).
Figure 3. Gastritis detected on tomography. Photo: Eigenes Werk
How to detect gastritis: diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of gastritis begins with a consultation with a gastroenterologist. In a conversation with a specialist, it is important to describe your complaints in detail and answer all questions about lifestyle, eating behavior, etc. This will help the doctor preliminarily determine the cause of poor health and pain.
To clarify the diagnosis and make sure that it is gastritis that needs to be treated, a specialist may prescribe:
- Gastroscopy;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- Tests of urine, feces, blood for various indicators;
- Test for the bacterium H. Pylori.
Only based on the results of the study will the doctor prescribe suitable medications and select non-drug treatment methods (including diet).
Treatment
Treatment is always selected individually depending on the type of gastritis and its cause. Timely treatment can reduce symptoms, if present, and reduce the likelihood of complications.
Medicines
Drug treatment of chronic gastritis can be symptomatic or etiological - aimed at eliminating one or another cause of the disease. If H. pylori is detected in a patient with gastritis, eradication therapy is used to destroy it. In particular, the “French method” is popular today, which involves a combination of three drugs - two antibiotics plus a proton pump inhibitor. Unfortunately, it is impossible to eliminate the infection forever; after some time, the harmful microorganism again enters the body from carriers, in particular, from the patient’s relatives. Helicobacter very quickly becomes resistant to drugs, so the same antibiotics cannot be prescribed all the time.
With chemical gastritis, it is enough to eliminate its cause. For example, stopping taking medications whose side effects caused the disease. If it is not possible to refuse such a medicine, measures are taken to protect the stomach with the help of coating agents and drugs that regulate the acidity of gastric juice. The use of antacid (anti-acid) drugs helps restore damaged mucosa. It must be remembered that with the disappearance of the acid, its powerful antibacterial function disappears.
The selection of therapy for autoimmune chronic gastritis depends on the severity of inflammation. Basically, the use of medications is aimed at reducing the acidity of gastric juice. These are proton pump inhibitors, antacids and antihistamines.
Nutrition
Chronic gastritis cannot be overcome with medications alone. Radical changes are required in the patient's lifestyle, diet and diet. Therefore, already at the first appointment, the gastroenterologist necessarily recommends a certain type of diet depending on the acidity of the gastric juice: if it is low, you need acidic (berries, fruits) and juice products, if it is high, you need those that reduce the production of hydrochloric acid.
Let us highlight products that are incompatible with the treatment of gastritis and are strictly contraindicated:
- Spices and seasonings, especially hot ones.
- Fat meat.
- Any fried food.
- Smoked and canned products.
- Concentrated fruit and berry juices, especially those with a high content of acids and sugars.
- Carbonated drinks.
Important ! It is recommended to limit the consumption of confectionery products (never eat them on an empty stomach!), rye bread, fresh wheat pastries, strong tea and coffee.
There are quite a few approved foods for gastritis. By consuming them, you can easily create a varied and complete diet. Patients with gastritis are shown:
- Dairy products.
- Stale yeast bread.
- Lean meat, fish, soft and semi-hard cheeses.
- Soft-boiled eggs and omelet.
- Boiled cereals.
- Puree soups.
- Boiled and baked vegetables, fruits.
Diet for patients with chronic gastritis
Photo: natabuena / freepik.com
A diet for chronic gastritis is aimed at developing favorable microflora in the gastrointestinal tract that regulates digestion and has a protective function. Meals should be fractional: regular meals 5-6 times a day. You should choose dishes that are boiled or steamed. Preferably boiled or baked meat, fermented milk products, high-fiber cereals, boiled or baked vegetables (Table 2).
The main amount of food should be consumed in the first half of the day.
It is necessary to avoid “snacks” of high-calorie foods and eating sweets on an empty stomach. Table 2. Dietary recommendations for patients with chronic gastritis
| Gastritis with low acidity | Gastritis with high acidity |
| Healthy | |
| lean meat, fish, poultry; boiled, chopped, baked or lightly fried without breading in breadcrumbs or flour | whole milk (reduces the production of gastric juice) after meals. If the patient does not tolerate it well, you can add milk to tea |
| soups: meat, fish, mushroom, vegetable, cereal | cream, low-sour cottage cheese |
| whole milk only in dishes and drinks (porridge, cocoa), fermented milk products, cottage cheese, soft-boiled eggs, omelet | boiled, stewed, baked vegetables |
| well-cooked porridge, boiled pasta | all porridges, except millet, pasta |
| toasted white bread | lean meat, lean fish and poultry |
| non-acidic varieties of apples, pears, bananas | |
| white bread, preferably not too soft | |
| Provokes exacerbation | |
| spicy, salty, fried foods | juice products |
| canned meat and fish | strong and fatty broths - meat, fish and especially mushroom |
| soft bread and other fresh products made from yeast dough, baked goods | raw vegetables, pickles, marinades, spicy vegetable snacks, smoked meats |
| pastry, pies, brown bread | |
| ice cream, cold drinks | |
| sour juices, black bread | |
Aids
The most recommended home remedy to alleviate the disease is a decoction of chamomile. Among plants exotic to our nature, aloe juice is used as a strong anti-inflammatory agent. Oat infusion is also useful for chronic gastritis, helping to restore the affected mucous membrane. Of course, traditional methods of treatment cannot replace qualified medical care and therapy.
Gastritis in children
Children usually get gastritis at school age due to irregular and irrational nutrition; there is even a diagnosis - “school gastritis”. Treatment in this case is aimed not only at getting rid of the disease, but also at developing healthy eating habits.
Gastritis and pregnancy
Difficulties in treating gastritis in pregnant women are associated with the possible effects of the medications used on the fetus. When selecting therapy, you have to weigh the possible benefits of the medication and the harm it can cause. This primarily concerns antibiotics, many of which are strictly contraindicated during pregnancy. Proton pump inhibitors are harmful during pregnancy.
Treatment for exacerbation of gastritis
The symptoms of the disease are similar to those of other diseases; it is better to consult a gastroenterologist to make a diagnosis, do not advance the course of the disease and strictly follow the instructions by taking medications and following a diet.
The duration of exacerbation of gastritis depends on the patient and a good doctor who has prescribed a suitable course of treatment.
Drug therapy
Drug therapy is carried out comprehensively. It will be necessary to eliminate the symptoms, find the cause and eliminate it in order to prevent remission of the disease.
If Helicobacter Pylori bacteria are the culprit of the disease, treatment is carried out in four directions:
- Antibacterial. Antibiotics in combination with De-Nol help cope with the disease.
- Regulating acidity. For high or normal acidity, acid and alkali neutralizers are used. If acidity is low, it is recommended to take artificial gastric juice.
- Protecting the gastric mucosa, enzymes are used to restore it.
- Symptomatic (antidiuretics, analgesics, antispasmodics, carminatives, antiemetics).
When choosing drugs for treatment, the main thing is that the patient does not have allergic reactions to the drug. If allergies cause gastritis, you will need to take antihistamines. After recovery, it is recommended to take probiotics to normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
The course of treatment is carried out at home, under the supervision of a doctor, for 2-3 weeks.
Folk recipes
To relieve symptoms during exacerbations, the secrets of traditional medicine are used. The course of treatment lasts up to two months.
Usually, decoctions and herbal infusions are used, which are taken 20 minutes before meals four times a day, a third of a glass. Herbs and berries are poured with boiling water and left overnight.
There is a division into infusions suitable for gastritis with low acidity and for gastritis with high acidity. To reduce gastric secretion, take elecampane, chicory, lingonberry and wormwood. For increased levels - celandine, mint, trifoliate leaves, yarrow, St. John's wort, dill seeds, licorice root, chamomile, honey, potato juice.
- Sea buckthorn oil reduces pain. You need to drink it half an hour before meals.
- Carrot juice relieves inflammation and reduces acidity. You need to drink freshly made food.
- Chicory decoction relieves the first symptoms of gastritis.
- Licorice reduces stomach acidity.
- Aloe is an excellent antiseptic and heals wounds.
- Calendula will help cope with gastritis that has developed due to the activity of Helicobacter Pylori bacteria.
- Sage will help cope with inflammation and bloating.
You cannot go on a diet, but a method of treating hunger is known; it should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor. The theory is expressed that during fasting the body is cleansed, the gastric mucosa is renewed, and the process takes place in 3 weeks.
Forecast
As a rule, the prognosis for gastritis is positive. Among patients who only go to doctors, many people do not experience any symptoms.
Treatment of any chronic disease is a long-term struggle with varying success. A chronically ill person cannot stay in the hospital for the entire period of illness. Life conditions are constantly changing, and success in treatment depends on this. A key role can be played by a meeting with a truly professional and competent doctor who is willing and able to find and eliminate the cause of the disease.
Prevention
Prevention of chronic gastritis involves preventing factors that can cause damage to the mucous membrane. These are hygienic measures against Helicobacter infection: thoroughly washing dishes, using each family member’s own cups, plates and cutlery. Care must be taken when handling medications and chemicals that are potentially harmful to the health of the digestive system.
If you do get gastritis, it is important to take timely measures to prevent it from becoming chronic. The main goal of prevention in this case is to maintain a favorable microbiome (microflora) of the digestive tract.
To prevent the development of the disease you should:
- eat often in small portions;
- avoid foods that may irritate the stomach;
- reduce or eliminate alcohol consumption;
- quit smoking;
- avoid stress.