Prices
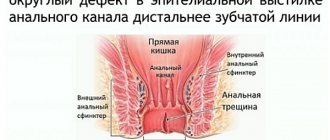
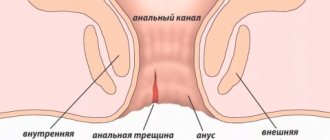
An anal fissure is a pathological damage to the mucous membrane of the anal canal (anodermis). A straight or ellipsoidal tear is localized in the area of the anus and has a longitudinal location - the tissue is damaged in the direction of the folds of the anal canal. There are 2 areas where damage is most likely to occur:
- the back of the wall of the anal sphincter (the area closer to the tailbone);
- the anterior surface of the anus (from the point of articulation with the genitals).
In some cases, a mirror-like anal fissure is observed, which continues on both the anterior and posterior walls of the sphincter in a mirror-like manner.
Anal fissure is a coloproctological disease, which in terms of the frequency of clinical cases is second only to hemorrhoids.
The course of the pathology is classified as acute or chronic, depending on the depth of damage and the timing of tissue healing:
- Acute rupture. Occurs due to a traumatic effect on tissue, heals independently (no longer than 30 days), without the formation of scar tissue.
- Chronic fissure. It is characterized by the presence of constant erosion of the mucosa, with the gradual formation of scarified scar tissue along the longitudinal edges of the open wound surface and a sentinel tubercle on one or both apexes of the wound.
The chronicity of the process is explained by the localization of the rupture. The natural tone of the sphincter and painful spasm lead to “retraction” of the mucous membrane, the folds of the anus tighten and hide the eroded area. With limited access, long-term inflammation develops, causing increased erosion of the anoderm.
How does an anal fissure appear?
The main symptom is pain, so it is difficult to ignore an anal fissure. Painful sensations can be of varying intensity, most often intensify during defecation, and gradually subside after it. The pain can be so severe that it makes you afraid to go to the toilet. Sometimes people with an anal fissure stop eating food because of this fear, hoping that this will delay the moment of defecation. This tactic often backfires.
In some situations, if you do not contact a coloproctologist for treatment for a long time, the intensity of the pain becomes so severe that it becomes painful to sit and walk. Most often this happens if an infection occurs.
There may be a feeling of “stiffness” in the anus, a foreign body in the anus.
Another equally frightening symptom is bleeding. Blood from an anal fissure is often bright red in color, may come out in drops or simply leave red marks on toilet paper. Sometimes traces of such blood can even be seen on underwear.
The appearance of blood, pain and any other unpleasant sensations in the anus should alert you. If you have the complaints noted above, you should immediately contact a specialist, since the sooner treatment is started, the faster it will be possible to get rid of the anal fissure completely.
What can an anal fissure be like?
Depending on the duration of the course, the crack can be acute or chronic.
Depending on the cause of development, primary and secondary anal fissure are divided.
Depending on the location in the anal canal, the fissure can be anterior, posterior, or lateral.
The diagnosis of acute anal fissure is established if a person consults a specialist immediately after the occurrence of unusual symptoms. In most cases, an acute crack can be called a process that lasts no more than 4-6 weeks. Such a crack is a thin defect of the mucous membrane, sharply painful when touched. There are usually no other changes in the anal canal with an acute fissure.
Rice. 1. Acute posterior anal fissure
If you do not start treating an anal fissure in a timely manner, then most likely it will become chronic, however, with properly selected conservative treatment, you can do without surgical treatment.
A chronic anal fissure occurs when a patient suffers from an acute anal fissure for a long time. Constantly occurring inflammation leads to thickening of the wound edges, which makes conservative therapy unsuccessful.
We can talk about a chronic fissure when there are at least two of the following symptoms: 1) pain after defecation, lasting more than three months; 2) the presence of secondary changes; 3) increased sphincter tone.
Rice. 2. Chronic posterior anal fissure (scarred edges are identified, which indicates a long course of the disease)
Anal fissure: symptoms, causes and treatment from experienced doctors at the MEDSI clinic
Table of contents
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Anal fissure in children
- Chronic fissure
- Consequences (complications) of anal fissures
- Diagnostics
- How to treat anal fissure?
- Prevention
- Advantages of treatment at MEDSI
An anal fissure (anal fissure) is a tear in the lining of the rectum. As a rule, pathology develops in people who suffer from chronic constipation or lead a sedentary lifestyle. Fissures are diagnosed in approximately 20% of patients who consult a doctor with the problem of discomfort in the rectal area. The pathology can be either independent - arising from exposure to traumatic factors, or secondary - a consequence of a number of concomitant diseases (external hemorrhoids, peptic ulcers, disorders of the gastrointestinal tract).
Causes
An anal fissure is caused primarily by trauma to the rectum or constipation and hemorrhoids.
Damage may result from:
- Gastritis, peptic ulcer, colitis
- Congestion in the rectum and pelvis caused by disruption of the cardiovascular system
- Pregnancy during which the uterus puts excessive pressure on internal organs
- Childbirth associated with prolonged pushing
Don't think that an anal fissure will heal on its own. If the patient does not change the nutritional system and eliminate traumatic factors, nothing will change. In addition, acute pathology often becomes chronic. In this case, the patient suffers from severe discomfort and often experiences not only physical, but also psychological problems. If you contact a specialist immediately after detecting signs of pathology, treatment will be carried out quickly using conservative methods. In advanced cases, treatment of chronic anal fissure is often only possible through surgery.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of anal fissure that require consultation with a doctor and treatment are:
- Discomfort after defecation
- Pain
- Minor bleeding
Over time, these symptoms are often accompanied by:
- Sphincter spasm
- Unpleasant sensations when sitting
- Constipation
The patient becomes irritable, sleeps poorly, and fears bowel movements.
Anal fissure in children
Children suffer from anal fissures less often than adults, but in some cases the pathology occurs even in newborns. To prevent the disease from becoming chronic and causing complications, treatment should be started as early as possible. Any self-medication is strictly prohibited, since it only relieves symptoms, but does not eliminate the problem, starting the course of the pathology.
Young children cannot report signs of pathology to adults, so you should monitor:
- Baby's behavior when excreting feces
- Stool density
- Child's behavior before going to the toilet. Children often become irritable and nervous and do not want to sit on the potty.
If a child cries before and during bowel movements, is afraid of going to the toilet, or suffers from constipation, you should definitely consult a doctor.
Chronic fissure
The acute form of anal fissure often becomes chronic. Especially often, pathology develops rapidly in the absence of adequate therapy. It develops into a chronic form mainly in women who have recently given birth. This is due to physiological changes in the body of a young mother. With pathology, the patient suffers not only during bowel movements, but also after it, with prolonged sitting and walking. Constant discomfort, itching and bleeding are added to the standard symptoms. The process is often aggravated by self-medication, taking laxatives, using suppositories and enemas.
Consequences (complications) of anal fissures
If an anal fissure is not treated, the following complications arise:
- Constant bleeding
- Infectious processes in the intestinal mucosa
- Prostatitis
- Rectal fistulas
- Colitis
- Acute paraproctitis
All of them are dangerous not only for health, but also for the life of the patient, and also lead to the development of a number of psychological problems.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, a comprehensive examination of the patient is performed.
It includes:
- Examination of the anus
. An anal fissure is diagnosed fairly quickly, as the mucous membranes lose their integrity and become swollen - Finger examination
. With such a study, the proctologist can determine the size of the crack and feel its edges - Sigmoidoscopy
. Allows you to examine the rectum to a depth of 20 centimeters
Laboratory diagnostics, colonoscopy and irrigoscopy may also be prescribed.
How to treat anal fissure?
Conservative therapy
Treatment of anal fissure is always carried out comprehensively. It is important to eliminate not only the symptoms of the pathology, but also its cause. The underlying disease must be eliminated. Treatment will be useless if the patient suffers from constipation and hard stool constantly damages the anus.
Typically therapy includes:
- Treatment of the anus with emollient compounds
- Relaxation of anal muscles in warm baths
- Preventing constipation
- Using ointments and suppositories for pain relief, wound healing and inflammation relief
Treatment is determined by the form of the pathology, the factors that provoked its development, and the individual characteristics of the patient. It can only be prescribed by a doctor after a comprehensive diagnosis.
Surgery
Surgical interventions are resorted to when conservative therapy does not give the desired result.
All methods used are divided into 2 types:
- Minimally invasive
. Usually the crack is removed using a laser. Its edges are simply sealed. Recovery after such an intervention does not take much time. Within a few days the patient returns to his normal lifestyle and does not experience discomfort. - Standard
. The sphincterotomy technique is used. During this intervention, the doctor makes an incision and separates the layers of sphincter muscle. Thanks to this, the existing spasm is eliminated, which allows you to reduce tension during bowel movements. Also, suturing of the walls and excision of the mucous membranes on which scars have appeared are carried out.
The choice of surgical intervention technique is made by the doctor.
Prevention
There is a set of preventive measures to prevent the formation of an anal fissure.
This includes:
- Healthy lifestyle. You should completely stop smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages, eating fatty, fried and salty foods, which stimulate problems in the cardiovascular system and digestive tract. It is important to consume foods rich in fiber, vitamins and valuable microelements in sufficient quantities.
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules. You should wash regularly and prevent the development of inflammatory and infectious processes.
- An active lifestyle, including regular, but not excessive or tiring physical activity. It is enough to walk at least 20-30 minutes a day
- Proper drinking regime. You need to drink at least 1.5-2 liters of fluid every day
- Avoiding eating foods that are too hot or cold
It is important not to restrain the urge to defecate and promptly treat any diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Advantages of treatment at MEDSI
- Use of current treatment methods. Our clinics use drug blockades, excision of anal fissures and other procedures and interventions.
- Experienced doctors. MEDSI proctologists constantly improve their qualifications and master modern methods of conservative therapy and surgical interventions
- Comfortable conditions. All examinations and treatment are carried out by experienced specialists whom our patients trust. There is no fear or embarrassment during the procedures
- No queues. You can consult a doctor at a convenient time
- Compliance with confidentiality rules
If you want to make an appointment with a proctologist at MEDSI, call +7 (495) 7-800-500.
What may be secondary changes in chronic anal fissure?
— sentinel tubercle (shown in the photo)
— skin fold (shown in the photo)
- fistula (shown in the photo)
Rice. 3. Anal fissure with the formation of a fibrous polyp similar to the hypertrophic anal papilla
Rice. 4. Progression of an anal fissure with the formation of a skin fold
Rice. 5. Anal fissure with the formation of a secondary fistula tract
If an anal fissure develops in a patient due to dense stools, frequent loose stools, anal sex or the use of sex toys, then it will be classified as a primary anal fissure. And if an anal fissure occurs in a patient who suffers from other diseases, such as anal cancer, cicatricial stricture of the anus, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, HIV, then we will classify it as a secondary anal fissure.
Based on location, cracks are divided into three types:
Rice. 6.
How do they occur and in whom are they more common?
Anal fissure is not only a medical, but also a social problem, as it causes discomfort to the patient. Fissure occurs equally often in both men and women.
Despite the long study of this disease, the exact etiology of anal fissure remains unknown.
The occurrence of anal canal fissures can be caused by defecation disorders (chronic constipation, diarrhea), mechanical injuries of the anal canal (anal sex, sex toys, etc.).
The onset of the disease is most likely caused by mechanical damage, which injures the mucous membrane of the anal canal.
There is a theory that the occurrence of a posterior anal fissure is associated with the peculiarity of the blood supply to the anal canal.
Against the background of the development of pain, the tone of the anal sphincter increases, which leads to a subsequent increase in muscle pressure of the anal sphincter.
Severe pain can be caused by excessive persistent contraction of the internal anal sphincter, leading to blockage of the vessels, which does not allow the fissure to heal on its own.
Pain is followed by spasm, spasm is followed by pain, and this is how a “vicious” circle develops with an anal fissure.
Rice. 7.
What is required for differential diagnosis of this disease?
A fissure can occur with inflammatory diseases of the colon, such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis. Infectious diseases (syphilis, HIV, herpetic infection, etc.) can also contribute to the development of anal fissure. Tumor diseases such as cancer, melanoma, leukemia can manifest themselves in the same way as an anal fissure. The patient will experience pain in the anus and bleeding from the anus.
Rice. 8. Cancer of the anal canal with transition to the perianal skin
Types and symptoms
There is no clear classification of rectal mutilation. It is customary to distinguish two main types:
- Peacetime injuries
that a person receives in the industrial or domestic sphere, as well as during sports; - Wartime injuries
due to gunshot wounds.
In each individual situation, the damage can be localized to the outer and mucous membrane of the intestine.
Diseases and injuries of the rectum are accompanied by intense symptoms. With injuries to muscle tissue or mucous epithelium, the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- sharp pain in the anorectal area, lower abdomen;
- bleeding from the anorectal area and blood in bowel movements;
- false urge to bowel movement;
- secretion of pus or feces, as well as gases from the wound;
- inflammation or infection.
Gunshot wounds can allow air and feces to enter the abdominal cavity.
At CELT you can get a consultation with a proctologist.
- Initial consultation – 3,000
- Repeated consultation – 2,000
Make an appointment
What tests do you need to undergo to start treatment?
Patients with an anal fissure are advised to undergo a colonoscopy and laboratory tests to clarify the cause of the disease. After all, if the crack is not an independent disease, then treatment of the crack may be ineffective.
There are cases when it is difficult to differentiate a disease without histological examination (taking a section of tissue to determine whether tissue cells are benign or malignant).
At KKMH (Clinic of Coloproctology and Minimally Invasive Surgery) you can undergo a full range of examinations that will help establish an accurate diagnosis.
A colonoscopy can be performed the next day after visiting a coloproctologist.
- Why not right away? - you ask.
The answer is simple:
— Because the study requires preparation (intestinal cleansing).
We will tell you how and how best to prepare for this study.
Laboratory tests are possible on the day of treatment (not always, because for some indicators you need to be on an empty stomach).
If you have diseases that require referral to related specialists, they will help you choose a doctor and make an appointment with him.
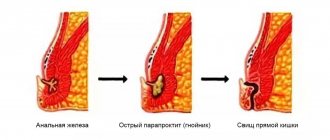
Proctitis
There are two groups of factors that cause the development of the disease - general and local. Local damaging factors include mechanical injuries, the introduction of chemicals, hot or cold solutions into the rectum, the transfer of infection from nearby organs, as well as neoplasms of the rectum. Proctitis can be caused by mechanical injuries during unqualified massage or self-massage of the rectum and prostate gland, homosexual sexual intercourse and the introduction of various objects into the rectum for the purpose of arousal and satisfaction.
Proctitis, caused by exposure to irritating chemicals, hot and cold solutions, usually occurs when trying to treat with “folk remedies”, improper or excessive use of enemas, rectal suppositories, etc. As “folk remedies” that provoke the development of proctitis, can be used alcohol, turpentine, essential oils (clove, eucalyptus, peppermint oil), iodine solution, concentrated calcium chloride solution, mustard and capsicum tinctures. All of these substances have an irritating effect, and patients often use them to treat hemorrhoids, anal fissures and other diseases, which aggravates the existing pathology and causes the development of inflammation of the mucous membrane.
Proctitis can also occur when infection spreads through contact from an inflamed vagina, urethra, bladder or perirectal tissue. Along with nonspecific infectious agents, the causative agent can be gonococci, chlamydia, trichomonas, etc. In patients suffering from cancer, the cause of proctitis can be disintegrating malignant tumors of the rectum and other perineal organs.
In the list of common causes of proctitis, experts include nutritional disorders, gastrointestinal infections, parasitic diseases, autoimmune diseases, disorders of motility, innervation or blood supply to the lower intestine, and radiation exposure. The disease is more often diagnosed in people who abuse alcohol, spicy and spicy foods. Proctitis can be detected in infectious diseases such as salmonellosis, dysentery and escherichiosis, as well as in enterovirus infection. With a protracted course of the listed diseases, proctitis is provoked not only by direct contact of pathogens with the rectal mucosa, but also by prolonged diarrhea, the release of toxins and other general causes.
In the list of autoimmune diseases that affect the colon and can cause proctitis, scientists include Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, amyloidosis and Whipple's disease. The list of parasitic diseases includes giardiasis, amoebiasis, enterobiasis and ascariasis. In people who have recently visited the tropics, the provoking parasitic disease can be American trypanosomiasis, but in Russia such cases are rare.
Proctitis is often diagnosed in patients with colon dyskinesia and irritable bowel syndrome, as well as in patients who have undergone surgery on the pelvic organs or suffer from chronic circulatory disorders in this area. The likelihood of developing proctitis increases with diseases of the pancreas, liver and gallbladder. Another reason for the development of proctitis is irradiation during the treatment of malignant neoplasia of the pelvic organs, most often uterine cancer and cervical cancer. The likelihood of developing a disease directly depends on the radiation dose.
How is the initial consultation with a coloproctologist?
When applying for an appointment, no complex special preparation is required, which can take you out of your normal daily routine.
The doctor will listen to you, ask you about your complaints, how long the disease has been, and then conduct an examination.
The examination in our consultation room is carried out in the supine position with the legs raised on supports (lithotomy position).
On the eve of the consultation, it is necessary to make a microenema and perform hygiene of the perineal area.
After the examination, a specialist doctor will tell you about your disease, prescribe additional examinations if necessary and suggest the most optimal treatment method.
Diagnosis and treatment
Primary diagnosis includes measures to collect the patient’s medical history, determine the circumstances of the injury, as well as a physical examination. The examination is carried out in a gynecological chair in a knee-elbow, lateral position or on the back.
The next stage of diagnosis involves an integrated approach:
- Clinical urine analysis;
- General and biochemical blood test;
- Hemostasiogram;
- Blood sampling to determine the group and Rh factor;
- Rectal examination of the rectum;
- X-ray examination;
- Ultrasound;
- Anoscopy and laparotomy of the rectum;
Based on the diagnostic results, test results, as well as the anatomical features of the patient’s body and the nature of the rectal injury, the doctor may prescribe a consultation and examination by other specialists, and additional examination.
The type and extent of injury, the condition of the organ and the general well-being of the patient determine the choice of treatment tactics. Treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis and poses the following tasks:
- limit the penetration of intestinal contents into the area of injury and beyond the boundaries of the abdominal area;
- treat damaged rectum;
- restore the anatomical structure and integrity of the organ;
- drain the damaged area, free it from feces and foreign objects (if any);
- restore regular bowel function.
The process of performing therapeutic measures is accompanied by compliance with a special diet, which involves excluding baked goods, lard, fatty meats and fish, fried, spicy and salty foods, and dairy products from the diet.
Food may include bread made from wheat and rye flour, dietary meats, fish and poultry, sausage, fruits, vegetables, low-fat broths, juices, tea and coffee drinks, herbal infusions, as well as jam, honey, mousse and jelly.
Treatment of anal fissure
The treatment strategy is aimed at the cause of the anal fissure.
The treatment of anal fissure is based on the creation of favorable conditions for the healing of the defect in the anal canal mucosa.
In most cases, treatment begins conservatively, this is due to the fact that the correct use of multicomponent conservative therapy leads to complete healing of an acute anal fissure in 90% of cases.
In the arsenal of a coloproctologist for the treatment of fissures, there is a fairly wide range of drugs that will help us cope with the disease together with you. All these drugs are available to patients at pharmacies without a prescription.
Such drugs include:
1) calcium channel blockers: relax the internal anal sphincter, which promotes the healing of fissures.
2) topical nitrates: their use leads to relaxation of the sphincter, which promotes healing.
3) regenerative therapy promotes wound healing by increasing cell growth.
4) also, currently, sphincter relaxation with the help of Botox drugs is widely used. Causes relaxation of both the external and internal anal sphincter, the relaxation effect lasts up to 3 months.
The first case of treatment of anal fissure using botulinum toxin was described in 1993. Since then, this technique has been used relatively often with good effect.
Conservative treatment continues for 2-3 weeks with monitoring of the patient’s condition once every 7-10 days. If positive dynamics are noted, then treatment can be continued for another 2-3 weeks.
Rice. 9. Chronic anal fissure before conservative treatment (at the time of contacting the clinic)
Rice. 10. Chronic anal fissure after 2 weeks of conservative treatment
In patients who have secondary manifestations of the fissure, such as the "sentinel" tubercle, skin fimbria, conservative treatment is not always effective, but conservative treatment can be attempted.
If a patient is diagnosed with a secondary manifestation such as rectal fistula, then conservative treatment becomes ineffective in 100% of cases and the patient will be recommended for surgical treatment.
Rice. 11. Chronic posterior anal fissure, complicated by the development of rectal fistula
The presence or absence of these changes will be confirmed or denied by the coloproctologist at the first appointment.
If conservative treatment is unsuccessful or secondary manifestations are present, various surgical techniques are used to treat chronic anal fissure.
Treatment and prevention
The approach to conservative treatment of anal fissure includes the use of medications. However, in case of severe damage, medical intervention cannot be avoided. Only a doctor can perform excision of an area of mucous membrane with chronic erosions or laser vaporization of an anal fissure.
Medical provides affordable medical services and helps to cope with even the most delicate problems. Specialists at the coloproctology center use innovative techniques that quickly relieve pain and restore damaged tissue. During the examination and treatment procedures, special attention is paid to the patient’s comfort.
Surgery
Excision of anal fissure
Using a scalpel, laser or electrocoagulation, the altered tissue of the anal canal is removed (removal of fissures, hypertrophied anal papillae, skin fimbriae, as well as fistulas, if any). A triangular tissue incision is formed in the perianal area, which allows for wound drainage. The wound is not sutured, it is left open, this promotes better healing and reduces pain in the postoperative period. The use of this technology results in a very low relapse rate.
Mandatory for this treatment is strict adherence to postoperative recommendations using drugs for medical sphincterotomy.
Sphincterotomy
Partial dissection of the posterior portion of the internal sphincter with the intention of reducing the tone of the anal sphincter, because according to many authors, an increase in the tone of the internal anal sphincter explains the pathogenesis of the anal fissure.
The disadvantage of this method is a persistent deterioration in holding function. Unnoticeable in the first years after surgery, but which can manifest itself at a later date.
Contraindications
Sphincterotomy is contraindicated in patients who suffer from fecal incontinence (inability to retain gases or feces).
Preoperative anorectal manometry provides information about possible sphincter muscle deficiencies. This examination is recommended for older people and patients who practice anal sex.
Sphincterotomy methods
Open lateral sphincterotomy
Sphincterotomy is performed from the anal canal. To carry it out, an anal retractor is inserted into the anal canal, then an arcuate incision is made along the left semicircle (from 2 to 4 o’clock). The incision is wide enough to visualize the internal sphincter. Using surgical scissors, the internal anal sphincter can be cut at its distal portion (open technique). Thus, the risk of injury to the anoderm is minimized. The size is closed with a suture.
Closed lateral sphincterotomy
A small radial skin incision is made on the anal edge at 3 o'clock on the conventional dial using a scalpel. This cut can also be made using scissors. The scalpel is moved forward in a flat direction, then it is rotated 90°, perpendicular to the internal anal sphincter.
The operation is performed under the control of the index finger inserted into the anal canal (closed technique). This can prevent unintentional damage to the rectum.
Rectal injury with subsequent fistula formation is considered a technique-dependent complication. Control with the index finger inserted into the anal canal should prevent this complication.
Anoplasty (excision of a fissure with the formation of a flap)
This method of surgical treatment differs from simple excision of an anal fissure in that the formed flap allows the wound to heal by primary intention.
It is used for wide defects in the anal canal mucosa. Delayed surgical intervention in such cases leads to cicatricial stenosis of the anal canal, due to wound healing by secondary intention.
The mucocutaneous flap is moved to the area of the crack, the bottom and edges of which are previously cleared of scar tissue, then the flap is fixed with sutures.
Manual anal dilatation (devulsion)
Used before. However, this method has shown that this technique leads to uncontrolled damage to the sphincter muscle fibers, which subsequently affects the function of holding.
Technique
The anal canal is stretched with your fingers for several minutes using general or local anesthesia.
We do not use manual anal dilatation to treat anal fissure due to high rates of incontinence.
Our clinic uses modern equipment for treatment.
Excision of the crack and secondary manifestations is carried out both with a laser and with the help of other instruments.
It is important not only to excise the fissure and secondary changes within healthy tissue, but also to avoid damaging the anal sphincter. After all, the anal sphincter is an important muscle component responsible for maintaining intestinal contents.
Rice. 12. Modification of the visual analogue scale, which is used in the clinic
Preparing for your first meeting with the doctor
If you have an anal fissure, you should seek medical help from a coloproctologist.
Our Clinic is open 6 days a week from Monday to Saturday from 8:30 to 20:00 (opening hours are subject to change).
Below is information that will help you prepare for your meeting with a specialist.
When you make an appointment, ask if you need to do anything in advance, for example, special preparation for the examination, how long before the appointment you need to come to the Clinic, because it will also take time to prepare a medical record for an inpatient.
To make the outcome of your visit to the doctor more effective, so that there are no unanswered questions, make a list:
- Your complaints.
- Your medical history (surgeries, chronic diseases, etc., even not related to the problem that is bothering you now).
- All medications, vitamins or other supplements you take.
- If you have a person whom you completely trust, then you can take him with you. So that it reminds you of the questions you wanted to ask.
Prepare questions for your doctor
Here are some basic questions to ask your doctor at your appointment if you do not get answers to them during the conversation:
- What could be the reason for my complaints?
- Are there other possible reasons for my complaints?
- Is there a need for tests and additional examinations?
- Is my condition temporary (acute) or chronic?
- Are there any dietary restrictions?
- Are there any restrictions that I must follow?
Feel free to ask any questions you have about your disease during your meeting with the doctor.