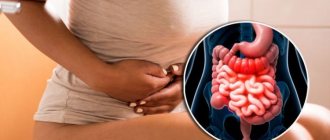
According to statistics, everyone has at least once experienced a feeling of heaviness in their stomach. What to do in such cases?
Painful feelings in the abdomen that many patients experience include belching air, heaviness in the stomach, and other uncomfortable sensations. All of them arise for two main reasons: due to an unbalanced diet or due to existing pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract. A gastroenterologist will help you get rid of this problem. You should not neglect a doctor’s examination, since illiterate therapy can only worsen the condition. But first of all, it’s worth understanding how heaviness in the stomach occurs after eating, the causes, and treatment.
How to recognize discomfort?
Bloating and heaviness in the stomach would seem to be understandable and familiar to many, but since they can arise for various reasons, they also have varying degrees of manifestation. For example, a feeling of fullness in the abdomen is common. The reasons are overeating and eating large amounts of food at one time. Among other things, patients experience other symptoms:
starts to feel sick;- the urge to vomit and vomiting appear;
- dyspnea;
- belching;
- heartburn;
- rapid change in body weight;
- increased sweating;
- changes in stool condition;
- pain in different parts of the abdominal cavity.
Depending on the factors that cause abdominal heaviness, symptoms may be short-lived. For example, take place several hours after eating. Some patients experience heaviness in the stomach 2 hours after eating.
If discomfort does not disappear for a long time, you should immediately contact a specialist. This may be a signal that more serious inflammation is developing in the body and organ pathologies are present. In this case, pain and heaviness in the stomach after eating require urgent treatment, because more severe symptoms may occur in parallel. For example, sharp and cutting pain that extends to the cervical region, jaw or even arms.
After eating, heaviness in the right hypochondrium and bloating may also develop. It is quite difficult to unambiguously describe the sensations that patients experience. Some people report a burning sensation and squeezing in the throat, while others compare this discomfort to a sore throat and difficulty swallowing. Along with heaviness in the stomach, belching may also appear. There are many reasons: problems in the functioning of the esophagus, hernia and other pathologies that require special research.
Heaviness in the right hypochondrium and bloating are also common symptoms. Heaviness and painful feelings appear in this area. They differ in intensity and localization. Such sensations usually occur due to diseases of the stomach and intestines, pathologies of the excretory system, appendicitis, gastritis and ulcers. In rare cases, such pain may be the result of gynecological diseases or ectopic pregnancy. But only a specialist can make a correct diagnosis by conducting the necessary laboratory tests.
Gallstone disease and chronic cholecystitis
With cholelithiasis, nausea and vomiting are observed.
Manifest in the form:
- nausea and vomiting of bile;
- belching with a bitter taste;
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- stool disorders;
- yellowness of the skin and eyeballs.
Liver cirrhosis or hepatitis. These diseases, caused by viral infections or alcoholism, can also have a negative impact on the gastrointestinal tract. Signs:
- dull pain in the right hypochondrium;
- jaundice and abnormal stool;
- with cirrhosis, there is also an expansion of the veins in the skin of the abdomen and an increase in its circumference (due to the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity).
Gastroenteritis or infection of the stomach or small intestine manifests itself in the form of nausea, repeated vomiting, fever and loose stools.
Poor appetite and heaviness in the epigastrium may persist for some time after recovery (from several days to several weeks).
Why do you feel a heaviness in your stomach?
Before starting therapy, you need to understand how and why heaviness in the abdomen appears. The reasons can be varied, but most often they are:
poor diet: frequent and quick snacks, abuse of junk food, carbonated drinks, predominance of carbohydrate foods, baked goods;- frequent overeating, especially before bedtime;
- eating a large amount of food at one time;
- violation of the diet (eating 1-2 times a day causes heaviness in the stomach after eating and belching);
- preparing dishes from inappropriate products that do not combine with each other and therefore affect the absorption of food;
- the use of exotic ingredients in cooking, which causes such a reaction in the body;
- excessive eating as a result of stress.
In addition, the feeling of a full stomach sometimes occurs due to the patient’s existing pathologies in the abdominal cavity. For example, gastrodiseases, pancreatitis, gallbladder pathologies.
Pregnant women also often develop heaviness in the abdomen after eating. The reasons for this are the load that the fetus puts on the stomach and other organs, high abdominal pressure over a long period of time, or the consequences of toxicosis.
Heaviness in the stomach in children
After eating, heaviness occurs not only in adults, but also in children. The main reasons for this are quite simple:
- the child consumed a large amount of food at one time;
- the food contained unusual and unusual products;
- poor quality of food or incorrect cooking method.
But in some cases, the factors causing such symptoms can be much more serious. For example, the development of appendicitis or infection with parasites. Preschool children often experience allergies to unfamiliar compounds, but in older adults, the cause of pain and heaviness in the stomach can be stress, fatigue and excessive exercise.
All this causes the development of a large number of diseases of the abdominal organs. But other signs can also occur in the opposite case, that is, as secondary manifestations of other diseases (infectious processes in the kidneys, gastritis, gallbladder pathologies).
Sometimes heaviness and bloating appear in the abdomen, the reasons for this are individual lactose intolerance, which can occur in children. In this case, it is necessary to consult a specialist and exclude the consumption of dairy products in order to make an accurate diagnosis.
Duodenal ulcer
Duodenal ulcer is a dangerous disease.
According to recent studies, pathology more often occurs due to infection of the stomach with H. Pylori. The heaviness in the stomach is accompanied by so-called “hunger pains” localized in the umbilical region.
They manifest themselves in the form of aching attacks with increasing intensity 2-3 hours after eating. In this case, the “attenuation” of attacks occurs, as a rule, after eating.
Heaviness in the stomach after eating
Belching with air and heaviness in the stomach also occur after eating, but can also be signs of the presence of other pathologies. In parallel with these symptoms, pain appears in the right side and a desire to vomit. As already mentioned, many gastrointestinal diseases have similar symptoms, so only the doctor is able to determine the factor in the appearance of heaviness in the stomach after eating or at another moment. It is important to visit a gastroenterologist in time so as not to worsen the situation.
In the event that a patient abuses unhealthy and fatty foods, heaviness in the stomach after eating is an expected symptom, but a feeling of fullness in the stomach after eating a small amount of food already indicates the presence of dangerous pathologies. In the first situation, the mechanism of action is simple: fatty, spicy or fried foods provoke an abundant release of acid, which is part of the gastric secretion. As a result of its excessive functioning, irritation of the mucous membrane develops and heaviness occurs. Of course, it’s worth visiting a doctor, but to get rid of the symptoms, it’s enough to follow a healthy diet, add more fiber, cereals and broths to your food, but under no circumstances starve yourself due to overeating. Then heaviness in the stomach and belching of air, the causes of which are not related to serious abnormalities, will go away on their own.
Bloating
Feeling of a full belly
Digestive disorders that manifest themselves as bloating can occur for a variety of reasons.
The main modern negative factors include daily stress, poor diet and taking a huge number of medications. All this, one way or another, affects the health of the gastrointestinal tract.
A bloated stomach not only causes a feeling of internal discomfort, but also objectively interferes with your usual activities. This disorder can occur at any time.
It is also important that bloating is not always directly related to food intake, which further complicates the search for possible causes of the disease. Getting rid of bloating can be quite difficult.
The feeling of a full stomach can be associated with dangerous diseases and trivial stomach or intestinal disorders. In healthy people, this problem may occur periodically and not cause much concern.
A constant feeling of fullness in the stomach indicates an unfavorable condition of the gastrointestinal tract.
Abdominal discomfort during pregnancy
Heaviness in the lower abdomen in women is a common symptom during pregnancy.
But it is important to distinguish the discomfort that arises due to the development of pathologies from the severity familiar to almost all pregnant girls. Before treatment, it is necessary to understand how heaviness appears in the stomach after eating and the reasons. Such sensations arise due to the fact that the child constantly puts a lot of stress on the stomach. This also happens due to toxicosis, intra-abdominal pressure in the later stages, which also provoke heaviness. Pregnant women are characterized by excessive gas formation, which also causes unpleasant bloating and heaviness in the stomach. Increased gas is a typical problem for expectant mothers; it is affected by excessive amounts of progesterone. Hormones slightly inhibit the peristalsis of the intestines and stomach, which retains food in these sections, so gases are formed more actively. Causes of heaviness in the abdomen:
- eating food quickly;
- inappropriate chewing;
- stressful conditions and severe fatigue;
- eating without feeling hungry;
- overeating before bed.
Certain foods can also cause similar symptoms. For example, some people develop lactose intolerance.
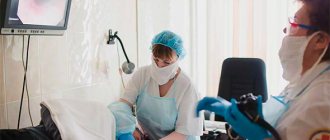
How to diagnose heaviness in the stomach?
Since it is usually quite simple to recognize heaviness in the abdomen and bloating, the main emphasis in diagnosing the pathology is on understanding the root cause of the symptoms and forming a further treatment plan. The gastroenterologist is responsible for determining therapy, but if the symptoms are not serious, a therapist can also help.
When faced with heaviness in the stomach, what should you do? Specialists independently determine examination methods:
- biochemical or general AA;
- Ultrasound;
- MRI;
- FGDS;
- X-ray;
- endoscopy of organs.
Any examination should begin with a consultation with a specialist; his task at this stage is to collect a detailed anamnesis, that is, to record a description of the complaints, their properties, and also to conduct an examination of the patient.
Heaviness in the lower abdomen, which does not develop due to gastrointestinal pathologies, appears as a result of an unhealthy eating schedule and poor foods. The patient may eat too much food, and if he eats this way regularly, the feeling of discomfort will not leave the patient. This is a big burden, because the body has to work harder to eliminate the consequences of overeating and other phenomena. Energy consumption increases, the quality of organ functioning decreases, and therefore the likelihood of developing serious diseases increases.
Therapy for a feeling of heaviness in the stomach
A feeling of heaviness in the stomach after eating or at any other time requires immediate treatment.
As a rule, heaviness in the stomach and diarrhea develop as a result of an unhealthy diet or gastrointestinal pathologies. It can be quite difficult for the body to cope with such a load, so it is important to consult a gastroenterologist and other specialists in a timely manner. Under no circumstances should you start self-therapy. All you need to do if you have nausea, heaviness in the stomach, or belching is to reconsider your diet and give preference to high-quality and healthy products.
The decision to take any pills for heaviness in the stomach can only be made by a specialist. To do this, he conducts a detailed examination, identifies the cause of the discomfort, and then prescribes therapy. For patients who feel heaviness in the stomach after eating, treatment must include the following simple rules:
- abstaining from foods high in fat and spicy ingredients;
- limiting the consumption of alcohol and soda;
- refusal of fast food;
- Irregular quick snacks should be replaced by eating food in small portions;
- establishing a diet.
It is important to visit the doctor regularly, since during the treatment process you will definitely need to conduct an intermediate examination and adjust the therapy. After all, medications for bloating and heaviness in the abdomen affect the deep mechanisms of the body; long-term use can disrupt the normal functioning of organs.
Causes of epigastric pain
Functional dyspepsia
Epigastric pain is provoked by errors in the diet, abuse of fast food and dry food.
Unpleasant symptoms usually occur during stress, travel and time zone changes. The pain is aching or nagging and has moderate intensity. Less commonly, patients report a sharp stabbing sensation in the upper abdomen. Such manifestations are observed periodically under the influence of predisposing factors. Along with the pain syndrome, a feeling of heaviness and fullness in the epigastrium, nausea, and heartburn increase. Characteristic belching is air, which develops as a result of aerophagia. With functional stomach disorders, gastrointestinal symptoms are accompanied by disorders of the autonomic nervous system. Characterized by pallor and coldness of the extremities, increased sweating, increased heart rate.
Gastritis
Gastritis with high acidity is characterized by sharp pain in the upper abdomen, which intensifies 20-30 minutes after eating and lasts for several hours. With gastritis with low acidity, there is a constant dull or aching pain that is not associated with food intake. After finishing a meal, patients complain of heaviness in the epigastrium, nausea, and belching.
In the acute form of gastritis or exacerbation of the chronic process, pain appears sharply against the background of errors in diet and alcohol intake. The pain syndrome can be very strong, reminiscent of an “acute abdomen”. Chronic gastritis is characterized by periodic moderate pain, accompanied by changes in stool, belching, and heartburn. Due to impaired iron absorption, pale skin, weakness, and dizziness occur.
Peptic ulcer
A stomach ulcer is manifested by severe pain in the epigastric region, which appears immediately after eating food, accompanied by nausea and heartburn. To relieve discomfort, patients induce vomiting. With a complication of a peptic ulcer - perforation of the ulcer - a “dagger pain” is suddenly felt in the upper abdomen. The person lies motionless with his legs pulled up to his stomach, since the pain intensifies with movement.
Pain in the upper abdomen
Pyloric stenosis
In the compensated stage, dull and bursting pain occurs in the epigastrium after a heavy meal, combined with a feeling of heaviness in the stomach and belching. With decompensation of pyloric stenosis, constant severe pain in the upper abdomen is noted, worsening after finishing eating. Vomiting begins with foods eaten the day before, after which the state of health improves for a short time.
Pancreatitis
In the acute course of pancreatitis, the pain is localized in the epigastric part and left hypochondrium, and has a girdling character. Unpleasant sensations intensify when lying on your back. The appearance of a painful attack is typical for heavy drinking. The pain is accompanied by repeated vomiting, which does not bring relief to the patient. Possible increase in body temperature, slight yellowness of the sclera.
Chronic pancreatitis is characterized by discomfort in the upper abdomen, occasionally radiating pain to the heart area. When following a diet, pain is rarely a concern; it is moderate and short-lived. Pancreatitis occurs with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, so the pain syndrome is accompanied by steatorrhea, lienterea, and flatulence.
Cholecystitis
With inflammation of the gallbladder, pain is localized in the upper abdomen and right hypochondrium. Symptoms are associated with consumption of fatty foods. In chronic cholecystitis, pain in the epigastrium is aching in nature, accompanied by heaviness in the abdomen and changes in stool. Acute cholecystitis is characterized by sharp, paroxysmal pain in the upper abdominal cavity. The clinical picture is complemented by vomiting with bile, yellowness of the skin and mucous membranes.
Hernias
A diaphragmatic hernia is manifested by severe pain in the retrosternal region and epigastrium, caused by compression of the stomach in the hernial sac. The symptom is provoked by physical activity, prolonged coughing, and vomiting. Increased pain occurs when the body bends forward and strains. In addition to the pain syndrome, constant heartburn is a concern, which gets worse after eating and when lying down. With large diaphragmatic hernias, shortness of breath is observed.
A rarer cause of epigastric pain is a hernia of the upper part of the linea alba. Characterized by constant aching sensations in the upper abdominal cavity, which do not have a clear localization. Symptoms are aggravated by physical activity and straining. A typical symptom of this pathology is the appearance of sharp pain when trying to raise your legs while lying on your back. Occasionally, a protrusion of soft elastic consistency can be felt in the middle of the epigastric region.
Intestinal infection
Epigastric pain is characteristic of food poisoning, which occurs with gastritis or gastroenteritis syndrome. They are often caused by rotaviruses, enteroviruses, and staphylococci. Symptoms appear within a few hours to 1-2 days after eating food of questionable quality. Suddenly, severe pain occurs in the abdominal cavity with nausea and repeated vomiting. Then comes watery diarrhea.
Neoplasms
With benign formations (polyps), periodic dull pain develops in the upper abdomen, not associated with food or other external factors. Stomach cancer is characterized by constant increasing pain in the epigastrium, which is not relieved by conventional analgesics and antispasmodics. In addition to pain, there is a deterioration in appetite and a change in taste preferences, as a result, patients rapidly lose weight.
Respiratory damage
Pain in the upper abdomen occurs with lower lobar lobar pneumonia, dry and exudative pleurisy. The irradiation of pain is determined by the proximity of the organs of the thoracic and abdominal cavities and their common innervation. The pain is dull or aching in nature, intensifies with deep breaths, coughing, and turning the body. The symptom is combined with high fever, shortness of breath, and lag of half of the chest when breathing.
Myocardial infarction
Severe epigastric pain occurs with the abdominal form of myocardial infarction. The pain syndrome develops suddenly, often preceded by emotional shock. The pain is accompanied by severe weakness. The skin becomes pale and covered in cold sweat. The pain is so severe that the patient is in a pre-fainting state.
Intercostal neuralgia
With damage at the level of the lower ribs, pain may radiate to the epigastric zone. The sensations are sharp and shooting, localized on one side. They occur when the body is in an awkward position, after bending or turning the body, or after staying in one position for a long time. The pain intensifies when you feel the intercostal spaces or try to bend in the opposite direction.
Complications of pharmacotherapy
A typical iatrogenic cause of upper abdominal pain is NSAID gastropathy. The disease is characterized by periodic discomfort in the epigastrium, which intensifies at night and on an empty stomach. There is a decrease in appetite, nausea, and flatulence. About 40-50% of gastropathy is asymptomatic and manifests itself with sharp pain in the projection of the stomach with the development of complications - perforated ulcers, gastrointestinal bleeding.
Rare causes
- Damage to the spleen
: splenomegaly, abscess or cyst of the spleen, perisplenitis. - Rare gastric diseases
: acute dilatation of the stomach, gastric volvulus. - Kidney diseases
: pyelonephritis, renal colic. - Vascular pathologies
: portal vein thrombosis, abdominal aortic aneurysm, ischemic abdominal syndrome. - Intoxication
: nicotine, morphine, heavy metals (lead, mercury). - Psychogenic conditions
: hysteria, masked depression, somatoform disorder.
How to prevent the development of heaviness in the stomach?
Heaviness after eating brings a lot of discomfort in life, especially when this feeling comes very often. It is much better to take the necessary measures in advance to avoid encountering a problem than to eliminate the consequences.
Since most often patients experience pain and a feeling of a full stomach, the causes of which lie in an unhealthy diet, they need to start with normalizing their diet. If there are signs of heaviness in the stomach after eating, what to do is the main question for patients. The answer is simple: eat more often, but less, avoid overeating and breakdowns, chew food diligently, and take your time. It is important to take care of creating a healthy and balanced diet, in which nutrient-rich, but not very heavy food will prevail. If there is heaviness after eating or belching, you need to give up heavy smoking, drinking alcohol, and reduce the consumption of fatty, spicy foods. It is necessary to stop eating without feeling hungry or fasting for a long time, and you should also avoid stress in the process of eating food, because this also affects absorption and the development of unpleasant sensations.
In addition, it is recommended to build your nutrition schedule in such a way that once a week you can reduce the absorption of particularly carbohydrate foods and increase the amount, for example, of fiber and useful minerals. Adhering to these rules is recommended not only for patients who have experienced heaviness in the stomach and nausea after eating, but also for those who want to normalize the functioning of the body as a whole and the abdominal organs.
In order to avoid the unpleasant consequences of heaviness in the stomach and nausea, you need to pay attention to your diet and lifestyle:
- reducing portion sizes and eating more frequently;
- choosing a lighter and healthier diet, since the most common situation is heaviness after fatty foods;
- following a regimen: have breakfast, lunch and dinner at the same time to allow the stomach to develop an activity mode;
- do not overeat before bed: experts advise not to eat 2 hours before bedtime;
- reducing stressful situations in life;
- high-quality chewing of food and no snacking on the go;
- eating fresh foods that are not too hot or too cold;
- getting rid of bad habits;
- reducing the volume of consumed semi-finished products, concentrates, etc.;
- increased physical activity;
- frequent walks in the fresh air.
In the event that there is heaviness in the stomach, the causes of which are related specifically to the culture of nutrition, following all these rules will help get rid of the symptoms, as well as eliminate problems with the gastrointestinal tract. It happens that the causes of discomfort lie in other serious pathologies. Such a regimen will have a beneficial effect on the condition of the body, will help to quickly cure diseases, nausea and heaviness after eating, especially when combined with drug therapy.
Prevention
- 1. Watch your portion sizes.
- 2.Drink enough water.
- 3. Follow a meal schedule.
- 4. Quit smoking and alcohol.
- 5. There should be short intervals between meals, no more than four hours.
- 6. Chew food thoroughly.
- 7. Maintain a balanced diet.
- 8.Try to have one or more days a week vegetarian (plant-based).
- 9. Don't eat without feeling hungry. First try drinking half a glass of water; perhaps the feeling of thirst is mistaken for a feeling of hunger.
The diet consists of soups with vegetable broths, low-fat poultry, rabbit, steamed, boiled and stewed vegetable dishes. Allowed are pasta, low-fat dairy products, eggs in casseroles, cheesecakes, steamed eggs, and omelettes. You can use white bread from yesterday, crackers from white bread.
You can make an appointment with specialists with extensive clinical experience by calling. or on the website of the New Hospital.