Appendicitis in a child is a condition caused by inflammation of the appendix, located in the lower abdomen. This is one of the most painful conditions a young child can encounter. Appendicitis can occur at any age. According to most pediatric specialists, this condition occurs more often in children than in adults. How to determine appendicitis in a child? You should know the signs of this condition or consult a doctor for advice if there is pain on the right side of the abdomen.
The pathology develops when the appendix becomes clogged with solid fecal material, foreign objects, growths or helminths. The pain usually starts around the belly button and then moves to the lower right side of the abdomen, although it can also spread throughout the abdomen. At this time, bacteria multiply rapidly. Mortality from acute appendicitis in children is about 3.5% and does not tend to decrease, therefore it remains the most pressing problem in pediatric surgery (among emergency conditions).
Types of appendicitis
The appendix is located in the lower right side of the abdomen and is a narrow, tubular extension protruding from the large intestine. This organ began to be called vestigial (not yet fully developed) because in the process of evolution it lost its original digestive functions. In humans, the appendix performs a number of secondary functions: protective (has many lymphoid formations); secretory (produces lipase and amylase); hormonal (produces hormones that take part in intestinal motility and the work of its sphincters).
There are different types of appendicitis:
- Catarrhal. The inflammatory process is localized in the appendix. Accompanied by morphological changes in the mucosa.
- Phlegmonous. An acute inflammatory process with severe swelling, the formation of purulent masses and the appearance of fibrin on the surface.
- Gangrenous. The presence of serous purulent fluid in the appendix. The walls of the appendix weaken due to impaired blood flow and increased internal pressure, and there is a risk of rupture.
- Perforated. The walls of the appendix rupture and release purulent-necrotic masses that penetrate into the interior of the abdominal cavity, causing peritonitis.
There are two forms of appendicitis: chronic and acute. Chronic appendicitis is characterized by milder symptoms that appear periodically. Identification of this form is delayed for a long period. How to recognize appendicitis in a child? Self-diagnosis is excluded in this case. If you have abdominal pain, consulting a doctor is mandatory.
The prognosis of acute appendicitis is favorable provided that the process is diagnosed early and undergoes surgical intervention without wasting time. Late detection and untimely surgical intervention can lead to peritonitis. In the acute form, the symptoms are more clear-cut and appear within 24-48 hours. Immediate treatment is required here.
Why does prostatitis occur?
Inflammation of the prostate gland can be bacterial or abacterial (that is, not associated with exposure to bacteria).
Bacterial prostatitis
The disease is caused either by pathogenic microbes that most often affect the genitourinary tract, such as Escherichia coli, Proteus or Klebsiella. In addition, sexually transmitted infections can lead to the development of bacterial prostatitis, for example, chlamydia - the causative agents of chlamydia, ureaplasma - the causative agents of ureaplasmosis, trichomonas - the causative agents of trichomoniasis and neisseria - the causative agents of gonorrhea.
Bacterial prostatitis can be acute, when the disease begins suddenly, with severe symptoms such as severe pain and fever, or chronic, when symptoms of the disease appear or disappear over three months or more.
Abacterial prostatitis
Abacterial prostatitis is today considered as one of the variants of chronic pelvic pain syndrome. The reasons why this condition occurs are varied. According to some reports, the problem may be associated with incomplete relaxation of the urinary sphincter - because of this, pressure in the bladder increases. As a result, part of the urine enters the prostate and provokes an inflammatory reaction there. Even more often, “prostatitis-like” symptoms are caused by stimulation of the pelvic nerves as a result of problems in the lumbosacral spine (for example, with a herniated disc) - as a result, we are dealing with chronic pelvic pain without inflammation.
In addition, it is believed that stress can also increase the risk of developing this disease.
Prostatitis, especially bacterial, can be found in any man. There are factors that increase the risk of developing the disease:
- the patient has already suffered from prostatitis in the past;
- a person has been diagnosed with a urinary tract infection;
- the patient has had a pelvic injury, has recently undergone a prostate biopsy, or has had a urinary catheter installed;
- the patient has a weak immune system, for example due to HIV or AIDS.
Reasons for development
What causes appendicitis in children? The main mechanism is obstruction of the appendicular lumen, which leads to increased pressure and bacterial growth. The intestinal microflora takes part in the development of the pathological process. Often the cause of appendicitis in children is lymphogenous, as well as hematogenous infection, since there is a connection with follicular tonsillitis, ARVI, otitis and sinusitis.
This condition can develop as a result of various factors:
- enlargement of regional lymph nodes;
- the presence of foreign bodies in the appendicular lumen;
- parasitosis caused by roundworms;
- overeating and constipation;
- dysbacteriosis and gastroenteritis;
- foreign bodies and adhesions;
- peritoneal tuberculosis, tumors and lymphomas.
Excessive mucus production and mechanical obstruction lead to increased pressure within the appendix. This is fraught with swelling of the mucous membrane of the appendix, which increases the tension of its walls. As a result, the perfusion of the appendix decreases, venous stagnation is noted, and pathogenic bacteria multiply. After 12 hours, the inflammatory process develops. The next stage is perforation of the appendix wall, in which purulent contents and feces are released into the abdominal cavity. The entire process takes from 24 to 36 hours.
Is it possible to remove a healthy appendix?
Scientific thought is rapidly developing, and if previously most scientists believed that organs that do not perform an essential function for the body can be easily removed in infancy, now opinions are divided. Doctors have discovered that there are lymphatic follicles on the walls of the appendix; they can protect the intestines not only from infection, but also protect against cancer. Another essential function of the appendix is to maintain the immune system of the whole body, so its preservation plays an important role. The best prevention for preventing appendicitis is a healthy diet and timely detection of various diseases.
Symptoms and signs of the disease
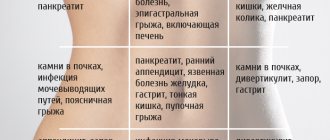
How does appendicitis manifest? Typically, pain appears suddenly around the navel or diffusely in the abdominal cavity, and is moderate and constant over time (4-6 hours). Usually the discomfort shifts to the lower right quadrant of the abdomen. Children develop symptoms more quickly than adults and there is a greater risk of perforation.
Appendicitis occurs most often in children aged 8 to 16 years. At an earlier age, the situation becomes more complicated, because children cannot talk about their well-being.
The main signs of appendicitis in a child:
- temperature rise to 38-40 degrees;
- nausea and vomiting (single or repeated);
- cardiopalmus;
- pain when urinating;
Lack of appetite is also an important sign of appendicitis in children. If the appendix is inflamed, the child does not want to eat, play, or move. The most painful area is located between the femur and the navel. The child bends over in pain and prefers to lie on the left side with his knees pressed to his chest.
Signs of appendicitis include stool retention and loose stool. Urination becomes more frequent only when the appendix is located in the pelvis.
What's the result?
Prostatitis is a disease of the prostate gland in which the patient complains of pain in the pelvic area, difficult or painful urination and/or painful ejaculation. If any of these three symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Bacterial prostatitis is treated with antibiotics and drugs that improve urination. The duration of treatment is usually from 2 to 4 weeks. The effectiveness of prostate massage and physical therapy has not been proven.
To avoid prostatitis, you need to strive to have regular sex life, do not forget about condoms and avoid severe hypothermia.
Establishing diagnosis
Diagnosis of appendicitis in children is complicated due to the similarity of symptoms with other diseases (gastroenteritis, Meckel's diverticulum, intussusception, Crohn's disease). Often children do not present typical complaints and characteristic symptoms are not detected during examination, especially when the appendix is in an unusual position.
To diagnose appendicitis, the following is carried out:
- physical examination to assess pain;
- blood test: used to confirm infection (with appendicitis, there is an increase in white blood cell levels);
- Urinalysis: used to rule out other causes of infection;
- X-ray of the abdominal cavity: allows you to detect the presence of fluid in the abdominal cavity and bloating;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs: shows an inflamed appendix or the presence of fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- CT (computed tomography): a reliable method for confirming appendicitis, widely used in doubtful cases.
Early diagnosis guarantees timely treatment and eliminates the risk of developing peritonitis and numerous complications.
How is prostatitis treated?
Treatment tactics for prostatitis depend on the cause of the disease. To distinguish bacterial prostatitis from abacterial prostatitis, before starting treatment, the doctor will prescribe a general analysis and culture of prostate secretions or urine obtained immediately after a prostate massage and containing prostate secretions. In some cases, a blood test for the level of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is also performed. These tests can detect signs of inflammation. In addition, urologists often prescribe tests for sexually transmitted infections, because their pathogens can also cause prostatitis.
In some cases, to make a differential diagnosis with other diseases that have symptoms similar to prostatitis, urologists urologists prescribe additional tests, such as a computed tomography scan of the urinary tract, ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the prostate, or cystoscopy. In this procedure, the doctor examines the patient's urinary tract using a cystoscope, an instrument that looks like a long, thin tube.
Konstantin Lokshin, urologist-andrologist at GMS Hospital:
Bacterial prostatitis is treated with antibiotics and drugs that improve urination. The duration of treatment is usually from 2 to 4 weeks.
Other therapies don't work. For example, these days prostatitis is no longer treated with prostate massage. Many of the physical procedures, in general, also do not have any evidence base, so it is useless to do them.
Treatment of prostatitis not associated with a bacterial infection is usually aimed at eliminating the unpleasant symptoms of the disease - that is, reducing pain, discomfort and inflammation. For each patient, therapy must be selected individually.
Treatment of appendicitis
Currently, appendectomy is the mainstay of treatment given the low incidence of serious complications. After 2-3 days of hospitalization, the child will return home.
An appendectomy can be performed as open surgery, through a 5 to 10 cm incision in the abdomen. Or the operation can be performed through small incisions in the abdomen (laparoscopic surgery).
During a laparoscopic appendectomy, the surgeon uses special instruments and a video camera to remove the appendix. After laparoscopy, the recovery period is shorter, there is less scarring and pain.
However, laparoscopic surgery is not for everyone. If the appendix has burst and the infection has spread beyond the organ, an open appendectomy is performed, which allows the surgeon to clean out the abdominal cavity.
Disease prevention
There is no way to prevent appendicitis. But there are several recommendations that may reduce the risk of developing a pathological condition:
- Include fiber-rich foods (fruits, vegetables and whole grains) in your diet. This will improve the digestive process.
- During the treatment process and especially in the initial stages, it is important to take antibiotics. Antibacterial drugs prevent the proliferation of microorganisms in the digestive tract, preventing the exacerbation of the disease.
If symptoms of appendicitis appear in a child, it is recommended to show the child to a doctor as soon as possible. This approach eliminates the likelihood of developing serious complications.
How to avoid developing prostatitis
Konstantin Lokshin, urologist-andrologist at GMS Hospital:
There are three ways to avoid prostatitis:
- Have sex regularly. A harmonious intimate life is the most reliable way of prevention.
- Use a condom. This primarily applies to people who have many sexual partners. A condom is needed to avoid contracting sexually transmitted diseases, which most often cause the disease.
- Avoid severe hypothermia, which also contributes to the occurrence of bacterial prostatitis.