Often people who “throw themselves” into work forget that they need to get enough nutrients, and this needs to be done through a balanced diet. However, few people adhere to these well-known rules.
As a result, a number of symptoms appear that signal the onset of diseases. Problems with the gastrointestinal tract are often the result of a frantic pace of life and insufficient attention to one’s health. Sometimes they develop into serious illnesses, which can be quite difficult and time consuming to treat.
Heaviness in the stomach signals problems that have already appeared. Moreover, this can be either a mild ailment or a symptom of a serious illness. Patients often complain of a feeling of fullness or discomfort, a feeling that “something is in the way,” and sometimes mild nausea or belching.
And since not only the gastrointestinal tract, but also the liver and pancreas are involved in the process of digesting food, often manifesting pathological symptoms may indicate problems in the functioning of these organs.
Possible causes of heaviness and discomfort in the epigastric area?
Frequent consumption of fried foods causes heaviness in the stomach.
- frequent consumption of fatty, fried, spicy foods and foods with a lot of seasonings and spices;
- overeating (especially in the evening and at night);
- passion for fast food and frequent snacking on the run and between main meals;
- violation of the diet and too monotonous nutrition. For example, eating one or two times a day instead of the prescribed five or six, eating a large amount of food at one time.
As for the monotony of the diet, when eating the same foods for a long time, a malfunction may occur in the body, which can also affect the digestive tract.
Feeling overeated during pregnancy
During pregnancy, the position of the internal organs changes due to the rapid growth of the fetus in the uterus.
The organs are displaced inside the abdominal cavity, the stomach rises higher. Feeling overeated during pregnancy:
- Very often this becomes the cause of bloating and discomfort in the abdominal area. During pregnancy, it is recommended to eat fractional meals, eat food in small portions, and do not overload the stomach.
- Preference should be given to liquid or mushy dishes. Avoid eating fatty, spicy foods. Avoid consumption of fast food, chips, and alcohol.
- To get rid of heartburn and the feeling of fullness during pregnancy, it is allowed to take enterosorbents that absorb toxic substances. Drugs that reduce stomach acidity are recommended. Proper nutrition and consumption of healthy foods prevents the feeling of fullness in the stomach during pregnancy.
In what cases can heaviness in the abdomen occur on an empty stomach?
The following can provoke discomfort in the epigastric area on an empty stomach:
- taking certain medications (for example, antibiotics);
- consumption of Coca-Cola, lemonade and alcoholic beverages, which are favorite among young people. Smoking can also irritate the stomach lining and cause heaviness and even pain;
- frequent stressful situations. They can affect not only the nervous and cardiovascular systems, but also our gastrointestinal tract. Stress contributes to increased production of hydrochloric acid, which negatively affects the gastric mucosa;
- period of pregnancy in women. The thing is that an enlarged uterus can put pressure on other internal organs surrounding it, including the stomach. This is the cause of heaviness and discomfort. As a rule, after delivery, unpleasant symptoms disappear;
- functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract are separately distinguished, which are manifested by heaviness, stool disorders (alternating constipation and diarrhea), nausea and severe pain in the epigastric region.
Why does the stomach feel overeated from a small portion?
Almost all nutritionists recommend minimizing the consumption of fatty meats and fried foods in the evening. It is better to eat this food in the morning or at lunch. In the evening, you are allowed to eat fish, stewed vegetables, and dairy products with a low fat content. Chops and cutlets with a high content of animal fat are best eaten at lunch. You should not drink these foods with large amounts of water; liquid can increase bloating and an unpleasant feeling in the stomach.
Why there is a feeling of overeating in the stomach from a small portion:
- Eating food from the canteen. This applies to people who spend most of their time at home, or regularly eat home-cooked food. Any visit to a restaurant or canteen can affect the condition of the digestive tract. In industrial canteens, where food is prepared in large portions, bone meal and bone broth are used to prepare first courses. Dishes are seasoned with internal fat and lard. Fatty foods are too heavy, especially if food in the house is fried in vegetable oil. The body may not accept large quantities of animal fat well.
- Consuming large amounts of lard and lard. These foods are heavy and require a high concentration of pancreatic enzymes and bile to digest them. Regular exercise can lead to disruption of the internal organs and cause heaviness.
Food
What diseases are characterized by the symptom of heaviness in the stomach?
Heaviness in the stomach is a sign of gastritis.
Of course, not only poor nutrition, stress and pregnancy can cause heaviness in the epigastrium. Sometimes this can be a signal of the development of serious pathological conditions and illnesses. Which ones?
Gastritis. It is characterized by the appearance of an inflammatory process on the inner wall of the stomach. The causes of the disease are different. These include:
Prevention and treatment
Prevention
Overeating is contraindicated to prevent the disease.
Overeating is contraindicated. You need to eat small portions at the same time 5 times a day. Last meal 2 hours before bedtime.- When a stressful situation occurs, try not to eat, but to calm down a little.
- Chew food thoroughly.
- Use only high-quality and fresh products. Avoid products containing preservatives, dyes and stabilizers. Drinks should also be without carbonation and sugar.
- Don't drink alcohol. Alcoholic drinks only harm and aggravate the situation if the disease is already present.
- No smoking.
- Lead an active lifestyle, move a lot, do exercises, play sports.
Treatment
Self-medication is dangerous. The course of treatment is prescribed by a doctor. The gastroenterologist will prescribe the necessary medications and determine the dosage. It can be:
- Enveloping drugs, such as suspensions of “Phosphalugel”, “Maalox”, “Gaviston” and others. They envelop the walls of the stomach, preventing gastric juice and acid in it from irritating the stomach.
- Enzyme preparations: tablets “Pancreatin”, “Creon”, “Mezima” - add enzymes for additional assistance in digesting food.
- Antispasmodic drugs: pills “No-shpy”, “Papaverine” and others. They relax the stomach muscles, relieve pain and spasms.
If your stomach problems are related to a psychological state, then you should make an appointment with a psychologist, attend conversations and, if necessary, take a course of medications to calm you down.
Stomach ulcer
Gastric ulcer is a lesion of the walls of the gastric mucosa.
This is a more serious disease, which is characterized by damage to the wall of the gastric mucosa in the form of the formation of defects (ulcers).
The causes are similar to those that cause gastritis. The symptoms are also similar. Therefore, in order to differentiate gastritis and gastric ulcers, it is necessary to undergo a special examination.
It is necessary to treat a stomach ulcer, as it can become a harbinger of other, even more serious pathologies and diseases that will require surgical intervention. Complications of peptic ulcer disease include:
- perforation (through-type defect in the wall of the stomach);
- bleeding;
- degeneration of an ulcer into a malignant formation.
These conditions threaten not only human health, but also human life. In addition to the symptoms described above, the following signs are added to the manifestations of a stomach ulcer:
- night pain in the epigastric region;
- vomiting of sour contents;
- seasonal exacerbations, which manifest themselves as an increase in the intensity of symptoms in spring and autumn.
Stenosis (narrowing) of the part of the stomach in the area of the so-called pylorus. It looks like a scar thickening located in the exiting section. Formed as a result of peptic ulcer disease or damage to the stomach by a tumor. Symptoms:
- heaviness in the epigastrium;
- diffuse stomach pain;
- nausea;
- vomiting of stagnant food (sometimes eaten several days before the attack).
This condition poses a clear threat to life, since developed (complete) stenosis does not allow food to pass further into the intestinal area, resulting in depletion of the body and death.
Functional (non-ulcer) dyspepsia
print version- home
- >
- For patients
- >
- Gastrointestinal diseases
- >
- Functional (non-ulcer) dyspepsia
Functional dyspepsia
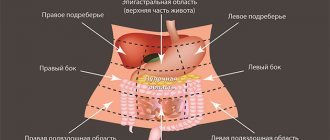
(FD) is a heterogeneous disease that represents a complex of symptoms, including pain and a burning sensation in the epigastric region, a feeling of fullness in the epigastrium (area 2 in the figure on the right) after eating and early satiety, which have been observed in the patient over the past 3 months (with a total duration of complaints of at least 6 months) and which cannot be explained by organic, systemic or metabolic diseases (Rome III criteria, 2006).
Patients with FD may also experience the following symptoms: pain and burning sensation in the epigastrium, bloating, belching, nausea, vomiting, general weakness, increased fatigue, decreased performance.
Functional dyspepsia is spoken of in cases where the patient does not have diseases (peptic ulcer, tumors, chronic pancreatitis, etc.) that would allow them to be included in the group of organic dyspepsia
.
The diagnosis of functional dyspepsia is a clinical
.
It reflects the presence in the patient of certain symptoms that arise not as a result of concomitant chronic inflammatory changes in the gastric mucosa, but as a result of disorders of gastric secretion, gastroduodenal motility, visceral sensitivity, i.e. sensitivity of the receptor apparatus of the wall of the stomach and duodenum to stretching, often caused by neuropsychic factors. This differs from the morphological
diagnosis of
chronic gastritis
.
| Areas and sections of the abdomen |
These two diseases do not contradict each other and in practice are almost always combined in the same patient.
There are two main clinical variants of FD:
- Epigastric pain syndrome
, previously called
the ulcer-like variant
. With this option, intermittent pain or a burning sensation in the epigastric region is noted. These pains are not localized in other parts of the abdomen and do not decrease after defecation. - Postprandial distress syndrome
, previously called the
dyskinetic
variant. With this option, at least several times a week, after eating, when taking the usual amount of food, a feeling of fullness in the epigastric region or early satiety occurs.
These syndromes can be combined and accompanied by nausea.
Unfortunately, these diagnostic criteria are not specific to functional dyspepsia and can occur in many other diseases. Therefore, the diagnosis of functional dyspepsia is a diagnosis of exclusion, which can only be made after a thorough examination of the patient.
First you need to exclude diseases included in the group of organic dyspepsia
. Let's list them:
- stomach ulcer;
- duodenal ulcer (DU);
- gastroesophageal reflux disease;
- diseases of the biliary tract;
- chronic pancreatitis;
- malignant tumors of the stomach, pancreas, colon;
- other infiltrative lesions of the stomach - malabsorption syndrome - vascular malformations;
- drug-induced injuries - after the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antibiotics, theophylline, digitalis, iron preparations;
- due to alcohol consumption;
- diabetes;
- hyper- or hypothyroidism;
- hyperparathyroidism;
- electrolyte disturbances;
- connective tissue diseases;
- liver diseases.
Functional dyspepsia is often combined with other functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract - functional heartburn, functional flatulence, functional constipation, functional diarrhea, functional abdominal pain syndrome.
The cause of the main symptoms of FD is considered to be a violation of the motor function of the stomach, mainly:
|
|
There is a correlation between symptoms and gastric motility disorders.
Nausea and vomiting are associated with gastroparesis, a feeling of fullness in the epigastrium is associated with impaired sensitivity of the stomach receptor apparatus to stretching, and a feeling of early satiety is associated with a disorder of gastric accommodation. Research methods for making a diagnosis
can be divided into basic and additional.
Basic methods:
- Clinical and biochemical blood tests.
- Stool analysis.
- Gastroduodenoscopy. Allows you to exclude gastrointestinal diseases of an organic nature and perform a biopsy to establish the morphological variant of concomitant chronic gastritis and duodenitis.
- Ultrasonography. Allows you to clarify the condition of the liver, gall bladder and pancreas.
- Diagnosis of H. pylori infection.
Additional methods:
- X-ray examination of the stomach and duodenum.
- Intragastric pH-metry.
- Daily monitoring of pH in the esophagus.
- Study of the motor function of the stomach (scintigraphy, electrogastrography, manometry), computed tomography, etc.
Treatment of functional dyspepsia
includes general measures to normalize lifestyle and nutrition, the use of medications, and in some cases, psychotherapeutic agents.
Patients with FD are recommended to eat frequent (6 times a day) split meals in small portions with a limit on fatty and spicy foods, as well as coffee. It is advisable to quit smoking, drinking alcohol, and taking NSAIDs.
Proton pump inhibitors are effective in the treatment of FD, mainly in the painful variant of the disease (especially with night pain), when FD is combined with GERD, in patients with excess body weight, but they help little in the dyskinetic variant. If the motor function of the stomach and duodenum is impaired, prokinetics are used for treatment - drugs that stimulate the motility of the gastrointestinal tract (for example, with an “irritable” or “lazy stomach”), or antispasmodics - drugs that reduce spasm of smooth muscles (for example, with “duodenal hypertension ").
Eradication of H. pylori infection does little to help eliminate dyspeptic complaints, but helps reduce the risk of peptic ulcers and stomach cancer in patients.
Doctors classify dyspepsia as K30
in the International Classification of Diseases ICD-10.
Patient Materials
The GastroScan.ru website contains materials for patients on various aspects of gastroenterology:
- “Advice from doctors” in the “Patients” section of the site
- “Popular gastroenterology” in the “Literature” section
- “Popular gastroenterology” in the “Video” section
Resources for healthcare professionals regarding functional dyspepsia
Articles, Guides and Recommendations for doctors
- Ivashkin V.T., Maev I.V., Sheptulin A.A. and others. Clinical recommendations of the Russian Gastroenterological Association for the diagnosis and treatment of functional dyspepsia // RZHGGK. 2022. No. 27 (1). pp. 50–61.
- Pimanov S.I., Ruselik E.A. Diagnosis and treatment of functional dyspepsia: refined algorithms // Consilium Medicum. Application. Gastroenterology. – 2010. – No. 2. – P. 11–17.
- Sheptulin A.A. Chronic gastritis and functional dyspepsia: is there a way out of the deadlock? // RZHGGK. - 2010. - T.20. — No. 2. — P. 84-88.
- Rachkova N.S., Khavkin A.I. Assessment and principles of differential treatment of gastric and duodenal motility disorders in patients with functional dyspepsia // Bulletin of pediatric pharmacology and nutrition. – 2007. – T. 4. – No. 5. – p. 25–29.
- Kolesnikova I.Yu., Volkov V.S. Diagnosis and treatment of acid-related diseases of the digestive tract. Guide for doctors / M.: Publishing House “Medical Information Agency”, 2014. - 432 p.
- Varghese C, Carson DA, Bhat S, Hayes TCL, Gharibans AA, Andrews CN, O'Grady G. Clinical Associations of Functional Dyspepsia with Gastric Dysrhythmia on Electrogastrography: A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. medRxiv 2021.01.19.21250140
On the website GastroScan.ru in the “Literature” section there is a subsection “Functional dyspepsia”, containing publications for healthcare professionals on this topic.
Video for doctors and medical students
Still from video: Shavkuta G.V. Combined functional disorders of the esophagus and stomach: actual clinical practice and modern recommendations for patient management
Still from video: Vyuchnova E.S. Optimization of therapy in a patient with overlapping GERD and postprandial distress syndrome
Still from video: Mukhametova E.M., Ipatova M.G. Functional disorders of the upper gastrointestinal tract in children: what, where, when?
Still from a video lecture for 4th year medical university students: Shvarts Yu.G. Dyspepsia. Gastritis
Alexandrov M.V. Acid-dependent diseases of the digestive system in the practice of a clinic physician. Lecture for sixth year students of the Faculty of Medicine of the Ivanovo State Medical Academy (IvSMA)
Still from video: Krasnova E.E.
Diseases of the upper digestive tract in children. Lecture for students of IvSMA On the website GastroScan.ru in the “Video” section there is a subsection “For doctors”, containing video recordings of reports, lectures, webinars in various areas of gastroenterology for healthcare professionals, as well as a subsection “For students of medical universities”
Duodenal ulcer
Duodenal ulcer is a dangerous disease.
According to recent studies, pathology more often occurs due to infection of the stomach with H. Pylori. The heaviness in the stomach is accompanied by so-called “hunger pains” localized in the umbilical region.
They manifest themselves in the form of aching attacks with increasing intensity 2-3 hours after eating. In this case, the “attenuation” of attacks occurs, as a rule, after eating.
Feeling overeated after a small meal: reasons
The problem is common, especially for residents of the former post-Soviet space. This is due to the peculiarities of the mentality and financial problems during perestroika. People who remember this time tend to overeat and want to try everything during the holiday. For such purposes, most people purchase enzymes that improve the digestion of food and relieve heaviness in the stomach. However, it happens that heaviness is observed even after a small amount of food.
Feeling of overeating after a small meal, reasons:
- Visiting exotic countries and getting used to unusual cuisine. In China and Vietnam, hot spices and unusual ingredients are introduced into food. A person living in a certain region develops its own microflora, designed to digest frequently consumed food. If a large number of unusual foods appear in the diet, the stomach may protest, and heaviness may be felt after eating.
- Frequent flights, naps during the day. The digestive organs are designed to work during the daytime and must rest at night. Some people work around the clock, or in shifts, and therefore sleep shifts to the day, and night becomes working time. You need to wait a little while the body readjusts. Try to reduce the amount of food you eat at night, replacing heavy foods with light ones. The ideal option is stewed vegetables.
Malignant tumor of the stomach (cancer)
The insidiousness of this disease is that for a long time it may not make itself felt. Then the first signs appear: heaviness, unstable stools, nausea and rare vomiting.
When the disease reaches its apogee, it manifests itself in increased pain and frequent vomiting. At the same time, accompanying signs appear that indicate the occurrence of a malignant formation in the stomach. This:
- fatigue and weakness;
- anemia, slightly elevated temperature;
- decreased appetite and weight loss.
Chronic pancreatitis. Develops as a result of a pathological process affecting the pancreas. Causes:
- alcohol abuse;
- formation of gallstones;
- serious errors in nutrition;
- damage to gland tissue of a viral or traumatic nature, resulting in a decrease in its capacity.
Signs:
- heaviness in the epigastrium;
- nausea and bloating;
- widespread pain in the left hypochondrium, near the navel and in the back at the level of the lower ribs. Such pains are also called shingles;
- frequent vomiting;
- The most obvious manifestation of the disease is “greasy, light yellow, mushy stool, which, due to the high content of unprocessed fats in it, is poorly washed off the walls of the toilet.
Reasons for not feeling full after eating
Let's look at several common reasons why you don't feel full after eating.
Eating disorders
Constantly balancing on a diet swing leads to the loss of muscle mass and the build-up of adipose tissue, the metabolic processes of which proceed extremely slowly. The brain refuses to understand when a person experiences a feeling of fullness: the neural connection between the processes of eating food and its entry into the stomach is disrupted. Severe emotional disturbances can affect the ability of parts of the brain to regulate hunger and appetite.
Three studies that will help stop aging
Such a simple element as water has always been considered vital and necessary.
But at the same time, the number of myths about water, scientific facts and opinions that are imposed every day and then refuted, encourages us to look for answers to our questions. To help you, my team and I have prepared a webinar and a gift: 3 unique materials based on the experience of our experts on prolonging youth with the help of water. After completing our free webinar you will learn:
Artyom Khachatryan
practicing physician-nutritionist, naturopath
Immediately after registration you will receive a selection of studies:
Aging: you can't stop it, you can't accept it
What conclusions did 21st century scientists come to when studying water and its ability to prolong youth?
In fact, we don't know anything about water.
Important information for prolonging youth that we could have been told back in school
Hydrogen water is the most powerful natural remedy for prolonging youth
Why hydrogen-enriched water is considered the most effective, safe and affordable way to prolong youth
Find out how water can take care of your health, youth and beauty at a free webinar by nutritionist Artyom Khachatryan!
Impact of stressful situations
In humans, as well as in mammals, there is an instinct to associate food with safety: a feeling of satiety gives a feeling of calm. If a person is full, in most cases all problems fade into the background, albeit temporarily.
However, in modern life, many people use this property of food to their detriment: any feeling of anxiety or stress is consumed, regardless of whether they are hungry or not. Food becomes encouragement, reward, moral support. In the end, a person ceases to objectively understand when he is really hungry and when he is simply anxious.
Impact of stressful situations
Having extra pounds
People who are overweight due to overeating are at risk of developing a persistent feeling of hunger. Large portions cause a distended stomach and, as a result, an unhealthy appetite.
Disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract system
A symptom of some gastrointestinal diseases, such as gastritis or ulcers, is a strong feeling of hunger. In this case, only a specialist can help. He will refer you for the necessary examination and prescribe appropriate treatment. If you do nothing or try to treat it yourself, you will only make the disease worse.
This is interesting!
“Tap water: can you drink it and in what cases” Read more
Lack of proper sleep
By regularly depriving yourself of proper sleep, a person forces the body to produce increased amounts of the neurotransmitter orexin, which regulates appetite, sleep and wakefulness, and blood sugar levels. Its excess slows down metabolism in adipose tissue. If you sleep significantly less than the required 8 hours a day and are constantly hungry, this is a reason to check your sugar levels and try to improve your sleep pattern.
Thyroid dysfunction
Hormones produced by the thyroid gland are responsible for the body's metabolic rate and many other processes. If there is a malfunction in the functioning of this organ, this may result in a problem with appetite. For example, an overactive thyroid gland leads to increased energy consumption by the body and, as a result, to a feeling of constant hunger. If such signs are detected, it is necessary to take tests for hormone levels and do an ultrasound.
How to Guaranteed Lose Weight with Water: 3 Simple Habits
There are almost no women in the world who have never been on a diet. Sooner or later, everyone faces the desire to lose a couple of kilograms.
In order for the treasured number to appear on the scales sooner, introduce 3 healthy and super simple habits into your life: we have prepared a document with experts where we describe them in detail.
How to Guaranteed Lose Weight with Water: 3 Simple Habits
Artyom Khachataryan
Practitioner, nutritionist, naturopath
75% of our course participants who follow these habits have significantly reduced their weight!
You can download the document for free:
PDF: 2 MB
Critical lack of vitamins
The body may respond with an increased feeling of hunger to a lack of B vitamins and amino acids. To cope with your appetite, you should consult a specialist for recommendations on a balanced diet and selection of vitamins.
After a full meal, a person should feel at least warm and relaxed, but definitely not hungry. If you don't feel full after eating, this is a sign that something is wrong with your body. You should not ignore or try to wait out attacks - this is a direct road to chronic diseases.
Critical lack of vitamins
It is necessary to undergo genetic testing. This is especially important for people who cannot cope with the feeling of hunger, which is why they gain weight. The results will show the presence or absence of autoimmune diseases and the risk of obesity, as well as whether there are mutational changes in genes responsible for eating behavior.
Gallstone disease and chronic cholecystitis
With cholelithiasis, nausea and vomiting are observed.
Manifest in the form:
- nausea and vomiting of bile;
- belching with a bitter taste;
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- stool disorders;
- yellowness of the skin and eyeballs.
Liver cirrhosis or hepatitis. These diseases, caused by viral infections or alcoholism, can also have a negative impact on the gastrointestinal tract. Signs:
- dull pain in the right hypochondrium;
- jaundice and abnormal stool;
- with cirrhosis, there is also an expansion of the veins in the skin of the abdomen and an increase in its circumference (due to the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity).
Gastroenteritis or infection of the stomach or small intestine manifests itself in the form of nausea, repeated vomiting, fever and loose stools.
Poor appetite and heaviness in the epigastrium may persist for some time after recovery (from several days to several weeks).
Symptomatic treatment of heaviness in the stomach
A proper diet will help get rid of the feeling of heaviness in the stomach.
Self-medication is not recommended. To begin with, it is better to adjust your diet and diversify it, be sure to find time for hot lunches, and eat vegetables and fruits daily that promote digestion.
You should also try to avoid eating dry food, snacking on pies and sandwiches, as well as nighttime overeating. It is advisable to eat food 3-4 hours before bedtime.
How to get rid of the feeling of overeating using folk methods?
If the feeling of fullness in the abdomen continues again and again, consult a doctor.
Take advantage of preventative measures that prevent you from feeling overfull. Tips and rules to help get rid of the feeling of overeating are presented below. How to get rid of the feeling of overeating using traditional methods:
- The body itself does not understand what it needs. Therefore, instead of a glass of water, you have to eat a portion of high-calorie food. Nutritionists recommend drinking a glass of boiled water 30 minutes before a meal. Perhaps the feeling of hunger has nothing to do with a lack of nutrients and energy.
- Try not to leave too many gaps between meals. They stimulate feelings of extreme hunger and contribute to overeating. Therefore, the optimal option is 3 hours.
- Don't skip breakfast and lunch. These meals should be complete and include all the necessary nutrients. The last meal, that is, dinner, should be light. If you eat the right food for breakfast and lunch, then by the evening there is practically no feeling of hunger; you can easily get by with a snack.
- If you have unpleasant sensations, you can also alleviate the condition. To do this, carry out light massage movements in a circle around the navel in a clockwise direction. This stimulates intestinal peristalsis and speeds up the passage of food through the digestive organs. This eliminates the feeling of overeating and satiety.
- Very often, the feeling of fullness is not associated with a large meal, but with the use of inappropriate foods. In adults, this may be gluten, lactase, or yeast. After eating these foods, there is increased activity of bacteria and yeast in the stomach. Due to a lack of enzymes, these substances are not completely broken down, which leads to the formation of a large number of gas bubbles. They can put pressure on the walls of the stomach and intestines, causing a feeling of fullness and discomfort. To get rid of them, eliminate foods containing a lot of carbohydrates, yeast and full-fat milk. To quickly get rid of unpleasant sensations, you can drink Espumisan. This is a simethicone-based drug that absorbs gas bubbles.
Vegetables
Read on the topic:
- Causes and consequences of compulsive overeating
- Increasing stress resistance: methods and exercises
- The simplest diet for the lazy - minus 12 kg in 2 weeks
- Egg-grapefruit diet: rules
- Soup diet for weight loss
Eat food only if you feel very hungry. You may feel dizzy and feel heaviness in your stomach. If a person wants to eat something specific, it is not hunger at all, but appetite.