Gastroenterology - a branch of medicine specializing in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Almost every person in his life has encountered acute or chronic diseases of the digestive system. But, probably, not everyone addressed them to a gastroenterologist. But it is advisable to make an appointment with a doctor at the first symptoms of dysfunction of these organs, since it is much easier to treat diseases in the initial stage. If you ignore the symptoms for a long time, there is a high probability that the pathology will become chronic.
In an advanced stage, some diseases of the gastrointestinal tract can cause life-threatening complications (perforation of an ulcer, acute pancreatitis, stuck gallstones, etc.). Moreover, it often happens that until the moment of acute resolution, the symptoms are erased, and the patient does not pay much attention to them, and therefore does not go to the doctor.
What diseases does a gastroenterologist treat?
A gastroenterologist specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of all organs of the gastrointestinal tract:
- esophagus : reflux disease, esophagitis, achalasia cardia, esophagospasm, hiatal hernia, diverticulum, Barrett's esophagus, tumors;
- stomach and duodenum : gastritis, erosion, ulcers, duodenitis, dumping syndrome, polyps, gastric diverticulum, tumors;
- small intestine : enteritis, Whipple's disease, lactase deficiency, Crohn's disease, tumors;
- colon : different types of colitis, Crohn's disease, dysbacteriosis, tumors;
- liver : hepatitis, hepatosis, cirrhosis, tumors, cysts;
- gallbladder : cholangitis, cholecystitis, dyskinesia, cholelithiasis, tumors;
- pancreas : pancreatitis, cysts and tumors.
In addition, gastroenterologists treat congenital anomalies of the gastrointestinal tract in children.
Basic tests, the direction for which is given by a gastroenterologist
Basic laboratory tests include:
- Clinical blood test necessary to detect anemia, signs of inflammatory and tumor processes.
- Coprogram, that is, stool examination. It shows how the body digests food. The indicators characterize the functionality of different parts of the digestive tract.
- Feces for occult blood are needed to diagnose bleeding caused by erosive and oncological processes. The test is necessary for all people 40+; its effectiveness in detecting colon cancer at an early stage reaches 97%.
These tests provide an objective picture of the patient's condition. However, they are not enough for diagnosis. The gastroenterologist will add to the list of recommended laboratory tests in accordance with the patient’s medical history and complaints.
Narrow specializations in gastroenterology
Among doctors specializing in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract there are several narrower specializations. This division helps the specialist to study in more depth and detail the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of a certain area of the gastrointestinal tract. The following specializations are distinguished:
- hepatologist - deals with diseases of the liver and gall bladder;
- proctologist - treats diseases of the rectum;
- coloproctologist - specializes in problems with the entire colon;
- gastroenterologist-surgeon - performs operations on the gastrointestinal tract.
The gastroenterologist sends the patient to these more specialized specialists if he discovers a disease that is difficult to diagnose or treat. And standard cases with easy differential diagnosis and treatment are handled independently.
The most common gastrointestinal problems
People often ask the question: what diseases does a gastroenterologist treat? Below we highlight the most common:
- Gastritis, ulcerative lesions of the duodenum, small and large intestine.
- Irritable bowel syndrome, Crohn's disease.
- Biliary dyskinesia.
- Refluxes and esophagitis.
Now you know who a gastroenterologist is and what he treats . Often he has to identify and treat diseases of the liver or bile ducts. It also happens that the gastroenterologist refers to other doctors. The digestive system consists of a huge number of organs, which is why highly specialized doctors deal with certain diseases:
- Proctologist - identifies and treats diseases of the colon.
- Hepatologist is a doctor who specializes in liver diseases.
If the gastroenterologist cannot find the cause of the symptoms, or he is sure that the cause is not in the gastrointestinal tract, then he will refer the patient to a general practitioner.
Have questions?
You can get detailed information about services and prices and make an appointment by phone. Information about the location of our clinic and directions can be found in the Contacts section.
For what symptoms should you contact a gastroenterologist?
- Abdominal pain of unknown etiology.
- Heartburn and belching.
- Pain when swallowing or difficulty passing food.
- Unpleasant taste in the mouth.
- Regular heaviness in the stomach after eating.
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Chronic and severe flatulence.
- Constipation or vice versa diarrhea.
- Unmotivated weight loss.
- Problems with the absorption of certain vitamins.
- Intolerance to some types of natural food.
- Chronic apathy and fatigue.
- Sallow or yellow complexion.
- Red or black blood in the stool.
In addition, you should definitely contact a gastroenterologist if you have a family history of problems with gastrointestinal diseases. Also, a general practitioner, infectious disease specialist, cardiologist or doctor of another specialization can refer you to a gastroenterologist if he discovers that the symptoms are actually caused by a pathology of the gastrointestinal tract.
Finally, it is very advisable to do regular preventive examinations, for healthy people - once every 2-3 years, and for those who already have a history of acute or chronic disease of the gastrointestinal tract - once a year. In addition, some professions require a certificate from a gastroenterologist stating that the person does not have serious diseases in this area.
Frequent heartburn
Many people know what heartburn is. It is important to understand that occasional heartburn should not be a cause for concern. However, if you feel heartburn constantly and there is a frequent need to take antacids, you should not think that this is the norm.
Frequent heartburn
Frequent heartburn can be a sign of gastritis, ulcers, dysbiosis, candidiasis, or gastric hernia. If your heartburn is accompanied by any of the symptoms, such as difficulty swallowing, food getting stuck, or painful swallowing, you should see a gastroenterologist immediately as this could be a sign of cancer.
When reflux is diagnosed, treatment is prescribed, and in rare cases, even surgical treatment may be recommended for a gastric hernia.
What to look for when choosing a gastroenterologist
A good gastroenterologist regularly takes advanced training courses and often has award certificates. A good sign is conducting scientific activities. The presence of a scientific degree indicates recognition of the doctor’s experience and professionalism by a special commission. If you need a gastroenterologist with an above-average level of qualifications, be sure to pay attention to a scientific degree.
The more experience the doctor has, the more reliable it is. It is better to choose a specialist who has at least 10 years of practical experience. The accumulated knowledge allows us to quickly make the correct diagnosis and better navigate treatment. This also affects the quality of hardware research and surgical operations, since this requires “training the hand” and the eye.
A good gastroenterologist will definitely ask about other diseases that the patient currently or previously suffered from. They can cause or be caused by gastrointestinal diseases. Also important is the attentiveness of the doctor, his desire to conscientiously understand the patient’s situation, explain the intricacies of diet and prevention, and answer all the patient’s questions.
Reviews on the Internet do not always directly correlate with the quality of the doctor, since they are often written for money. In practice, it happens that the higher a doctor’s salary, the more positive reviews he has on the Internet. Also, doctors from private clinics have more positive reviews than from public clinics, since the clinic’s management cares about the reputation of its employees.
How to prepare for an appointment with a gastroenterologist
Most often, no preparation is required for the first appointment with a gastroenterologist. After all, only there the doctor will make the first examination and determine the paradigm for further examination. But you will already need to prepare for the hardware examination procedures. Only in exceptional cases, before the first consultation, a gastroenterologist may prescribe a special diet before the examination, an enema or abstinence from food in the morning. If you want to do an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, then three days before it you need to exclude from your diet foods that cause flatulence: rye bread, legumes, cabbage, etc.
Is there a gastroenterologist at the clinic?
Each city clinic is required to have such a set of specialists as prescribed by the Ministry of Health in its order. A gastroenterologist is not a mandatory physician for medical institutions providing outpatient care to fewer than 50 thousand people. If a city clinic serves an area whose population does not exceed 49 thousand people, it is not required to employ a gastroenterologist.
However, for medical institutions in larger areas, this specialist becomes mandatory, as do a number of other doctors of narrow specialties. In addition, such clinics must be equipped with everything necessary for organizing rehabilitation rooms, magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography machines.
How does an appointment with a gastroenterologist proceed?
First of all, the doctor will question you in detail about the symptoms that bother you, when the disease began, whether it is related to any food products, whether your relatives have the same problems, whether you had the same symptoms earlier in life, what other diseases you have, etc. etc. Also, the specialist will be interested in a list of medications taken against other diseases, since they can have side effects on the gastrointestinal tract.
After taking a thorough history, the doctor begins a physical examination of the patient. A phonendoscope is used for listening. The doctor determines the boundaries of the organs using the tapping method (percussion). The doctor will also feel the abdomen and check to see if it causes pain.
At the final stage of the first consultation, the doctor writes a list of tests and examinations that the patient needs to undergo to clarify the preliminary diagnosis. At the next consultation you will need to bring the results of these tests and examinations and, based on them, the doctor will draw up a complete picture and make a final diagnosis. The gastroenterologist will then prescribe a treatment regimen and observe what effect it has on a particular patient.
What tests do you need to undergo before your appointment?
Every patient wants to save money, and this is absolutely normal. However, independently ordering and undergoing examinations leads to a completely opposite result: some of them will turn out to be unnecessary, while others, on the contrary, will have to be taken additionally.
The maximum you can do is take a general blood test with leukemia formula. This will help you understand whether there is an inflammatory process in your body and assess your overall health. But you shouldn’t take a blood test for biochemistry before visiting a doctor - after a visual examination and taking an anamnesis, the specialist will write out a referral where he will indicate the indicators he is interested in (the more of them, the higher the price of the analysis). Typically this is:
- total protein,
- ALT and AST,
- total and direct bilirubin,
- glucose,
- cholesterol.
It is important! Only a specialist can interpret the test results. If you do not understand the diagnosis of a gastroenterologist and want to understand the problem in detail, do not hesitate to ask questions.
Treatment methods
The most effective method of treating chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract is following a special diet. There are special diets by numbers that are used for various diseases. The doctor can make individual adjustments to them depending on the characteristics of the patient’s body. You need to follow a diet for a long time, it should become part of your lifestyle.
If the diet does not completely help, as well as in cases of pain that significantly interferes with the patient, the doctor prescribes medication. The following groups of drugs are used: antacids, gastroprotectors, adsorbents, enzymes and antienzymes, carminatives, probiotics, painkillers. Often several drugs from different groups are prescribed simultaneously for complex treatment.
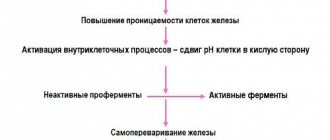
In acute, life-threatening conditions, surgery is indicated. Most often this happens when a stomach or duodenal ulcer is perforated, stones get stuck in the bile ducts, and some other emergency pathologies. If complex conservative treatment does not help, then surgery is also indicated for the patient, but not as urgently.
Advice from a gastroenterologist
The first thing gastroenterologists advise almost all patients is to adjust their diet and diet. Not only the condition of the stomach and intestines, but also the normal functioning of the liver and the entire biliary system (gallbladder, its ducts) depends on what enters the body in the form of food.
If a person continues to consume fatty, spicy, high-calorie foods, treatment, no matter how comprehensive, will not bring the desired result. Consequently, the basic advice of a gastroenterologist concerns, first of all, the following points:
- Assortment and diet. Eliminate heavy foods, eat small meals, possibly according to the prescribed diet (dietary rations according to Pevzner).
- Body weight control. Both obesity and exhaustion significantly reduce the activity of the digestive organs. Body weight must correspond to generally accepted medical standards. (BMI).
- Rejection of bad habits. Neither excessive drinking of alcoholic beverages nor smoking contributes to the normal functioning of the digestive tract. About 85% of liver pathologies are associated with alcohol consumption, smoking is a direct path to gastric ulcer (peptic ulcer).
- Refusal from uncontrolled use of medications and self-medication. Over-the-counter dispensing of many drugs, so-called “folk” remedies, often leads to either chronicization of the pathological process or threatening complications. This is especially true for such a popular method as liver cleansing. More than 45% of people who risk cleansing the liver without prior examination and consultation with a doctor end up on the operating table due to obstruction of the bile ducts.
- Compliance with all medical recommendations even during periods when acute pain and exacerbations have been relieved. Treatment must be completed to the end, then it is possible to reduce the risk of relapses, as well as completely get rid of the disease.
- Undergoing regular medical examinations, which should be comprehensive and include a visit to a gastroenterologist.
Diseases of the digestive system are diseases familiar to every second person. Often such conditions become chronic and are combined with other pathologies. Preventing and preventing dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract is a common task, not only of the doctor, but also of the patient himself.
A gastroenterologist at the Clinic on Komarova will help solve any problems of the digestive system. It is important to remember that the sooner you see a doctor, the more effective the treatment, and the faster the restoration of the functions of the digestive system.
Prevention of gastrointestinal diseases
There are general rules of life that can significantly reduce the harmful effects on the gastrointestinal tract and extend the period of its flawless operation:
- eat more often, but in portions not exceeding 350 ml;
- exclude chips, crackers, marinades, smoked meats;
- every day eat a portion of oatmeal, buckwheat, wheat or millet porridge;
- replace white bread with bran bread;
- reduce the amount of fat in the diet;
- eat a portion of fresh vegetable salad every day;
- drink at least 1.5 liters of liquid;
- include natural probiotics in your diet: kombucha, fermented milk products, sauerkraut;
- exclude carbonated drinks;
- do not abuse coffee;
- exclude medications from the NSAID group (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs);
- If possible, avoid alcohol.
If these measures become a way of your life, then the likelihood of developing a chronic gastrointestinal disease will become much lower. Also, this will help avoid recurrence of diseases that have already occurred, but have been successfully treated.