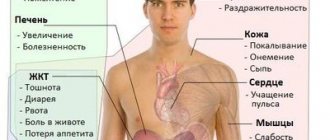
Bleeding as an important symptom
Anal bleeding is an important symptom
The sudden spontaneous disappearance of bleeding from the anus is not a reason for peace, since this is a temporary condition before a re-exacerbation of the disease. But this quiet time can complicate treatment or make a positive outcome of the disease impossible.
Based on the color of the bloody discharge, a preliminary conclusion can be made about its origin. Bleeding can occur from any part of the digestive tract, and the higher the organ is located (esophagus, stomach), the darker the color of the blood.
This fact is explained by the effect of digestive enzymes on the hemoglobin of red blood cells, which changes the color of the blood from scarlet to dark brown or black. An exception to this rule may be the presence of a symptom such as diarrhea, in which the blood released into the intestinal lumen does not have time to darken due to its accelerated passage.
Main causes of gastrointestinal bleeding
Dilatation of hemorrhoidal veins of the rectum
The pathogenesis of the disease involves dilatation of the veins of the lower parts of the rectum, which leads to the rupture of one or more small veins and the release of blood. As a rule, bleeding occurs after defecation or physical activity; the patient notices the release of several drops of scarlet blood on the stool, underwear or toilet paper. There may also be copious bleeding, which may indicate a ruptured hemorrhoid.
The mechanism of bleeding in hemorrhoids is associated with mechanical damage to the dilated veins of the lower rectum by passing feces or as a result of increased pressure in them during straining or physical activity. Typically, such bleeding does not cause pain in the patient, however, when an anal fissure forms or its complication occurs in the form of paraproctitis, pain is present during and after defecation. Less commonly, frequent hemorrhoidal bleeding can lead to the initial stages of anemia with all its manifestations.
With the progression of hemorrhoids and the absence of adequate treatment, the size of the nodes gradually increases, bringing increasing anxiety to the patient, and more often they become traumatized, complicated by bleeding of various volumes. If you suspect the presence of hemorrhoids, you should urgently visit a proctologist, because timely treatment of the disease will prevent the development of its complications.
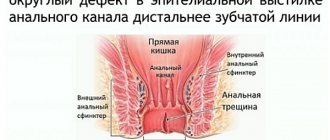
Rectal fissures
Hemorrhoids as a cause of anal bleeding
This disease develops as a result of the mechanical impact of dense feces on the wall of the rectum, in which a rupture of varying length is formed, and as a result, bleeding. The patient notices the discharge of scarlet blood immediately after defecation or during it, as well as sharp pain when feces pass through the area of the rectum with a crack.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of any disease, proctology is no exception, is, first of all, an examination by a doctor. Based on what the doctor reveals during the examination, a diagnosis will be made and treatment will be prescribed. An examination by a proctologist at the Alan Clinic gives a complete picture of your problem, since it is based on two pillars - the doctor’s experience and modern diagnostic equipment.
Comprehensive diagnostics in the Alan Clinic Proctology Department includes:
- Digital examination of the rectum
- Hardware diagnostics Videoanoscopy
- Video sigmoidoscopy
Useful tips for gastrointestinal bleeding
- toilet paper for anal bleeding should have a soft and smooth structure so as not to injure the anal area, which can cause bleeding in the case of anal fissure and hemorrhoids;
- the use of toilet paper should be done with extreme caution, without unnecessary pressure on the anus, so as not to injure the area where the fissure or hemorrhoid is located;
- Untrimmed fingernails can also become a traumatic factor for the affected area.
- in addition, bleeding areas are entry points for infection and failure to comply with hygiene rules and constant trauma to the anal area threatens the occurrence of complications such as inflammation of the hemorrhoid or paraproctitis, which are already acute surgical pathologies and require immediate intervention by a proctologist or surgeon;
- to reduce the traumatic effects of feces during defecation, it is justified to use emollients based on petroleum jelly or another similar substance, which are applied immediately before defecation to the anus;
- It does not hurt to be careful and attentive while eating, especially for people with diseases manifested by gastrointestinal bleeding, since any object that cannot be digested in the gastrointestinal tract, or even unchewed food, can become a traumatic factor and cause bleeding;
- drinking a large amount of liquid prevents the formation of feces of a solid consistency, thereby eliminating the factor of trauma when passing through the anus. The recommended minimum amount of fluid to drink is 2 liters per day.
- Eating foods high in fiber plays a positive role in reducing the factors of trauma to the anus. This group of food products includes vegetables and fruits, dishes made from legumes and unground cereals. When consuming these products, the consistency of stool becomes elastic and soft, which facilitates its unhindered passage through the anus.
If, after observing all the listed precautions, bleeding from the anus has stopped, then you should still not neglect visiting a doctor, since the task of medicine is not only to eliminate the symptom, but also to find out its origin and cure its root cause, thereby preventing recurrence of bleeding.
Discharge of mucus and (or) pus from the anus
Discharge of mucus and pus from the anus is a relatively common symptom of coloproctological diseases. It can be observed during bowel movements, as an admixture in the stool, spontaneously, be permanent, or manifest itself in the form of periodic exacerbations.
Let us immediately make a reservation that the production of mucus is one of the functions of the large intestine, and an excess amount of mucus, which leads to the appearance of macroscopically visible impurities in the feces, is most often a sign of inflammatory processes that are both specific (for example, food poisoning, infectious diseases) and nonspecific in nature - toxic effects, abuse of salty, spicy foods, alcoholic beverages, as well as irritable bowel syndrome, dysbacteriosis, ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease.
Discharge of mucus mixed with blood or ichor should be a mandatory reason for examination, since in this way life-threatening conditions can manifest themselves - in addition to the mentioned nonspecific colitis, these are villous polyps and tumors of the rectum and sigmoid colon. Particularly alarming is the combination of false urges (tenesmus) accompanied by copious mucus secretion.
Sometimes a regular excess amount of mucus can lead to maceration of the perianal skin, multiple erosions and poorly healing deep fissures occur, which is accompanied by anal itching, burning and acute pain. With severe activity of ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease, especially with lesions of the lower parts of the colon - the sigmoid and rectum, the discharge may be mucopurulent in nature and accompanied by an admixture of blood or ichor. The frequency of bowel movements can increase significantly and reach tens of times a day.
Spontaneous discharge of mucus from the anus is possible when the function of holding intestinal contents is impaired - insufficiency of the anal sphincter and rectal prolapse.
Discharge of pus from the anus occurs with severe purulent inflammation: mucous membrane - during acute attacks of ulcerative colitis; perianal and pararectal tissue as well as mesorectum - with incomplete internal fistulas of the rectum, caudal teratomas and pararectal abscesses draining into the rectum.
Discharge of pus from the perianal area is characteristic of pararectal fistulas and epithelial coccygeal tract. Similar complaints are also possible with perianal genital warts and a number of processes accompanied by damage to the perianal skin, but not related to proctology (perianal dermatitis).
Taking into account the fact that some of the diseases accompanied by the discharge of mucus and pus from the anus can be quite dangerous, the presence of such a symptom should be a reason for mandatory examination.
- -Discharge of blood from the anus
- -Pain in the anus and rectum
- - Diarrhea (“diarrhea”).
- -Stomach ache
- -Anemia (“anemia”)
- - Intestinal obstruction
- -Constipation
- -Increased gas formation (flatulence)
- - Tenesmus (false urge to defecate)
- -Fecal and gas incontinence
Treatment methods for hemorrhoids
Choosing toilet paper is an important issue!
In the treatment of hemorrhoids, patients should adhere to the following recommendations:
- avoid constipation, especially during the period of exacerbation of the disease and the occurrence of its complications (bleeding, inflammation of the hemorrhoid). The basis for this task should be a diet high in fiber and fluid. You need to try to develop a conditioned reflex to defecate at the same time and stimulate it with fluid intake. The duration of the act of defecation should not be too long to avoid increasing pressure in the intestines. If these simple measures do not have an effect, then laxatives should be used;
- conduct a daily course of local water procedures in the form of sitz baths for the anal area. They are carried out in the evening in cool water, which has a vasoconstrictor effect and stimulates blood supply to the anal area, or with chamomile decoction, which has disinfectant properties. The decoction is prepared from 4 tablespoons of chamomile flowers, poured into one liter of cold water, by bringing it to a boil and then cooling to room temperature;
- follow a diet that excludes spicy foods, coffee, strong tea, alcohol and includes in the diet a large amount of liquid (up to 2 liters per day) in the form of juices, fruit drinks, water, as well as foods rich in fiber, to form stool of a soft consistency and elastic structure; getting rid of excess weight, especially with fat deposits in the abdominal area, which is a factor that disrupts the venous outflow from the large intestine;
- strict adherence to general hygiene rules and the anal area in particular, which implies washing after each act of defecation with cool, clean water, which helps to narrow the blood vessels and normalize the tone of the vascular wall; exclude heavy lifting as a factor causing an increase in intra-abdominal and, accordingly, intra-intestinal pressure;
- Focus on moderate, non-strength exercise for the lower body. Walking, which stimulates venous outflow from the pelvic organs, as well as gymnastics and swimming have a particularly positive effect. It is recommended to do special gymnastics for the muscles of the anal area every 2 hours, alternately tensing and relaxing them 10-15 times, as well as performing circular movements of the pelvis and bending forward and backward;
- do not use tight-fitting underwear and trousers, so as not to disrupt the venous outflow from the pelvis;
- do not take a long hot bath or shower, which increases blood flow to the pelvis and reduces venous outflow from it.