Computed tomography is one of the proven and reliable methods for studying various pathologies of internal organs located in the abdominal cavity. This type of diagnosis allows you to quickly obtain three-dimensional images of the area under study, which allow you to quickly identify pathological formations of even small size. Thanks to this, the doctor can detect benign and malignant tumors, damage to the lymph nodes, changes in blood vessels, as well as other anomalies in the development of internal organs at the earliest stage of their appearance.
Features of computed tomography:
- high research accuracy. Using tomography, it is possible to accurately identify the organic causes of the disease, since this diagnostic method makes it possible to distinguish between tissues that differ slightly from each other in density;
- minimum time for processing results. This study does not require much time for preparation, so tomography is very often performed in emergency cases when there is a real threat to the patient’s life;
- safety for human health. Modern tomographs fully comply with safety requirements, guaranteeing the absence of any side effects after the examination procedure.
What will an abdominal CT scan show?
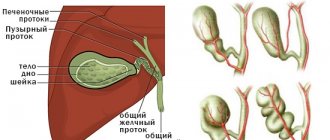
Abdominal CT provides reliable information about the size and location of organs, the condition of their parenchyma and walls, the system of blood vessels and nerves (primarily autonomic), the structure of the ribs, sternum, lumbar and lower thoracic spine.
A CT scan of the abdomen will show:
- internal bleeding;
- accumulations of free fluid (ascites of various origins);
- foreign bodies;
- parasitic cysts;
- inflammation;
- benign and malignant tumors;
- cysts and polyps;
- vascular changes, including thrombosis of mesenteric vessels;
- blood diseases;
- damage to the lymph nodes;
- hepatitis, cirrhosis, liver hepatosis;
- congenital anomalies of organ structure;
- stones in the gall bladder, kidneys and ureters.
- abscesses, phlegmon and other purulent lesions;
- pinched nerve or intervertebral hernia;
- hydronephrosis.
How is an abdominal CT scan performed?
To prepare for an abdominal CT scan, remove any metal accessories, jewelry, or other metal objects as soon as you enter the room. If you have an implant in your abdomen, chest, or pelvis, tell your doctor about it.
During the procedure, the patient lies down on a retractable table, which smoothly enters the chamber of the device. Rotating, the scanning system takes pictures. The doctor views images on a computer in an adjacent room. If the patient lay motionless during the procedure and the photo quality is satisfactory, the diagnosis ends and the specialist begins to compile a report. Otherwise, you will have to do a CT scan of the abdominal cavity again.
Data analysis in St. Petersburg takes 2 hours to prepare. Photos and conclusion can be received in person or by email.
Watch the video to see how the examination is performed.
Contraindications
Patient reviews confirm that the procedure does not cause disease complications or other negative consequences. But this does not mean that everyone without exception can take it. Abdominal CT has contraindications:
- pregnancy - to avoid radiation exposure, patients are prescribed MRI;
- hyperkinesis (involuntary body movements) - the quality of the images will be unsatisfactory, which will interfere with their interpretation;
- extremely pronounced pain syndrome - with severe pain it is difficult for a person to remain still;
- weight more than 150 kg (the device is not designed for heavy loads).
Also, children under five years of age are not examined on a tomograph.
Decoding
Based on the images obtained, the radiologist enters into the examination protocol information about the size, shape, structure and relative position of organs, notes congenital anomalies and detected disorders. Enters his observations into a research protocol, which, together with the images, is transferred to the attending physician or given to the patient. Many diagnostic clinics can record the results on a computer disk, flash card, or send them by email. It is worth considering that the final diagnosis is made by a doctor of the appropriate profile based on the results obtained.
What can you eat before an abdominal CT scan?
Diagnostics are done on an empty stomach so that the digestive process does not distort the results. It is necessary to prepare in advance. Two days before the procedure, you should try to eat little, exclude everything that leads to flatulence (apples, cabbage, legumes, fermented milk and fermented products, yeast products, carbonated drinks), do not drink alcohol, difficult-to-digest and constipating foods.
It matters how long the doctor's appointment is scheduled. If the procedure is planned:
- in the morning - you need to limit yourself to dinner from non-calorie liquid food;
- in the afternoon - 4-5 hours before a CT scan of the abdominal cavity, a light breakfast is allowed;
- in the evening – the patient has breakfast and refuses lunch.
Preparation for an abdominal CT scan may include bowel cleansing. Then before the examination, after discussion with the treating doctor, it is recommended to do an enema or take a laxative solution orally the night before.
The process of performing a computed tomography scan of the lungs
After preliminary preparation, the patient is escorted to the diagnostic room and placed on the CT machine table. If necessary, contrast is introduced.
The scanning process goes unnoticed by the patient, without causing any discomfort. To obtain the clearest possible image, the patient must remain motionless, and also, at the request of the doctor, hold his breath when necessary.
It is important to pay attention to the parameters of the equipment used for diagnostics. To conduct a high-quality study, the number of CT slices must be at least 64.
CT scan of the abdomen with contrast
Native CT scan of the abdominal organs is performed without contrast. If more accurate data is needed, an examination with a contrast agent is prescribed. Once in the blood, the dye makes pathologically altered tissues better visible in the image.
Additional tools are needed when diagnosing tumors and metastases and, if necessary, studying the blood flow in detail.
An abdominal CT scan with contrast will show oncology in the initial stages, ureteral obstruction and other abnormalities. Angiographic examination will reveal:
- aneurysms;
- thrombosis;
- atherosclerosis;
- abnormal narrowing of the walls of blood vessels;
- tumors;
- vascular injuries;
- dissection of the aortic wall.
Abdominal CT with contrast often causes side effects:
- chills or fever, dizziness, nausea, general weakness when contrast spreads throughout the body;
- skin irritation at the injection site during intravenous administration.
According to patient reviews, these symptoms go away on their own within a short time.
If complications appear in the form of shortness of breath, bronchospasm, urticaria, itching, facial swelling, nausea, vomiting or low blood pressure, this indicates that an allergic reaction to the contrast agent has occurred. In such cases, the patient is provided with medical care.
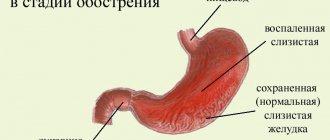
What does a CT scan of the stomach show?
Tomograms visualize the esophagus, stomach, vascular architecture, and lymph nodes.
Complaints for which a CT scan of the stomach is justified:
- dyspepsia;
- nausea and vomiting;
- belching and heartburn;
- coated tongue and bad breath;
- loss of appetite;
- feeling of rapid filling of the stomach;
- abdominal pain and heaviness in the epigastric region;
- the appearance of blood in the vomit;
- melena (bloody diarrhea);
- low-grade fever, suspicious for stomach cancer;
- weight loss;
- weakness, fatigue, pale skin (signs of anemia and cancer intoxication).
These complaints can occur not only with tumors, but also with other gastrointestinal pathologies:
- peptic ulcer;
- acute and chronic gastritis;
- developmental anomalies;
- esophageal stricture, etc.
A CT scan of the stomach can help determine the cause of the following conditions that often accompany advanced gastric cancer:
- abnormal peritoneal effusions (fluid accumulation in the abdomen);
- stomach bleeding;
- cachexia (exhaustion).
If a CT scan of the stomach suspects a malignant neoplasm, you can additionally do a computer or magnetic resonance scan of the brain, chest, abdomen and pelvic organs, which will help determine the stage.
During endoscopic examination, due to the location of the tumor in the thickness of the wall, it is not possible to confirm the diagnosis, which is an indication for CT scanning of the stomach.
The radiology doctor pays attention to the following criteria:
- evenness and clarity of the external and internal contours of the organ;
- polypous protrusions;
- wall infiltration;
- uniform contrast distribution;
- wall thickness;
- condition of the fat layer around the stomach;
- size of lymph nodes, etc.
Contraindications to the procedure with contrast
To avoid complications, abdominal CT is not performed in patients with:
- allergy to iodine;
- severe renal failure with elevated creatinine levels in the blood (creatinine testing is included in the services of our diagnostic center);
- hyperthyroidism and other thyroid diseases.
Children over 12 years of age have their internal organs checked with contrast only according to indications with a doctor’s referral.
For women breastfeeding, the procedure is not prohibited. Radiation exposure does not affect milk, but the dye partially penetrates into it. Therefore, you will have to give up at least two consecutive feedings. Before the study, the woman must express and store the milk. After CT or MSCT with contrast, you must wait until the drug leaves the body and after two pumpings, feed the baby as usual.
Any questions you may have and the price for contrast examinations can be clarified with the administrator.
What else should you consider?
When going for an examination, you must take with you a change of shoes, clean drinking water and medical documents related to the disease - a card, extracts, certificates, results of previous studies. It is advisable to choose clothes that do not have metal elements. Before the contrast agent is administered, you are allowed to have a snack for about an hour before the examination to prevent nausea. For such a snack, light food is suitable, for example, cottage cheese or fruit.
Some categories of patients require special preparation. Before examining the body using a CT scan with contrast, nursing mothers are advised to express milk in an amount that will be enough for the baby for a day. This time passes until the drug is completely removed from the body.
Patients with diabetes should discuss with their doctor the use of medications that may affect the accuracy of the scan results.
Based on the results of the examination, the patient receives a transcript on paper and a recording on a disk or flash drive. Rate this article: (1 rated 5 out of 5)
Taking urografin before abdominal CT scan
Urografin belongs to the ionic group of radiocontrast agents. Such drugs are characterized by high chemical toxicity and an increased risk of developing undesirable reactions (pain in the vascular area, feeling of heat, surges in blood pressure, etc.). Therefore, in the Magnit clinic, for CT scans of the abdominal cavity they use not Urografin, but its more advanced analogue Ultravist. This is a nonionic contrast agent that is well tolerated. With bolus administration of the substance, side effects occur much less frequently, are moderate in nature and quickly disappear after the end of the procedure.
In what cases does a doctor prescribe a CT scan of the lungs?
Examination of the chest organs using computed tomography is prescribed for certain indications:
- Diagnosis or clarification of diagnosis for pneumonia, bronchitis, thromboembolism, etc.;
- Diagnostics or clarifying examination for the presence of space-occupying formations such as tumors, abscesses, cysts;
- Relapse of the inflammatory process in the lungs;
- Tendency for the patient to develop certain pathologies (lung cancer in close relatives);
- Chest injuries;
- Assessment of disseminated pathological processes developing in lung tissue - sarcoidosis, tuberculosis, metastases;
- In-depth diagnostics of patients with a history of smoking for at least 20 years, or consumption of more than 20 cigarettes per day);
- Assessing the effectiveness of therapy, preoperative diagnosis, identifying a site for biopsy;
- Identification of the causes of cough, hemoptysis, sputum production, shortness of breath, fever, weakness, etc. in cases where other diagnostic methods did not provide an informative picture of the course of the disease.
CT scan of the abdomen - early diagnosis of cancer
If you suspect cancer, you should do a CT scan of the abdominal cavity as soon as possible. According to experts, this is the most reliable method for detecting tumors of internal organs at an early stage. The photo shows cancer cells in the stomach, liver, and pelvic organs (retroperitoneal space), when there are no external symptoms yet.
Thanks to CT scanning of the abdominal organs, the oncologist has the opportunity to select the optimal treatment tactics to prevent the growth of malignant cells into neighboring tissues and metastasis through the blood and lymph throughout the body.
Sign up for an MRI and in!
Alternative examination methods
An X-ray or MRI can replace a CT scan. The advantage of CT scanning of the abdominal cavity over them is the ability to check the structure of hollow organs, including the intestines and stomach. In addition, magnetic resonance imaging, unlike CT, is not indicated for patients using pacemakers, insulin pumps and metal implants. X-ray is less informative compared to CT scan of the abdominal cavity.
Another examination option is ultrasound. Due to its high safety and almost complete absence of contraindications, ultrasound diagnostics is prescribed quite often. Especially if primary diagnosis is required. CT is used if ultrasound turns out to be uninformative.
Evaluation of results
Both the radiologist and the attending physician evaluate the results. The first gives a general description of the tomography results, and the second compares the image with the medical history. The attending physician also takes into account information obtained from other studies, which gives a clear picture of what is happening.
Tomography visualizes the relief of the organ, the thickness and structure of its walls. The procedure helps to identify cancerous tumors, erosive changes, infectious or inflammatory foci, ulcers, etc. It is important to consider that CT equipment is not capable of detecting small lesions (from 1 millimeter or less) and diagnosing the disease in the first stages of development. Also, the procedure does not allow assessing the color of the mucous layer or obtaining material for further laboratory research.