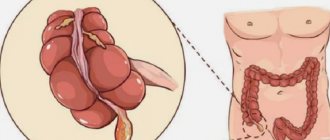
Acute inflammation of the appendix is called appendicitis and is rightfully considered an extremely dangerous disease that can provoke the development of peritonitis and ultimately lead to death. This disease affects both adults and children of both sexes, but the most frequently mentioned diagnosis is confirmed in young people aged 15 to 35 years.
The consequences of appendicitis are eliminated exclusively by surgery. At the same time, in order to avoid complications, surgery to remove the appendix should be carried out as soon as possible. That is why a patient who discovers signs of this disease should immediately call an emergency medical team for prompt hospitalization. How is appendicitis excised?
About the reasons for the development of appendicitis
The development of appendicitis can be triggered by an excess of intestinal bacteria.
For what reason can the appendix become inflamed? Today doctors cannot yet give a definite answer to this question. However, it is known for certain that the development of the disease can most likely be provoked by the following factors:
- Excess of intestinal bacteria. Normally, the human intestine is “home” to almost 3 kg of active bacterial masses. If the number of these bacteria sharply increases (this can happen as a result of an infection entering the body), the appendix becomes inflamed.
- Blockage of the appendix. Normally, this vermiform appendix communicates with the rest of the intestine through a special lumen. However, due to blockage of this area with feces, seeds and seeds from berries or fruits eaten the day before, as well as small foreign bodies (including those that entered the intestines through the anus), the appendix may become inflamed. It is curious that in some cases, narrowing of the lumen between the intestinal sections is possible as a result of ordinary muscle spasm.
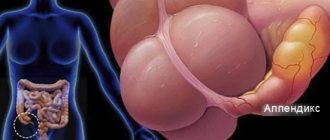
Where is the appendix located and why is it needed?
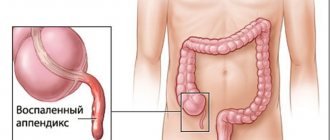
The appendix is located in the lower abdomen, approximately midway between the navel and the right ilium. The location of the appendix can vary: the appendix can be raised to the right hypochondrium or lowered into the lower part of the pelvis. The appendix is tubular in shape, its length ranges from four to 15 cm, and its diameter is up to ten mm.
The appendix is needed for the formation of immunity and intestinal biocenosis, as well as for regulating the level of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli in the intestines. In addition, the organ performs secretory and protective functions. Thanks to the powerful lymphatic apparatus, the vermiform appendix regulates the outflow of lymph in the intestines.
About the stages of disease development
Catarrhal appendicitis is the initial stage of the disease.
As a rule, acute appendicitis occurs quite rapidly, successively passing through several stages of its development:
- Catarrhal appendicitis. At the initial stage of the disease, the inflamed appendix increases slightly in size, which may be accompanied by pain in the abdominal area and periodic nausea.
- Purulent appendicitis. As the name suggests, at this stage of development of the disease, the walls and internal cavity of the appendix become covered with purulent foci. This process is accompanied by acute pain in the right side.
- Phlegmonous appendicitis. At this stage of the disease, the appendix is almost completely saturated with pus, due to which it significantly increases in size. Pain in the right side during this period becomes almost unbearable.
- Rupture of the appendix. The appendix bursts, and its contents spill throughout the abdominal cavity, causing the development of peritonitis and other complications.
Disadvantages of the method
Despite the effectiveness of the method and the ability to detect pathology in the appendix, ultrasound analysis has disadvantages, including:
- blurred image due to insufficient sensor area;
- having a lower resolution than computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging;
- the need to carry out special preparatory measures before diagnosing the abdominal region and retroperitoneal organs (exclusion of gas-forming products, use of anti-flatulence agents);
- the presence of a large amount of interference, which can be explained by the heterogeneity of the internal structures of the abdominal region.
Recommended video:
Ultrasound is an effective method for diagnosing the appendix, which allows you to identify signs of inflammation. Therefore, there is no need to be afraid of such an event.
About common complications of appendicitis
Intestinal obstruction can cause appendicitis.
Acute appendicitis often occurs with complications. The most common problems that accompany inflammation of the appendix are listed below:
- Intestinal obstruction. As mentioned above, often the cause of appendicitis is blockage of the lumen between the appendix and the rest of the gastrointestinal tract. If the factors that provoked the disease were not immediately eliminated, the risk of a similar problem occurring in other parts of the intestine and, as a result, the development of obstruction is extremely high. This complication can be diagnosed by the accompanying symptoms - bloating, nausea and repeated vomiting.
- Inflammation of the portal vein. If appendicitis was caused by an infection, inflammatory processes can affect other organs of the gastrointestinal tract. Most often, the portal vein, which is involved in the blood supply to the liver, spleen, stomach and pancreas, as well as most of the intestines, suffers from purulent inflammation.
- Peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum). In the event of a rupture of the appendix, the pus accumulated in it spreads throughout the abdominal cavity, provoking the development of inflammatory processes of varying severity. It is peritonitis that causes most fatal cases of acute appendicitis and minimizes the patient’s chances of a full recovery.
Preparing for an appendectomy:
In acute appendicitis, preparation for appendectomy is carried out promptly; as a rule, the condition of the patient's cardiac and respiratory systems is assessed.
For a planned operation , the results of blood tests, urine tests, fluorography, and an electrocardiogram are required. Women need to be examined by a gynecologist to rule out inflammatory processes that can lead to complications.
You should not take food or water for at least six hours before surgery. In case of laparoscopic surgery, it is necessary to first perform an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
How is appendicitis diagnosed?
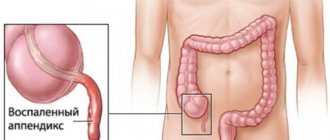
Abdominal pain may be a sign of appendicitis.
The patient’s symptoms play a huge role in the accurate diagnosis of acute appendicitis. If inflammation of the appendix is suspected, doctors usually pay attention to the following patient complaints:
- constant aching pain in the abdomen, slightly more acutely felt in the navel area, as well as in the lower right side (or in the liver area, if the appendix is located high);
- increased body temperature;
- occasional nausea or vomiting;
- any symptoms of inflammation of organs adjacent to the appendix (lower back pain, cystitis, etc.).
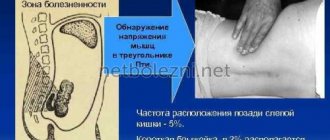
To more accurately determine the source of pain, the doctor may ask the patient to simulate a cough. For this diagnostic method to work, the patient should refrain from taking painkillers immediately before the examination.
If, by the time of examination by a doctor, the patient stops complaining of pain in the abdominal cavity, this may be an alarming sign. Often the relief is temporary and is directly related to the fact that the patient’s appendix has already burst (that is, a so-called perforation has occurred).
Diagnostics
The symptoms of chronic appendicitis are smoothed out, so diagnosis is difficult. To correctly make a diagnosis, it is necessary to exclude diseases of other abdominal and pelvic organs. A comprehensive examination is required.
- A general blood test can detect moderate leukocytosis and a shift in the leukocyte count to the left in patients with chronic appendicitis. Urine examination is necessary to exclude pathology of the urinary organs.
- X-ray with a contrast agent helps to detect obstruction of the opening connecting the appendix to the cecum. The examination may also show accumulations of stool and fibrous adhesions.
- Ultrasound diagnostics reveals an abscess of the appendix and helps to exclude pathologies of the ovaries and uterus in women.
- Computed tomography is the most informative examination method. With its help, it is possible to determine the location of the process, the thickness of its walls, changes in the cavity and in the surrounding tissues.
- Diagnostic laparoscopy allows you to examine in detail the location of pain and determine all pathological changes.
During a comprehensive examination, the doctor excludes chronic cholecystitis, ulcers, kidney pathologies, helminthic infestations, and gynecological diseases in women.
How to provide first aid during an attack of acute appendicitis?
At the slightest sign of acute appendicitis, you should consult a doctor.
At the slightest sign of acute appendicitis, in order to avoid complications, the patient should see a doctor as soon as possible and be hospitalized.
Due to the fact that this disease requires urgent surgical intervention, if characteristic symptoms appear, it is quite acceptable to go to emergency medical care. How can you help a patient while waiting for an emergency medical team that has already been called?
Place the patient in bed and apply cold to his right side. Lack of physical activity, of course, does not guarantee safety, but it minimizes the risk of appendix rupture.
Do not use painkillers. Taking appropriate medications can make it much more difficult for doctors to diagnose the disease. For the same reason, the patient should refuse any drink or food shortly before the doctor arrives.
Any means that alleviate the symptoms of the disease should be used with caution!
Laxatives may help relieve the feeling of heaviness in the intestines, but will almost certainly lead to a rupture of the appendix. The same goes for a warm heating pad placed on your stomach.
Bibliography
- Barsukova, I.M. Acute appendicitis: history and modern organization of medical care// I.M. Barsukova, M.V. Gavshchuk, A.P. Krivov. - text: direct // Scientific notes of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. I. P. Pavlova, 2022.- No. 3 – P.43-49, DOI: 10.24884/1607-4181-2018-25-3-43-49.
- Clinical guidelines “Acute appendicitis in adults”, 2022, Developers: All-Russian public association “Russian Society of Surgeons”, All-Russian public organization “Russian Society of Endoscopic Surgeons”. - Text: electronic. - URL: (access date: 09.29.2021).
- Draft clinical guidelines “Acute appendicitis in children”, 2016. Developer: Russian Association of Pediatric Surgeons, -Text: electronic.- URL: (access date: 09.29.2021).
Author:
Pugonina Tatyana Alekseevna, Therapist
How are patients with appendicitis operated on?
The operation to remove the appendix takes no more than 40 minutes.
As mentioned above, today the only effective treatment for appendicitis is surgery aimed at removing the inflamed organ. This procedure is called appendectomy, and it goes like this:
- the patient is given local anesthesia (when operating on young children, for obvious reasons, the choice is often made in favor of general anesthesia);
- A small incision is made on the patient’s right side along an oblique line;
- Using special instruments, the appendix is removed from the abdominal cavity through the resulting hole;
- Sutures are placed on the incision.
Normally, the entire procedure to remove the appendix takes no more than 40 minutes. As an alternative method of surgery, endoscopy can be used - that is, removal of the organ through several barely noticeable punctures in the abdominal cavity.
This approach allows the patient to recover faster after the procedure. In addition, after such an intervention, the patient will almost certainly not have surgical scars, which also greatly contributed to the popularization of this method.
It is worth understanding, however, that in advanced stages of the disease (in particular, after the appendix has ruptured), endoscopy is not effective.
Recovery
Appendectomy
Emergency and planned surgical removal of the appendix in medical. Professional doctors will perform the operation quickly and painlessly.
After the operation is completed, the patient is transferred to a hospital, where he will spend 2-5 days, depending on the chosen surgical technique and the presence of complications. To relieve temporary pain and prevent the development of postoperative infection, painkillers and antibiotics are prescribed. The patient can have a drainage system installed to avoid a purulent inflammatory process. Rehabilitation continues until the stitches are removed (7-9 days).
Post-operative care
Removing appendicitis is not a complicated operation, after which the patient will fully recover and be able to return to their normal lifestyle within 2 months. Until then, he will have to somewhat limit his physical activity. However, the person operated on will be able to move independently and take care of himself within 7-10 days after the procedure (as a rule, by this time the stitches have already been removed from the wound).
An unpleasant surprise for the patient may be a special diet prescribed for everyone who has undergone surgery to remove appendicitis. So, in the first hours after the operation, the patient will have to limit himself to only tea or water. A little later, broths and liquid porridges will be added to his diet. It is recommended to eat in small portions. More specific recommendations on this matter are given to patients by their attending physicians on an individual basis.
Advantages of performing an appendectomy at Euromed Clinic:
- Euromed Clinic is a full-service clinic. Before the operation, if necessary, we will arrange for you consultations with a therapist, cardiologist and any other specialist;
- Our own laboratory allows you to take the necessary tests at once and quickly get results;
- all surgeons at Euromed Clinic are experienced and qualified specialists;
- the operating room is equipped with modern medical equipment;
- use of the latest generation of anesthesia;
- own hospital with modern comfortable rooms;
- experienced surgeons at the clinic use the most modern dressing and suture materials and disposable instruments;
- All reusable metal instruments undergo a three-stage sterilization system and are then placed in vacuum packaging to ensure the sterility of the instrument.
You can make an appointment at a convenient time with a surgeon at Euromed Clinic by calling + 7 812 327 03 01 or online.
Prices
Price (rub.)In installments* (rub.)Consultation with a surgeon on the operation (SPECIAL)0—Online doctor’s opinion on the operation (SPECIAL)0—Appendectomy Cat. I. complexity 26000—Appendectomy Cat. II. difficulty 36000—* You can read more about the conditions here - Treatment on credit or in installments
The cost is preliminary. The exact cost of the operation can only be determined by a surgeon during a free consultation.