Pain in the left side is always alarming. Many vital organs are concentrated in this area, which can thus signal malfunctions. The nature of the sensations varies. The pain can be dull, sharp, aching, bursting. The more intense it is, the sooner you need to seek medical help. However, you should not endure and eliminate even mild but long-lasting pain on your own. It can be a symptom of excessive exercise or constipation, or it can indicate kidney damage and even intestinal tumors. In women, left-sided pain is often a consequence of gynecological diseases.
Most often, pain in the left side is not the only symptom. It is accompanied by other signs indicating pathology or infection. Their correct interpretation will allow us to understand in which direction further diagnosis and treatment should be carried out.
What kind of pain can there be in the left side?
Pain in the left side is not always typical. It will differ depending on the disease that provoked it. Based only on the nature of the pain, it will not be possible to make an accurate diagnosis, but one or another pathology can be suspected.
Features of the pain syndrome:
- Blunt pain. It most often indicates damage to the female reproductive system.
- Dull pain accompanied by increased body temperature, fatigue and weakness is a sign of an inflammatory process.
- Nagging pain can act as a signal of suppuration of the inflammatory focus, especially if it occurs against the background of hyperthermia.
- Nagging pain without fever may indicate a strangulated hernia and cancer.
- A stabbing acute pain in the lower abdomen in women is a signal of ovarian rupture. It is intense and does not go away over time.
- Stitching migrating pain may be a symptom of intestinal overflow with gases. Similar sensations occur with damage to the kidneys and ureters.
- Sharp spasm-type pain can signal renal colic due to exacerbation of urolithiasis. Other causes include inflammation or rupture of the ovary, damage to the bladder.
Not only the nature of the pain, but also its concentration is of important diagnostic importance:
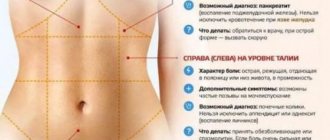
- Left hypochondrium: pancreatitis, diseases of the digestive system, damage to the spleen, myocardial infarction.
- Closer to the center: nonspecific ulcerative colitis, intestinal infections.
- In the lower abdomen: damage to the left ovary or appendage, hernia, constipation.
- With irradiation to the back: kidney disease, lung damage.
Pain in the left side, depending on the provoking factor:
- During meals.
- Due to a long period of hunger.
- After physical activity.
- Against a background of stress.
According to the mechanism of development, pain is of 4 types:
- Spastic.
- Peritoneal.
- Vascular.
- Distensional.
You should consult a doctor immediately if the pain is acute, intensifies and does not stop within half an hour. The situation can be aggravated by bleeding, high body temperature, vomiting, and lethargy. Such symptoms require hospitalization.
Anatomical features of the left half of the abdomen
Abdominal pain on the left can be caused by any anatomical structure located in this area. These include the digestive organs:
- stomach;
- pancreas;
- duodenum and half of the small intestine;
- part of the large intestine from the transverse colon, descending, sigmoid and rectum.
The organ of hematopoiesis and immune defense is the spleen. Organs of urination and excretion: left kidney, ureter, bladder. At the same time, it is necessary to take into account the possibility of damage to:
- abdominal wall and layers of peritoneum lining the internal cavity;
- lower ribs on the left;
- vessels and nerves of the abdominal cavity.
We do not consider here the pelvic organs, which lie in the lowest part. Their role in the examination of women and men for pain cannot be reduced to identify, for example, the source of inflammation or the original tumor.
Causes of pain in the left side
Pain in the left side is not always a sign of illness. There are often cases when its cause is physiological in origin. So, the left side can prick after excessive stress on the body. Training promotes a rush of blood to the abdominal organs, which fills the spleen. Therefore, after performing intense exercise, people often complain of discomfort in the left side. To eliminate it, just rest for about 10 minutes.
The next day after training, the abdominal muscles may feel pain in the left side. It intensifies with tension in the abdominal wall, when turning the body, coughing, and straining. Normally, the discomfort goes away within a few days.
Other risk factors that can cause left side pain include:
- Being in the cold. People say “it’s blown.” In this case, unpleasant sensations can radiate to the lumbar region, and sometimes there are complaints of shooting in the spine.
- Menu with consumption of fatty , fried, spicy foods, drinking alcoholic beverages. Problems may occur in people with previously diagnosed pancreatitis, gastric and duodenal ulcers.
- Injuries. Even minor bruises can cause pain for a long time. With rib fractures, your side may hurt for several months.
- Menstrual cycle. The intensity of pain depends on the individual characteristics of the female body. However, there should not be severe discomfort requiring painkillers.
- A condition where menstruation is so painful that it significantly reduces a woman's quality of life is called dysmenorrhea. With dysmenorrhea, pain may occur both in the left side and in the abdomen, more often in the lower part. Other symptoms - headache, nausea, vomiting, fever, chills, aches, myalgia can also bother you during menstruation.
Recently, a new drug for women’s pain, Nexemezin, appeared on the Russian market. A single dose of Nexemesin helps relieve pain during menstruation and lasts up to 12 hours. The drug is of high quality and reasonable price.
Intestinal diseases
- Constipation. If there is no stool for two or more days, then a person may experience dull pain in the left side, in the lower abdomen. Additional signs: a feeling of fullness in the intestines, periodic urge to defecate, painful spasms, burning in the rectum when dry feces are released.
- IBS. With irritable bowel syndrome, the pain is concentrated in the left side. It can be dull and acute, occur like contractions or be present on an ongoing basis. The pain reaches its maximum intensity in the morning, after waking up. In this case, the person experiences severe discomfort and the urge to empty the intestines. After going to the toilet the pain disappears. Additional symptoms: several attempts to defecate in the morning, no discomfort at night, increased pain before menstruation (in women).
- Sigmoiditis. The inflammatory process in the area of the sigmoid colon is accompanied by intense pain in the left side, which radiates to the perineum and thigh. Additional signs: false urge to have a bowel movement, foul-smelling diarrhea, blood in the stool. If the process is in a chronic stage, then an increase in symptoms can be caused by nutritional disturbances and stress on the body physically or psychoemotionally.
- Diverticulitis. The formation of diverticula leads to pain in the left side, which increases in severity during bowel movements. After its completion, the discomfort goes away. If the patient develops constipation, the pain becomes more intense. Attacks are rare, but sometimes they can last up to several days. Additional signs: flatulence, unstable stool, in which constipation alternates with diarrhea.
- UC. In this long-term and sluggish process that accompanies intestinal inflammation, the pain is concentrated under the ilium on the left. As the disease progresses, it spreads to the entire left half of the abdomen. Additional signs: loose stools with blood, which is noticeable to the naked eye, loss of appetite, false urge to have a bowel movement, accompanied by pain.
- Polyps. Benign neoplasms are accompanied by a dull pain that can radiate to the left side. The larger the tumor, the greater the discomfort. Additional signs: constant constipation, which occurs due to a mechanical obstruction in the path of feces.
- Cancer of the sigmoid or colon. At first, the patient experiences a certain discomfort; as the tumor grows, it turns into severe pain that bothers him on an ongoing basis. Additional signs: stool disorders, blood in the stool, constipation, diarrhea.
- Left-sided inguinal hernia. The pain is dull, becomes pronounced when the abdominal wall is tense, when bending and turning the body. When a hernia is strangulated, the pain becomes very severe.
- Dysbacteriosis. Disorders of the intestinal microflora often develop when taking antibacterial drugs. Discomfort is constantly present, intensifying after eating and before attempting to empty the intestines. Additional signs: feces have a strong smell, stool occurs up to 7 times a day, gas formation increases, appetite disappears.
Intestinal infections
Amoebiasis, dysentery, escherichiosis, salmonellosis. The entry of infectious agents into the intestines leads to painful sensations in the left side, which occur like contractions. The disease manifests itself approximately one day after infection. Additional signs: diarrhea, stool can occur up to 20 times a day, stool with blood and mucus.
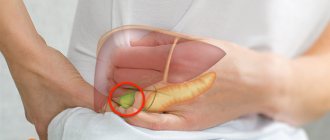
Pancreatic damage
- Chronic pancreatitis. The pain is concentrated in the left side, it is weak, aching, but present on a constant basis. A tendency to increase is observed with errors in nutrition with the consumption of fatty foods. Additional signs: constipation alternating with diarrhea, increased gas formation, rumbling in the stomach.
- Acute pancreatitis. The pain is unbearable, concentrated in the left hypochondrium, and occurs suddenly. Strengthening occurs in the supine position and on the left side. Additional signs: vomiting, high fever, feeling unwell.
Diseases of the female reproductive system
The most common causes of pain in the left side in women:
- Adnexitis (inflammation of the left appendage of the uterus).
- Ectopic pregnancy concentrated in the left tube.
- Endometriosis.
The intensity of pain depends on the degree of progression of the pathological process. However, it will always intensify a few days before the onset of menstrual bleeding. Additional signs: pain during intimacy, spreading to the pubis and perineum.
Diseases of the urinary system
- Left-sided renal colic due to urolithiasis. The pain does not stop, it exhausts the person, occurs in the form of attacks, and spreads to the lumbar region, lower abdomen, and perineum. Additional signs: urination is difficult or absent at all, hyperthermic reaction.
Diseases of the stomach and intestines
- Gastritis and stomach ulcers. With these pathologies, pain radiates to the left hypochondrium. They can be aching and dull, and during exacerbation - cramping. Additional signs: symptoms intensify after eating, stool disorder is observed, most often in the form of diarrhea.
- Duodenal ulcer. The pain is concentrated in the left hypochondrium and in the epigastric region. Increased discomfort is observed on an empty stomach and at night. Additional signs: nausea, belching, constipation and diarrhea.
Spleen damage
- Spleen injuries. The pain is severe and can radiate to the shoulder. Its intensity depends on the severity of the organ damage.
- Splenic infarction. The pain is concentrated in the left side and under the ribs, radiating to the shoulder blade and to the heart.
- Abscess of the spleen. The pain is severe, throbbing, and can radiate to the lower back. Additional signs: fever, weakness, digestive disorders.
- Thrombosis of the splenic vein. The pain is paroxysmal, concentrated in the left hypochondrium. It is not related to food intake or exercise. Additional signs: vomiting blood.
Intercostal neuralgia
The discomfort is concentrated in the left hypochondrium and radiates to the left side. Patients indicate lumbago, reminiscent of electric shocks. Provoking factors include uncomfortable body position and physical activity. During an attack, a person tries to avoid taking deep breaths so as not to increase the pain.
Rare causes of pain
- Tietze syndrome. With this disease, the cartilaginous segments of the ribs become inflamed. When the lower left ribs are affected, the pain is concentrated in the left side. The disease can be provoked by injuries to the sternum and excessive physical stress. Young people under 35 years of age are most often affected.
- Angina pectoris. Pain when the heart muscle is damaged can spread to the left hypochondrium and radiate to the arm. Additional signs: the attack lasts 15 minutes, it can be relieved by taking nitroglycerin.
- Some hereditary diseases. Pain in the left side can occur with porphyria and histiocytosis X.
- Pregnancy. Pain in the left side occurs when the intestinal loops are compressed by the enlarged uterus. Women may complain of constipation.
Characteristics of pain in diseases of the urinary organs
Urinary diseases occur in cases of pathology of the kidneys, bladder, and ureter. The localization we are studying includes local pain in the ureter caused by its stretching and radiating pain from the left kidney.
Pyelonephritis
Inflammation of internal structures (pelvis, calyces) caused by infection. It begins suddenly with high fever, vomiting, chills, pain in the lower back on the left, radiating to the left side of the abdomen. Impaired urination, pain, and urinary retention occur. Pulsating pain is an unfavorable sign indicating the formation of an abscess in the kidney.
In the chronic course, exacerbations are milder, but with the same symptoms. As a result, scars appear in place of the inflamed tissue, the kidney becomes deformed and loses function. Kidney failure occurs when the second healthy kidney stops working hard to compensate for the diseased organ. The disease is treated by urologists with antibacterial agents, diuretics, and, if necessary, by opening the suppuration or resection of part of the kidney.
Urolithiasis disease
Often accompanied by inflammation of the urinary tract and metabolic disorders. It is caused by the loss of crystalline sediment in the urine, its settling in the pelvis and gluing into stones. The most common compositions are phosphates, oxalates, and urates.
The stone causes a disruption in the process of urine outflow, so stagnation and distension form in the higher-lying sections. The movement of a stone along the ureter explains why the lower abdomen hurts. Clinically, after intense shaking or running, the patient experiences an attack of renal colic.
The pain is very intense in nature, cutting. Localized in the lower back or to the left of the navel. Acute urinary retention occurs. The duration of the attack is up to several hours. For emergency care, painkillers and antispasmodics are administered. Frequent recurrence of attacks is an indication for surgical removal of the stone.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the cause of abdominal pain begins with interviewing the patient and palpating the area about which the patient complains. Often the doctor gets the data he needs by palpating the intestines. Women with complaints of pain in the left side are referred to a gynecologist for consultation.
The following tests may be needed to confirm the diagnosis:
- Contrast radiography of the intestines, irrigoscopy.
- Colonoscopy. This method allows you to visualize the intestines from the inside, detecting areas of inflammation or neoplasm.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs. It is prescribed for suspected damage to the spleen and pancreas.
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs. It is indicated for women with suspected gynecological diseases.
- Taking tests: stool, urine, blood.
- Endoscopy is prescribed to patients with gastric and duodenal ulcers and gastritis.
- MRI and CT. These complex diagnostic procedures are prescribed when cancerous tumors are suspected. With their help, it is possible to visualize hernias.
- ECG in 12 leads. An examination is required if damage to the heart muscle is suspected.
After receiving the results, the doctor will select the appropriate therapy for the patient.
Prevention
As for prevention, the basis is a proper balanced diet. It is advisable to minimize hot and spicy foods. Legumes can irritate the mucous membranes and cause flatulence.
It is important to give up bad habits such as smoking and alcohol , get proper rest and get a good night's sleep. Any training should be carried out only 1.5-2 hours after eating.
To avoid gynecological problems, women need to treat existing inflammation of the genital organs and undergo regular examinations by a gynecologist.
Treatment
If the pain is provoked by physiological factors, then therapy is not prescribed. It is enough to reduce the load on the body and wait for the discomfort to disappear. This takes no more than 3 days.
When pain in the left side is caused by constipation, the menu is adjusted. Vegetables and fruits rich in fiber are introduced into the diet, and fermented milk drinks are added. Compliance with the drinking regime is mandatory.
With irritable bowel symptoms, eliminating stress factors comes to the fore. Sometimes consultations with a psychologist can help cope with the disease.
To make the patient feel better until complete recovery, painkillers and anti-spasm medications can be prescribed. Sometimes anesthetics are administered in the form of blockades. This approach will not eliminate the cause of left-sided pain, but will only muffle it.
Depending on the diagnosis, medications are selected:
- In case of dysbacteriosis, correction of the microflora is required; enzymes can be added to the therapeutic regimen.
- For constipation, suppositories, laxatives, and oils are used.
- To treat intestinal infections, a drug is selected that will affect the pathogenic flora. Antibiotics are rarely used.
- If the pancreas is damaged, follow a diet. After the exacerbation is relieved, digestive enzymes are used.
Surgery may be required in severe conditions, for example, in the presence of cancerous tumors in the intestines, rupture of the spleen, complications of diverticulitis, and more. The decision about the advisability of surgical intervention is made by the doctor.
Disturbances in the functioning of the urinary system
Cystitis is one of the most common causes of aching pain in women. The bladder can become inflamed after simple hypothermia. Pain when urinating, false and frequent urges are characteristic symptoms of this disease. Other frequently diagnosed pathologies of the urinary system include pyelonephritis and urethritis, in which case discomfort occurs not only in the lower abdomen, but also in the back (especially in the lumbar region).
If pain is dull in nature and occurs in the area above the pubis, bladder polyps can be assumed.
What to do if you have pain in your left side?
You should not endure pain in your left side; you should seek medical help. If the situation is not an emergency, and the diagnosis has not yet been established, it is necessary to follow a diet, eating soft foods (meat soufflé, pureed dishes). Spicy, salty, and spicy foods are excluded from the diet. Products must undergo gentle heat treatment, frying is excluded.
Acute “dagger” pain requires calling an ambulance. In most cases, such a symptom requires emergency surgical intervention.
When to see a doctor
If the pain takes you by surprise, you need to seek help from a doctor as soon as possible, especially since the symptom often occurs without any previous signs.
Medical attention is required if the following additional symptoms occur:
- The pain is intense and growing in nature.
- The abdomen changed in size and became hard.
- Your temperature has risen, you experience general weakness and dizziness.
- Attacks of nausea and vomiting and diarrhea appeared.
- An admixture of blood and mucus in the vomit and feces.
- Sudden changes in pressure.
- Change in facial skin color.
- Tachycardia.
- Cold sweat. If the condition does not require urgent intervention, then you should contact a medical facility.
If dangerous symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor for diagnosis. In this case, treatment should be carried out by a gastroenterologist, but the help of an immunologist, urologist or gynecologist may also be needed.