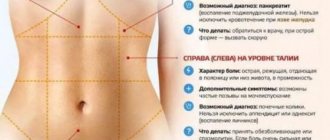
Pain in the liver refers to complaints ranging from discomfort in the right hypochondrium to intense (in some cases continuous) pain. Interesting fact: the liver itself cannot hurt - anatomy does not allow it. There are no pain receptors on it; nature did not provide them. The pain symptom is caused by its shell (capsule) or neighboring organs, which may signal a problem. The best way to notice the “approaching disaster” in time is to undergo a special diagnosis, which will be prescribed by a gastroenterologist.
Why does pain occur? Even the most minor deviations in the organ change its size, which contributes to the stretching of the membrane on which there are receptors. Pathology of the pancreas, gallbladder, bile ducts can also be accompanied by pain in the right hypochondrium.
Pain and discomfort in this organ are of a different nature: aching or cutting pain, constant or short-term, it can intensify from excessive stress, appear after taking even a small amount of fatty or spicy foods, or in stressful situations. Sometimes a painful symptom in the right hypochondrium is accompanied by flatulence, stool problems, heartburn and bad breath.
If the disease is in a period of exacerbation, the temperature may rise, severe weakness and headache may appear.
Causes of hepatic colic
The pain of renal colic is simply unbearable
Before moving on to considering the main symptoms of hepatic colic, great attention must be paid to the reasons for which it occurs. The main causes of hepatic colic in humans include:
- Impaired patency in the bile ducts, which is caused by problems directly with the gallbladder itself
- Complete blockage of the bile flow, which most often occurs due to the presence of stones. Almost all patients who have gallstones are warned about the possibility of developing such an attack
- Compression of the bile duct by a tumor, both malignant and benign
- Partial blockage of the duct with coagulated blood or a clot of pus
- A spasm that occurs in smooth muscle and can be caused by various factors
- Poor nutrition, namely abuse of spicy and fatty foods. Of course, we are not talking about one-time intake of fatty and spicy foods. Colic can occur when these foods predominate in a person's diet.
- Alcohol abuse. As in the case of spicy food, here we are talking about frequent and uncontrolled consumption of alcohol
- Stress, which, as many people know, negatively affects human health and can provoke the development of hepatic colic
- Great physical activity. This, first of all, includes staying in a bent over position for a long time, which is typical for summer residents and for those who often wash clothes by hand.
Almost all causes of colic are caused by the person himself, and only a few can be hereditary. That is why, in order to avoid illness, it is recommended to pay as much attention to your health as possible.
Etiotropic drugs
Etiotropic therapy drugs are medications whose action is aimed at suppressing vital activity and destroying infectious agents. This group includes:
- antiviral agents
– natural and recombinant interferons. Recommended for the treatment of viral hepatitis; - antibiotics
– macrolides, fluoroquinolones, cephalosporins, tetracyclines. Used in the treatment of diseases of the gallbladder and biliary tract; - antifungals
– medications for the treatment of deep mycoses (fungi). Prescribed for disseminated candidiasis, aspergillosis, cryptococcosis, candidomycosis; - antiprotozoal
- antigiardiasis drugs metronidazole and furazolidone.
Symptoms of colic
Every person should know how hepatic colic begins in order to take timely measures and provide first aid. So, the main symptoms of hepatic colic include:
- Pain that is characterized as sharp, intense and quite severe. Typically, a painful attack occurs at night, when a person is in a supine position. If we talk about the beginning of an attack, then in the first minutes the pain will be localized in the area of the right hypochondrium, and then begins to radiate to the back, arm, etc. In addition, in some cases the pain can cover the entire abdomen. It should be noted that a painful attack can begin not only in a supine position. Many patients note that the pain began to increase when inhaling
- Nausea that will be so severe that the person sometimes cannot tolerate it
- Vomiting, repeated and not bringing any relief. It occurs due to the fact that a person is tormented by severe attacks of nausea, which cannot be drowned out by anything and cannot be controlled.
- Pale skin that appears against the background of a painful attack. And also the person sweats. In some cases, a slight yellow tint appears on the skin, which indicates problems with bile excretion
- Abdominal bloating, which may be detected by a doctor when examining a patient
- Painful sensations during examination, namely palpation of the abdomen. Also, there is strong tension in all muscles located in this area.
- Increased body temperature, the indicators of which vary depending on the individual characteristics of the human body
- White color of stool
- Dark color of urine
It should be noted that an attack of hepatic colic can last from several minutes to several hours. In any case, if at least one of the listed symptoms appears and the person is suffering from severe pain, then it is necessary to immediately call an ambulance, since hepatic colic is one of those conditions when the patient requires urgent medical attention.
Content:
- Corona is always a risk
- Why does the liver suffer?
- Impact of COVID-19 on the liver
- Effect of Covid-19 therapy on the liver
- Hepatoprotective therapy
- Liver recovery after coronavirus infection
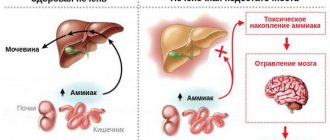
Many patients who have suffered from Covid-19 ask the doctor how to restore the liver after the disease. Liver pathologies indeed often develop due to a progressive viral infection. Their symptoms cannot be ignored, since it is not known whether the organ will be able to organize its work on its own.
It is much wiser to resort to methods that promote the renewal of liver cells and eliminate the local inflammatory process. In this article we will tell you how COVID-19 affects the body’s main “filter” and how to treat the liver after coronavirus.
First aid to a patient
Poor nutrition as a cause of renal colic
If there is a person nearby who has an attack of hepatic colic, there is no need to be afraid. It is necessary to gather courage and provide first aid to the person, which will consist of the following:
- First of all, you need to try to calm the person down, since anxiety and fear provoke pain even more.
- Call an ambulance and tell them what symptoms the patient has
After the person has calmed down, he must be laid on his right side, after placing a heating pad under him. Heat is required in order to relieve muscle spasm, at least a little, which in most cases provokes severe pain. True, you need to be careful with heat, since it can only be used if a person does not have gallstones.
If an attack occurs for the first time, and the person himself does not know its cause, then it is better to simply lay him on his right side and not use heat, as it can cause harm.
If possible, give the person pain medication. It should be noted that it is best to administer the drug intramuscularly for it to have a positive effect. If there are no necessary medications nearby and there is no person who can give an injection, then it is better not to give the patient any pills. The tablets will definitely not have the desired effect, since, combined with nausea and frequent vomiting, they simply will not reach the stomach and will not dissolve. After this, you need to wait for the ambulance to arrive and distract the person, although this will not be very easy.
Phosphogliv* – restoration and protection of the liver
Phosphogliv* is a liver treatment drug with anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and antifibrotic properties. In its production, two active components are used: essential phospholipids and glycyrrhizic acid.
Essential phospholipids
– structural elements of liver cell membranes. In the treatment of liver diseases, phospholipids have restorative and regenerative effects.
Glycyrrhizic acid
is a substance with pronounced anti-inflammatory, antifibrotic and antioxidant properties.
Acting in combination, the active components of the drug Phosphogliv* mutually enhance and complement each other, significantly increasing the effectiveness of therapy. The hepatoprotector Phosphogliv* can be indicated for use as a drug for the restoration of liver cells in the treatment of acute and chronic forms of viral hepatitis, steatosis, toxic lesions and as part of complex therapy for liver cirrhosis.
What not to do if you have colic
Not everyone can recognize the symptoms of hepatic colic.
There are a number of measures that should never be taken when there is a suspicion of hepatic colic. True, not all people know about this, and can harm a person, doing it with the best intentions. So, with hepatic colic it is prohibited:
- Make any movements. It is advisable to simply lie down and remain in this position until the doctor arrives or until the attack ends.
- Massage the area where the pain occurred, as you can provoke an even worse attack
- Apply a heating pad to the area where it hurts, because heat can cause swelling to develop. In this case, it is better, on the contrary, to use a cold compress to reduce the pain.
- Take some food, even if it’s not solid food
- Drink, even plain water
- As for food and drink, this cannot be done because any new portion of food will provoke additional secretion of bile, and as a result, either the occurrence of a new attack or an intensification of the previous one.
Not every person will be able to distinguish the symptoms of hepatic colic from the symptoms of any other disease. In fact, without a medical education, it is very difficult to do this. That is why, if a loved one or someone you just know has such an attack, you must immediately call an ambulance and explain to them what happened. You shouldn't try to help, especially if you don't know how, because it can only cause harm.
Diagnostics
Patients with complaints of heaviness in the hypochondrium are examined by a gastroenterologist, who, if necessary, gives a referral to specialized specialists (hepatologist, oncohematologist). During the initial examination, the doctor palpates the liver and spleen, determines their size, and examines the skin for the presence of jaundice, spider veins, and dilated superficial vessels. A full diagnostic complex is prescribed, which includes:
- Ultrasound of the liver.
With an ultrasound examination, the doctor evaluates the size and structure of the organ parenchyma, identifies focal processes (cysts, abscesses, tumors), and detects signs of hepatitis or fibrous changes. The scan is complemented by Doppler ultrasound to check blood flow in the hepatic vessels. - ERCP.
Endoscopic examination is recommended for a comprehensive diagnosis of the state of the biliary system, finding stones, and deformations of the organ. To assess the contractile function of the bladder and obtain a bile sample for analysis, fractional duodenal intubation is performed. - Radiography.
On a survey image of the abdominal cavity, hepatosplenomegaly and displacement of neighboring organs are possible. To exclude damage to the respiratory system as the cause of heaviness in the hypochondrium, a chest x-ray is performed in two projections. - Biopsy of liver tissue.
Based on the results of histological analysis of biopsy specimens, the doctor differentiates benign and malignant neoplasms and establishes a diagnosis of parasitic infestations. The method is informative for assessing the prevalence of fibrosis and diagnosing autoimmune hepatitis. - Laboratory methods
. In a biochemical blood test for liver pathologies accompanied by heaviness in the hypochondrium, the content of cytolysis enzymes (ALT and AST) increases and the levels of bilirubin and cholesterol increase. To confirm infectious hepatitis, ELISA and PCR are performed. Hematological problems are excluded based on hemogram and coagulogram data.
In modern hepatology, static scintigraphy is used to clarify the diagnosis and assess the functional activity of the liver. Elastography is a widely used non-invasive method for studying the degree of fibrosis of the liver parenchyma. To identify a tumor process of the spleen or liver, MSCT of the abdominal organs is informative. In difficult situations, doctors resort to diagnostic laparoscopy.
Ultrasound of the liver
Literature:
- Complete reference book for infectious disease specialists / N.I. Zryachkin et al. - M.: Eksmo, 2004 (JSC Mozhaisk Printing Plant). – 990 s.
- RMJ. 2022, No. 9: Clinical recommendations and algorithms for practicing physicians. — 2022. — 80 p.
- COVID-19 and liver damage/ Ilchenko Lyudmila Yurievna, Nikitin I.G., Fedorov I.G./ 2022 / Journal “Archives of Internal Medicine”
The text was checked by medical experts: Head of the socio-psychological service of the Alkoklinik MC, psychiatrist-narcologist L.A. Serova.
CAN'T FIND THE ANSWER?
Consult a specialist
Or call: +7 (495) 798-30-80
Call! We work around the clock!