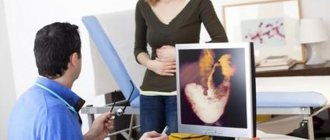
With standard vertigo syndrome, the condition is characterized by a feeling of the body moving in space, imaginary rotation, lack of ground underfoot, “helicopter flights,” etc. For the treatment of dizziness in the head when standing up (at normal pressure), the causes of this condition are of primary importance, since this condition itself is not a disease, but a symptom indicating the presence of a particular disease. At the moment, about 80 pathologies are known, the symptoms of which may be dizziness, weakness, headache, nausea and vomiting, and the causes of these conditions are very diverse and require immediate treatment.
The most common causes of persistent dizziness, tinnitus, weakness in the legs and other symptoms:
- Pathologies of the inner ear;
- Basilar migraine;
- Meniere's disease;
- Psychogenic dizziness - in the treatment of psychogenic vestibular dizziness with nausea, vomiting, weakness and pain in the eyes, the help of not only a general practitioner, but also a psychologist or even a psychotherapist is required;
- Vestibular neuritis;
- Widespread benign paroxysmal positional vertigo with weakness, drowsiness, apathy;
- A brain tumor;
- Multiple sclerosis;
- Cerebrovascular accident, characterized by vasoconstriction, drowsiness, dizziness, numbness and other symptoms;
- Pathologies of the cervical spine, vertebrobasilar insufficiency;
- A history of head or spinal injuries;
- Anemia;
- Low blood pressure;
- Diabetes.
- PMS - in some cases, assistance to a woman with dizziness, abdominal pain and low temperature before menstruation should be provided at a professional medical level; menopause can also cause dizziness in women, and only a specialist can tell you how to get rid of it;
- Noise, ringing and pain in the ears, nausea, diarrhea and dizziness can be symptoms of a number of infectious diseases;
- Severe stress leads to darkening of the eyes and prolonged dizziness, which causes a lot of inconvenience.
Many patients want to understand why dizziness, pressure when walking, sweating and fatigue in men accompany them for many years. Others experience severe dizziness and nausea with normal blood pressure while lying down or sitting. Mild benign positional vertigo may also occur in adolescents and young adults. In all these cases, careful diagnosis is required.
Trembling in the limbs, severe weakness, unsteadiness, neck pain with dizziness and chills may indicate a previous injury, stenosis of the subclavian artery or circulatory disorders in the brain (hypoxia, neurocirculatory dystonia, encephalopathy). One of the causes of dizziness in the back of the head in the morning may be Meniere's disease. The underlying disease is sometimes a brain tumor, perlymphatic fistula, BPPV and a number of other diseases.
Causes of chills
Hypothermia
Chills without fever most often occur under the influence of an external cause - during the cold season or when clothing does not match the weather. The symptoms increase gradually: first, a person feels cold and a desire to warm up, then a downward trembling of small muscles begins - from the masticatory muscles and shoulder girdle to the muscle groups of the lower extremities. The skin turns pale. Short-term symptoms of chills are observed when a cold wind blows. The symptoms disappear on their own after warming up. Severe hypothermia requires medical attention.
Stress
During emotional stress, adrenaline is released in excess, which causes spasm of skin vessels and muscle tremors. A short-term feeling of muscle tension and trembling, combined with a feeling of extreme cold and increased sweating, is noted with fright and fear. In women, such attacks of chills of a psychogenic cause without fever are more common, which is due to the lability of the nervous system. Unpleasant symptoms disappear after normalization of the emotional state. If the signs bother you often, or even more so constantly, you should visit a doctor.
The influence of sex hormones in women
Menopause and menopause are the most common reasons why chills occur in females. The presence of the symptom is due to sudden changes in the levels of estrogen and progesterone, which disrupt the functioning of the nervous and cardiovascular systems. Patients report alternating periods of coldness and trembling in the body with hot flashes and redness of the face. Chills without fever in women are observed in the premenstrual period and on the first day of menstruation, which is associated with fluctuations in estrogen and blood loss.
The disorder worries pregnant women starting from the first trimester, when the secretion of sex hormones changes and the synthesis of tropic hormones in the anterior pituitary gland increases. Symptoms of chills appear at any time of the day, last a short time and do not significantly affect general well-being. In the second and third trimesters, the frequency of discomfort decreases. If prolonged severe chills develop, the general condition persistently worsens, urgent medical attention is needed.
Fever
Muscle tremors and a strong feeling of cold are observed in the first period of fever (with a cold, acute respiratory viral infection or non-infectious pathology), when the body temperature is just beginning to rise. The symptom is associated with centralization of blood circulation and spasm of peripheral vessels. Chills always develop at fever; the severity of the disorder depends on the speed of onset of fever and the cause of the symptoms. A person feels a sharp cold, he begins to shake, while the skin turns pale, the area of the nasolabial triangle becomes cyanotic (cyanotic).
Chills are accompanied by headache, severe weakness, and malaise. To keep warm, patients cover themselves with several blankets. When the temperature reaches its maximum, which indicates the transition of the fever into the second period, the feeling of cold and trembling disappear, the skin becomes bright pink. Manifestations of chills more often occur in adults, since in children the temperature often rises sharply without a prodromal period. Chilling is sometimes possible with a rapid (critical) decrease in temperature to normal levels.
Chronic inflammation
Frequent causes of chills at night are sluggish infectious or somatic inflammatory diseases. The development of the disorder is caused by chronic intoxication of the body, changes in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system. In men, the main cause of chills without fever is tuberculosis of the lungs or lymph nodes. With this infection, patients wake up in the middle of the night from malaise and feeling cold, and take another blanket to keep warm. Increased sweating and pronounced pallor of the skin are also characteristic. Other reasons for chills include:
- Autoimmune diseases
: rheumatoid arthritis, vasculitis, Hashimoto's thyroiditis. - Damage to internal organs
: chronic pyelonephritis, liver pathology.
Purulent processes
Purulent inflammation of any localization causes sharp, shaking chills, when a person shakes almost continuously, the skin becomes pale in color, and a marble pattern is formed on the distal parts of the extremities due to insufficient filling of the blood vessels and a decrease in blood pressure. Symptoms appear against the background of hectic or constant high fever; profuse sweats are typical as a consequence of massive intoxication of the body. The most common purulent causes of chills:
- Skin lesions
: panaritium, numerous boils and carbuncles, suppuration of wounds. - Pathologies of internal organs
: intestinal and liver abscess, pleural empyema, purulent cholecystitis and cholangitis. - Pylephlebitis.
- Gynecological diseases
: purulent mastitis, pyosalpinx and pyometra.
Vegetovascular dystonia
Violation of the coordinated work of the sympathetic and parasympathetic components of autonomic regulation, as the cause of the appearance of chills without fever, is noted quite often, especially in young people against the background of excitement and emotional turmoil. The symptom is caused by a narrowing of the lumen of peripheral vessels and a decrease in blood flow in the skin, which is perceived by the body as severe cold. Therefore, with VSD, the main symptoms of chills occur: slight muscle tremors, especially in the face and shoulder girdle - teeth begin to “chatter”, the skin turns pale and becomes covered with characteristic pimples.
Endocrine disorders
Common causes of chills without fever, which are more typical for women, are thyroid dysfunction. The organ secretes the hormone thyroxine, which is responsible for thermoregulation: with its deficiency, the basal metabolism slows down and body temperature decreases. The body reacts to such changes with contractile thermogenesis - generalized trembling of all muscle groups. The skin looks very pale and dry and feels cold to the touch. The sudden appearance of chills and excessive sweating are the first signs of hypoglycemia in diabetes mellitus.
Rare causes
- Systemic allergic reactions
: Quincke's edema, anaphylactic shock, allergic alveolitis in children. - Raynaud's disease and syndrome
. - Blood loss
: massive external bleeding, hemorrhages into organs and natural body cavities. - Psychogenic factors
: panic attacks, depressive states. - Neurological pathology
: amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, temporal lobe epilepsy. - Chronic fatigue syndrome.
- Iatrogenic causes
: post-transfusion reactions, complications of kidney transplantation.
Attacks of unbearable nausea, anxiety, shaking throughout the body, strong heartbeat
Anna
June 14, 2016
Hello, I'm 20 years old. In September 2015, for the first time in my life, I had an attack, which was characterized by simply unbearable nausea, my whole body seemed to be turning inside out, there was some blurred vision, my whole body was tense to the limit, there was no way to relax. This condition was very frightening, I thought I was dying. The body periodically shook very strongly, the mouth became very dry, there was pressure on the chest, and in general there was a heaviness throughout the whole body. This state came suddenly, nothing foreshadowed it. The only thing was that a month or two before it there was periodic nausea (not as strong as during an attack), not caused by anything, but it went away. The attack lasted 4 days, during which I could not eat, sleep, lay flat without even being able to turn on my side (it got even worse), opening all the windows because there was not enough air, and sometimes I felt feverish. I went to the student hospital, where they decided to treat me for gastritis (because FGD showed that I had superficial gastritis). I had serious doubts that superficial gastritis, which occurs in every second person, could cause SUCH symptoms. Urine, stool, and blood tests were good. I was prescribed Omeprazole, Creon, Allochol, Duspatalin, Motilak, which did not affect my condition in any way. I called an ambulance, they injected Cirukal, but in response to my complaints that it didn’t help me at all, they shrugged their shoulders. Every day it became a little easier, and on the fifth day it completely went away. At the end of August of the same year, I had a rupture of a cyst on the right ovary with hemorrhage, I was urgently taken away by ambulance, a laparotomy was performed, and partial resection of the ovary. In the hospital, an increase in blood sugar was first detected: morning - 7.0, afternoon - 7.9, evening - 8. I went to an endocrinologist, they identified the risk of developing type 1 diabetes, and told me to follow a diet without insulin therapy for now. To my questions about whether this condition could be caused by a slight increase in blood sugar (above 8 and did not rise at all at the time of the attack), the doctor gave a negative answer. On March 16, 2016, the attack repeated with the same symptoms and began just as suddenly. Before this, I had been feeling nauseous again for a month, I went to the hospital in fear that this condition would reoccur, they again prescribed Omeprazoles, Creons, and gave me glucose (!) with Riboxin, apparently due to the doctor’s carelessness, although I warned about problems with sugar. These days, for the second time in my life, I still had an attack, which also lasted 4 days, but was much more severe. After stopping it, I was left with nausea that has not gone away to this day. For 3 months now I have been tormented by CONSTANT nausea, which cannot be relieved by any pills. The student hospital gave me a referral for hospitalization in the endocrinology department because I had ketosis. There they finally made a diagnosis - type 1 diabetes, prescribed Lantus insulin - 6 units at night, 9 tables. Sugar levels range from 6.7 on an empty stomach to 8.4 in the evening. Again, endocrinologists say that nausea cannot be caused by such indicators. They gave me a referral to a gastroenterologist. I was tested for parasites and opisthorchiasis - everything was negative. Blood test for hormones is good. I did an FGD again - superficial gastritis. The gastroenterologist prescribed Itomed, Khairabezol, propyl - no changes. I went to neurologists, ECHO, REG - everything was fine. The therapist no longer knew where to send me, so he gave me a referral to a psychotherapist with a supposed diagnosis of “psychosomatic syndrome.” I told the psychotherapist about the severe stress associated with the rupture of the cyst; in 2014, I also experienced severe stress associated with the death of a close friend, maybe this somehow triggered such processes in the body, because nothing like this had happened before. The psychotherapist said that it was very similar and prescribed Eglonil for 2 weeks. The nausea remained. Then he prescribed Chloroprotexen for 2 weeks, no changes. Then I took phenazepam for 3-4 days, no progress. The psychotherapist said that he prescribed drugs from different groups, and since they had no effect on me, I was not their patient. I don't know where to turn. Moreover, I have had migraines since I was 7 years old. She spent her entire childhood in hospitals and was examined. I suffer a lot with severe frequent headaches. My head hurts almost every day. I did an MRI and didn't show anything. I relieve pain with pentalgin and sedalgin. The attacks stop only when I take sumatriptan-teva. I asked this question to a therapist on a similar site, the doctor’s opinion was that it was a severe form of migraine, occurring in parallel with depression. The doctor says that I need inpatient treatment in a neurological department and proper selection of therapy. But the fact is that no matter how much I was examined, the doctors said that simple migraine cannot be treated, and the pain can only be relieved with pills. My nausea has nothing to do with the headache and taking these pills, that is, it does not get worse and remains unchanged. Help me please! I am absolutely exhausted, nausea poisons my life. Thank you in advance.
The question is closed
migraine
constant nausea for 3 months
Diagnostics
The causes of chills with or without fever are determined by the local physician, who draws up a plan for the initial examination and, if necessary, refers the patient for consultation to other specialists. The diagnostic search involves excluding the most common etiological factors of chilling, for which instrumental and laboratory tests are used. The most informative methods are:
- Blood analysis
. All subjects with chills for no apparent reason have a general blood test taken, which shows signs of inflammation or bleeding. A biochemical study reveals symptoms of damage to internal organs, primarily the liver. The levels of thyroid and adrenal hormones are determined. - Bacteriological method
. If chilling is accompanied by a runny nose, cough, and symptoms of gastrointestinal damage, it is necessary to collect appropriate biological material for microscopy and culture on selective nutrient media. If signs of night chills persist for a long time, three-time examination of sputum for tuberculosis is informative. - Neurological examination
. Chills without fever are often a symptom of disorders of autonomic innervation, for the diagnosis of which special tests are used: orthostatic, Danini-Aschner. To exclude severe neurological disorders, the symmetry and integrity of basic reflexes, muscle tone and coordination of movements are checked. - Ultrasound diagnostics
. Periodic complaints of chills without an increase in body temperature are an indication for an ultrasound of the thyroid gland. The method makes it possible to identify space-occupying formations and diffuse replacement of parenchyma with lymphoid or connective tissue. An ultrasound of the abdominal organs is also performed, with special attention paid to the adrenal glands. - X-ray imaging
. When chilling is combined with possible damage to internal organs, a plain radiography of the abdominal cavity and a radiograph of the lungs in two projections are recommended. In case of constant chills of the whole body for no reason, highly sensitive thyroid scintigraphy is prescribed. - Additional Research
. Serological tests (RIF, ELISA, PCR) are performed for rapid diagnosis of viral infections. To exclude a gynecological cause of severe chills in a woman, the vagina and cervix are examined in a speculum and smears are taken. Patients with exudative diathesis are prescribed an extended immunogram study.
Treatment of persistent headaches and fainting
When answering the question of what to do if you experience severe dizziness and nausea, especially if you feel sick when bending over, you need to understand that this is not a momentary phenomenon, but a symptom. Dizziness does not arise or disappear on its own - it is evidence of a disease, sometimes very serious and life-threatening. Self-medication and negligent attitude towards these disorders entails serious consequences for human health and life. Treatment with drugs and tablets for severe dizziness should only be prescribed by a specialist.
To diagnose and treat the causes of severe dizziness, headaches and sudden weakness, it is necessary to undergo examination by a neurologist, otolaryngologist, ophthalmologist, endocrinologist. In addition, you should undergo a number of other laboratory and instrumental studies.
- general blood test;
- blood glucose level analysis;
- electrocardiogram;
- audiographic examination;
- tomography - computer or magnetic resonance imaging;
- duplex scanning (otherwise Doppler ultrasound) of the vessels of the head;
- radiography.
In a number of diseases, the following symptoms may be observed: dizziness, palpitations, temperature, fever, etc. The combination of such symptoms can indicate either a regular panic attack or a serious illness.
The treatment program is selected based on diagnostic data. Treatment of dizziness itself includes drug therapy and special sets of physical exercises to train the vestibular system. Remember that only a highly qualified doctor can decide what to do about the causes of severe dizziness in men, women and children.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
If the cause of severe chills without fever is general hypothermia, you need to take the person to a warm room as quickly as possible, give him hot tea, cover him with several blankets or prepare a warm bath. Chilling caused by stress goes away on its own after the traumatic situation is resolved; tea with mint, which has a sedative effect, also helps to calm down. If chills develop for no apparent reason and are combined with a deterioration in health or general malaise, you should consult a doctor.
Hot tea will help you warm up when you have a chill.
Conservative therapy
Medical tactics depend on the etiological factor of the discomfort and the general condition of the patient. If you feel chills without an increase in temperature, etiotropic treatment is indicated to eliminate the underlying disease. If symptoms occur against the background of a high fever, you first need to lower the temperature. For colds, physiotherapeutic treatment methods are successfully used: gargling, nasal rinsing, electrophoresis and local electromagnetic effects. The drug therapy regimen may include:
- Antipyretics
. Medicines with an antipyretic effect (usually paracetamol) are prescribed for fever over 38.5 °C. Children's temperature is reduced starting from 38 degrees. Aspirin should not be taken due to its toxic effect on the liver and red blood cells. - Antispasmodics
. The drugs are especially effective for chills without fever. They relax the smooth muscles of blood vessels, which helps to expand their lumen and normalize blood flow. Medicines can be used in the first stage of fever. - Sedatives
. Mild herbal remedies help normalize vegetative reactions and the tone of superficial vessels. The drugs are indicated for VSD, stress and chronic fatigue syndrome. Sometimes the treatment regimen is supplemented with “daytime” tranquilizers. - Hormonal agents
. If the appearance of chills without fever is due to fluctuations in female sex hormones during menopause, replacement therapy with estrogen drugs is recommended. For hypothyroidism, take levothyroxine. - Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
. If chills occur without fever, but are accompanied by signs of inflammation, NSAIDs are indicated. The drugs block the synthesis of specific mediators and cytokines. To consolidate the results, they are used in long courses.
Attacks of dizziness with cervical osteochondrosis
The spine and its diseases have the most direct impact on chronic dizziness. Degenerative disorders of the cervical spine are accompanied by disruption of the internal receptors and impaired blood circulation in the vertebral arteries, which leads to nausea, fainting, dizziness when turning the head and other not very pleasant phenomena. When diagnosed with cervical osteochondrosis, dizziness may be accompanied by various symptoms. With osteochondrosis, treatment of vomiting after eating, weakness and dizziness is impossible without addressing the main source of troubles. Effective treatment of persistent dizziness with cervical osteochondrosis involves the use of a complex of medical techniques and a number of procedures.