Malfunctions of the liver and gallbladder are studied by hepatology. Hepatologists at our clinic treat hepatitis, cirrhosis, cholecystitis, tumor neoplasms, diseases of the biliary tract and much more. The clinic performs a thorough examination to establish an accurate diagnosis, as well as identify the causes of the disease. Next, our qualified doctors select the appropriate treatment method. We use the latest equipment. If you are concerned about hepatological problems, we are guaranteed to help you get rid of them.
When should you contact a gastroenterologist?
Diseases of the liver, biliary tract, and gallbladder are accompanied by certain symptoms. Symptoms that require you to contact a hepatologist are as follows:
- nausea
- discomfort, heaviness or pain in the right hypochondrium
- bitterness in the mouth
- loss of appetite
- yellowing of the skin and sclera (whites of the eyes)
- itchy skin
- ascites (excess fluid in the abdominal cavity)
- urine too dark
- grayish white stool
- bloody vomiting.
What diseases may your symptoms indicate?
The above symptoms may accompany various diseases of the gallbladder and liver, namely:
- hepatitis: autoimmune, hepatitis C, chronic viral B, C, D, toxic hepatitis, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
- primary biliary cirrhosis.
- alcoholic liver disease.
- liver cirrhosis of any etiology.
- hereditary hemochromatosis (excessive iron accumulation).
- primary sclerosing cholangitis.
- cholelithiasis.
- Wilson-Konovalov disease.
- chronic cholecystitis.
- fatty hepatosis.
- biliary dyskinesia.
Symptoms
In the early stages, symptoms of liver disease may be mild. Over time, signs of liver and biliary tract disease become more distinct.
- dyspepsia: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, flatulence, belching;
- yellowing of the skin, mucous membranes;
- skin itching;
- fatigue, weakness;
- dark urine and at the same time light feces;
- symmetrical red spots on the palms;
- sometimes - an increase in temperature;
- heaviness in the epigastric region, right hypochondrium;
- swelling of the legs;
- increase in abdominal size (ascites);
- drowsiness during the day, insomnia at night;
- the appearance of spider veins;
- weight loss, loss of appetite.
If these symptoms occur, you should consult a gastroenterologist-hepatologist!
What diagnostic methods will be offered to you at the clinic?
Sometimes an experienced hepatologist at the clinic can assume the diagnosis immediately, at first glance, since some of the symptoms of liver disease are visible to the naked eye (typical types of jaundice, skin rash). But more often, diseases of both the liver and gall bladder go unnoticed for quite a long time, manifesting clinically in the later stages, and then it can be more difficult to help.
Therefore, it is so important to notice in time minor but inexplicable symptoms, such as fatigue, poor appetite, and discomfort in the right hypochondrium. Not only notice, but also come to our clinic in a timely manner.
Diagnosis of gallbladder and liver diseases begins with a conversation with a specialist about your symptoms. It is also important to find out what diseases you have suffered.
A medical examination will reveal a number of symptoms. You will be offered all the necessary instrumental and clinical examinations to accurately diagnose your disease.
Laboratory research methods are as follows:
- blood biochemistry
- general blood and urine tests
- serological reactions
- molecular genetic research.
Instrumental diagnostic methods:
- Ultrasound of the liver, biliary, biliary tract
These examinations are often sufficient to identify liver diseases and can be completed in our clinic. For a more detailed examination, the doctor may refer the patient to a diagnostic center to conduct:
- radiology diagnostics
- fibroelastography
- computed tomography
- magnetic resonance imaging
- X-ray examination
- liver biopsy
- invasive studies
- colonoscopy.
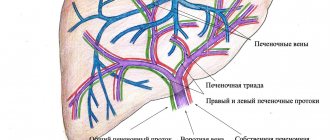
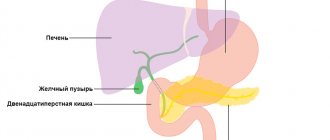
Liver and gallbladder diseases
Diseases of the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts can be acute and chronic; acute conditions, such as acute cholecystitis, acute hepatitis, biliary colic, require immediate medical attention in a hospital. Treatment of chronic liver and gallbladder diseases in our center begins with a consultation with a gastroenterologist.
Often, many diseases of the gallbladder and especially the liver occur without pronounced symptoms and are detected when the hepatobiliary system has already suffered quite serious damage and the course of the disease becomes severe and difficult to reverse. an ultrasound of the liver and gallbladder at least once a year and visit a gastroenterologist or hepatologist . This will not require a lot of time and money, but it will allow you to detect diseases of the liver and gallbladder at an early stage, when they can be more easily and quickly treated or achieved stable remission.
The most common gallbladder diseases are chronic cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder) and cholelithiasis . Often these diseases are interrelated; the formation of stones in the gallbladder can cause inflammation, and conversely, a long-term inflammatory process in the gallbladder leads to the formation of stones. In our center, we conduct a comprehensive examination and treatment of patients with gallstone disease without surgery, if such therapy is possible. If necessary, it is possible to consult a gastroenterologist together with a surgeon to decide whether there are indications for surgical treatment. Gallbladder deformity is a common pathology that can be congenital or acquired throughout a person’s life and requires treatment in the presence of unpleasant symptoms.
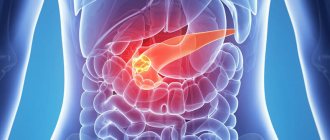
Liver diseases are divided into groups according to the cause that caused them and the stage of liver damage. The most common disease among chronic liver diseases is non-alcoholic fatty hepatosis . The main symptom of this disease is the accumulation of fat in the liver cells. The disease often occurs without pronounced symptoms, so patients with fatty hepatosis rarely seek help, and many doctors are not familiar with this disease. The danger of fatty hepatosis is that, with an almost asymptomatic course in some patients, fatty hepatosis is accompanied by inflammation of the liver cells - steatohepatitis, which can lead to liver cirrhosis and cancer. In addition, such patients have an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease and osteoporosis. According to the latest recommendations of the Russian Society for the Study of the Liver, non-alcoholic fatty hepatosis and steatohepatitis are combined into one disease called non-alcoholic fatty liver disease .
Alcoholic liver disease develops due to alcohol abuse; the main condition for its treatment is abstinence from alcohol. 90-95% of people who constantly abuse alcohol develop alcoholic fatty hepatosis, which is histologically similar to non-alcoholic fatty liver. This condition is almost always reversible if you stop drinking alcohol, otherwise the disease progresses and some patients develop cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Not only fat deposits and alcohol can cause liver damage, but also the accumulation of high levels of copper or iron caused by genetic diseases. Our hepatologists and neurologists have experience in treating genetic diseases associated with impaired transport of copper and iron in the human body. Wilson-Konovalov disease is associated with the accumulation of high levels of copper in organs and tissues, leading to damage to their cells and causing dysfunction of the damaged organs. Hereditary hemochromatosis is expressed in the gradual accumulation of iron in organs, endocrine glands and skin. In both cases, the liver is affected. Timely diagnosis and treatment of these diseases eliminate or prevent their symptoms; without treatment, such diseases end in death.
The most common gallbladder diseases are chronic cholecystitis and cholelithiasis . Often these diseases are interrelated; the formation of stones in the gallbladder causes its inflammation, and vice versa, a long-term inflammatory process in the gallbladder leads to the formation of stones. In our center we provide comprehensive examination and treatment of patients with gallstone disease. Immediately deciding together with the surgeon the question of whether there are indications for surgical treatment.
In 40% of cases, after removal of the gallbladder, patients experience abdominal pain and disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, called postcholecystectomy syndrome (PCES) . The reason for these phenomena is, on the one hand, the influence of loss of gallbladder functions and the presence of organic and functional causes of impaired bile transport. Properly selected therapeutic therapy and diet will help get rid of the unpleasant symptoms of PCES.
Treatment technologies
After processing all the data, three options are possible: the doctor will prescribe a special diet for you; will prescribe complex drug treatment to eliminate the causative agent of the disease; or will also prescribe additional treatment, taking into account the existence of other pathologies (diseases of the cardiovascular system, respiratory, urinary, etc.)
Acute diseases of the liver and gallbladder are completely curable in most cases, but chronic diseases are almost impossible to completely cure. During chronic treatment in our clinic, doctors achieve rapid relief of exacerbation, long-term remission, preservation of maximum liver function (that is, compensation for liver failure), and the gall bladder.
Timely diagnosis and prompt initiation of treatment will reduce medical intervention, as well as the consequences of the disease, to a minimum. Contacting a gastroenterologist at our clinic guarantees you qualified diagnostic and therapeutic services. You will be treated according to an individual program.
Diagnostics
THE INSTITUTE OF ALLERGOLOGY AND CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY has a fundamental base that allows it to carry out a full range of diagnostic and therapeutic measures that meet the level of international standards. Many of the diagnostic and treatment methods were developed by the staff of our Institute.
Instrumental and radionuclide methods are informative methods of research. At the initial stages, laboratory tests of blood, urine, and feces will be mandatory methods.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs gives a picture of obstructions in the patency of the biliary tract, allows one to determine the size, structure and location of the liver, structural anomalies;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS) allows you to assess the condition of the esophageal veins and determine the risks of bleeding;
- MRI reveals narrowing of the bile ducts, the presence of stones, neoplasms;
- computed tomography (CT) – detects small, from 1 cm, neoplasms. Allows you to diagnose changes in the structure of the liver, cirrhosis, fatty degeneration;
- computed tomography with contrast determines the patency of the hepatic ducts and vessels;
- Liver scintigraphy (scan) is a radiological procedure to detect liver cancer, hepatitis, cirrhosis, tumors and abscess. It can also be used to assess the body's response to therapy.
Viral inflammation of the liver: prevention and treatment
Prevention of viral hepatitis comes down to preventing infection - limiting contact with a sick person or carrying out preventive vaccination. How to treat viral liver inflammation? If viral inflammation of the liver is confirmed, the symptoms and treatment in women for this pathology do not essentially differ from those in men. Treatment measures may differ depending on the type of virus.
Inflammation of the liver, regardless of its nature, is a severe condition for the body, characterized by a significant decrease in the functional activity of the liver. However, with timely consultation with a doctor and complete treatment of liver inflammation, there is a high probability that it will be eliminated. Therefore, the diagnosis of “liver inflammation” should be considered not as a death sentence, but as an incentive to pay attention to your health.
Is your liver inflamed? Treatment should be started as soon as possible!
At the first symptoms of possible liver inflammation, you should immediately seek medical help. Yes, not all hepatitis requires special antiviral treatment, and not every type of liver inflammation becomes chronic. However, only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe a treatment program that will cure inflammation and prevent the development of complications. In some cases, the goal of treatment will be long-term remission of the disease - for example, with viral hepatitis type B, which cannot be completely cured.
Non-viral liver inflammation: treatment and prevention
How to treat an inflamed liver? The first step in treating non-viral hepatitis should be to eliminate the damaging effects on the liver. As a rule, treatment of liver inflammation in a hospital setting for non-viral hepatitis is required exclusively during the acute period of the disease. When diagnosed with liver inflammation, treatment at home is most often carried out.
Inflamed liver: how to treat it? Whatever the origin of liver inflammation, its treatment certainly includes taking hepatoprotective drugs. This is the name given to a large group of drugs, different in composition, origin and chemical formulas, but united by a common action: stimulating the restoration of both the structure and functional activity of liver cells. The result of this is a general beneficial effect on liver tissue and restoration of the functions of this organ.
Among the wide range of hepatoprotectors, drugs containing the active substance extracted from milk thistle extract, silibinin, in particular Legalon, have proven themselves to be effective.
This drug, thanks to the degree of purification of the active substance, unique among analogues, is maximally bioavailable to the body, which helps to obtain a quick and noticeable beneficial effect on liver tissue: stimulation of hepatocyte regeneration, restoration of their functions, relief of inflammation and restoration of normal bile outflow.
Prevention of non-viral hepatitis involves limiting the body's exposure to liver-damaging factors. Thus, taking hepatotoxic drugs should be carried out under close medical supervision, alcohol should be excluded, and work with toxic substances should be carried out using personal protective equipment.
Liver inflammation: types and causes
In general, all hepatitis is divided into two main groups depending on what triggered the development of the pathological process: infectious inflammation of the liver and hepatitis of non-infectious origin.
The first group includes hepatitis that developed as a result of damage to liver cells by viruses (hepatitis viruses types A, B, C, and so on; cytomegalovirus) and pathogenic bacteria (Salmonella, Yersinia and some others). Hepatitis that develops as a result of sepsis is also classified as infectious.
The group of non-infectious liver inflammations includes: toxic liver damage (and its separate type, alcoholic damage), autoimmune, metabolic, allergic, cholestatic and hereditary hepatitis.
There are also acute (the disease lasts up to eight weeks) and chronic hepatitis.