Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are usually associated with problems in the functioning of other systems of the human body. They are accompanied by unpleasant, painful symptoms and require urgent treatment.
Every person always wants to be healthy, full of strength and enjoy all the delights of life. However, unfortunately, recently there has been a trend towards the development of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract all over the world.
According to scientists, the reason for this is poor nutrition, regular stress, environmental problems and many harmful substances that surround us constantly.
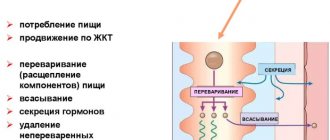
The main task of the digestive system is to perform vital functions in our body. Life without it is absolutely impossible, since due to its basic processes (digestion of the nutrients received and their absorption), a person receives the necessary energy for work and rest. The stomach and intestines are the main organs of digestion, the activities of which are associated with both the initial and final stages of the entire digestive tract. If your stomach and intestines are healthy, they will never let you down.
It is worth noting that the human digestive system is quite sensitive. It immediately reacts to any, even minor changes, both in the internal environment of the whole body and in the entire external world, leading to various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. They cause a lot of discomfort to the patient: discomfort and pain.
What is the gastrointestinal tract (GIT)
In order to understand the principle of the gastrointestinal tract, you must first understand what it actually is. The gastrointestinal tract is a system of organs whose purpose is to process and extract from food all the nutrients the body needs, assist in the absorption of the resulting beneficial substances into the blood, and also remove food debris that has not been completely digested from the body.
The entire gastrointestinal tract in the body is represented by a continuous tube that connects the oral opening to the anal opening. Food masses move along it in the caudal direction, which in the process of movement are split into smaller particles suitable for absorption.
For example, the average length of the gastrointestinal tract in an adult male reaches 6.5 meters.
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are a group of diseases that affect this anatomical region. All pathologies are divided into several main groups, among which are:
- by the nature of development, infectious and non-infectious;
- according to the location of the disease: small intestine, large intestine, stomach or esophagus;
- acquired and hereditary diseases.
Diseases of the small intestine
The final process of food digestion occurs in the small intestine, followed by the absorption of digestive substances, vitamins and minerals. Various diseases of the small intestine manifest themselves in the same way. Most often, our doctor in this case diagnoses “poor absorption syndrome.”
Manifestations of the disease that you may notice in yourself
Diseases of the small intestine usually manifest themselves:
- stool disorders
- rumbling and bloating
- pain.
The most common manifestation is diarrhea 3-6 times a day. Pain occurs in the navel area, sometimes in the epigastric region or the right half of the abdomen. They are most often pulling, aching, bursting and decrease after the passage of gas. There may be intestinal colic: very severe pain with intestinal spasms.
Small intestine: briefly about diseases
Chronic enteritis is inflammation of the small intestine. The causative agents of acute intestinal diseases play a primary role in its occurrence. Enteritis itself is often a post-infectious process. Vascular diseases : abdominal pain that occurs after eating, stool disorders. Timely contact with a professional is very important, since complete blockage of blood vessels may occur. Allergies manifested by intestinal disorders. Celiac enteropathy : deficiency of the enzyme peptidase, which breaks down gluten, a protein ingredient in grain plants; The disease manifests itself as severe diarrhea and weight loss. A rare Whipple's disease , characterized by severe diarrhea, fever, cramping abdominal pain, weight loss, and enlarged lymph nodes. Tumors are mostly benign.
Colon diseases
Colon diseases are:
- ulcerative colitis
- ischemic colitis
- Crohn's disease
- irritable colon
- dolichosigma, megacolon
- diverticulosis
- colon tumors.
Symptoms you may notice
- stool disorders
- stomach ache
- pathological discharge
- rumbling and bloating.
Stool disorders: constipation is more common. Pain in the anus, sides of the abdomen, above the navel or in the epigastric region. The pain is cramping or aching, bursting and is usually not associated with eating. They weaken after bowel movements and the passage of gases.
Large intestine: briefly about diseases
Ulcerative colitis affects the mucous membrane. Dangerous due to the possible development of polyps and tumors. Irritable colon is a complex of intestinal disorders due to disruption of intestinal motility. Crohn's disease : the entire intestine, esophagus, and stomach are affected. With ischemic colitis, inflammation occurs due to narrowing of the vessels that nourish the intestinal walls. Diverticulosis means the presence of multiple diverticula (ending in blind pouch-like protrusions of limited areas of the intestine) and leads to constipation. Dolichosigma - elongation of the sigmoid colon; megacolon - expansion of individual zones or the entire colon. Both diseases cause persistent constipation. Of benign and malignant neoplasms, the latter are more common. Now colon and rectal cancer is the most common malignant tumor.
Causes of gastrointestinal diseases
The main reasons for the development of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract include: improper diet or its complete absence, strict diet or overeating, various stressful situations, infections, sedentary lifestyle and others.
For example, Tibetan medicine views the human body as something holistic, interconnected and absolutely indivisible. Here we highlight another reason for problems with the gastrointestinal tract, namely problems in the functioning of other systems of the human body. For example, the health of the spine is reflected in the functioning of all digestive organs.
Absolutely all internal organs are internalized by nerves that emerge from the spinal canal. Any organ can function fully only if nerve impulses flow to it unhindered. A disease such as osteochondrosis pinches nerve endings and thereby slows down and even prevents the normal passage of impulses.
Because of this, the stomach becomes sluggish, and the smooth muscles of its walls become more relaxed. In case of prolonged disruption of innervation, the stomach descends. Moreover, sluggish and weak muscles of the gastrointestinal tract are one of the reasons for poor digestion of food.
In turn, poorly digested food is not able to fully nourish the body and thereby disrupts the functioning of other important body systems. Improper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract also manifests itself in the form of decreased immunity, skin damage and metabolic disorders.
The main symptoms of diseases of the digestive system:
- Pain in the abdomen, both of different localization and of varying intensity;
- Belching and heartburn;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Stool disorders;
- Flatulence and rumbling in the stomach;
- White coating on the tongue;
- Rapid weight loss;
- An aversion to certain foods that were previously favorites, or a complete lack of appetite.
The use of butyric acid for radiation injuries of the intestine
One of the promising methods of drug prevention for maintaining remission in patients with UC is the use of the drug butyric acid and inulin, Zakofalka, as part of complex therapy (for example, in combination with mesalazine).
A decrease in the level of butyric acid in inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) has been found in many studies, which served as the basis for studying the effectiveness of its use in IBD. One of the reasons for the decrease in butyric acid in patients with IBD is a significant decrease in the number of microbes that synthesize this metabolite. The state of mucosal and fecal microflora associated with it was studied in patients with Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis and in healthy people. There is a sharp decrease in bacteria that synthesize butyric acid (in particular Faecalibacterium prausnitzii) both in the feces and in the colon mucosa in patients with IBD, compared with healthy individuals.
Application of Zakofalk as a means of enhancing primary therapy for the prevention of exacerbation of ulcerative colitis
justified by the decrease in the concentration of this metabolite in these patients and the main effects of butyric acid on the colon mucosa:
1. Anti-atrophic effect - restoration of trophism of the colon mucosa.
2. Anti-inflammatory effect. Restoring the barrier functions of the colon.
3. Regulation of the processes of normal maturation and development of cells in the colon mucosa.
4. Antidiarrheal effect – regulation of water and electrolyte balance in the colon.
5. Prebiotic effect – creating a favorable environment for the growth of your own beneficial microflora.
The effectiveness of Zakofalk has been confirmed in a large number of studies. Thus, in a large study conducted on the basis of 19 gastrocenters that are part of the IBD study group in Italy, patients with mild to moderate forms of ulcerative colitis (number of patients = 196), who did not achieve a satisfactory response to standard mesalazine therapy within 6 months Zakofalk was added 1 tablet 3 times a day. After 6 months, patients receiving a combination of mesalazine and Zakofalk showed a statistically significant decrease in the frequency of bowel movements, blood and mucus, as well as a reduction in the clinical activity index - 86% were in clinical remission (had no symptoms of the disease).
To prevent exacerbation (maintain remission) of ulcerative colitis, Zakofalk in combination with the main therapy (mesalazine) is used 1 t 3-4 times a day, the minimum course is 3-6 months, maintenance therapy is possible 1 t 2 times a day for a long time.
Diagnosis of gastrointestinal diseases
Today, thanks to technological progress in modern gastroenterology, a thorough diagnosis of all organs of the gastrointestinal tract is possible. It consists of:
- Ultrasound - ultrasound examination;
- FGDS and irrigoscopy – endoscopy of the gastrointestinal tract;
- intragastric pH-metry;
- manometry of all digestive organs;
- electrogastroenterography;
- radiology diagnostics;
- biopsies.
Treatment, as well as diagnosis of any gastrointestinal diseases, is recommended to be carried out exclusively by a qualified gastroenterologist. This will help minimize discomfort.
Irritable bowel syndrome: causes and treatment of IBS, medications, diet and prevention
Table of contents
- Causes of the disease
- Symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome
- Irritable bowel syndrome in adults: women and men
- Irritable bowel syndrome in children
- Diagnostics
- Treatments for Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Nutrition and diet for irritable bowel syndrome
- Prevention
- Advantages of contacting MEDSI
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a specific condition associated with recurrent pain, bloating, and bowel movements.
The disorder can occur with a certain frequency, spontaneously and always causes severe discomfort. Both adults and children suffer from it. How to get rid of irritable bowel syndrome? What are its true causes, how is treatment carried out? Let's look into these issues.
Causes of the disease
Psychosocial changes
Irritable bowel syndrome in women, men and children can be a consequence of depression, increased anxiety, insomnia and stress. IBS can also be caused by an unbalanced and unhealthy diet, lack of a normal rest and work schedule, lack of physical activity, overeating and chronic fatigue.
Physiological changes
They are divided into several groups:
- Biological. Disruption of intestinal microflora can lead to the development of irritable bowel syndrome. The process is triggered by both acute infections and a lack of lactobacilli and excess putrefactive deposits
- Hormonal. In women, irritable bowel syndrome can be triggered by hormonal changes during menstruation, menopause, pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Hereditary. If IBS is diagnosed in parents, then there is a high probability that it will develop in children as well.
Symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome
The main signs of the pathological condition include regularly occurring abdominal pain.
The severity and frequency of such pain may vary. In some patients they occur every day, in others several times a week or even a month. Abdominal pain can occur after eating or regardless of food intake, only during stress or physical exertion. Moreover, patients are usually not bothered by unpleasant sensations at night. As a rule, the pain is localized in the left side of the abdomen. It is stable and rarely increases.
Pain may be accompanied by:
- Flatulence and bloating
- Feeling of intestines not being completely emptied after going to the toilet
- Too rare or frequent bowel movements
- The presence of mucus in stool, etc.
Some patients also complain of symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome that have nothing to do with the functioning of the digestive system. These include: frequent headaches (including migraines), fatigue and weakness, chest and back discomfort, difficulty breathing. Some patients additionally experience difficulty urinating.
Irritable bowel syndrome in adults: women and men
The worldwide prevalence of IBS varies from 1 to 28%. The frequency of occurrence of pathology is influenced by the place of residence. Typically, violations are recorded among residents of large cities, rather than rural areas and small towns. This is associated with the greater prevalence of various psychological disorders and the increased frequency of emotional experiences there.
In women, the pathology is more common. According to statistics, the difference is approximately 50%. That is, women with this problem visit doctors approximately 2 times more often.
Irritable bowel syndrome in children
In children, the pathology usually develops between the ages of 14 and 17 years. The prevalence of the disorder in them is no less than in adults. Functional disorders are more common in girls. In this case, the pathological condition significantly worsens the child’s quality of life. In some cases, he loses the ability to concentrate and his memory decreases. The child may even refuse to attend school.
Diagnostics
To identify a pathological condition, a gastroenterologist evaluates the clinical picture, studies the patient’s medical history, and conducts an examination. Particular attention is paid to the influence of psychological factors. For this reason, psychologists and psychotherapists are often involved in the diagnosis and further treatment of irritable bowel syndrome.
To clarify all the features of the pathology, the following is carried out:
- Clinical blood test. It eliminates infectious and inflammatory processes, as well as anemia
- Biochemical blood test. It is carried out to control metabolic disorders. The fact is that frequent diarrhea with IBS can cause electrolyte imbalance
- Scatological research. Typically, the patient undergoes stool tests for occult blood, helminth eggs, etc. This allows us to identify all possible factors that provoke the pathological condition
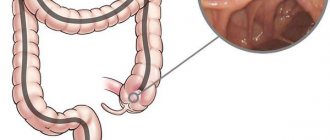
- Colonoscopy. The examination is carried out to assess the condition of the colon
- Irrigoscopy. X-rays are performed with a contrast agent, which makes it possible to study the condition of the intestine and identify all possible neoplasms (polyps, etc.), as well as evaluate the structure of the organ, its lumen and the elasticity of the walls
Additionally, the patient’s psychological status is assessed and the level of depression and anxiety is identified. Other laboratory and instrumental examinations may also be performed.
Treatments for Irritable Bowel Syndrome
The basis of therapy is:
- Correction of diet
- Ensuring a normal rest and work schedule
- Eliminating the main symptoms
- Achieving psychological balance
Important! Medicines are taken exclusively during an exacerbation.
Therapy largely depends on how irritable bowel syndrome manifests itself.
- IBS with diarrhea. In this case, the patient is prescribed special medications with an astringent and enveloping effect. They allow you to normalize stool. Drugs that reduce intestinal motility are also recommended.
- IBS with constipation. When treating this pathology, mild laxatives are prescribed. In this case, the goal is to enhance peristalsis and accelerate the movement of feces
- Irritable bowel syndrome with flatulence. In this case, therapy is carried out using antispasmodics and other means that normalize stool. If there is an imbalance of microflora, antibacterial drugs may be recommended
For neurasthenia, depression, increased anxiety and other psychological problems, the patient is referred to a psychologist and psychotherapist. These doctors can both conduct courses of special therapy and prescribe sedatives and antidepressants.
Nutrition and diet for irritable bowel syndrome
Establishing a proper diet can help reduce the dosage of medications used and ensure a reduction in symptoms.
The patient must adhere to a number of recommendations.
You should:
- Include a sufficient amount of boiled or baked vegetables in your grocery list. They will enrich your diet with essential dietary fiber. This diet is relevant for IBS with constipation.
- Avoid cereals and whole milk, eat rice, oatmeal and other slimy porridges with water for diarrhea
- Eliminate sugar, fresh vegetables, grapes, baked goods and sweets, alcohol and carbonated drinks from your diet. This will eliminate the problem of increased gas formation
Important! A detailed diet for irritable bowel syndrome and nutrition plan are drawn up by a doctor. They are prescribed by a nutritionist and gastroenterologist.
Prevention
To prevent symptoms of pathology, you should not only follow a diet and adhere to a certain diet, but also establish a drinking regime
. If a patient with IBS complains of constipation, he needs to drink more clean, still water.
It is important to take care of ensuring a stable emotional state
, maintaining his balance. To do this, patients learn to control reactions and master methods of complete relaxation. To reduce stress levels, it is important to maintain a proper daily routine, ensure adequate rest, and avoid excessive physical activity. Creative activities and other hobbies can help relieve emotional stress.
Regular moderate physical activity can also help overcome irritable bowel syndrome
Don't start serious training! They can make the condition worse. But regular walking and short jogging to maintain an optimal heart rate won't hurt. Swimming and yoga are also helpful.
Regular physical activity will allow you to:
- Relieve mental stress
- Improve overall emotional state
- Resist stress
- Eliminate excess weight (if any)
- Protect the body from colds
- Improve overall well-being
In addition, exercises help to form a muscle corset, which ensures correction of intestinal motility.
Important! In order to select the optimal physical activity regimen, it is better to contact a rehabilitologist or exercise therapy specialist. The training plan is drawn up taking into account the current health status and level of physical fitness of the patient. The diet for irritable bowel syndrome is also adjusted to physical activity. It is important to ensure that at least 1.5–2 hours pass between workouts and meals.
Advantages of contacting MEDSI
- Modern expert class equipment.
It allows you to quickly conduct a comprehensive examination of the patient and identify the main causes of the pathology. - Multidisciplinary approach.
Thanks to it, complex therapy is provided. Specialists eliminate not just the signs of pathology, but its causes. This allows you to forget about the problem and return to a normal lifestyle. - Treatment according to the latest recommendations.
We use both our own achievements and the international experience of our colleagues in therapy. This makes the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome both effective and safe.
To clarify the terms of service or make an appointment, just call +7 (495) 7-800-500. Our specialist will answer all questions. Recording is also possible through the SmartMed application.
Preventing irritable bowel
Disorder of the functions of the intestinal organ leads to its irritation. The disorder is accompanied by pain, discomfort and heaviness. For pronounced syndromes, a comprehensive course of therapy is required using a number of medications, such as:
- antibiotics;
- antispasmodics;
- laxatives;
- sedatives.
For preventive purposes, you should adhere to a healthy lifestyle, diet, and exercise.
Treatment of intestinal pain
To make a diagnosis, symptoms alone are not enough, so the doctor prescribes an additional examination, including:
- A coprogram is a detailed examination of stool, with the help of which medical experts determine the nature of the completeness of food digestion. This diagnostic test determines whether the patient is suffering from gastrointestinal disorders.
- Bacteriological examination of stool. Bacteriological examination of stool provides informative data about the presence of the causative agent of intestinal infection in the body and the ratio of bacteria of healthy and opportunistic flora.
- Endoscopy. An endoscopic examination of the body is carried out by inserting a fiber optic tube into the upper or lower parts of the gastrointestinal tract. The fiber optic tube is equipped with a special camera and lighting. This diagnostic examination makes it possible to directly see the condition of the mucous membrane.
- Colonoscopy. An intestinal examination is performed using a device that allows you to visually evaluate the surface of the intestinal walls.
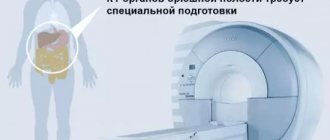
- Computed tomography can detect tumor diseases and internal changes in organs.
After a diagnostic examination, the patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs. This group of medications will relieve pain syndromes and stop the progression of the disease.
For consultation, tests and various studies, we advise you to contact the private clinic “KDS Clinic”. You will receive qualified assistance, attention from the best proctologists in the Russian Federation and treatment at affordable prices. For more accessible information about services, please visit the official website of our medical institution.
The most accurate methods for diagnosing intestinal diseases are colonoscopy and computed tomography. These diagnostic examinations have a number of contraindications. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are strictly prohibited:
- Children under sixteen years of age. The human body at this age is quite weak, so diagnostic tests using radiation can damage healthy organs.
- Pregnancy or lactation period. During pregnancy, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are contraindicated. They can harm the condition of the fetus, especially in the early stages. During the lactation period, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are not performed. If these diagnostics are necessary, then it is advisable for the woman to express milk after the procedure and refrain from feeding the baby for 48 hours.
The medical specialist diagnoses and treats intestinal diseases and conducts a comprehensive examination. We invite you to make an appointment with a proctologist and endoscopist.