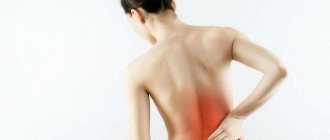
Every person has experienced pain at least once in their life. Everyone knows how inopportune she always is, how she unsettles her and ruins her plans. Everyone is always looking for a way to end this nightmare as quickly as possible. And each person has his own proven remedy. In fact, some painkillers are not entirely harmless. Therefore, you should not grab the first available remedy for pain. It's better to listen to specialists.
Types of pain
There are different types of pain.
Experts divide all pain into two categories:
- acute, appears suddenly, usually due to injury, does not last long;
- chronic, lasts a long time, occurs as a result of chronic inflammation.
When taking medications for pain, you should consider the type of pain. In some cases, it is prohibited to use painkillers. For example, with acute abdominal pain. This way the disease can be veiled, as a result doctors will not be able to accurately diagnose the disease.
How to choose tablets for kidney pain
Treatment for kidney pain or flank pain depends on the underlying cause of the sensation. Kidney infections and kidney stones that cause pain are often treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic, and pain medications, or sometimes with small amounts of narcotic analgesics (for renal colic). However, these drugs treat pain (the main effect is pain relief), and not the root cause of the pain.
In some patients, the pain may resolve spontaneously (urine flushes the irritating stone from the ureter or urethra), and small kidney stones (usually less than 6 mm in diameter) may gradually pass away. Urinary tract infections (UTIs) and pyelonephritis usually require treatment with antibiotics in addition to pain medications.
Good to know
What to do if you have been diagnosed with pyelonephritis
If kidney stones completely block the ureter or are about 6 mm in diameter or larger, urological surgery may be required. Typically, recovery time is quick (same day or a few days later) if kidney stones are removed using retrograde surgical methods.
Other underlying causes of flank pain may require similar pain management and simultaneous treatment of the cause. However, patients with known kidney problems or impaired kidney function should not be treated with pain medications that are either filtered (removed) through the kidneys or may cause further kidney damage.
Mechanism of action of painkillers
When tissue damage or inflammation occurs, a signal travels along the nerve endings to the brain. In the damaged area, irritation of the nerve endings occurs. As a result of muscle contraction, a spasm occurs.
Painkillers act as follows:
- inhibit nerve impulses that transmit pain;
- soothe irritated nerve endings;
- relieve muscle spasms.
Depending on the type of pain, painkillers are used.
Popular questions and answers
Regarding the treatment of kidney pain and its causes, the choice of the most suitable drugs, we talked with a urologist, ultrasound diagnostic specialist, and a doctor of the highest category at the Center for Disaster Medicine, Yuri Bakharev.
Why might pain in the kidneys occur?
Many of the causes that lead to kidney pain (also called flank pain) are due to acquired underlying conditions that may occur acutely or may have a chronic effect on kidney function.
Some diseases are present at birth. Children may be born with a genetically determined pathology that affects the kidneys. Kidney pain or pain in the side can be acute, relatively constant and paroxysmal. This is called "renal colic". This type of pain usually occurs when the ureter is blocked by a kidney stone or blood clot, preventing the urine produced in the kidney from flowing out. However, other processes can also cause chronic dull pain or attacks of acute pain. Some of the causes of kidney pain or flank pain are: ● Urinary tract infection (UTI); ● bladder infection (cystitis); ● kidney infections (pyelonephritis); ● hydronephrosis; ● kidney stones (nephrolithiasis and/or ureterolithiasis); ● kidney cancer; ● anything that compresses the kidney (for example, a large tumor); ● glomerulonephritis; ● blood clots in the kidneys (renal vein thrombosis); ● polycystic kidney disease (congenital); ● congenital anomalies in the renal system, leading to complete or partial blockage of the ureters; ● medications or toxins that harm kidney tissue; ● renal bleeding (hemorrhage), for example, from penetrating or blunt trauma (“renal rupture”); ● end stage renal failure.
What to do if you have kidney pain?
Stones usually form in the kidneys or urinary tract. Kidney stones that do not cause symptoms are called "silent" stones. When symptoms appear, they are usually sudden and include excruciating, spasmodic pain in the lower back or abdomen, side or groin. Changing body position does not reduce pain. In this case, you need to take an antispasmodic and call an ambulance.
When should you call a doctor at home?
You should not put off visiting your doctor because of kidney or side pain.
Although flank pain is often seen with serious kidney problems, there are many other conditions that can mimic kidney pathologies, and a doctor can help accurately diagnose the underlying problems that lead to kidney or flank pain. Any acute onset of intense pain in the kidneys or flank should be assessed immediately by calling a doctor. Warning signs that kidney disease is present include: ● blood or protein in the urine (white flakes); ● more frequent urination, especially at night, or difficult, painful urination; ● high blood pressure; ● swelling of the arms and legs or puffiness around the eyes.
Additionally, if you have diabetes or any of the congenital problems that lead to kidney dysfunction, you should be checked regularly by your doctor to check for kidney dysfunction or kidney failure.
Types of painkillers
Remedies for pain are divided into several types:
- Narcotic drugs. They depress the nerve centers that respond to pain. As a rule, such drugs cause relaxation, euphoria, and drowsiness. Such products are issued only with a medical prescription.
- Non-narcotic drugs. They do not affect the nervous system, do not cause drowsiness or euphoria. Therefore, such drugs are sold without a prescription. They usually also have anti-inflammatory and antipyretic properties.
Non-narcotic painkillers are divided into groups:
- NSAIDs (non-steroidal drugs) have an anti-inflammatory effect, lower temperature, relieve pain;
- Antispasmodics for spasms;
- mixed preparations eliminate spasms and pain.
Narcotic drugs are not commercially available and therefore are not used for self-medication. The most common drugs are NSAIDs. They quickly relieve pain and inflammation, but have many contraindications and side effects. They are especially dangerous in case of ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract or if they are suspected. Because they can cause gastric bleeding and aggravate ulcers of the stomach and intestinal mucosa. This can sometimes be fatal.
What medications should I take for osteochondrosis?
Medicines for osteochondrosis differ not only in the form of release. They are also divided into the following pharmacological groups.
Anti-inflammatory drugs for the treatment of osteochondrosis
The work of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for osteochondrosis is based on suppressing the production of prostaglandins - hormone-like substances that cause inflammation and pain in the affected areas. Non-steroidal drugs for osteochondrosis can quickly eliminate pain and hot skin, restore local metabolism, relieve swelling, discomfort and deterioration of sensitivity, and relieve pressure on the nerve roots of the spine.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for the treatment of osteochondrosis are produced in various dosage forms - capsules and tablets, gels and creams, solutions for intramuscular, intravenous or subcutaneous administration. Treatment of NSAID drugs for osteochondrosis usually involves a combination of different forms. For example, tablets are used as the main therapy, gels and ointments “quench” residual inflammation, and injections are needed for pain relief. Patches (for example, Voltaren, Versatis) help relieve inflammation at all stages of treatment.
The list of NSAID drugs for osteochondrosis includes:
- artradol;
- ibuprofen (nurofen, dolit, ibuprom);
- ketoprofen (ketonal, fastum, bystrumgel, flexen);
- diclofenac (Voltaren, Diclac, Diclobene, Dicloran Plus, Ortofen);
- ketorolac;
- xefocam;
- indomethacin (indovazin, indobene, indocid);
- nimesulide (nimesil, nise, nimulid, nimika);
- naproxen;
- piroxicam;
- Celebrex (celecoxib);
- febrofide;
- meloxicam (movalis, movasin).
Steroid (hormonal) anti-inflammatory drugs for osteochondrosis are rarely used - mainly in the most advanced cases. These include prednisolone, cortisone, dexamethasone and others.
Chondroprotectors
With osteochondrosis, the spring function of the intervertebral discs deteriorates, which directly depends on the volume of cartilage tissue and its elasticity. To maintain sufficient cartilage thickness, the body must regenerate cartilage cells (chondrocytes) at a rate that roughly matches their destruction. But with dehydration, unbalanced nutrition, stress, metabolic or anatomical disorders, the rate of decay of chondrocytes increases, and new cells are either inhibited in growth or have an insufficient margin of safety. To protect cartilage and restore its normal growth rate, it is worth taking special products based on glucosamine and chondroitin - chondroprotectors. Chondroprotective drugs for the effective treatment of osteochondrosis can stabilize the condition of cartilage, prevent its further destruction and, subject to all medical recommendations, even help restore lost chondrocytes.
Chondroprotective drugs for osteochondrosis include:
- artracs;
- chondrolone;
- rumalon;
- Don;
- chondroxide;
- osterepar;
- teraflex;
- alflutop;
- collagen ultra.
Some of them (for example, Dona) contain only glucosamine, others (Structum, Chondroxide) - only chondroitin. Modern drugs combine active ingredients and additionally include vitamins (artracam).
For a sustainable effect, chondroprotectors (in the form of tablets, injections or external agents) must be taken for life, in courses of 3-6 months.
Warming drugs
To eliminate discomfort in osteochondrosis, the so-called. warming medications. They:
- dilate blood vessels in the skin, which inhibits the transmission of pain impulses to the brain;
- improve blood microcirculation in connective tissue;
- distract the patient from unpleasant sensations.
When irritating drugs are applied, the peak effect is observed after half an hour, and the analgesic effect lasts for 2-4 hours. A local increase in skin temperature is normal.
The list of drugs for the treatment of osteochondrosis includes ointments, creams, gels and tinctures based on:
- camphor (camphor ointment);
- turpentine;
- benzyl nicotinate;
- nonivamide;
- capsaicin (espol ointment, capsicum tincture);
- bee and snake venom.
Most of these drugs have a combined composition - for example, bee venom and NSAIDs or snake venom, salicylic acid and turpentine. Therefore, before use, you must make sure that you are not allergic to each of the components.
Local and general analgesics
Painkillers for osteochondrosis are usually used in the form of tablets and injections. For moderate pain, the usual medicines in the medicine cabinet can help - analgin or paracetamol. Nefopam and Ambene are also effective (has an anti-inflammatory effect, which reduces pain).
In the later stages of osteochondrosis, opioids are prescribed - potent drugs with a number of contraindications. These include tramal (tramadol).
For complex pain relief (for example, blockade), the so-called. “cocktails” that simultaneously have an analgesic, decongestant, anti-inflammatory, local anesthetic and allergen-reducing effect. The composition may include lidocaine or novocaine, bupivacaine, corticosteroids, vitamin B12 and other components.
Important! Analgesics only relieve pain without affecting its cause. Therefore, without proper treatment, osteochondrosis continues to progress, requiring a transition to increasingly serious painkillers.
Vasodilators
Vasodilators for osteochondrosis, or vasodilators, help restore normal blood supply to the tissues around the affected intervertebral joints.
Pain and muscle tension cause the blood vessels to narrow. This impairs tissue nutrition, causes oxygen starvation of the brain and accelerates the progression of the disease. Therefore, in case of cervical osteochondrosis, drugs to normalize blood circulation are especially important. During rehabilitation therapy the following are used:
- pentoxifylline, or trental (vasodilator);
- xanthinol nicotinate (improves blood flow, reduces swelling of nerve roots);
- aminophylline (eliminates circulatory failure);
- Mexidol (pressure and metabolic processes stabilizer);
- vasonite-retard, octolipene (microcirculation stimulants);
- actovegin (tissue regeneration stimulator);
- Cavinton (promotes saturation of tissues with oxygen, dilates blood vessels);
- berlithion (antioxidant).
Vascular medications for osteochondrosis improve peripheral blood circulation and cellular metabolism and relieve pain.
Antispasmodics and muscle relaxants
To eliminate spasm and tension, antispasmodics and muscle relaxants are used. They normalize blood circulation, relieve pain, and restore mobility. Patients are prescribed:
- sirdalud (tizanadine);
- mydocalm (tolperizole);
- baclofen;
- cyclobenzaprine;
- novocaine, lidocaine, trimecaine.
To enhance the effect of drugs to relax muscles in osteochondrosis, they can be prescribed together with clonazepam or diazepam (prescription drugs). These drugs can be addictive, so they are used with caution.
Sedatives
Symptoms of osteochondrosis and treatment with drugs often provoke chronic stress, emotional stress, depression and other disorders of the psycho-emotional spectrum in patients
For general calming and combating insomnia, you can use herbal preparations - for example, tincture of valerian, motherwort, peony.
For more serious disorders, antidepressants are recommended - gidazepam, Cymbalta, Eglonil, Donormil.
Vitamin and mineral complexes
Since osteochondrosis is considered a disease of the whole body, complex vitamin and mineral therapy (complivit, duovit, doppelhertz, multi-tabs) is of great importance. Vitamins A, groups B, C, D, E, calcium and phosphorus preparations help to significantly improve the condition.
Vitamin A
(retinol acetate) is a natural antioxidant that stimulates collagen production and reduces the destruction of chondrocytes, promotes the renewal of joint tissue.
B vitamins
(cyanocobalamin, milgamma, neuromultivit, neurobion, neurorubin, neuroplex, celtican complex, pyridoxine, thiamine) reduce pain, inflammation and numbness of the hands, improve the sensitivity of nerve fibers.
Vitamin D
(calciferol, aquadetrim, vigantol) is responsible for the absorption of calcium and helps restore bone tissue lost due to osteochondrosis.
Vitamin E
(tocopherol) is necessary for normalizing blood circulation, protecting against free radicals and cartilage regeneration.
Don't self-medicate! Good luck to you in the treatment of osteochondrosis!
Images designed by Freepik
Non-narcotic painkillers
The most popular drug Aspirin belongs to this group. It contains acetylsalicylic acid. In addition to relieving pain, it lowers temperature and thins the blood. Therefore, it should not be taken by persons with reduced blood clotting. It is also contraindicated for damage to the gastric and intestinal mucosa. The drug may cause bleeding.
It is also not given to children under fifteen years of age.
There are analogues of aspirin:
- Upsarin Upsa;
- Aspirin Cardio;
- Aspicor;
- Citramon;
- Thrombo-ass;
- Cardio-magnyl;
- Anopyrine.
Paracetamol is also included in the group of non-narcotic painkillers. It is the most harmless of the drugs in this group. It is even prescribed to pregnant women and children. But it should not be taken uncontrollably, because it has a negative effect on the liver.
There are analogues of Paracetamol:
- Panadol;
- Daleron;
- Solpadeine;
- Panadol Extra;
- Trigan-D;
- Coldrex;
- Sanidol;
- Perfalgan;
- Meksalen;
- Medipirin;
- Panadol active.
The most common painkiller is Ibuprofen. It effectively relieves pain, but is classified as an NSAID, so it should not be taken by patients with gastrointestinal ulcers or people with reduced blood clotting.
Ibuprofen analogues:
- Nurofen;
- Ibusan;
- Moment;
- Ibufen;
- Advil;
- Pedea;
- Burana;
- Ibuklin Junior.
Drotaverine is a well-known antispasmodic. It is even used during childbirth. Relieves various spasms. It is not prescribed to children under six years of age, or to nursing mothers. Otherwise the medicine is called No-shpa.
Ketarolac is the most powerful drug in this group. It is taken for severe toothaches and conditions after operations. Not prescribed to children under sixteen years of age, nursing mothers, or persons with kidney, heart, or stomach diseases.
Diclofenac is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. Relieves pain from arthrosis, arthritis, toothache.
Analogues:
- Voltaren;
- Ortofen;
- Dorosan;
- Orthoflex;
- Naklofen.
Oxycams relieve pain in joint diseases. Not prescribed for children, stomach ulcers, or kidney disease.
Use of analgesics
After the patient is examined, the doctor prescribes medication for muscle pain. Non-narcotic analgesics have an analgesic effect. Medicines in this group are considered the most effective for muscle and joint pain. They have side effects only with long-term, uncontrolled use. Tablets for muscle and joint pain are recommended to be taken for a short time.
Sulpiride and analgin contain the active ingredient metamizole. These tablets can relieve moderate pain in joints and muscles. You can relieve muscle pain due to severe overexertion with the help of drug injections.
Ketalgin, Ketanov, Ketoprofen, Ketolong are tablets for muscle pain that quickly relieve pain. The active substance is metamizole. The period of influence on the body is 6-8 hours.
What else helps with muscle pain? Dexalgin tablets are considered an anesthetic drug that can effectively relieve muscle and joint pain. The main active ingredient is dexketoprofen.
Larfix and Xefocam are among the most effective non-narcotic analgesics. They contain lornoxicam. Due to the high cost of the drug, doctors prescribe it only for severe pain. The analgesic effect when using these tablets lasts about 8 hours.
How to get rid of muscle pain? Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs not only relieve pain in muscles and joints, but also have an anti-inflammatory effect. Non-steroidal medications include the following tablets for muscle pain in the neck, back, legs and arms:
- ortofen;
- diclofenac;
- methindol;
- indomethacin;
- movalis.
They have significant side effects - they irritate the gastric mucosa. Therefore, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital, when prescribing these tablets for muscle pain, additionally prescribe tablets that reduce gastric secretion - famotidine and omeprazole.
Disadvantages of tablets
Painkillers also have a downside: almost all pills have side effects.
- Negatively affect the functioning of the digestive system. Erosion and ulcers can form on the walls of the stomach, so if there are problems with the gastrointestinal tract, it is better to choose a different method.
- Disturbs liver function.
- They can cause headache, shortness of breath, swelling, skin rashes, etc.
Most analgesics are prohibited for expectant and nursing mothers, young children and people with systemic diseases that are included in the list of contraindications. Therefore, it is recommended to consult a doctor before use.